Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Subdural Hematoma
Subdural Hematoma
Uploaded by
rodamel gundan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
728 views4 pagesAfter assessing a patient who fell and developed a subdural hematoma, the nurse formulated 3 nursing care plans to address the patient's priority needs: 1) ineffective airway clearance related to hypoventilation from brain injury, 2) ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion from interrupted blood flow to the brain manifested by changes in mental status, and 3) risk for injury related to impaired physical mobility
Original Description:
Original Title
subdural-hematoma
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAfter assessing a patient who fell and developed a subdural hematoma, the nurse formulated 3 nursing care plans to address the patient's priority needs: 1) ineffective airway clearance related to hypoventilation from brain injury, 2) ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion from interrupted blood flow to the brain manifested by changes in mental status, and 3) risk for injury related to impaired physical mobility
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
728 views4 pagesSubdural Hematoma
Subdural Hematoma
Uploaded by
rodamel gundanAfter assessing a patient who fell and developed a subdural hematoma, the nurse formulated 3 nursing care plans to address the patient's priority needs: 1) ineffective airway clearance related to hypoventilation from brain injury, 2) ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion from interrupted blood flow to the brain manifested by changes in mental status, and 3) risk for injury related to impaired physical mobility
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
NAME: Gundan, Rodamel A.
SECTION: BSN-3C
The 62y/o patient stumble while walking and fell down on the ground on May 5, 2020 and ignored it
because all he thought it is a mild bump but after three days he experienced nausea, vomiting, body
weakness, dizziness and acute headache with fever. He was brought to emergency hospital, upon
assessment the doctor ordered Laboratory exams and CT scan. It reveals blood clotting(hematoma) seen
in his subdural space. The patient was admitted with diagnosis of subdural hematoma left temporal area
with medication of Nalbuphine Hcl 10mg IV now then prn for pain, Mannitol 150ml IV bolus every 4
hours, omeprazole 40mg IV OD and Cefoxitin 500mg IV every 8 hours.
Formulate 3 NCP according to patient priority needs
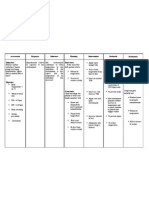
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNIN INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATI
G ON
Objective: Ineffective After 8 1. Assess 1. These After 8
Adventitio airway hours of respiratio signs and hours of
us breath clearance nursing n and symptom nursing
sounds related to interventi breath s are interventi
such as hypoventila ons, the sounds, indicative ons, the
ronchi and tion patient noting of patient
wheezing secondary will be rate and respirator was able
Presence to brain able to sounds y distress to
of whitish, stem injury manifest ( tachypn and/ or manifest
tenacious breath ea, accumula breath
secretions sounds stridor, tion of sounds
approxima crackles, secretions
tely 20 cc wheezes) 2. To
Decreased 2. Evaluate determin
level of cough/ e ability
conscious gag reflex to protect
ness and own
swallowi airway
ng ability 3. Maintaini
3. Assess ng the
airway airway is
for always
patency first
4. Assess priority,
changes especially
in mental in cases
status of trauma
4. Lethargy
and
somnolen
ce are
late signs
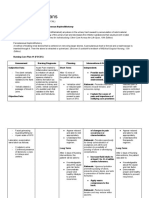
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSI PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATIO
S N
Objective: Ineffective After 1 day 1. Assess 1. To check After 1 day
Both eyes cerebral of nursing mental for of nursing
with tissue intervention status and affected intervention
negative perfusion s, the changes in cranial s, the
reaction to related to patient will the level nerve patient was
light the be able to of functions able to
Restlessne interrupti improve conscious in the improve
ss on of the level of ness brain, level of
Memory blood flow consciousne 2. Position check for consciousne
loss to the ss client in cerebral ss
Behaviour brain low- hypoperf
changes fowler’s usion and
Altered position hypoxia
consciousn 3. Avoid 2. Help
ess extreme venous
rotation drainage
of the from the
neck brain and
4. Avoid promote
extreme brain
hip flexion expansion
5. Maintain 3. This will
patent compress
airway the
6. Restore or jugular
maintain veins
fluid leading to
balance an
increased
intracrani
al
pressure
4. Increase
in intra-
abdomina
l and
intra-
thoracic
pressure
leading to
increased
intracrani
al
pressure
5. Prevents
build-up
of
secretions
leading to
increase
in carbon
dioxide
and
intracrani
al
pressure
6. It
maximize
s cardiac
output
and
prevents
decreased
cerebral
perfusion
associate
with
hypovole
mia.
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSI PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATI
S ON
Objective: Impaired After 4 1. Monitor 1. To provide After 4
Limited physical days of patient’ baseline days of
range of mobility nursing s vital data nursing
motion related to interventio signs 2. Identifies interventio
Inability sensory n, the 2. Review probable n, the
to perceptua patient will function functional patient
perform l be able to al impairments was able to
gross impairme maintain/ ability and maintain/
motor nt increase and influences increase
skills secondary strength reasons choices of strength
Difficulty to injury, and for intervention and
upon bed rest function of impair s function of
turning and affected ment 3. Maintains affected
Unable to unrespons and/or 3. Provide mobility and and/or
transfer ive state compensat / assist function of compensat
to bed ory body with joints/ ory body
Decrease part and range of functional part and
d muscle regain motion alignment of regain
strength optimal exercise extremities optimal
position s and reduces position
function as 4. Place venous function as
evidenced the stasis evidenced
by absence client in 4. Designated by absence
of designa therapeutic of
contractur ted position contractur
es and foot therape should es and foot
drop utic cause no drop
position undue stress
5. Elevate on muscles
the or joint
head of 5. The head of
the bed the bed may
as be elevated
appropr to provide
iate counteractio
n of for
comfort if
permitted
You might also like
- Edexcel As Biology Revision Guide PDF FreeDocument108 pagesEdexcel As Biology Revision Guide PDF Freebody fayez100% (1)
- Sick Sinus SyndromeDocument12 pagesSick Sinus Syndromelaura100% (1)
- Long Term:: Iloilo Doctors' College College of NursingDocument7 pagesLong Term:: Iloilo Doctors' College College of NursingAbie Jean BalbontinNo ratings yet
- NCP TbiDocument4 pagesNCP TbiWyen CabatbatNo ratings yet
- A Case Study Presentation On Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Presented byDocument78 pagesA Case Study Presentation On Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Presented byNina100% (1)
- Care Plan 5Document13 pagesCare Plan 5مالك مناصرةNo ratings yet
- NCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 pagesNCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisAya BolinasNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheets For Ventilation 5Document19 pagesCheat Sheets For Ventilation 5Syed Shahrul Naz Syed100% (1)
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Nanda NCP BasedDocument14 pagesNanda NCP Baseddeliejoyce100% (1)
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocument9 pagesFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Client With Pulmonary Tuberculosis Utilizing Orem's TheoryDocument13 pagesCare of The Client With Pulmonary Tuberculosis Utilizing Orem's TheoryRazel Kinette AzotesNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaPastor James PacadaljenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions EvaluationsAjay SupanNo ratings yet
- NCP Icu-CcuDocument6 pagesNCP Icu-CcuJohn CenasNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaNo ratings yet
- NCP and DStudyDocument8 pagesNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJamaica SaranquinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument20 pagesNursing Care PlanZamranosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanKath RubioNo ratings yet
- NCP TB MeningitisDocument1 pageNCP TB MeningitisMark Adrian D. DizorNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationDocument3 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationDocument2 pagesAnxiety Related To Hospitalization and Disease Condition As Manifested by Fiscal Expression and VerbalizationmonaNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument3 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)Document3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions Expected Outcome: (List 5 Unique To The Given Nursing DX)joyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaLeo_Rabacca_3610100% (1)
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument28 pagesNursing Care PlanChristine Karen Ang Suarez67% (3)
- CholecystitisDocument1 pageCholecystitisDianne ParungaoNo ratings yet
- NCP TBDocument7 pagesNCP TBLorraine CilloNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Hydrocephalusstar7707100% (1)
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Intracranial HemorrhageDocument41 pagesIntracranial Hemorrhagedoctormussieaberra100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument11 pagesNursing Care Planaycee0316100% (1)
- Nursing Management For Acute Respiratory FailureDocument7 pagesNursing Management For Acute Respiratory FailureEvolynNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- 8 Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pages8 Liver Cirrhosis Nursing Care PlansAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- NCP KateDor NewDocument6 pagesNCP KateDor NewSteffi GolezNo ratings yet
- PCNL Nursing Care Plan 2Document11 pagesPCNL Nursing Care Plan 2ISICLE GTNo ratings yet
- NCP Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesNCP Liver CirrhosisIris Jimenez-BuanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanNo ratings yet
- Aetiology Heart Diasease in Children May Be Congenital or AcquiredDocument23 pagesAetiology Heart Diasease in Children May Be Congenital or AcquiredkasondaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- NCP Cad ElectiveDocument1 pageNCP Cad ElectivejoegeNo ratings yet
- NCP Near DrowningDocument1 pageNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 pagesCardiogenic Shockmerin sunilNo ratings yet
- Karen Elizabeth B. Valdez Rle 2 Cues and Clues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesKaren Elizabeth B. Valdez Rle 2 Cues and Clues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Implementation Rationale EvaluationKaren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Nursing NotesDocument6 pagesNursing Notesmendozajanice0601No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Goals/ Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationGene Chavez AppleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan: Artery Blockage May BeDienizs Labini TadenaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map, Neil Floyd Ventura PDFDocument1 pageConcept Map, Neil Floyd Ventura PDFNeil Floyd VenturaNo ratings yet
- NCP CvaDocument3 pagesNCP CvaRachel Anne Cabral EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Peros: General AssessmentDocument4 pagesPeros: General AssessmentKaycee TolingNo ratings yet
- Clinical Picture of Head InjuryDocument2 pagesClinical Picture of Head InjuryVictor YanafNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Senam Kaki Terhadap Kadar Glukosa Darah Dan Nilai ABI Penderita DMDocument6 pagesPengaruh Senam Kaki Terhadap Kadar Glukosa Darah Dan Nilai ABI Penderita DMSetyardiNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - Specialized CellsDocument60 pagesWeek 5 - Specialized CellsDesiree Pescasio DimasuayNo ratings yet
- Acupuncture For Pain Management (PDFDrive - Com) 2Document108 pagesAcupuncture For Pain Management (PDFDrive - Com) 2Albert Slasher100% (1)
- M T (DR Sadiq)Document62 pagesM T (DR Sadiq)DR-Muhammad ZahidNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Is A Lifesaving Technique Useful in Many Emergencies, Including A Heart Attack or Near Drowning, in Which Someone's Breathing or Heartbeat Has StoppedDocument5 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) Is A Lifesaving Technique Useful in Many Emergencies, Including A Heart Attack or Near Drowning, in Which Someone's Breathing or Heartbeat Has StoppedMukesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Histo Lec Module 5 BookDocument54 pagesHisto Lec Module 5 Bookchuchu lalaNo ratings yet
- Taquicardia Supraventricular y CetoacidosisDocument5 pagesTaquicardia Supraventricular y CetoacidosisAlejandro CárdenasNo ratings yet
- 2.2 TCA CycleDocument14 pages2.2 TCA Cyclesabirinaly30No ratings yet
- Physiological Changes During Second Stage of LabourDocument44 pagesPhysiological Changes During Second Stage of LabourTami SelviNo ratings yet
- Personal Trainer Flashcards W ThemeDocument98 pagesPersonal Trainer Flashcards W ThemeFeriena KusairiNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument2 pagesDaftar PustakaloveummyabbyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Cells and Organs IIDocument30 pagesLecture 3 - Cells and Organs IIAhmed Examination100% (1)
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument19 pagesLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsCHRISTIE MONTANO100% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The Immune System: Retchel-Elly D. Dapli-AnDocument60 pagesDrugs Acting On The Immune System: Retchel-Elly D. Dapli-AnJoshua MendozaNo ratings yet
- Santa Monica Institute of Technology: Science 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grade (Biology and Chemistry)Document8 pagesSanta Monica Institute of Technology: Science 1: Teaching Science in Elementary Grade (Biology and Chemistry)Chapz PaczNo ratings yet
- #3 Balance of Liquid and Electrolite in Animal BodyDocument13 pages#3 Balance of Liquid and Electrolite in Animal BodyYodi MainantoNo ratings yet
- ABG Ebook PDFDocument13 pagesABG Ebook PDFM DNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Seeleys Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Cinnamon Vanputte and Jennifer Regan and Andrew Russo DownloadDocument48 pagesTest Bank For Seeleys Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Cinnamon Vanputte and Jennifer Regan and Andrew Russo DownloadBenjaminWilsongaco100% (17)
- Sistem Konduksi Jantung (Pembekalan) - DR PUT&DrHARDocument32 pagesSistem Konduksi Jantung (Pembekalan) - DR PUT&DrHARNur FarinahNo ratings yet
- Diabetes InsidipusDocument2 pagesDiabetes InsidipusLena RoweNo ratings yet
- Tensiometro Shock ProofDocument2 pagesTensiometro Shock ProofjessikaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rows's Step 1 Resources For Step 3Document4 pagesDr. Rows's Step 1 Resources For Step 3agar agar100% (1)
- Frog - S Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesFrog - S Nervous SystemTaggart Siao100% (3)
- Science10 Q3 Ver4 Mod3Document31 pagesScience10 Q3 Ver4 Mod3Berliese FriasNo ratings yet
- Human Body - A Visual Encyclopedia (PDFDrive) - 69-71Document3 pagesHuman Body - A Visual Encyclopedia (PDFDrive) - 69-71Neeha NMNo ratings yet
- Cyclic AMP Signalling PathwayDocument5 pagesCyclic AMP Signalling Pathwayrawatpooran05No ratings yet