Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 9 Module 5 GIT Algorithm
Group 9 Module 5 GIT Algorithm
Uploaded by
KIM LORIE YAP PASCUALOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group 9 Module 5 GIT Algorithm
Group 9 Module 5 GIT Algorithm
Uploaded by
KIM LORIE YAP PASCUALCopyright:
Available Formats
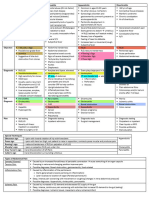
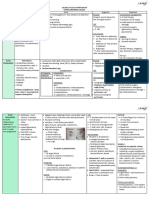
SGD 9 – Surgery Module 5: Surgical Diseases of the Digestive System
Lapoot, Legaspi, Lopez, Loquias, Lucman, Macabalang, Macabando, Macadato, Madrona
FN, 52-year old, Female, Businesswoman, Married,
RC, from Bulua CDOC 4 days PTA: PE Salient point:
-Bloatedness associated with two episodes of vomiting, Abdomen: distended abdomen, hypoactive bowel sounds,
PRESENTATION
Chief Complaint: Abdominal Distention non-bilous tense, tympanitic
- Passage of watery stools DRE: Collapsed Rectal Vault
CLINICAL
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS: 2 days PTA: Other salient points:
2 months PTA: -Bloatedness persisted, increasing abdominal discomfort
Noted decrease in caliber of stools noted Past Medical History: S/P CS-2001
(+) Obstipation, (+)Bilious vomiting with mild abdominal Personal History: Chronic Alcoholic Drinker
distention
Day of admission:
2 weeks PTA: -1 episode of vomiting
-Watery stools, yellow to brownish in character -Persistence of abdominal Distention prompted consult to
(-) Melena, (-) Hematochezia ER, and subsequently admitted
Decreased caliber to watery stools Abdominal distention
Complete obstruction Large Bowel Obstruction
Pencil-like stools LLQ pain S/P CS (2001) Bilious vomiting
Complete Bowel Obstruction Complete Bowel Obstruction Complete Bowel Obstruction Complete Bowel Obstruction
DIGANOSIS Secondary to Cancer secondary to Sigmoid Volvulus secondary to Adhesion secondary to Gallstone Ileus
CBC, BUN, electrolytes CBC, BUN, electrolytes, History of previous surgical procedure CBC, BUN, electrolytes
X-ray Abdomen Supine + Upright Abdominal X-ray and CT-scan CBC, BUN, electrolytes
DIAGNOSTIC
Chest X-ray PA Gastografin enema (Confirmatory) Diagnosed intraoperatively via Plain Abdominal X-ray
TESTS laparoscopy
CT scan of the Whole Abdomen with Contrast CT scan of the whole abdomen
Barium Enema
Colonoscopy
CBC Abdominal X-ray Laparoscopy Plain Abdominal X-ray
Assess anemia (Iron deficiency Inverted U-shaped, sausage- "Fat-bridging sign", Twisting Obstructive bowel gas pattern,
anemia common in Colon Cancer) like loop, "Omega sign", of the mesentery (-) Radiolucent stone
and elevated WBC with left shift "Coffee bean sign", Bent inner
tube sign
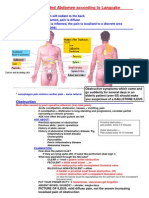
X-ray Abdomen Supine + Upright CT scan of the whole
Gas-dilated bowel loops, air-fluid Abdominal CT-scan abdomen
level seen, Whirl pattern, Bird's beak Rigler triad (Pneumobilia,
and no gas seen in the rectal vault. appearance Small bowel obstruction,
Impression: Ectopic gallstone); Site of
Large Bowel Obstruction fistulation often visible
Gastografin enema
(Confirmatory)
Bird's beak appearance
Chest X-ray PA
Atheromatous Aorta, Thoracic
Spondylosis
EXPECTED RESULTS
CT scan of the Whole Abdomen
with Contrast
Marked dilatation of the colon
particularly in the cecum,
ascending colon, hepatic
flexure,and transverse colon,
contrast and air-fluid level
Lesser degree of distention of the
descending colon with
circumferential wall thickening.
Proximal sigmoid colon is dilated
measuring 5cm with note of a
short segment (3cm) constricting
mass (2cm) diameter obliterating
the bowel lumen demonstrating
"Apple core deformity".
The sigmoid segment beyond the
mass and the rectum are well-
distended with retrogadely
introduced contrast with no
discrete lesion.
Impression: findings consistent
with distal large bowel obstruction
secondary to a short segment
constricting sigmoid mass with
malignant features.
Barium Enema
Detect small polyps even <=1cm;
large polyps >1cm
Pain control via IV medication Pain control via IV medication Pain control via IV medication Pain control via IV medication
IV fluid resuscitataion and electrolyte IV fluid resuscitation and electrolyte IV fluid resuscitation and IV fluid resuscitation and
PHARMACOLOGIC
replacement - Isotonic crystalloid replacement electrolyte replacement electrolyte replacement
PPI 40mg via IVTT Broad spectrum antibiotics with gram Broad spectrum antibiotics with Broad spectrum antibiotics with
negative, anaerobic coverage gram negative, anaerobic gram negative, anaerobic
Broad spectrum antibiotics with gram coverage coverage
negative, anaerobic coverage
Place bladder catheter to monitor Place bladder catheter to monitor Place bladder catheter to monitor
Place patient in NPO urine output urine output urine output
PHARMACOLOGIC
Perform bowel decompression via
Nasogastric tube placement and
NON-
NGT (Clear watery fluid- 50cc)
decompression
Insert Foley Catheter and Monitor
urine output
Pre-operative Diagnosis: Complete Initial Management: Detorsion via Laparoscopy or laparotomy Open/Laparoscopic
Bowel Obstruction secondary to Left rigid proctoscope; Hartmann's with adhesiolysis Enterolithotomy
sided Colonic new-growth procedure
Primary anastomoses of
remaining intestine
MANAGEMENT
4 to 6 weeks after
Exploratory Laparotomy, Subtotal Right hemicolectomy with a primary
Colectomy with end to end colorectal ileocolic anastomosis (for cecal
anastomosis. volvulus)
Repair of the choledochoenteric
Intra-operative findings: 3cm fistula + Cholecystectomy
constricting mass at sigmoid colon;
Emergent exploration and resection
markedly dilated proximal sigmoid
(for transverse colon volvulus)
colon up to the Cecum, multiple
serosal laceration with patchy
necrosis at the Cecum up to the
transverse colon. Liver is grossly
SURGICAL
normal, no palpable nodules, Minimal
clear intra-peritoneal fluid. No
carcinomatosis, No palpable pericolic
lymph node.
Post-operative Diagnosis: Closed
Loop Bowel Obstruction secondary to
Constrictive Sigmoid Colon Cancer
Stage IIB (cT4N0M0)
Histopathologic diagnosis: Well-
differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the
sigmoid with Infiltration up to the
Serosa. No lympho-vascular
invasion. Negative for tumor: 0/27
pericolic lymph node harvested. All
resection margins.
Pathologic Stage: Stage IIB
(pT4aN0M0)
Bowel Ischemia and perforation Risk for bowel strangulation Infection
Perforation
Recurrence Pancreatitis
Recurrence of symptoms
Recurrence of 20-40% to most Secondary peritonitis if there is Acute Renal Failure
common sites :local site within the perforation
abdomen, liver, and/or lung) Intraabdominal hematoma Biliary Fistula
Short bowel syndrome if a large
COMPLICATIONS
Metastasis part of the small bowel has to be Intra abdominal Abscess
removed due to necrosis
Lymph node involvement
Death (46%)
Metachronous disease (a secondary
primary tumor)
- Colonoscopy performed within 12 Follow-up after 6 months. Check Follow up after 11 months Follow-up visit 1 to 2 weeks after
months after the diagnosis of the patients exhibiting signs of (mean) to check for recurrence of surgery
FOLLOW-UP
original cancer; if normal, should be recurrence on physical or symptoms that may require
repeated every 3 to 5 yrs thereafter. radiological examination. repeat intra-abdominal surgery
- Endoscopic examinations (every 3-6
months for 3 years, then every 6
months for 2 years)
- Carcinoembryonic Antigen every 3-6
months for 2 years
- CT scans performed annually for 5yrs
You might also like
- Concept Map On AppendicitisDocument6 pagesConcept Map On Appendicitisitalisayan_rondario80% (5)
- NFPA 13 PRESSURE TEST PROCEDURES (Fire Pro)Document2 pagesNFPA 13 PRESSURE TEST PROCEDURES (Fire Pro)Mechanical Engineer33% (3)
- Gastro HistoryDocument4 pagesGastro HistoryAsma SikanderNo ratings yet
- MS-2 GallbladderDocument2 pagesMS-2 Gallbladderelijahdale.guillergan-05No ratings yet
- Department of Surgery: Case Presentation Intestinal ObstructionDocument46 pagesDepartment of Surgery: Case Presentation Intestinal Obstructionhadil ayeshNo ratings yet
- Alicia's CCFP Exam GuideDocument133 pagesAlicia's CCFP Exam Guidejpdavid95No ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal Pain Intern DR Shamol PrintDocument12 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain Intern DR Shamol PrintmaybeNo ratings yet
- Im - Acute PancreatitisDocument14 pagesIm - Acute PancreatitisTrisNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersDocument4 pagesMed Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersMaxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- Presenting Symptoms:: Gastrointestinal HistoryDocument4 pagesPresenting Symptoms:: Gastrointestinal HistoryTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing EnterocolitisDocument24 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitisfadhila khairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Feeding Intolerance - Gut Obs - DownDocument30 pagesFeeding Intolerance - Gut Obs - Downภาวิต วัฒนกูลNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument8 pagesCholelithiasissaranya amuNo ratings yet
- History Taking For CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesHistory Taking For CholelithiasisToria053100% (1)
- Acute Abdominal Pain RevisiDocument40 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain RevisinadiasalmaNo ratings yet
- Radiology of The Colon: Bambang Soeprijanto, DR., Sprad. Medical Faculty Airlangga University SurabayaDocument61 pagesRadiology of The Colon: Bambang Soeprijanto, DR., Sprad. Medical Faculty Airlangga University SurabayayudisNo ratings yet
- Bowel ObstructionsDocument24 pagesBowel ObstructionsArchie ZhangNo ratings yet
- Critical Disorders and Complications of The GDocument2 pagesCritical Disorders and Complications of The GVictor MurilloNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis - Knowledge at AMBOSSDocument1 pageCholelithiasis - Knowledge at AMBOSSManar AlahmadiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To A Case of Obstructive JaundiceDocument22 pagesClinical Approach To A Case of Obstructive JaundiceEsraa SalemNo ratings yet
- 116 - Alterations in GI EliminationDocument12 pages116 - Alterations in GI EliminationGino-o, KyleNo ratings yet
- SURG Abomen CLINICSDocument5 pagesSURG Abomen CLINICSMeg AmoonNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis ProtocolDocument3 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitis Protocoleddy riachyNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal SurgeryDocument12 pagesGastrointestinal SurgeryHafsa AliNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing GastroDocument3 pagesPediatric Nursing GastronieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rami Radilology LecDocument25 pagesDr. Rami Radilology LecmarwaalgheilaniNo ratings yet
- Bowel OcclusionDocument4 pagesBowel OcclusionAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- IBS Presentation Week 213Document17 pagesIBS Presentation Week 213A MITCHELLNo ratings yet
- C A S H I A: Stomach Is Sterile, No Bacteria For Synthesizing Vit KDocument2 pagesC A S H I A: Stomach Is Sterile, No Bacteria For Synthesizing Vit KMhae TabasaNo ratings yet
- Small Bowel ObstructionDocument38 pagesSmall Bowel ObstructionRUSSELL CILOTNo ratings yet
- A&p - All Files in OneDocument104 pagesA&p - All Files in OneElvira MirandaNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)MattNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis CholecystitisDocument1 pageCholelithiasis Cholecystitissamliebareng77No ratings yet
- Chronic Inflammation of The Gallbladder Eventually The Bile DuctDocument2 pagesChronic Inflammation of The Gallbladder Eventually The Bile DuctYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal SystemDocument9 pagesGastrointestinal SystemMikaella CondeNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Chronic DiarrheaDocument1 pageGastroenterology Chronic DiarrheaNour SamadNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument5 pagesGastrointestinal Manifestations of Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDaniela Constanta SirbuNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument47 pagesAcute AbdomenDani LeeNo ratings yet
- Gastro Reviewer FinalsDocument5 pagesGastro Reviewer Finalsadd.bdrcNo ratings yet
- Angel Problem 4a GITDocument48 pagesAngel Problem 4a GITMaxend Arselino SilooyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal ChartsDocument3 pagesAbdominal ChartsAmanda MuchaNo ratings yet
- Internal Diagnostic Ii Examination Procedures: Patient EvaluationDocument76 pagesInternal Diagnostic Ii Examination Procedures: Patient EvaluationbjpalmerNo ratings yet
- Causes of Acute PeritonitisDocument6 pagesCauses of Acute PeritonitisYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- 227 Ramirez, Diana Rose S. July 13, 2022Document2 pages227 Ramirez, Diana Rose S. July 13, 2022Diana Rose RamirezNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Abdomen (Gastrointestinal System) : Deep Internal AnatomyDocument4 pagesAssessment of The Abdomen (Gastrointestinal System) : Deep Internal AnatomyHNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction in Pediatric PatientsDocument25 pagesIntestinal Obstruction in Pediatric PatientsHaryo Priambodo100% (1)
- Gastro-Intestinal System Diagnostic TestsDocument11 pagesGastro-Intestinal System Diagnostic TestsFev BanataoNo ratings yet
- Presentation From Today's Meeting !Document67 pagesPresentation From Today's Meeting !chaitanya varmaNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument19 pagesAcute Abdomenmazin89No ratings yet
- 2020 FP2 Systemic Surgery GIDocument65 pages2020 FP2 Systemic Surgery GIVon FlickNo ratings yet
- The Acute Distended AbdomenDocument2 pagesThe Acute Distended AbdomenTom Mallinson100% (1)
- CH 21 Abdomen JARVISDocument34 pagesCH 21 Abdomen JARVISAndy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Summary Case Peptic Ulcer and PeritonitisDocument8 pagesSummary Case Peptic Ulcer and PeritonitissyududNo ratings yet
- Preceptorial Format 2023 Group 2Document5 pagesPreceptorial Format 2023 Group 2Cayla DeniceNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Radiology - Gastrointestinal RadiologyDocument20 pagesDiagnostic Radiology - Gastrointestinal RadiologyhalesipsumNo ratings yet
- NL1 Gi Tu 2024Document32 pagesNL1 Gi Tu 2024semessor021245No ratings yet
- Docc NotesDocument4 pagesDocc Noteslovegoodluna812No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Acalculous Cholecystopathy, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Senior Clerk 2022 2023 Case Requirement Orthopedics Word 1Document2 pagesSenior Clerk 2022 2023 Case Requirement Orthopedics Word 1KIM LORIE YAP PASCUALNo ratings yet
- Coniendo Scanned Chart PDFDocument86 pagesConiendo Scanned Chart PDFKIM LORIE YAP PASCUALNo ratings yet
- Application Form: Professional Regulation CommissionDocument1 pageApplication Form: Professional Regulation CommissionKIM LORIE YAP PASCUALNo ratings yet
- Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver DiseaseDocument1 pageNon Alcoholic Fatty Liver DiseaseKIM LORIE YAP PASCUALNo ratings yet
- p.346 Williams P. 362 PDF P. 371 Williams P. 371 PDF P. 388 Williams P. 404 PDFDocument1 pagep.346 Williams P. 362 PDF P. 371 Williams P. 371 PDF P. 388 Williams P. 404 PDFKIM LORIE YAP PASCUALNo ratings yet
- Patho Lec 19: Effects of Alcohol in The Liver: D. Regenerating NoduleDocument15 pagesPatho Lec 19: Effects of Alcohol in The Liver: D. Regenerating NoduleKIM LORIE YAP PASCUALNo ratings yet
- Lipid Transport and StorageDocument34 pagesLipid Transport and StorageGuru Kiran C KNo ratings yet
- Nizam'S Institute of Medical Vs Prasanth S Dhananka Ors On 14 May 2009Document26 pagesNizam'S Institute of Medical Vs Prasanth S Dhananka Ors On 14 May 2009Saket SubhamNo ratings yet
- Region 4-ADocument22 pagesRegion 4-Aapi-251414497No ratings yet
- GIT Pathology Lecture 2005Document161 pagesGIT Pathology Lecture 2005api-3700579100% (5)
- Industrial Multi Strand Cables HSN CODE: 85.44.60.20 Price List: 1 December 2021 LP NO. KEI/W&F/LP/21-22/06 DT.01.12.2021Document2 pagesIndustrial Multi Strand Cables HSN CODE: 85.44.60.20 Price List: 1 December 2021 LP NO. KEI/W&F/LP/21-22/06 DT.01.12.2021Sanket PhatangareNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Service IndustryDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Service Industrysamy7541No ratings yet
- Food AdulterationDocument20 pagesFood AdulterationMahanth ThoraviNo ratings yet
- EMS14 EMS Products Only Catalogue 2022 V17 FINAL ScreenDocument20 pagesEMS14 EMS Products Only Catalogue 2022 V17 FINAL ScreenAbdallah MohamedNo ratings yet
- Position Size Calculator NQDocument2 pagesPosition Size Calculator NQKingston GroupNo ratings yet
- Medical Glossary Midterms ExamDocument7 pagesMedical Glossary Midterms ExamFev BanataoNo ratings yet
- Next Step Advanced Medical Coding and Auditing 2017 2018 Edition 1st Edition Buck Test BankDocument7 pagesNext Step Advanced Medical Coding and Auditing 2017 2018 Edition 1st Edition Buck Test Bankqueeningalgatestrq0100% (30)
- Guides For Storage Tanks Nozzles Orientation - LinkedInDocument5 pagesGuides For Storage Tanks Nozzles Orientation - LinkedInragulNo ratings yet
- Sample Project Propsal BasisDocument3 pagesSample Project Propsal BasisNoel Vincent AgonoyNo ratings yet
- Kalas BK DP SGR UlDocument2 pagesKalas BK DP SGR Ulmatthew_edwards_49No ratings yet
- ENKO 24VDC 20A ChargerDocument2 pagesENKO 24VDC 20A ChargerMohammad kazem DehghaniNo ratings yet
- Power System Nagrath Kothari SolutionsDocument88 pagesPower System Nagrath Kothari SolutionsChandra Sekhar Chebiyyam81% (16)
- PFD P&id PDFDocument431 pagesPFD P&id PDFA.R.100% (1)
- Fireman's Rule and Its Extension To EMT'sDocument7 pagesFireman's Rule and Its Extension To EMT'sShahin DamouiNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Synthetic ImportanceDocument28 pagesReactions of Synthetic ImportanceRx Nadeem ChhipaNo ratings yet
- DuacDocument4 pagesDuaciloveyoubabesNo ratings yet
- K K A C D W K P S K T: Eteraturan Unjungan Ntenatal ARE I Ilayah Erja Uskesmas Lawi Abupaten EgalDocument6 pagesK K A C D W K P S K T: Eteraturan Unjungan Ntenatal ARE I Ilayah Erja Uskesmas Lawi Abupaten EgalSelly MonicaNo ratings yet
- Tlm4all@NMMS 2019 Model Grand Test-1 (EM) by APMF, TenaliDocument12 pagesTlm4all@NMMS 2019 Model Grand Test-1 (EM) by APMF, TenaliThirupathaiah100% (2)
- List of Headings: CarbohydratesDocument5 pagesList of Headings: Carbohydratessneh1509No ratings yet
- Ingles Unidad 2 (Neftali)Document4 pagesIngles Unidad 2 (Neftali)NEFTALI TRUJILLO FLORESNo ratings yet
- Catchbox PlusDocument18 pagesCatchbox PlusmalejklusinaNo ratings yet
- Eim 8 Summative TestDocument2 pagesEim 8 Summative TestMaribel G. Montiar100% (2)
- Jet Compressors Pulp PaperDocument10 pagesJet Compressors Pulp PaperIsmail SalihNo ratings yet
- Thomas MaltusDocument3 pagesThomas MaltusJose Antonio Castro SanchezNo ratings yet
- First Steps SE TOOL KITDocument10 pagesFirst Steps SE TOOL KITSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet