Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1&2: Modal Verbs
English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1&2: Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
Roxan Pascua GanadoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1&2: Modal Verbs
English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1&2: Modal Verbs
Uploaded by
Roxan Pascua GanadoCopyright:
Available Formats
SCHOOL OF SAINT MATTHIAS, INC
Brgy. 04, Tumauini, Isabela
S. Y. 2020-2021
ENGLISH 9
Quarter 1 – Module 1&2:
Modal Verbs
LEARNING PACKAGE
“Be a Matthiasian, Make a Difference” 1
Topics:
Modal Verbs
Content Standard:
The learner demonstrates understanding of how Anglo-American literature
and other text types serve as means of enhancing the self; also how to use processing,
assessing, summarizing information, word derivation and formation strategies,
appropriate word order, punctuation marks and interjections to enable him/her to
participate actively in a speech choir.
Performance Standard:
The learner actively participates in a speech choir through using effective
verbal and non-verbal strategies based on the following criteria: Focus, Voice,
Delivery, Facial Expressions, Body Movements/ Gestures and Audience Contact.
Most Essential Learning Competency:
Express permission, obligation, and prohibition using modals
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the module, the learners are expected to:
1. Express permission, obligation, prohibition, probability, possibility,
uncertainty, impossibility, (in)ability;
2. Use modals in asking/giving advice and direction, drawing conclusions and
predicting outcomes; and
3. Form sentences using appropriate modals.
PRAYER
Good morning class! Before we start our lesson, let us first feel the presence of the
Lord.
COME HOLY SPIRIT
Come Holy Spirit, fill the hearts of your faithful and kindle in them the fire of your
love.
V. Send forth your Spirit, and they shall be created.
R. And You shall renew the face of the earth.
Let us pray.
O, God, who by the light of the Holy Spirit, did instruct the hearts of the faithful,
grant that by the same Holy Spirit we may be truly wise and ever enjoy His
consolations. Through Christ Our Lord. Amen.
DEVELOPMENT OF THE LESSON
This lesson helps students to recognize and be able to use modals which express
prohibition, obligation and permission properly.
LESSON 1: Modals: Prohibition, Obligation and
Permission
Modals are special verbs that use to indicate modality such as prohibition,
obligation, permission, probability, ability, request and suggestion.
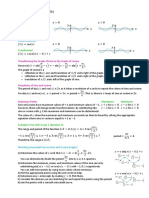
M ODAL M EANING/USE EXAM PLE
can Used to express ability I can make banana
(to be able to do chips.
something) She can’t speak
Spanish.
Used to ask for Can I use your
permission computer?
“Be a Matthiasian, Make a Difference” 2
Can I go now?
Used to make requests Can I have more cake?
or suggestions Can I have the book?
Could (past Describes an ability that I could dance when I
form of can) someone had in the past was young.
You could see the light
flickering.
Often used in auxiliary Could I take this bag
functions to express with me?
permission politely You could borrow my
phone.
Used to express All of them could ride
possibility in the bus.
You could always stay
at the villa.
May Used to ask for formal May I talk to you in
permission private?
May I get my talent
fee now?
Used to suggest She may agree with
something that is your suggestion.
possible They may not be
coming tonight.
Might (past Used to suggest a He might have rescued
form of may) smaller possibility than the dog.
may does I might go see a dentist
Must Used to express I must finish the
something formally cooking by noon.
required or necessary The government must
provide free COVID-19
vaccine for everybody.
Used to show that He must be a jewel.
something is very likely You must hurry!
Modals mainly add information to other verbs. How are these modals formed
in sentences?
Grammatically, modal verbs have their own rules. Let’s learn about them.
1. A modal verb never change in form.
Incorrect Correct
He cans. He can.
They woulded… They would…
2. Use the original form of the verb, meaning NO -s, -ing, or ed after the verb.
Original verb form(underlined) Subject + Modal + original verb form
He dances. He can dance.
The students wore an ID. The students must wear an ID.
I am taking my dog in the park. I should take my dog in the park.
Popcorn is sick. Popcorn might be sick.
3. Modals can’t be used in different times and tenses. Modals don’t have past,
perfect or future tense like regular verbs have.
Incorrect Correct
“Be a Matthiasian, Make a Difference” 3
He can danced all night. He can dance all night.
The students must wearing an ID The students must wear an ID.
Stores may will open on holidays. Stores may open on holidays.
4. Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs which means you make negatives by adding NOT
at the end of the verb
can-can’t could- couldn’t must- mustn’t
will- won’t would-wouldn’t shall- shan’t
may – may not might- might not should-shouldn’t
Simple and Phrasal modals
Simple modals are the single-word modals while phrasal modals (also known
as periphrastic modals) are phrases formed from a single verb group with another
verb that change the meaning of a verb.
Simple modals Phrasal modals Express
Can, could Be able to Ability
Can, may Be allowed to Permission
May, might may be able to, probability
might be able to,
may be allowed to,
or might be allowed to
Should Ought to , had better Advice
Simple modals Phrasal modals Express
must be supposed to, necessity or obligation
be obligated to,
be going to,
have to
have got to.
Forming Sentences Using Modals:
Both simple and phrasal modals follow the same formula in forming
sentences:
SUBJECT + SIM PLE M ODAL + BASE FORM OF THE VERB
Note: Examples following this formula are in italics.
Simple Modals Meaning/Use Example
Can To express ability I can speak a little Russian.
To request permission Can I open the window?
Could To describe an ability that I could dance when I was
someone had in the past young.
May To ask for formal permission May I talk to you in private?
To suggest something that is She may agree with your
possible suggestion.
Must To express obligation I must go now.
“Be a Matthiasian, Make a Difference” 4
To express strong belief She must be over 90 years old.
Might To suggest a smaller I might go see a dentist.
possibility than may does
Will/Shall To suggest future time He shall call me tonight.
reference (more formal)
The train will leave at dawn
Would To request or offer If I were you, I would ask for an
in if-sentences advice.
Should To give advice You should quit smoking.
Phrasal (Periphrastic) M odals
SUBJECT + PHRASAL M ODAL + BASE FORM OF THE VERB
Note: Examples following this formula are in italics.
Phrasal Modals Meaning/Use Example
be able to To express ability Example:
We are able to speak three languages.
I’m not able to drive a truck.
be allowed to To express Example:
permission The manager said, he is allowed to
receive his bonus.
He isn’t
(He’s not) allowed to receive his bonus,
however.
I wasn’t allowed to receive any bonus
last year.
I wonder if we’ll be allowed to receive
our birthday bonus next year.
may be able to, To express Example:
might be able to, probability She may be able to come to the meeting
may be allowed, tomorrow.
be allowed to He might not be allowed to borrow
money next month.
Ought to , To imply an Example:
had better advice You ought to get your car checked. It’s
making loud brake noises.
You shouldn’t come. Come back later.
He had better pay his school fees.
He’d better not be anxious.
supposed to be To express I’m supposed to be in school at 7:00
obligation every morning. I’m not supposed to
or necessity be there at 6:00 am, though.
“Be a Matthiasian, Make a Difference” 5
Maria is obligated to send money to her
family in Pampanga every month.
obligated to She wasn’t obligated to send it last year,
though.
She will be obligated to send cards for
many years in the future, however.
We are going to walk for 3 miles in the
field
Making questions with modals:
Study the given formula in forming a question and follow the format using
modals.
Modal + subject +main verb Sentence: You could come early to my
party.
1. Could + you + come Q: Could you come early to my party?
Wh-question+modal+subject+verb
WH- question +Could +you +come Q: When could you come early to my
party?
Modal + subject +main verb Sentence: I have to dance.
2. Have to: Q: Do I have to dance?
Do/does/did+subject+have to+ main
verb
WH-question+do/does/did+have to + Q: When do I have to dance?
main verb
Modal + subject +main verb Sentence: We should practice tonight.
3. Should+ we +practice Q: Should we practice tonight?
WH-question+should+we+practice Q: Where should we practice tonight?
References:
ECAS pages 139-140
Internet
https://znnhs.zdnorte.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Eng9_Q1_W1.pdf
---
This is now the end of our module. I would like to congratulate you for being patient
and for exerting effort in finishing your task. May God continue to give you wisdom
and may he continue to bless and guide you in order to achieve your goals and
aspirations in life. God bless for your next task!
“Be a Matthiasian, Make a Difference” 6
You might also like
- Question 1 (1 Point)Document44 pagesQuestion 1 (1 Point)milanchabhadiya288No ratings yet
- Compressor Valves and Unloaders For Reciprocating CompressorsDocument19 pagesCompressor Valves and Unloaders For Reciprocating CompressorsGeorge Dom100% (2)
- A Quantum Explanation of Sheldrakes Morphic Resonance by A GoswamiRupert SheldrakeDocument13 pagesA Quantum Explanation of Sheldrakes Morphic Resonance by A GoswamiRupert SheldrakeDavid Jaramillo KlinkertNo ratings yet
- Adding and Subtracting Polynomials LessonDocument4 pagesAdding and Subtracting Polynomials Lessonapi-249037964100% (4)
- Sentence Structurehhkkkhg Fronting Fun Activities Games Grammar Guides 29562Document6 pagesSentence Structurehhkkkhg Fronting Fun Activities Games Grammar Guides 29562Amparo De La HeraNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic TestDocument2 pagesDiagnostic TestAngelyn B. GaydaNo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1ADocument22 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1ACarlo GilberoNo ratings yet
- Dreams DeferredDocument39 pagesDreams DeferredMark CAÑETANo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 2 - Week 4Document14 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 2 - Week 4KAERYLL MAY NAVALESNo ratings yet
- A Learning Module In: English 9Document17 pagesA Learning Module In: English 9sandy navergas100% (1)
- Connotation Tone Word ChoiceDocument8 pagesConnotation Tone Word Choiceapi-468525987No ratings yet
- 4 Pics One Word PuzzleDocument8 pages4 Pics One Word PuzzleLadylyn Punzalan - SusiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 15Document53 pagesLesson 15Gelly LadagaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Prejudicially BiasedDocument3 pagesActivity 3 Prejudicially BiasedJubileen CasidaNo ratings yet
- Englis 9-L6 ModuleDocument12 pagesEnglis 9-L6 ModuleDog GodNo ratings yet
- Pronouns G10Document10 pagesPronouns G10Israel AsinasNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Quarter 3 Module 1 Creative Writing Defined - CompressDocument16 pagesCreative Writing Quarter 3 Module 1 Creative Writing Defined - CompressLucille GalangNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 EnglishDocument2 pagesGrade 9 EnglishRenDenverL.DequiñaIINo ratings yet
- Eng10 Q2 Module 5 Argumentative EssayDocument11 pagesEng10 Q2 Module 5 Argumentative Essayclairearabelle iloyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of 7 Ages of MenDocument6 pagesAnalysis of 7 Ages of MenJosiah Ruth RosarioNo ratings yet
- English 9 Test Questionaire 2ND QuarterDocument14 pagesEnglish 9 Test Questionaire 2ND QuarterFretzyl Labrador Destreza0% (1)
- Eng8 Mod4 Q3 TrimmedDocument15 pagesEng8 Mod4 Q3 TrimmedAlyssa Sheerene MacalinoNo ratings yet
- Expanding Sentences Through Verb ModificationDocument4 pagesExpanding Sentences Through Verb ModificationJanine de VeraNo ratings yet
- English 10 Q3 Module 4Document34 pagesEnglish 10 Q3 Module 4Elsiefranciso CruzNo ratings yet
- Elements of A Short StoryDocument4 pagesElements of A Short StoryA CNo ratings yet
- 3bagrut Module F Answers To The Road Not TakenDocument3 pages3bagrut Module F Answers To The Road Not TakenSyed Yusuf Saadat100% (1)
- Group Dynamics For Psalm of LifeDocument1 pageGroup Dynamics For Psalm of LifeRudy EsposoNo ratings yet
- English 10 Q4W3Document28 pagesEnglish 10 Q4W3NOEL MENDOZANo ratings yet
- SLM E9q3m4Document16 pagesSLM E9q3m4Jade BaliolaNo ratings yet
- SC21LIT - Handout 6 Lesson 6 Biographical Linguistic and Sociocultural ContextDocument8 pagesSC21LIT - Handout 6 Lesson 6 Biographical Linguistic and Sociocultural ContextAaron John CapistranoNo ratings yet
- New Eng Act Sem BreakDocument4 pagesNew Eng Act Sem BreakDivine Grace CabungcagNo ratings yet
- ACHIEVEMENT TEST SDO PAMPANGA GRADE 9 Edited 3Document8 pagesACHIEVEMENT TEST SDO PAMPANGA GRADE 9 Edited 3jobert de jesus100% (1)
- HOMEROOM GUIDANCE (Learning Activity Sheet) : Quarter 1 - Week 6: Enhancing Self-AwarenessDocument3 pagesHOMEROOM GUIDANCE (Learning Activity Sheet) : Quarter 1 - Week 6: Enhancing Self-AwarenessSalve SerranoNo ratings yet
- Unit Learning Plan: Notre Dame of Masiag, IncDocument21 pagesUnit Learning Plan: Notre Dame of Masiag, IncThelma LanadoNo ratings yet
- ApolonioDocument2 pagesApolonioRomesor ApolNo ratings yet
- What?!: A Semantic Analysis On The Types of Meaning Found in SB19's What? Lyrics Based On Geoffrrey Leech's Seven Types of MeaningDocument14 pagesWhat?!: A Semantic Analysis On The Types of Meaning Found in SB19's What? Lyrics Based On Geoffrrey Leech's Seven Types of MeaningDaniele Clarise NogaNo ratings yet
- Poetic Conventions - Sound Devices WorksheetDocument6 pagesPoetic Conventions - Sound Devices WorksheetCHRISTIAN CANASNo ratings yet
- Later That Year, MLK JR. Is: AwardedDocument13 pagesLater That Year, MLK JR. Is: AwardedVergel BerdanNo ratings yet
- Name: - Grade Level & Section: - Pre-Test A. Directions: Read and Understand Each Statements and Questions Carefully. Then Write TheDocument35 pagesName: - Grade Level & Section: - Pre-Test A. Directions: Read and Understand Each Statements and Questions Carefully. Then Write TheAdee Buniel HuerteNo ratings yet
- Class 1 - Weekly AssignmentDocument4 pagesClass 1 - Weekly AssignmentMuhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- English 9 2ND Grading Module 1 and 2Document8 pagesEnglish 9 2ND Grading Module 1 and 2Abigail GumabayNo ratings yet
- English 9 q3 Module 2Document33 pagesEnglish 9 q3 Module 2Mary Joy GeraldoNo ratings yet
- Verbals Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesVerbals Lesson PlanAriane BatuaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document34 pagesLesson 1jay meily100% (2)
- FallacyDocument39 pagesFallacyArien kaye Vallar0% (1)
- Feminist Approach To Literature: Russel J. AporboDocument30 pagesFeminist Approach To Literature: Russel J. AporboRussel AporboNo ratings yet
- Types of NounsDocument8 pagesTypes of Nounsapi-277200711No ratings yet
- Pe 4TH Quarter Exam ReviewerDocument2 pagesPe 4TH Quarter Exam ReviewerHaitham TomawisNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 SPJ Summative 2Document2 pagesGrade 9 SPJ Summative 2Ryan BustilloNo ratings yet
- S O Y C E T I: Grade 8-EnglishDocument6 pagesS O Y C E T I: Grade 8-EnglishJennifer AntazoNo ratings yet
- Figures of SpeechDocument16 pagesFigures of SpeechKarla Javier PadinNo ratings yet
- E9Q1 Module2 Lesson1 VelosoDocument27 pagesE9Q1 Module2 Lesson1 VelosoSteffen RamirezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document15 pagesLesson 2Ma Nichole L. JugaoNo ratings yet
- LINEAR and NONLINEAR TEXTDocument7 pagesLINEAR and NONLINEAR TEXTjallilah barambanganNo ratings yet
- Not Proficient 5 Pts Close To Proficient 10 Pts Proficient 20 Pts Excellent 25 PtsDocument5 pagesNot Proficient 5 Pts Close To Proficient 10 Pts Proficient 20 Pts Excellent 25 PtsAroma EyreNo ratings yet
- Noun Exercise AnswerDocument2 pagesNoun Exercise AnswerNatalia ErvinaNo ratings yet
- English 10 (Week 1 & 5)Document27 pagesEnglish 10 (Week 1 & 5)Jubylyn AficialNo ratings yet
- Q3W4M (English)Document20 pagesQ3W4M (English)Peridot PinesNo ratings yet
- Oral Com. Week 8Document3 pagesOral Com. Week 8Steven Paul BacantoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English For Grade 10 Empathizing With OthersDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in English For Grade 10 Empathizing With Othersmica simanesNo ratings yet
- Personal Narrative Essay Example For High School PDFDocument2 pagesPersonal Narrative Essay Example For High School PDFMudassir PgcNo ratings yet
- Critical Approaches in Writing A Critique: Grade 12 - English For Academic and Professional Purposes (WEEK 5)Document7 pagesCritical Approaches in Writing A Critique: Grade 12 - English For Academic and Professional Purposes (WEEK 5)CAGULADA, SAMANTHA CAMILA B.No ratings yet
- Pre-Test: Multiple Choice: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer On ADocument20 pagesPre-Test: Multiple Choice: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write Your Answer On AI am julia VillagonzaloNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade X: I. ObjectivesDocument5 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Grade X: I. ObjectivesJeremie GermanNo ratings yet
- Steps in Using ZoomDocument13 pagesSteps in Using ZoomRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- Steps To Use Google MeetDocument7 pagesSteps To Use Google MeetRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 3 - Module 5&6: GeneralizationDocument6 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 3 - Module 5&6: GeneralizationRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 3&4: ConditionalsDocument7 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 1 - Module 3&4: ConditionalsRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Types of CommunicationDocument5 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Types of CommunicationRoxan Pascua Ganado67% (3)
- English 9: Quarter 4 - Module 1&3: I'm Glad I Was Born Poor by Nilda G. MilanDocument6 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 4 - Module 1&3: I'm Glad I Was Born Poor by Nilda G. MilanRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 4 - Module 1&3: I'm Glad I Was Born Poor by Nilda G. MilanDocument6 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 4 - Module 1&3: I'm Glad I Was Born Poor by Nilda G. MilanRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 4 - Module 4&5: How To Make Your StandDocument5 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 4 - Module 4&5: How To Make Your StandRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 4 - Module 4&5: How To Make Your StandDocument4 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 4 - Module 4&5: How To Make Your StandRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1&2: Modal VerbsDocument6 pagesEnglish 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1&2: Modal VerbsRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 10: I.Objectives A. Identify The Elements of The Story of KeeshDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 10: I.Objectives A. Identify The Elements of The Story of KeeshRoxan Pascua GanadoNo ratings yet
- Circular Functions PDFDocument2 pagesCircular Functions PDFShane RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- Deluxe Programmable Thermostat: Climate PerfectDocument12 pagesDeluxe Programmable Thermostat: Climate PerfectBrian TseNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor Specification Sheet: Operating ConditionsDocument6 pagesCentrifugal Compressor Specification Sheet: Operating ConditionsIsmail SayyedNo ratings yet
- Rift Valley University: Department: - Weekend Computer ScienceDocument13 pagesRift Valley University: Department: - Weekend Computer ScienceAyele MitkuNo ratings yet
- MICFL Annual Report 2017-18Document147 pagesMICFL Annual Report 2017-18Hasan Mohammad MahediNo ratings yet
- Oana Adriana GICADocument42 pagesOana Adriana GICAPhilippe BrunoNo ratings yet
- Carole King - Hard Rock CafeDocument1 pageCarole King - Hard Rock CafeauresmikeNo ratings yet
- 02 Energy Harvesting For Aut. SystemsDocument304 pages02 Energy Harvesting For Aut. SystemsJúlio Véras100% (2)
- Power Calculation Drum MotorsDocument2 pagesPower Calculation Drum MotorsFitra VertikalNo ratings yet
- Africa Business Map 2022Document80 pagesAfrica Business Map 2022SaktiMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- KITEPDocument207 pagesKITEPMarleneAgustinNo ratings yet
- Info 15614 - 2017Document34 pagesInfo 15614 - 2017uğur özdemirNo ratings yet
- Date - 1 - 9 - 2024 Time - 8 - 42 - 56 - 850Document1 pageDate - 1 - 9 - 2024 Time - 8 - 42 - 56 - 850ANKUSH 87205312No ratings yet
- Lovato 2013Document5 pagesLovato 2013AjaNo ratings yet
- 2023 California Model Year 1978 or Older Light-Duty Vehicle SurveyDocument10 pages2023 California Model Year 1978 or Older Light-Duty Vehicle SurveyNick PopeNo ratings yet
- Future Trends in European Public Administration and Management: An Outside-In PerspectiveDocument45 pagesFuture Trends in European Public Administration and Management: An Outside-In PerspectivevickyNo ratings yet
- An5265 LT5265Document4 pagesAn5265 LT5265maldomattNo ratings yet
- Piping Material Specification - Tsmto 99fu M 99 Pt0 001 Rev0!3!65Document64 pagesPiping Material Specification - Tsmto 99fu M 99 Pt0 001 Rev0!3!65epbamdad100% (1)
- DTU EE 4th Sem Midsem SyllabusDocument5 pagesDTU EE 4th Sem Midsem SyllabusHimanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Riksbanken Nat UpplagaDocument528 pagesRiksbanken Nat UpplagaOscar Ubeda SegmarNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis JollibeeDocument5 pagesCase Analysis JollibeeMicah Charish DomingoNo ratings yet
- Extractor de Probetas DEMTECHDocument2 pagesExtractor de Probetas DEMTECHPaul Alex Quiroz BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- Drama 30 Year Plan RittingerDocument2 pagesDrama 30 Year Plan Rittingerapi-490177257No ratings yet
- Rina Floating Docks Res7-Eng2022Document28 pagesRina Floating Docks Res7-Eng2022Osman ÖzenNo ratings yet
- Research Paper 1Document14 pagesResearch Paper 1Fatima SinghNo ratings yet