Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polysaccharide From Plant Starch or Amylum Is A Polymeric Carbohydrate Consisting of Numerous Glucose Units Joined by
Polysaccharide From Plant Starch or Amylum Is A Polymeric Carbohydrate Consisting of Numerous Glucose Units Joined by
Uploaded by
Pranchiska Vira Jimenez GierranOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polysaccharide From Plant Starch or Amylum Is A Polymeric Carbohydrate Consisting of Numerous Glucose Units Joined by
Polysaccharide From Plant Starch or Amylum Is A Polymeric Carbohydrate Consisting of Numerous Glucose Units Joined by
Uploaded by
Pranchiska Vira Jimenez GierranCopyright:
Available Formats
POLYSACCHARIDE FROM PLANT
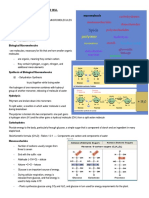
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by
glycosidic bonds. The chains formed during the condensation reaction are either linear or highly
branched molecules. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants as energy storage through
the process of photosynthesis. The iodine test reacts with starch to form deep to purple complex.
Natural starches are mixtures of 10 to 20%amylose and 80-90% amylopectin. The function of
amylopectin is to aid in energy supply for plants. Amylose is starch responsible for the color formation
in the presence of iodine. The iodine molecule slips inside the amylose coil. The iodine reagent is
composed of iodine, water, and potassium iodide. (Josue & Ocenar, PhD, 2014). If starch amylose is not
present, then the color will stay orange or yellow.
POLYSACCHARIDE FROM ANIMAL TISSUE
Glycogen is a polysaccharide that is present in the body and stores in the liver and the muscles.
It serves as a reserve supply of glucose. The liver stores glycogen to provide rapid
replenishment of glucose during fasting. Muscle and other tissues store glycogen as a source of
intracellular glucose to oxidized for energy. Glycogen is the only carbohydrate of animal origin.
The total amount of glycogen in a well- nourished adult human body is about 350grams divided
almost equally between the liver and muscle. Glycogen forms a colloidal dispersion in water and
gives off a red color with iodine. It is formed
You might also like
- Cho Chon FatsDocument26 pagesCho Chon FatsKit LaraNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5Document12 pagesLab Report 5aryavijay78% (9)
- PolysaccharidesDocument7 pagesPolysaccharidesAkram ZayedNo ratings yet
- PolysaccharidesDocument7 pagesPolysaccharidesgayathriNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument8 pagesCarbohydratesCyrus Flores,No ratings yet
- Starch and Iodine - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument1 pageStarch and Iodine - Chemistry LibreTextsMeow CattoNo ratings yet
- The Human's FoodDocument6 pagesThe Human's FoodNikko Adhitama100% (2)
- CarbohydratesDocument33 pagesCarbohydratesCris PorlasNo ratings yet
- Sources and Applications of Carbohydrates.Document10 pagesSources and Applications of Carbohydrates.Narges Malik100% (1)
- CARBOHYDRATES Biochem Pre-LabDocument50 pagesCARBOHYDRATES Biochem Pre-LabGlen MangaliNo ratings yet
- Structure of Disaccharides & PolysaccharidesDocument12 pagesStructure of Disaccharides & PolysaccharidesD K SRIVASTAVA100% (1)
- Biochemistry 1 Lesson 5 (Polysaccharides Homopolysaccharides)Document44 pagesBiochemistry 1 Lesson 5 (Polysaccharides Homopolysaccharides)ansuben961No ratings yet
- PolysachharidesDocument24 pagesPolysachharidesshizarahimNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument43 pagesCarbohydratesEvangelene Esquillo Sana100% (1)
- Grade 10Document27 pagesGrade 10Julius SalasNo ratings yet
- Week 1Document12 pagesWeek 1Prima LebananNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates: Prepared By, Aparna M AjayDocument46 pagesCarbohydrates: Prepared By, Aparna M AjayAparna KinginiNo ratings yet
- Biological Importance of Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument17 pagesBiological Importance of Carbohydrates and LipidsAnaitum SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document112 pagesChapter 2Oltagon Nicole DupingayNo ratings yet
- Starch - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Starch or Amylum Is ADocument12 pagesStarch - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Starch or Amylum Is AAttila TamasNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Are Made of Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen Atoms. These Atoms Form Chemical Bonds That Follow The Laws of NatureDocument13 pagesCarbohydrates Are Made of Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen Atoms. These Atoms Form Chemical Bonds That Follow The Laws of NatureMadhavi DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- bIOLOGICAL CHO, CHONDocument82 pagesbIOLOGICAL CHO, CHONgalauraaprilrose96No ratings yet
- Q4 Science 10 Week3Document4 pagesQ4 Science 10 Week3Edison Caringal0% (1)
- AdditionalDocument7 pagesAdditionalIN MaulizaNo ratings yet
- Figure 7.16 Acetals and Ketals Can Be Formed From Hemiacetals and Hemiketals, RespectivelyDocument29 pagesFigure 7.16 Acetals and Ketals Can Be Formed From Hemiacetals and Hemiketals, RespectivelylklkelwlNo ratings yet
- CHO Chemistry: Functions of CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesCHO Chemistry: Functions of CarbohydratesSaadia AnjumNo ratings yet
- Chemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesChemistry and Structure of The Cell Biological MacromoleculesJohn ManciaNo ratings yet
- Q2 WEEK 9 10 Polymers and BiomacromoleculesDocument52 pagesQ2 WEEK 9 10 Polymers and BiomacromoleculesJay-mee Claire V. DioNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Study CentreDocument26 pagesBiomolecules: Study CentreNeeraj VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate WsDocument8 pagesCarbohydrate WsJakie UbinaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet COT4Document5 pagesActivity Sheet COT4Abbie Gail CabatañaNo ratings yet
- Starch: Amylose: Amylose Is Linear Polysaccharide of DDocument3 pagesStarch: Amylose: Amylose Is Linear Polysaccharide of DpreetyNo ratings yet
- 1142 L6 CarbohydratesDocument27 pages1142 L6 CarbohydratesjanindujayathmaNo ratings yet
- HBC 104 Polysaccharides Lecture 4Document21 pagesHBC 104 Polysaccharides Lecture 4craigNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument35 pagesCarbohydratesJaezean Jules B. GomezNo ratings yet
- Food Chem Lecture NotesDocument33 pagesFood Chem Lecture NotesMa Josefa Jocson BalusaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MacronutrientsDocument9 pagesIntroduction To MacronutrientsBenard NyaumaNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingDocument9 pagesBIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingRuskin Jamir AquinoNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesCarbohydratesMohd FarhanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PDFDocument31 pagesCarbohydrates PDFDara Arabella AndalesNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2Document32 pagesBio Notes 2Sinin VegaNo ratings yet
- What Are Carbohydrates?Document1 pageWhat Are Carbohydrates?Inês CarmoNo ratings yet
- Abdul Rahman AlwiDocument46 pagesAbdul Rahman Alwiaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Lectrure 2Document36 pagesLectrure 2mpokiev17No ratings yet
- Starch - WikipediaDocument11 pagesStarch - WikipediaFebiana YusidaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate ChemistryDocument6 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistrygaakash2992003No ratings yet
- Fiber: Plants Pick Up Carbon Dioxide From The Air and Water From The Soil and Combine Them ToDocument7 pagesFiber: Plants Pick Up Carbon Dioxide From The Air and Water From The Soil and Combine Them ToDanica Calalang SagutNo ratings yet
- 6.polysaccharides 10Document22 pages6.polysaccharides 10Ally RamsoNo ratings yet
- StarchDocument12 pagesStarchNahusenay TewodrosNo ratings yet
- Cahbohydrates I, Type N StructureDocument18 pagesCahbohydrates I, Type N StructuresilvyfebryNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULES (Part 2) - CARBOHYDRATESDocument7 pagesBIOMOLECULES (Part 2) - CARBOHYDRATESAmrit SinghNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument33 pagesCarbohydratesDeboo X Xavier100% (1)
- Carbohydrates PresentationDocument18 pagesCarbohydrates PresentationRahmayuni FItrianti100% (2)
- Carbohydrates: Lecturer: Mr. NW MokoenaDocument16 pagesCarbohydrates: Lecturer: Mr. NW MokoenaMahlodi LamolaNo ratings yet
- Biology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDocument15 pagesBiology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- Sự Tiêu Hóa Và Hấp Thụ CarbonhydrateDocument51 pagesSự Tiêu Hóa Và Hấp Thụ CarbonhydrateSỹ NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Features Maltose Cellobiose Lactose Sucrose: Malt Sugar Cellobiose Milk Sugar Table SugarDocument1 pageFeatures Maltose Cellobiose Lactose Sucrose: Malt Sugar Cellobiose Milk Sugar Table SugarPranchiska Vira Jimenez GierranNo ratings yet
- Sugar Source Importance Clinical SignificanceDocument1 pageSugar Source Importance Clinical SignificancePranchiska Vira Jimenez GierranNo ratings yet
- 4 6 NotesDocument28 pages4 6 NotesPranchiska Vira Jimenez GierranNo ratings yet
- Apple FermentationDocument7 pagesApple FermentationPranchiska Vira Jimenez GierranNo ratings yet