Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 17 Elements
Group 17 Elements
Uploaded by
snehana yogeshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group 17 Elements
Group 17 Elements
Uploaded by
snehana yogeshCopyright:
Available Formats
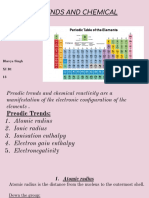
Group 17 elements
General electronic
configuration : ns2np5
Atomic size :
• Smallest in their respective period( due to maximum effective nuclear
charge).
• Atomic size increases down the group as new shells are added.
Ionization enthalpy :
• the maximum value of ionization enthalpy in their respective. Indicates
these elements prefer to accept electrons rather than losing electrons.
This is because these elements are just one electron short from their
respective nearest noble gas configuration.
• Ionization enthalpy decreases down the group due to increasing atomic
size.
Electron gain enthalpy:
• Halogens have maximum negative electron gain enthalpy in the corresponding periods.
• In general, electron gain enthalpy decreases down the group becomes less negative, as the tendency to
accept electrons decreases down the group. However negative electron gain enthalpy offloading is less
than that of chlorine because off small size of fluorine atom and strong inter electronic repulsions in
relatively small to be or vitals off fluorine.
Electronegativity:
• These elements have very high electronegativity.
• The electronegativity decreases down the group.
• Fluorine is the most electronegative element in the periodic table.
Physical properties
1. Melting and boiling points:
Is found to increase in with increase in molecular weight.
2. Density:
is found to increase down the group, as increase in molecular weight outweighs the increase in molecular
volume.
3. Bond dissociation enthalpy:
relatively large electron-electron repulsion among lone pair of fluorine In F2 molecule makes the molecule
to have less bond dissociation enthalpy with respect to chlorine. Bond dissociation enthalpy follows the
order Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2.
Quick Notes Page 1
You might also like
- Corrosion Technology: Cathodic and Anodic ProtectionDocument36 pagesCorrosion Technology: Cathodic and Anodic Protectionsohrab25100% (1)
- Ib Chemistry: Topic 3 PeriodicityDocument90 pagesIb Chemistry: Topic 3 Periodicitynoob masterNo ratings yet
- Halar 3404DADocument3 pagesHalar 3404DAJayvee FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Trends-CompiledDocument20 pagesPeriodic Table Trends-CompiledMahnoor JamshiadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Periodic Relationships Among The ElementsDocument20 pagesChapter 8: Periodic Relationships Among The Elementsorganic Aau pharmacyNo ratings yet
- Week 6Document42 pagesWeek 6Muhammad aniq Helmi raisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of ElementsDocument42 pagesChapter 7 Periodic Properties of ElementsClaire SanshineNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 An Overview of The Periodic TableDocument37 pagesTopic 1 An Overview of The Periodic TableHafizh PpNo ratings yet
- Trends in The Periodic TableDocument25 pagesTrends in The Periodic TableHanna GalatiNo ratings yet
- K03398 - 20210309182549 - SKT3033 - Topic 1 An Overview of The Periodic TableDocument35 pagesK03398 - 20210309182549 - SKT3033 - Topic 1 An Overview of The Periodic Tableliana aliaNo ratings yet
- Periodic PropertiesDocument30 pagesPeriodic Propertiescleofe omas-asNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- Electron AffinityDocument51 pagesElectron AffinityS K MishraNo ratings yet
- The Periodic TableDocument43 pagesThe Periodic TableSharmaine AquinoNo ratings yet
- PeriodicTable and Trends DPDocument109 pagesPeriodicTable and Trends DPSurya NairNo ratings yet
- Period 4.: Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Document1 pagePeriod 4.: Chemistry SPM - Quick Review F4Sze Hao CheahNo ratings yet
- Periodic Relationships Among The ElementsDocument31 pagesPeriodic Relationships Among The ElementsJhonel EspanolaNo ratings yet
- 3.1.1 Periodicity: Classification of Elements in S, P, D BlocksDocument5 pages3.1.1 Periodicity: Classification of Elements in S, P, D BlocksstudierNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapter 07Document51 pages4 Chapter 07shireenfNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryMark Wael Karam GergasNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument10 pagesPhysical Science ReviewerJAMES GAMERNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 5.1Document25 pagesSem 1 5.1SyiekhNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesAtomic Structurejordangrierson12No ratings yet
- Chm524 4 RadiochemistryDocument67 pagesChm524 4 Radiochemistryasyraf azlan99No ratings yet
- 2 - Periodic TableDocument12 pages2 - Periodic TableselNo ratings yet
- Science P4-Knowledge-Organiser Atomic StructureDocument1 pageScience P4-Knowledge-Organiser Atomic StructureAsh SmithNo ratings yet
- Periodicitiy PDFDocument14 pagesPeriodicitiy PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- MYP4 Chemistry Periodic TrendsDocument31 pagesMYP4 Chemistry Periodic TrendsAref Dahabrah100% (1)
- A105 ESE Revision SlidesDocument22 pagesA105 ESE Revision Slides65scgdwmbkNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document2 pagesCH 7Heather SiuNo ratings yet
- 2 chapter 2 原子半径以及电离能Document33 pages2 chapter 2 原子半径以及电离能Pingping chenNo ratings yet
- Group VII ElementsDocument28 pagesGroup VII ElementsTichafara Paul ShumbaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science - AssignmentDocument8 pagesPhysical Science - AssignmentMae Ann TamaraNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends StudsDocument28 pagesPeriodic Trends StudsGlaiza PagasNo ratings yet
- Trends in The Periodic TableDocument12 pagesTrends in The Periodic Tableoanoxenosiral1211No ratings yet
- Valence ElectronsDocument18 pagesValence ElectronsAlvin Piedragoza LealNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PhysicsDocument55 pagesNuclear PhysicsMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Ionisation Energy: A Guide For A Level StudentsDocument37 pagesIonisation Energy: A Guide For A Level StudentsLalitha KurumanghatNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Chemical BondingDocument48 pagesConcepts of Chemical BondingtalktotiffanychengNo ratings yet
- Ionisation EnergiesDocument2 pagesIonisation EnergiesthrowawayemailorangesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Classes NotesDocument8 pagesChemistry Classes NotesBhavya SinghNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Feb 2024Document1 pageAdobe Scan 05 Feb 2024krishrajput88888888No ratings yet
- Lecture 3+4: Periodic Properties Off The ElementsDocument34 pagesLecture 3+4: Periodic Properties Off The ElementsHIEP PHAM HOANGNo ratings yet
- Atomic and Nuclear PhenomenaDocument3 pagesAtomic and Nuclear PhenomenababaNo ratings yet
- Ionisation EnergyDocument23 pagesIonisation EnergyNurfarhanah KNo ratings yet
- Type of Forces 1 Notes 2010Document26 pagesType of Forces 1 Notes 2010Mohd Iruan JanalNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms.Document62 pagesElectrons in Atoms.Md.Tanjim reza TurjoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table (4,5,6)Document37 pagesPeriodic Table (4,5,6)rehanfazal9669No ratings yet
- Periodic Table..Document5 pagesPeriodic Table..rachelNo ratings yet
- 4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument68 pages4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Alkenes:: Atom EconomyDocument9 pagesAlkanes: Alkenes:: Atom EconomyHyder OmarNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: ElectronegativityDocument2 pagesPeriodic Trends: ElectronegativityZaara RyeenNo ratings yet
- 05 - CHEM 111 - Lecture 5 - Periodicity of The ElementsDocument50 pages05 - CHEM 111 - Lecture 5 - Periodicity of The ElementsBrian NkhomaNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument56 pagesPeriodic Trendsiinew.yorkii21No ratings yet
- Development of Periodic TableDocument17 pagesDevelopment of Periodic TableGerald AlbasinNo ratings yet
- (New Specification) (Document34 pages(New Specification) (Anuki PereraNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Lesson 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Lesson 2Andrea Marie LaquiñaNo ratings yet
- Booklet Periodic Trends PERIODICITY CLASS NOTESDocument34 pagesBooklet Periodic Trends PERIODICITY CLASS NOTESVed PatelNo ratings yet
- Periodicity in Elements NotesDocument7 pagesPeriodicity in Elements NotesjqgjwgnnwkNo ratings yet
- Radiation Biolog1Document20 pagesRadiation Biolog1Degoma, Mary NoelynNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties and Their Graduation in Group andDocument14 pagesPeriodic Properties and Their Graduation in Group andbhogalsahib1408No ratings yet
- Periodic Table of Elements - Week 9Document6 pagesPeriodic Table of Elements - Week 9Raul BerrellezaNo ratings yet
- Msds 13X-PGDocument1 pageMsds 13X-PGNduong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in Petroleum RefiningDocument23 pagesCorrosion in Petroleum Refininghrk100No ratings yet
- MEMBRANE PLASMA - Mind MapDocument1 pageMEMBRANE PLASMA - Mind MapSimNo ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument9 pagesAromatic CompoundsAmany100% (1)
- BAB 2 Principle of Cellular LifeDocument49 pagesBAB 2 Principle of Cellular LifeMuhammad Dalili Al FarisNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Spectrophotometric Study of Some New Azo Dyes Derived From MetoclopramideDocument9 pagesSynthesis and Spectrophotometric Study of Some New Azo Dyes Derived From MetoclopramideDarian HerascuNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis 9700 CieDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis 9700 CietrinhcloverNo ratings yet
- Lec 25Document17 pagesLec 25john cenaNo ratings yet
- RhymeZone - Educate RhymesDocument14 pagesRhymeZone - Educate RhymesAdamBeyonceLoweNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom AssignmentDocument20 pagesStructure of Atom Assignmentrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Development of Porous Fly Ash-Based GeopolymerDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Porous Fly Ash-Based GeopolymerEstefania Loyola FernandezNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - NPTEL Material For MOOC E-Waste - BKDDocument21 pagesWeek 3 - NPTEL Material For MOOC E-Waste - BKDRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3 - KEY: Due Tuesday, 10/20/17Document14 pagesProblem Set 3 - KEY: Due Tuesday, 10/20/17Trần Nguyễn Quỳnh NhưNo ratings yet
- PETE 311 Lab 1 MemoDocument3 pagesPETE 311 Lab 1 MemoTyler MroskoNo ratings yet
- Intertek Testing Services LTD., Shanghai Ningbo BranchDocument4 pagesIntertek Testing Services LTD., Shanghai Ningbo BranchKalpesh PatelNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0022286019306131 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0022286019306131 MainDuvan Leandro Parra VelandiaNo ratings yet
- EdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 2 Mark Scheme Results Paper 1 Jan 2006Document8 pagesEdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 2 Mark Scheme Results Paper 1 Jan 2006sg noteNo ratings yet
- Unified Soil Classification SystemDocument8 pagesUnified Soil Classification SystemTidus Farron100% (1)
- Nuevos MineralesDocument206 pagesNuevos MineralesdiegoNo ratings yet
- CH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsDocument3 pagesCH-12 - MCQS Ald, Ket & Car - AcidsPranav ShankarNo ratings yet
- 4 Chemical Examination of Urine PDFDocument12 pages4 Chemical Examination of Urine PDFLovely B. AlipatNo ratings yet
- CE 301-GeologyDocument1 pageCE 301-GeologychndriuhNo ratings yet
- ASTM Molybdenum in Water PDFDocument4 pagesASTM Molybdenum in Water PDFAna MiraNo ratings yet
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Reaction PHR-122Document36 pagesSN1 SN2 E1 E2 Reaction PHR-122zakariansu67% (6)
- CM DesorptionDocument3 pagesCM DesorptionADevilSwordNo ratings yet
- Alexander M. Spokoyny Et Al - Carborane-Based Pincers: Synthesis and Structure of SeBSe and SBS PD (II) ComplexesDocument2 pagesAlexander M. Spokoyny Et Al - Carborane-Based Pincers: Synthesis and Structure of SeBSe and SBS PD (II) ComplexesGomsajNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE (TM) Chemistry Study and Revision Guide Third Edition (David Besser) (Z-Library)Document172 pagesCambridge IGCSE (TM) Chemistry Study and Revision Guide Third Edition (David Besser) (Z-Library)ShanayaNo ratings yet