Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Skema Cemerlang Kadar TB
Skema Cemerlang Kadar TB
Uploaded by
DOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Skema Cemerlang Kadar TB
Skema Cemerlang Kadar TB
Uploaded by
DOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeCopyright:
Available Formats
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
PAPER / KERTAS 1
1 C 6 B 11 A 16 B 21 C 26 A
2 D 7 C 12 B 17 D 22 B 27 B
3 B 8 A 13 C 18 D 23 D 28 C
4 D 9 A 14 B 19 C 24 D 29 C
5 D 10 C 15 D 20 A 25 D 30 A
PAPER / KERTAS 2
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
1(a) Hydrogen / Hidrogen 1 1
1(b) P1 : Axes with label and unit 1
P2 : Uniform scale, smooth curve, size of graph is more than ½ 1
of the graph paper
P3 : All points transferred correctly 1
1(c)(i) P1 : Show tangent on the curve 1
P2 : Rate of reaction / Kadar tindak balas = 0.183 cm3 s-1 ± 0.05 1
with correct unit
@JU KIMIA PERAK 1
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
1(c)(ii) 45.00 cm3 // 0.214 cm3 s-1 1 1
210 s
1(d)(i) Increase temperature / Naikkan suhu // 1 1
Add catalyst / Tambah mangkin //
Increase concentration of acid, but lower the volume of acid /
Tingkatkan kepekatan asid tetapi rendahkan isi padu asid
1(d)(ii) Factor: Temperature
P1 : Kinetic energy of particles is higher in K 1
Tenaga kinetik zarah-zarah lebih tinggi dalam K
P2 : Frequency of collision between hydrogen ion and 1
magnesium atom is higher in K
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara ion hidrogen dan atom
magnesium lebih tinggi dalam K
P3 : Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen ion and 1 Max.
magnesium atom is higher in K 2
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara ion hidrogen dan
atom magnesium lebih tinggi dalam K
Or
Factor: Catalyst
P1 : Catalyst / copper(II) sulphate lowers activation energy
Mangkin / kuprum(II) sulfat merendahkan tenaga
pengaktifan
@JU KIMIA PERAK 2
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
P2 : More colliding particles achieve the lower activation energy
Lebih banyak zarah yang berlanggar dapat mencapai
tenaga pengaktifan yang lebih rendah
P3 : Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen ion and
magnesium atom is higher in K
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara ion hidrogen dan
atom magnesium lebih tinggi dalam K
Or
Factor: Concentration
P1 : The number of particles per unit volume is higher in K
Bilangan zarah per unit isi padu lebih tinggi dalam K
P2 : Frequency of collision between hydrogen ion and
magnesium atom is higher in K
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara ion hidrogen dan atom
magnesium lebih tinggi dalam K
P3 : Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen ion and
magnesium atom is higher in K
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara ion hidrogen dan
atom magnesium lebih tinggi dalam K
1(d)(iii) The number of moles of hydrochloric acid / hydrogen ion / H+ 1 1
in M is half of L / 0.025 mol
Bilangan mol asid hidroklorik / ion hidrogen / H+ dalam M ialah
separuh daripada L / 0.025 mol
Total 11
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
2(a) Change in the volume of gas released per time taken 1 1
Perubahan isi padu gas yang terbebas per masa yang diambil
2(b) P1 : Correct formulae of reactants and products 1
P2 : Balanced equation 1 2
Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
2(c) Size / Total surface area of magnesium 1 1
Saiz / Jumlah luas permukaan magnesium
2(d)(i) Experiment / Eksperimen I :
P1 : 50 cm3 // 10 cm3 min-1 // 50 cm3 // 0.167 cm3 s-1 1
5 min 300 s
Experiment / Eksperimen II :
P2 : 50 cm3 // 16.67 cm3 min-1 // 50 cm3 // 0.278 cm3 s-1 1 2
3 min 180 s
2(d)(ii) P1 : Size of magnesium in Experiment II is smaller than 1
Experiment I
Saiz magnesium dalam Eksperimen II lebih kecil berbanding
Eksperimen I //
@JU KIMIA PERAK 3
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Total surface area of magnesium in Experiment II is bigger
than Experiment I
Jumlah luas permukaan magnesium dalam Eksperimen II
lebih besar berbanding Eksperimen I
P2 : Frequency of collision between hydrogen ion and 1
magnesium atom is higher in Experiment II
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara ion hidrogen dan atom
magnesium lebih tinggi dalam Eksperimen II
P3 : Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen ion and 1 3
magnesium atom is higher in Experiment II
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara ion hidrogen dan
atom magnesium lebih tinggi dalam Eksperimen II
#adp hydrogen ion and magnesium atom in P3 from P2
1(e) Mass / Number of moles of magnesium in both experiments are 1 1
the same
Jisim / Bilangan mol magnesium dalam kedua-dua eksperimen
adalah sama
Total 10
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
3(a) Concentration of sulphuric acid // Kepekatan asid sulfurik 1 1
3(b) P1 : Functional diagram – rubber stopper above the mouth of 1
conical flask, burette clamped, rubber
hose inserted into burette, dashed line
for acid and water
P2 : Label – zinc / zink, hydrochloric acid / asid hidroklorik, 1 2
water / air
3(c)(i) Zn + 2H+ Zn2+ + H2 1 1
@JU KIMIA PERAK 4
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
3(c)(ii) P1 : Number of moles of acid
0.1 × 0.5 // 0.05 1
P2 : Ratio of moles
2 mol HCl : 1 mol H2
0.05 mol HCl : 0.025 mol H2 1
P3 : Volume of H2
0.025 × 24 dm3 // 0.6 dm3 // 600 cm3 1 3
3(d)(i) 1 1
3(d)(ii) P1 : Rate of reaction in Experiment II is higher than Experiment 1
I // Kadar tindak balas dalam Eksperimen II lebih tinggi
berbanding Eksperimen I
P2 : Concentration of hydrogen ion / H+ is higher in Experiment 1
II than Experiment I // Kepekatan ion hidrogen / H+ dalam
Eksperiment II lebih tinggi berbanding Eksperimen I //
The number of hydrogen ion per unit volume of acid in
Experiment II is higher than Experiment I // Bilangan ion
hidrogen per unit isi padu asid dalam Eksperimen II lebih
tinggi berbanding Eksperimen I
P3 : Frequency of collision between hydrogen ion and zinc atom 1
in Experiment II is higher than Experiment I // Frekuensi
perlanggaran antara ion hidrogen dan atom zink dalam
Eksperimen II lebih tinggi berbanding Eksperimen I
P4 : Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen ion and 1 Max.
zinc atom in Experiment II is higher than Experiment I // 3
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara ion hidrogen dan
atom zink dalam Eksperimen II lebih tinggi berbanding
Eksperimen I
Total 11
@JU KIMIA PERAK 5
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
4(a) Size of reactant / Saiz bahan tindak balas // Concentration of 1 1
reactant / Kepekatan bahan tindak balas // Temperature / Suhu //
Catalyst / Mangkin // Pressure / Tekanan
4(b)(i) Rate of reaction in Experiment II is higher 1 1
Kadar tindak balas Eksperimen II lebih tinggi //
Concentration of hydrogen ion in Experiment II is higher
Kepekatan ion hidrogen dalam Eksperimen II lebih tinggi
4(b)(ii) Increase the temperature / Naikkan suhu // 1 1
Heat the acid / Panaskan asid //
Increase concentration of sulphuric acid / Tambahkan kepekatan
asid sulfurik
[r : mixture / campuran]
4(c) P1 : Hydrochloric acid is a monoprotic acid, sulphuric acid is 1
diprotic acid
Asid hidroklorik ialah asid monoprotik / monobes, asid
sulfurik ialah asid diprotic / dwibes
P2 : The number of moles / concentration of hydrogen ions / H+ 1 2
in Experiment II is double
Bilangan mol / kepekatan ion hidrogen / H+ dalam
Eksperimen II ialah dua kali ganda
4(d)(i) Mg + H2SO4 MgSO4 + H2 1 1
4(d)(ii) P1 : Number of moles of H2SO4 1
25 × 0.1 // 0.025 × 0.1 // 0.0025
1000
P2 : Ratio of moles 1
1 mol H2SO4 : 1 mol H2
0.0025 mol H2SO4 : 0.0025 mol H2
P3 : Volume of H2 1 3
0.0025 × 24 dm3 // 0.06 dm3 // 60 cm3
4(e) P1 : Correct label with units on both axes 1
P2 : Correct shape of graph 1 2
Total 11
@JU KIMIA PERAK 6
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
5(a) P1 : Correct formulae of reactants and products 1
P2 : Balanced equation 1 2
Zn + 2H+ Zn2+ + H2
5(b) P1 : Temperature / Suhu 1
P2 : Concentration of hydrochloric acid / Kepekatan asid 1 2
hidroklorik
5(c) P1 : Rate of reaction in Experiment II is higher 1
Kadar tindak balas dalam Eksperimen II lebih tinggi
P2 : Temperature in Experiment II is higher 1
Suhu dalam Eksperimen II lebih tinggi
P3 : Kinetic energy of hydrogen ions / particles is higher 1
Tenaga kinetik ion hidrogen / zarah-zarah lebih tinggi
P4 : Frequency of collision between zinc atoms and hydrogen 1 4
ions is higher
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara atom zink dan ion hidrogen
lebih tinggi //
Frequency of effective collision between zinc atoms and
hydrogen ions is higher
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara atom zink dan ion
hidrogen lebih tinggi
5(d) Correct curve that shows the volume is double 1 1
5(e) P1 : Cut the meat into smaller pieces 1
Potong daging kepada saiz yang lebih kecil
P2 : Larger total surface area of meat will absorb more heat 1 2
Jumlah luas permukaan daging yang lebih besar akan
menyerap lebih banyak haba
OR
P1 : Cook in pressure cooker 1
Masak dalam periuk tekanan
P2 : High pressure in the pressure cooker will increase the 1 2
kinetic energy of particles
Tekanan yang tinggi dalam periuk tekanan akan
meningkatkan tenaga kinetik zarah
Total 11
@JU KIMIA PERAK 7
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
6(a)(i) P1 : Metal / Logam P – Zinc / Zink / Magnesium / Aluminium 1
[r : Zn / Mg]
P2 : Acid / Asid Q – hydrochloric acid / asid hidroklorik // nitric 1
acid / asid nitrik // sulphuric acid / asid
sulfurik // ethanoic acid / asid etanoik
[r : HCl / HNO3 / H2SO4 / CH3COOH]
P3 : Correct formulae of reactants and products 1
P4 : Balanced equation 1 4
Zn + 2HCl ZnCl2 + H2 //
Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2 //
2Al + 6HCl 2AlCl3 + 3H2 //
Zn + 2HNO3 Zn(NO3)2 + H2 //
Mg + 2HNO3 Mg(NO3)2 + H2 //
2Al + 6HNO3 2Al(NO3)3 + 3H2
Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 //
Mg + H2SO4 MgSO4 + H2 //
2Al + 3H2SO4 Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2 //
Zn + 2CH3COOH Zn(CH3COO)2 + H2 //
Mg + 2CH3COOH Mg(CH3COO)2 + H2 //
2Al + 6CH3COOH 2Al(CH3COO)3 + 3H2 //
6(a)(ii) Experiment I
P1 : 30 cm3 // 3 cm3 s-1 1
10 s
Experiment II
P2 : 30 cm3 // 1.5 cm3 s-1 1 2
20 s
6(a)(iii) P1 : Rate of reaction in Experiment I is higher 1
Kadar tindak balas dalam Eksperimen I lebih tinggi
P2 : Concentration of acid Q in Experiment I is higher 1
Kepekatan asid Q dalam Eksperimen I lebih tinggi
P3 : Number of particles / hydrogen ions per unit volume in 1
Experiment I is higher
Bilangan zarah / ion hidrogen per unit isi padu dalam
Eksperimen I lebih tinggi
P4 : Frequency of collision between P atoms and hydrogen ions 1 4
in Experiment I is higher
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara atom zink dan ion hidrogen
dalam Eksperimen I lebih tinggi //
Frequency of effective collision between P atoms and
hydrogen ions in Experiment I is higher
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara atom P dan ion
hidrogen dalam Eksperimen I lebih tinggi
6(b) Case 1
P1 : Measure [50 – 250] cm3 of [0.1 – 2.0] mol dm-3 sodium 1
thiosulphate solution
Sukat [50 – 250] cm3 larutan natrium tiosulfat [0.1 – 2.0]
mol dm-3
@JU KIMIA PERAK 8
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
P2 : Pour sodium thiosulphate solution into a conical flask 1
Tuang larutan natrium tiosulfat ke dalam kelalang kon
P3 : Measure and record the initial temperature of the solution 1
Sukat dan rekod suhu awal larutan itu
P4 : Put the conical flask on a paper marked ‘X’ 1
Letak kelalang kon ke atas kertas bertanda ‘X’
P5 : Measure [5 – 10] cm3 of [0.1 – 2.0] mol dm-3 sulphuric / 1
hydrochloric / nitric acid and add into the conical flask
Sukat [5 – 10] cm3 asid sulfurik / hidroklorik / nitrik [0.1 –
2.0] mol dm-3 dan tambah ke dalam kelalang kon
P6 : Start the stopwatch immediately 1
Mulakan jam randik serta-merta
P7 : Swirl the mixture 1
Goncang campuran itu
P8 : Stop the stopwatch when the ‘X’ mark is no longer visible 1
and record the time
Hentikan jam randik apabila tanda ‘X’ tidak kelihatan lagi
dan rekodkan masanya
P9 : Repeat step 1 to 9 by heating the sodium thiosulphate 1
solution at 40°C, 45°C, 50°C and 55°C
Ulang langkah 1 hingga 9 dengan memanaskan larutan
natrium tiosulfat pada suhu 40°C, 45°C, 50°C dan 55°C
P10 : Functional apparatus [dashed line for solution, ‘X’ mark] 1
Rajah berfungsi [garis sempang untuk larutan, tanda ‘X’]
P11 : Label [sodium thiosulphate solution, acid] 1 Max.
Label [larutan natrium tiosulfat, asid] 10
OR
Case 2
P1 : Fill a burette with water 1
Isi buret dengan air
P2 : Invert the burette into the water in a basin 1
Telangkupkan buret di dalam air dalam satu besen
P3 : Record initial reading of burette 1
Rekod bacaan awal buret
P4 : Measure [50 – 250] cm3 of [0.1 – 2.0] mol dm-3 sulphuric / 1
hydrochloric / nitric acid
@JU KIMIA PERAK 9
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Sukat [50 – 250] cm3 asid sulfurik / hidroklorik / nitrik [0.1
– 2.0] mol dm-3 1
P5 : Pour the acid into a conical flask
Tuang asid ke dalam kelalang kon 1
P6 : Measure and record the initial temperature of the acid
Sukat dan rekod suhu awal asid 1
P7 : Weigh 5 g of [calcium carbonate / magnesium / zinc] and
put into the conical flask
Timbang 5 g [kalsium karbonat / magnesium / zink] dan
masukkan ke dalam kelalang kon
P8 : Start the stopwatch immediately 1
Mulakan jam randik serta-merta
P9 : Record the burette reading at intervals of 30 seconds 1
Rekod bacaan buret pada sela masa 30 saat
P10 : Repeat step 1 to 9 by heating the acid at 40°C, 45°C, 50°C 1
and 55°C
Ulang langkah 1 hingga 9 dengan memanaskan larutan
natrium tiosulfat pada suhu 40°C, 45°C, 50°C dan 55°C
P11 : Functional apparatus [position of rubber stopper, delivery 1
tube inserted into burette, burette clamped, dashed line for
acid and water]
Rajah berfungsi [kedudukan getah penyumbat, tiub
penyambung dimasukkan ke dalam buret, buret diapit,
garis sempang untuk asid dan air]
P12 : Label [acid, metal / metal carbonate, water] 1 Max.
Label [asid, logam / logam karbonat, air] 10
Total 20
@JU KIMIA PERAK 10
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
7(a) P1 : Activity / Aktiviti 1
P2 : Explanation / Penerangan 1 2
Activity / Aktiviti Explanation / Penerangan
Using small sized charcoal Total surface area exposed to
when barbecuing / grilling heat is bigger
Menggunakan arang bersaiz Jumlah luas permukaan yang
kecil semasa membakar terdedah kepada haba lebih
besar
Cooking small pieces of meat Total surface area exposed to
/ potatoes / carrots heat is bigger
Memasak ketulan daging / Jumlah luas permukaan yang
kentang / lobak merah bersaiz terdedah kepada haba lebih
kecil besar
Making fire pit using small Total surface area exposed to
sized branches / twigs heat is bigger
Membuat unggun api Jumlah luas permukaan yang
menggunakan kayu bersaiz terdedah kepada haba lebih
kecil besar
Keep food in the fridge Lower temperature in the
Menyimpan makanan dalam fridge causes bacteria to be
peti ais inactive
Suhu yang lebih rendah
dalam peti ais menyebabkan
bakteria tidak aktif
Hot water is used to dissolve Higher temperature causes
sugar / salt / coffee / tea reaction to be faster
Air panas digunakan untuk Suhu yang lebih tinggi
melarutkan gula / garam / mempercepatkan tindak balas
kopi / teh
Pressure cooker is used in Higher pressure increases the
cooking temperature, hence decreasing
Periuk tekanan digunakan the amount of time for
untuk memasak cooking
Tekanan yang lebih tinggi
menyebabkan tenaga kinetic
zarah meningkat, seterusnya
mengurangkan masa
memasak
*or any other relevant answers
7(b)(i) P1 : Correct formulae of reactants and products 1
P2 : Balanced equation 1 2
CaCO3 + H2SO4 CaSO4 + H2O + CO2
7(b)(ii) Experiment I
P1 : 960 cm3 // 4 cm3 s-1 1
240 s
@JU KIMIA PERAK 11
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Experiment II
P2 : 960 cm3 // 6 cm3 s-1 1 2
160 s
7(b)(iii) P1 : Size of marble / CaCO3 in Experiment II is smaller than 1
Experiment I
Saiz marmar / CaCO3 dalam Eksperimen II lebih kecil
berbanding Eksperimen I //
P2 : Total surface area of marble / CaCO3 in Experiment II is 1
bigger than Experiment I
Jumlah luas permukaan marmar / CaCO3 dalam
Eksperimen II lebih besar berbanding Eksperimen I
P3 : Frequency of collision between hydrogen ions and calcium 1
carbonate / CaCO3 molecules is higher in Experiment II
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara ion hidrogen dan molekul
kalsium karbonat / CaCO3 lebih tinggi dalam Eksperimen II
//
Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen ions and
calcium carbonate / CaCO3 molecules is higher in
Experiment II
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara ion hidrogen dan
molekul kalsium karbonat / CaCO3 lebih tinggi dalam
Eksperimen II
P4 : Rate of reaction in Experiment II is higher than in 1 4
Experiment I
Kadar tindak balas dalam Eksperimen II lebih tinggi
berbanding Eksperimen I
7(c) Procedure / Prosedur
P1 : Fill a burette with water and invert it into the water in a 1
basin
Isi buret dengan air dan telangkupkan buret di dalam air
dalam satu besen 1
P2 : Measure 50 cm3 of hydrogen peroxide solution and pour
into a conical flask
Sukat 50 cm3 larutan hidrogen peroksida dan tuang ke
dalam kelalang kon 1
P3 : Add one spatula of manganese(IV) oxide into the conical
flask
Tambah satu spatula mangan(IV) oksida ke dalam kelalang
kon 1
P4 : Close the conical flask with a stopper fitted with delivery
tube, immediately
Dengan cepat, tutup kelalang kon dengan gabus yang
disambung kepada salur penghantar 1
P5 : Start the stopwatch
Mulakan jam randik 1
P6 : Record the volume of gas released every 30 seconds
Rekod isi padu gas yang terbebas setiap 30 saat 1
P7 : Repeat step 1 to 6 without adding manganese(IV) oxide
@JU KIMIA PERAK 12
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Ulang langkah 1 hingga 6 tanpa menambah mangan(IV)
oksida
Sketch of graph / Lakaran graf 1
P8 : Correct axes with unit 1
P9 : Correct shape of curve I (with MnO2) 1
P10 : Correct shape of curve II (without MnO2)
Conclusion / Kesimpulan 1 Max.
P11 : When manganese(IV) oxide is added to hydrogen 10
peroxide, the rate of reaction increases
Apabila mangan(IV) oksida ditambah kepada hidrogen
peroksida, kadar tindak balas meningkat
Total 20
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
8(a)(i) P1 : Magnesium / Mg // Zinc / Zn / Zink // Aluminium / Al 1
P2 : Hydrochloric acid / HCl / Asid hidroklorik // 1 2
Nitric acid / HNO3 / Asid nitrik //
Sulphuric acid / H2SO4 / Asid sulfurik //
Ethanoic acid / CH3COOH / Asid etanoik
8(a)(ii) P1 : Catalyst / Mangkin – Copper(II) sulphate / CuSO4 / 1
Kuprum(II) sulfat
P2 : Catalyst / Copper(II) sulphate lowers the activation energy 1
Mangkin / Kuprum(II) sulfat merendahkan tenaga
pengaktifan
P3 : More colliding particles are able to achieve the lower
activation energy 1
Lebih banyak zarah dapat mencapai tenaga pengaktifan
yang lebih rendah
P4 : Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen ions and
[magnesium / zinc / aluminium] atoms increases 1 4
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara ion hidrogen dan
atom [magnesium / zink / aluminium] meningkat
@JU KIMIA PERAK 13
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
8(b) P1 : Temperature of 60°C is higher than 27°C 1
Suhu 60°C adalah lebih tinggi berbanding 27°C
P2 : Water and sugar molecules gain higher kinetic energy 1
Molekul air dan gula memperoleh tenaga kinetik yang lebih
tinggi //
Water and sugar molecules move faster
Molekul air dan gula bergerak lebih laju
P3 : Easier for the molecules to overcome the intermolecular / 1
attraction force between molecules
Lebih mudah untuk molekul-molekul itu mengatasi daya
antara molekul / tarikan antara molekul
P4 : Therefore, it takes shorter time to dissolve sugar in water at 1 4
60°C
Maka, masa yang lebih singkat diambil untuk melarutkan
gula dalam air pada suhu 60°C
8(c) P1 : Name of substance / Nama bahan M : 1
Magnesium / Zinc / Zink / Aluminium / Calcium carbonate /
Kalsium karbonat
[Any suitable metal / metal carbonate]
[r : Mg / Zn / Al / CaCO3]
P2 : Fill a burette with water 1
Isi buret dengan air
P3 : A burette filled with water is inverted into the basin 1
Telangkupkan buret di dalam air dalam besen beris separuh
penuh air 1
P4 : Record initial reading of burette
Rekod bacaan awal buret 1
P5 : Measure [50 – 250] cm3 of [0.1 – 2.0] mol dm-3 sulphuric /
hydrochloric / nitric acid
Sukat [50 – 250] cm3 asid sulfurik / hidroklorik / nitrik [0.1
– 2.0] mol dm-3 1
P6 : Pour the acid into a conical flask
Tuang asid ke dalam kelalang kon 1
P7 : Weigh 5 g of [magnesium / zinc / aluminium / calcium
carbonate] granules and put into the conical flask
Timbang 5 g ketulan [magnesium / zink / aluminium /
kalsium karbonat] dan masukkan ke dalam kelalang kon 1
P8 : Start the stopwatch immediately
Mulakan jam randik serta-merta 1
P9 : Record the burette reading at intervals of 30 seconds
Rekod bacaan buret pada sela masa 30 saat
P10 : Repeat step 1 to 9 by using 5 g of [magnesium / zinc / 1 10
aluminium / calcium carbonate] powder to replace the
[magnesium / zinc / aluminium / calcium carbonate]
granules
Ulang langkah 1 hingga 9 dengan menggunakan serbuk
[magnesium / zink / aluminium / kalsium karbonat] bagi
menggantikan 5 g ketulan [magnesium / zink / aluminium /
kalsium karbonat]
@JU KIMIA PERAK 14
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Total 20
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
9(a) P1 : The smaller size beef / meat has larger total surface area 1
exposed to heat
Daging bersaiz kecil mempunyai jumlah luas permukaan
terdedah kepada haba, yang lebih besar
P2 : More heat is absorbed 1 2
Lebih banyak haba dapat diserap
9(b)(i) P1 : Name of metal carbonate P / Nama logam karbonat P - 1
Calcium carbonate / magnesium carbonate / zinc carbonate
// kalsium karbonat / magnesium karbonat / zink karbonat
[any suitable metal carbonate]
P2 : Name of acid Q / Nama asid Q - 1 2
Hydrochloric acid / Asid hidroklorik //
Nitric acid / HNO3 / Asid nitrik //
Sulphuric acid / H2SO4 / Asid sulfurik //
Ethanoic acid / CH3COOH / Asid etanoik
9(b)(ii) Experiment I
P1 : 30 cm3 // 3 cm3 s-1 1
10 s
Experiment II
P2 : 30 cm3 // 1.5 cm3 s-1 1
20 s
P3 : Experiment I has higher rate of reaction 1
Eksperimen I mempunyai kadar tindak balas yang lebih
tinggi
P4 : Size of carbonate P in Experiment I is smaller 1
Saiz karbonat P dalam Eksperimen I lebih kecil //
Total surface area of carbonate P in Experiment I is bigger
Jumlah luas permukaan karbonat P dalam Eksperimen I
lebih besar
P5 : Frequency of collision between carbonate P and ion 1 5
hydrogen ion in Experiment I is higher
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara karbonat P dan ion
hidrogen dalam Eksperimen I lebih tinggi
Frequency of effective collision between carbonate P and
ion hydrogen ion in Experiment I is higher
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara karbonat P dan
ion hidrogen dalam Eksperimen I lebih tinggi
9(c)(i) Sulphur / Sulfur 1 1
9(c)(ii) Materials / Bahan
P1 : Sodium thiosulphate solution / Larutan natrium tiosulfat, 1
Sulphuric acid / Asid sulfurik,
Paper marked ‘X’ / Kertas bertanda ‘X’
Apparatus / Radas
@JU KIMIA PERAK 15
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
P2 : Conical flask / Kelalang kon, 1
Stopwatch / Jam randik,
Thermometer / Termometer,
Bunsen burner / Penunu Bunsen
Procedure / Prosedur
P3 : Measure [50 – 250] cm3 of [0.1 – 2.0] mol dm-3 sodium 1
thiosulphate solution
Sukat [50 – 250] cm3 larutan natrium tiosulfat [0.1 – 2.0]
mol dm-3
P4 : Pour into the sodium thiosulphate solution a conical flask 1
Tuang larutan natrium tiosulfat ke dalam kelalang kon
P5 : Measure and record the initial temperature of the solution 1
Sukat dan rekod suhu awal larutan itu
P6 : Put the conical flask on a paper marked ‘X’ 1
Letak kelalang kon e atas kertas bertanda ‘X’
P7 : Measure [5 – 10] cm3 of [0.1 – 2.0] mol dm-3 sulphuric acid 1
and add into the conical flask
Sukat [5 – 10] cm3 asid sulfurik [0.1 – 2.0] mol dm-3 dan
tambah ke dalam kelalang kon
P8 : Start the stopwatch immediately 1
Mulakan jam randik serta-merta
P9 : Swirl the mixture 1
Goncang campuran itu
P10 : Stop the stopwatch when the ‘X’ mark is no longer visible 1
and record the time
Hentikan jam randik apabila tanda ‘X’ tidak kelihatan lagi
dan rekodkan masanya
P11 : Repeat step 1 to 9 by heating the sodium thiosulphate 1
solution at 40°C, 45°C, 50°C and 55°C
Ulang langkah 1 hingga 9 dengan memanaskan larutan
natrium tiosulfat pada suhu 40°C, 45°C, 50°C dan 55°C
Conclusion / Kesimpulan
P12 : The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of reaction 1 Max.
Semakin tinggi suhu, semakin tinggi kadar tindak balas 10
Total 20
@JU KIMIA PERAK 16
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
Question Mark Scheme Mark
No. Sub Total
10(a) P1 : The pressure in container B is higher than in container A 1
Tekanan dalam bekas B lebih tinggi berbanding bekas A
P2 : The number of particles / hydrogen and chlorine molecules 1
per unit volume is higher in container B
Bilangan zarah / molekul hidrogen dan klorin per unit isi
padu lebih tinggi dalam bekas B
P3 : Frequency of collision between hydrogen and chlorine 1
molecules is higher in container B
Frekuensi perlanggaran antara molekul hidrogen dan klorin
lebih tinggi dalam bekas B
P4 : Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen and 1
chlorine molecules is higher in container B
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara molekul hidrogen
dan klorin lebih tinggi dalam bekas B
P5 : Rate of reaction is higher in container B 1 5
Kadar tindak balas lebih tinggi dalam bekas B
10(b)(i) Manganese(IV) oxide / Mangan(IV) oksida 1 1
10(b)(ii) P1 : Catalyst / Manganese(IV) oxide lowers the activation 1
energy
Mangkin / Mangan(IV) oksida merendahkan tenaga
pengaktifan
P2 : More colliding particles are able to achieve the lower 1
activation energy
Lebih banyak zarah dapat mencapai tenaga pengaktifan
yang lebih rendah
P3 : Frequency of effective collision between hydrogen ions and 1 3
[magnesium / zinc / aluminium] atoms increases
Frekuensi perlanggaran berkesan antara ion hidrogen dan
atom [magnesium / zink / aluminium] meningkat
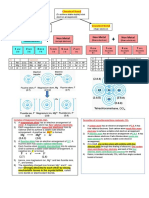
10(b)(iii) P1 : Arrow with energy and two different energy level 1
P2 : Correct formulae of reactant and products 1
P3 : Shows activation energy without catalyst correctly 1
P4 : Shows activation energy with catalyst correctly 1
P5 : Shows ΔH = -98.2 kJ mol-1 1 5
Sample answer:
@JU KIMIA PERAK 17
KIMIA MODUL PEACE CEMERLANG 2018
10(c) P1 : Put in ice box / Letakkan dalam kotak ais 1
P2 : Lower temperature in ice box / Suhu lebih rendah dalam 1
kotak ais
P3 : Reduces bacteria activity / Mengurangkan aktiviti bakteria 1 3
// Bacteria becomes inactive / Bakteria menjadi tidak aktif //
Less toxin is produced by bacteria / Kurang toksin
dihasilkan oleh bakteria
10(d) P1 : Satay in Diagram 10.2 will cook faster 1
Sate dalam Rajah 10.2 masak lebih cepat
P2 : By fanning, concentration of oxygen increases, to react with 1
charcoal
Dengan mengipas, kepekatan oksigen meningkat, untuk
bertindak balas dengan arang
P3 : Rate of combustion of charcoal is higher 1 3
Kadar pembakaran arang lebih tinggi
OR
P1 : Satay in Diagram 10.2 will cook faster 1
Sate dalam Rajah 10.2 masak lebih cepat
P2 : Temperature in Diagram 10.2 is higher because fanning 1
causes more oxygen to move towards the satay
Suhu dalam Rajah 10.2 lebih tinggi kerana mengipas
menyebabkan lebih banyak oksigen bergerak ke arah arang
P3 : More heat can react with charcoal and makes charcoal burn 1 3
hotter
Lebih banyak haba boleh bertindak balas dengan arang
menyebabkan arang terbakar dengan lebih panas
Total 20
@JU KIMIA PERAK 18
You might also like
- Adiabatic Reactors Final Lab Group 1-ADocument22 pagesAdiabatic Reactors Final Lab Group 1-AHaris SheikhNo ratings yet
- Speed of Reaction: Test Yourself 18.1 and 18.2 (Page 355)Document5 pagesSpeed of Reaction: Test Yourself 18.1 and 18.2 (Page 355)Jack Kowman25% (4)
- Solutions Manual For Thermodynamics and Chemistry: Howard DevoeDocument110 pagesSolutions Manual For Thermodynamics and Chemistry: Howard DevoeAshna GautamNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics Lecture Notes Second Edition: July 2017Document19 pagesEnzyme Kinetics Lecture Notes Second Edition: July 2017Rao WasimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Answers PDFDocument126 pagesChemistry Answers PDFNurafiqah FarhaniNo ratings yet
- Kimia Trial TRG Bk3 k2 Skema 2017Document14 pagesKimia Trial TRG Bk3 k2 Skema 2017shintasamtoNo ratings yet
- Skema Upk1 Kimia 2019Document8 pagesSkema Upk1 Kimia 2019Fadyana GhaniNo ratings yet
- Skema Upk1 Kimia 2019Document8 pagesSkema Upk1 Kimia 2019donutNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 5Document37 pagesChem Form 5Ashwin Boy Ash100% (1)
- 4 Skema Pemarkahan Rate of ReactionDocument47 pages4 Skema Pemarkahan Rate of ReactionJun QiangNo ratings yet
- BK7 Jawapan Kertas 2Document7 pagesBK7 Jawapan Kertas 2Iza MohdSabriNo ratings yet
- 2021 EJC JC2 Prelim H2 Chemistry Paper 1 QPDocument10 pages2021 EJC JC2 Prelim H2 Chemistry Paper 1 QPclarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- 0625 w18 QP 22Document16 pages0625 w18 QP 22Dairin DindaNo ratings yet
- JC2 Chemistry H2 2018 MeridianDocument109 pagesJC2 Chemistry H2 2018 MeridianYao Le Titanium ChenNo ratings yet
- Kinetics SLDocument16 pagesKinetics SLAmiraliNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Test 1: 1 AS/SEP 2018/TEST 1/CHM131Document4 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Test 1: 1 AS/SEP 2018/TEST 1/CHM131EzzarenNo ratings yet
- TEST 1 LatihanDocument4 pagesTEST 1 LatihanNURUL AIDA OTHMANNo ratings yet
- June 2022 (9701 - 12) QPDocument20 pagesJune 2022 (9701 - 12) QPHung Mang ThiNo ratings yet
- MS Chem F5Document4 pagesMS Chem F5Muhamad Aizuddin Abd RazakNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences: Paper Ii: Please Turn OverDocument16 pagesPhysical Sciences: Paper Ii: Please Turn OverBonga DubeNo ratings yet
- (DragonVision) Chemistry 5090 Variant2 s18 PDFDocument16 pages(DragonVision) Chemistry 5090 Variant2 s18 PDFDragonVisionNo ratings yet
- DPP4 Chemical KineticsDocument6 pagesDPP4 Chemical KineticsAbhishek SinglaNo ratings yet
- Anglo-Chinese Junior College Department of Chemistry Preliminary ExaminationDocument18 pagesAnglo-Chinese Junior College Department of Chemistry Preliminary ExaminationZach EganNo ratings yet
- Test1 Ch15 Kinetics Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesTest1 Ch15 Kinetics Practice ProblemsVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- MEP1 and AnsDocument13 pagesMEP1 and AnsWONG YUE SHAN MoeNo ratings yet
- November 2022 (9701 - 12) QPDocument20 pagesNovember 2022 (9701 - 12) QPHung Mang ThiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/13Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Chemistry 9701/13chris chongNo ratings yet
- 2022 Pahang - MPSM Chemistry K1 - K2 JawapanDocument14 pages2022 Pahang - MPSM Chemistry K1 - K2 JawapanCrystal GohNo ratings yet
- 2009 UNIT 1 Paper 1Document5 pages2009 UNIT 1 Paper 1cilacax404No ratings yet
- J1 Promos 2015 Paper 1Document11 pagesJ1 Promos 2015 Paper 1aliciaNo ratings yet
- Exam 7 - Paper 2 (Model 2)Document16 pagesExam 7 - Paper 2 (Model 2)m.altokhy07No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics For Grade 11Document15 pagesChemical Kinetics For Grade 11Leul KassaNo ratings yet
- 7.chemical Reactions PDFDocument18 pages7.chemical Reactions PDFHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Kedah Skema Modul 2 Kimia Paper 2 Trial SPM 2015Document10 pagesKedah Skema Modul 2 Kimia Paper 2 Trial SPM 2015azmibhr100% (1)
- GRADE 8 CHEMISTRY SEMESTER 2 FINAL EXAM MS PAPER 2 (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesGRADE 8 CHEMISTRY SEMESTER 2 FINAL EXAM MS PAPER 2 (AutoRecovered)dodoNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Group 2 MCQDocument4 pages3.1.2 Group 2 MCQanwins46No ratings yet
- 2015 PSPM Kedah Kimia2 W AnsDocument38 pages2015 PSPM Kedah Kimia2 W Ansjee2kk100% (2)
- Final HSSC-I Chemistry Model Paper MergedDocument10 pagesFinal HSSC-I Chemistry Model Paper MergeddasddaNo ratings yet
- Kimia Modul Peace Cemerlang (Answer) 2018: Bab 6: ElektrokimiaDocument8 pagesKimia Modul Peace Cemerlang (Answer) 2018: Bab 6: ElektrokimiaKamala MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Practicetopics 6 Paper 1.pagesDocument13 pagesPracticetopics 6 Paper 1.pagesnadia sykesNo ratings yet
- 7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Document14 pages7 Skema Kimia K1 & K2 Trial SPM Terengganu MPP3 2019Ain MiorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STD - IXDocument17 pagesChemistry STD - IXPrem GomesNo ratings yet
- TEST 2 Topic 3Document3 pagesTEST 2 Topic 3Ashutosh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Paper 2 Paper 3: Chemistry Trial-Exam SPM 2012 Marking SchemeDocument21 pagesPaper 1 Paper 2 Paper 3: Chemistry Trial-Exam SPM 2012 Marking SchemeHarun Din HairuddinNo ratings yet
- 4541 KIM - Skema Kertas 1 & 2Document13 pages4541 KIM - Skema Kertas 1 & 2Yeow Pow Choo100% (1)
- June 2003 QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument20 pagesJune 2003 QP - Paper 1 CIE Chemistry IGCSEMedo O. EzzatNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Pre-U CertificateDocument16 pagesCambridge International Examinations Cambridge Pre-U Certificatelaksh bissoondialNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/12Mohammed khaled GhazalNo ratings yet
- 2016 Chemistry H2 JC2 Victoria Junior CollegeDocument78 pages2016 Chemistry H2 JC2 Victoria Junior CollegemagnusremixicoNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document8 pagesPaper 1Nur Dinah Alesha Mohd Ali ZarNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences: Paper Ii: Please Turn OverDocument18 pagesPhysical Sciences: Paper Ii: Please Turn OverBonga DubeNo ratings yet
- ACJC H2 CHEM P1 (Worked Solution)Document26 pagesACJC H2 CHEM P1 (Worked Solution)Zach EganNo ratings yet
- KimiaDocument4 pagesKimiaijah rosmiNo ratings yet
- Answer Key B and D Exam Iii Dec 5TH Chem 102Document11 pagesAnswer Key B and D Exam Iii Dec 5TH Chem 102M.SNo ratings yet
- Mdcat Crash Test 1 ChemistryDocument6 pagesMdcat Crash Test 1 ChemistryMUHAMMAD NOMAN SALEEMNo ratings yet
- Catholic Junior College: JC1 Mid-Year Examinations Higher 2Document8 pagesCatholic Junior College: JC1 Mid-Year Examinations Higher 2Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Cemi - 321 - Lecture 12 - 2023Document21 pagesCemi - 321 - Lecture 12 - 2023VILLA KGAMADINo ratings yet
- SKEMA TEST 1 Form 5Document3 pagesSKEMA TEST 1 Form 5Floreo BlossomNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STD-XDocument17 pagesChemistry STD-XPrem GomesNo ratings yet
- Tonmo y Roy: Unit 3 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesTonmo y Roy: Unit 3 Multiple Choice QuestionsjenifaNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument7 pagesRate of ReactionNubar MammadovaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Archivetemp04 Modul A + Kimia Tg5 - Bab 4Document22 pagesArchivetemp04 Modul A + Kimia Tg5 - Bab 4DOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines To Essay Writing SPM by MR Shukri Ayob A) What Is Writing?Document3 pagesGuidelines To Essay Writing SPM by MR Shukri Ayob A) What Is Writing?DOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Archivetemp01 Modul A + Kimia Tg5 - Bab 1Document54 pagesArchivetemp01 Modul A + Kimia Tg5 - Bab 1DOROTHY LING YU CHANG Moe0% (1)
- F5C3 Electricity Part 2Document44 pagesF5C3 Electricity Part 2DOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeNo ratings yet
- F4C5 Key Concept: Metal Non Metal Non Metal Non MetalDocument2 pagesF4C5 Key Concept: Metal Non Metal Non Metal Non MetalDOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 3 Electricity (Part 1) : Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowDocument34 pagesForm 5 Chapter 3 Electricity (Part 1) : Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowDOROTHY LING YU CHANG MoeNo ratings yet
- General Organic and Biochemistry 8Th Edition Denniston Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument28 pagesGeneral Organic and Biochemistry 8Th Edition Denniston Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFBradMartiniczn100% (12)
- Chapter 2 Chemical KineticsDocument83 pagesChapter 2 Chemical KineticsRaymond KakalaNo ratings yet
- ICTAC Kinetics Committee Recommendations For Analysis of Multi-Step KineticsDocument23 pagesICTAC Kinetics Committee Recommendations For Analysis of Multi-Step KineticsBahnmiNo ratings yet
- Manuscript For (CSTR - Batch Mode) - Group 1 - Ceeh2205iDocument8 pagesManuscript For (CSTR - Batch Mode) - Group 1 - Ceeh2205iNURSYAHIRAH MOHD NAZIRNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Chemical KineticsDocument37 pagesUnit 5 Chemical KineticsSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- RohitDocument24 pagesRohitVedantNo ratings yet
- Jftot PDFDocument5 pagesJftot PDFKeyang SunNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Module - 5Document23 pagesChemical Kinetics: Module - 5TeachingTrainingCoaching KnowledgeSharingSessionNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 and 2-ChemicalKineticsDocument86 pagesTopic 1 and 2-ChemicalKineticsNOR AZAM BIN ENDOT / FSNo ratings yet
- Application of The Acid Hydrolysis of Sucrose As A TemperatureDocument8 pagesApplication of The Acid Hydrolysis of Sucrose As A Temperaturefaizfrasat123No ratings yet
- Chemistry Level N Chapter 12 BQ-AK 2223Document19 pagesChemistry Level N Chapter 12 BQ-AK 2223Dema IhabNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Aging and Lifetime Prediction: Review of Non-Arrhenius Behaviour Due To Two Competing ProcessesDocument10 pagesAccelerated Aging and Lifetime Prediction: Review of Non-Arrhenius Behaviour Due To Two Competing ProcessesguschinNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 FinalDocument13 pagesExperiment 6 FinalFroileth Pulido100% (1)
- Justice 3Document27 pagesJustice 3Arierhi JusticeNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Introduction To Physical Chemistry Student VersionDocument22 pagesUnit 4 - Introduction To Physical Chemistry Student VersionAmadu sallieuNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Quarter 1 Module 8Document32 pagesPhysical Science Quarter 1 Module 8Luanne Jali-JaliNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Document10 pagesUnit 4 CHEMICAL KINETICS 2017Gaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetic - Dec2016 PDFDocument137 pagesChemical Kinetic - Dec2016 PDFFaisal AzamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Chemical ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 19 Chemical ThermodynamicsRSLNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinietics PDFDocument19 pagesChemical Kinietics PDFYoNo ratings yet
- Chep 424 2ND Semester 2013 Quiz 1Document1 pageChep 424 2ND Semester 2013 Quiz 1Clarissa AlfaroNo ratings yet
- PROYECTO 3 The Leaching of Gold, Silver and Their Alloys in Alkaline Glycine-PeroxideDocument5 pagesPROYECTO 3 The Leaching of Gold, Silver and Their Alloys in Alkaline Glycine-Peroxidearmando josueNo ratings yet
- JEE AssignmentsDocument12 pagesJEE AssignmentsKriti GargNo ratings yet
- Sulfonation Mechanism of Benzene With SO3 in Sulfuric Acid or Oleum PDFDocument37 pagesSulfonation Mechanism of Benzene With SO3 in Sulfuric Acid or Oleum PDFLaely Dian MarlindawatiNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis Conway StudentDocument240 pagesPHD Thesis Conway StudentSeyed Schwan HosseinyNo ratings yet
- U15 S3-4 HW KeysDocument35 pagesU15 S3-4 HW KeysRohith GudatiNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1749772817300854 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S1749772817300854 Mainsally.marshNo ratings yet
- Activation Energy For Diffusion: Thermal VibrationDocument8 pagesActivation Energy For Diffusion: Thermal VibrationChinar MathurNo ratings yet