Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Volcanoes 2
Volcanoes 2
Uploaded by
Aliyah Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesThe document discusses the basic parts of a volcano and factors that affect volcanic eruptions. It also provides a volcanic explosivity index (VEI) that rates the size of volcanic eruptions from 0-8 based on the volume of ejected material. The VEI scale ranges from nonexplosive eruptions that emit less than 10,000 cubic meters of material to supervolcanic eruptions that eject over 1,000 cubic kilometers of ash and lava.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the basic parts of a volcano and factors that affect volcanic eruptions. It also provides a volcanic explosivity index (VEI) that rates the size of volcanic eruptions from 0-8 based on the volume of ejected material. The VEI scale ranges from nonexplosive eruptions that emit less than 10,000 cubic meters of material to supervolcanic eruptions that eject over 1,000 cubic kilometers of ash and lava.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views2 pagesVolcanoes 2
Volcanoes 2
Uploaded by
Aliyah CruzThe document discusses the basic parts of a volcano and factors that affect volcanic eruptions. It also provides a volcanic explosivity index (VEI) that rates the size of volcanic eruptions from 0-8 based on the volume of ejected material. The VEI scale ranges from nonexplosive eruptions that emit less than 10,000 cubic meters of material to supervolcanic eruptions that eject over 1,000 cubic kilometers of ash and lava.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
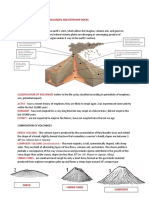
Basic Parts of Volcano
Magma chamber or reservoir - underground compartment where the magma is stored.
Vent - opening where volcanic materials are released. A conduit or passageway through which magma
travels to reach the Earth’s surface.
Crater - a basin-like depression over a vent at the summit of the volcano.
Flank - the side of a volcano.
Factors Affecting Volcanic Eruptions
Magma composition - high silica content increases magma’s viscosity.
Magma temperature - the higher the temperature, the lower the viscosity.
Amount of dissolved gases - gas dissolved in magma tends to increase its stability to flow.
VOLCANIC EXPLOSIVITY INDEX (VEI
VEI EJECTA VOLUME ERUPTION DESCRIPTION PLUME HEIGHT EXAMPLES
Effusive Kilauea,
0 < 10 000 m3 Hawaiian < 100 m Piton de Fournaise
An outpouring of lava on the ground
Gentle
1 > 10 000 m3 Hawaiian/ 100 - 1000 m Nyiragongo
Strombolian Low-level, small to medium volume 2002
Explosive Ruapehu
2 > 1 000 000 m3 Strombolian/ 1- 5 km 1971
Vulcanian Dense cloud of ash and gases with volcanic bombs Mt. Sinabung
2010
Severe Soufriere Hills
3 > 10 000 000 m3 Vulcanian/ 3 - 15 km 1995
Pelean Glowing avalanche of hot ash and pyroclastic flows Nevado del Ruiz 1985
Cataclysmic Mt. Pelee
4 > 0.1 km3 Pelean/ 10 - 25 km 1902
Plinian Columns of gas and ash that extends to stratosphere Eyjafyallajokull
2010
5 > 1 km3 Mt. Vesuvius
Plinian Paroxysmal 20 - 35 km Mt. St. Helens
1980
6 Krakatoa
> 10 km3 Plinian/ > 30 km 1883
Ultra-Plinian Colossal Mt. Pinatubo
1991
7 Tambora
> 100 km3 Ultra-Plinian Super-colossal > 40 km 1815
Yellowstone
8 > 1 000 km3 Supervolcanic Mega-colossal > 50 km (Pleistocene)
You might also like
- VOLCANOESDocument40 pagesVOLCANOESQueenie Bars OgirdorNo ratings yet
- Sci9 - Q3 - Mod1 - Types of Volcanoes and Volcanic Eruptions - Version3Document24 pagesSci9 - Q3 - Mod1 - Types of Volcanoes and Volcanic Eruptions - Version3Precious Arni69% (16)
- Geology Lecture-527Document48 pagesGeology Lecture-5272022-205418No ratings yet
- Earth. Sci. QTR 1Document6 pagesEarth. Sci. QTR 1Illu SoryNo ratings yet
- Volcanism and Volcanic HazardsDocument79 pagesVolcanism and Volcanic HazardsOkaayNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanic Eruptions (Word)Document14 pagesTypes of Volcanic Eruptions (Word)MaMtNo ratings yet
- Paper - Pululahua 2013-10-03 PDFDocument13 pagesPaper - Pululahua 2013-10-03 PDFCARDENAS MALDONADO MICHAEL JONATHANNo ratings yet
- Q3 Sci Rev FinalDocument10 pagesQ3 Sci Rev FinalReigne Daniella OgatisNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Hazards: - 1300 Volcanoes Known To Have Erupted in Holocene (Last 10 000 Years)Document48 pagesVolcanic Hazards: - 1300 Volcanoes Known To Have Erupted in Holocene (Last 10 000 Years)Sheila MarieNo ratings yet
- Science RevDocument8 pagesScience RevAndrea BascaraNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoDocument56 pagesTypes of VolcanoZyden Gabriel EscudoNo ratings yet
- Cap 7 Convergent Margin MagmatismDocument19 pagesCap 7 Convergent Margin Magmatism6m9jrdfyv9No ratings yet
- DRRR Volcanoes ReviewerDocument27 pagesDRRR Volcanoes ReviewerAtria Mariz OrbistaNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument37 pagesVolcanoesSHERRIE MAE BIJASANo ratings yet
- Volcano PPTDocument54 pagesVolcano PPTjocelyn.matigaNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesEarth Science ReviewerClarence DeitaNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes PDFDocument56 pagesVolcanoes PDFIsabelle GonzaloNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument25 pagesVolcanoesjenjang yannieNo ratings yet
- NORSU - Stratigraphy Southeast Negros - Reduced PDFDocument53 pagesNORSU - Stratigraphy Southeast Negros - Reduced PDFNonoy Ruelo100% (2)
- Types of VolcanoesDocument6 pagesTypes of VolcanoesCheska Reese Tan SilvaNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE2Document10 pagesSCIENCE2Pia DebbieNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes - Module 1 FinalDocument69 pagesVolcanoes - Module 1 FinalAngel rose OrbeNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sciencevolcanic EruptionsDocument46 pagesEarth and Life Sciencevolcanic EruptionsAngelou LagazonNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and The Different Volcanic Activities: Quarter 4Document38 pagesVolcanoes and The Different Volcanic Activities: Quarter 4Amor VeNo ratings yet
- VOLCANO MendeleevDocument62 pagesVOLCANO MendeleevJuliana deLunaNo ratings yet
- Karst Hydrogeology of The Takaka Valley Golden Bay Northwest NelsonDocument7 pagesKarst Hydrogeology of The Takaka Valley Golden Bay Northwest NelsonDima MithaNo ratings yet
- L3S VolcanicityDocument90 pagesL3S Volcanicitymichael wongNo ratings yet
- 9 QST 3 ScienceDocument9 pages9 QST 3 ScienceJhaniella QuinlogNo ratings yet
- How Are Lava Type, Volcano Shape and Eruption Style Linked?Document8 pagesHow Are Lava Type, Volcano Shape and Eruption Style Linked?Vicki Taylor100% (1)
- Module 3 Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards - MMVillegas 2021Document98 pagesModule 3 Volcanoes and Volcanic Hazards - MMVillegas 2021JHON PATRICK MALINAWANNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument65 pagesVolcanoesajeebusman513No ratings yet
- Morphology of VolcanoesDocument34 pagesMorphology of VolcanoesMagistrado Drew67% (3)
- Volcanos: Chapter 6: Volcanos and Volcanic Hazards (11/02/2020)Document59 pagesVolcanos: Chapter 6: Volcanos and Volcanic Hazards (11/02/2020)Megan RomeroNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes PresentationDocument18 pagesVolcanoes PresentationDafchen Nio MahasolNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes g9Document33 pagesVolcanoes g9rvnsj28No ratings yet
- RbbebDocument6 pagesRbbebauvqliaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 - Module 1: (Types of Volcanoes and Volcanic Eruption)Document20 pagesQuarter 3 - Module 1: (Types of Volcanoes and Volcanic Eruption)Gregson Gucela100% (1)
- Week 1 TYPES OF VOLCANOESDocument2 pagesWeek 1 TYPES OF VOLCANOESNorraine Denice Jabalde NoricoNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument36 pagesVolcanoesjhoms8No ratings yet
- l1 VolcanoesDocument73 pagesl1 VolcanoesMilba MaciasNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Volcanic HazardsDocument5 pagesVolcanoes and Volcanic Hazardskyle jzNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes: Grade 9, Module 3 Lesson 1.1Document36 pagesVolcanoes: Grade 9, Module 3 Lesson 1.1precious maningasNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Landforms GEO 321 Lecture # 3 J. Steven Kite West Virginia UniversityDocument33 pagesVolcanic Landforms GEO 321 Lecture # 3 J. Steven Kite West Virginia UniversityRio CendrajayaNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes, Magma & PlutonsDocument37 pagesVolcanoes, Magma & Plutonswonder-chef-4677100% (1)
- E114 - Volc - Day5 - DW 2017W1Document50 pagesE114 - Volc - Day5 - DW 2017W1John GongNo ratings yet
- CSSCI02Document2 pagesCSSCI02Bey VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument3 pagesTypes of VolcanoesTrishajoy MabesaNo ratings yet
- VOLCANOESDocument45 pagesVOLCANOESCyrus Bantugon GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nature and Types of Volcanoes Autosaved 1Document31 pagesNature and Types of Volcanoes Autosaved 1jairolostreNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes ReviewerDocument6 pagesVolcanoes ReviewerAtria Mariz Ricamonte OrbistaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Unit 3 Module 1Document3 pagesScience 9 Unit 3 Module 1Jeddie SuanNo ratings yet
- Cataclysmic Eruptions: The Really Big Ones!Document15 pagesCataclysmic Eruptions: The Really Big Ones!bestbryantNo ratings yet
- VulkanianDocument27 pagesVulkaniancaymauNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument13 pagesScience ReviewerMatthues Ace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Reviewer-3rd Quarter SRSTHSDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Science Reviewer-3rd Quarter SRSTHSKaryll Heart Layug67% (3)
- 10 Wilson - 2008 - Elements Supervolcanoes ProcessesDocument6 pages10 Wilson - 2008 - Elements Supervolcanoes ProcessesANGELA KENNYA MENDOZA PRIETONo ratings yet
- Holy Smokes Its A VolcanoDocument39 pagesHoly Smokes Its A VolcanoMary AnnNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Volcanic EruptionsDocument20 pagesVolcanoes and Volcanic Eruptionssuren kambleNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoDocument58 pagesTypes of VolcanoAndrea Mai CondeNo ratings yet
- RevelationDocument36 pagesRevelationAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson FaithDocument58 pagesLesson FaithAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Revisiting FractionsDocument24 pagesLESSON 1 Revisiting FractionsAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Precautions Before During and After A Volcanic EruptionDocument1 pagePrecautions Before During and After A Volcanic EruptionAliyah Cruz0% (1)
- Ancient China MapsDocument1 pageAncient China MapsAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Laborem ExercensDocument4 pagesLaborem ExercensAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Javascript Is The Programming Language For The Web: Web Servers Web Server Internet ServerDocument3 pagesJavascript Is The Programming Language For The Web: Web Servers Web Server Internet ServerAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Climate and Stars HODocument4 pagesClimate and Stars HOAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Business ManagementDocument24 pagesBusiness ManagementAliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes 2Document2 pagesVolcanoes 2Aliyah CruzNo ratings yet
- Mount VesuviusDocument10 pagesMount VesuviuscarleighnicoleNo ratings yet
- Mueller 2011 - The Porosity of Pyroclasts As An Indicator of Volcanic ExplosivityDocument7 pagesMueller 2011 - The Porosity of Pyroclasts As An Indicator of Volcanic ExplosivityJuan TurraNo ratings yet
- Summative TestDocument4 pagesSummative Testmenchie ismaelNo ratings yet
- Geo19 1 Geomorphology 2 PF PDFDocument70 pagesGeo19 1 Geomorphology 2 PF PDFpoochoozzNo ratings yet
- AESB1430 Geology 3 Virtual Excursion, Part 3: The Volcanic EifelDocument47 pagesAESB1430 Geology 3 Virtual Excursion, Part 3: The Volcanic EifelChristopher BetzNo ratings yet
- TMP 8 FA2Document19 pagesTMP 8 FA2FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Eruption Types (Volcanic Eruptions) : January 2013Document26 pagesEruption Types (Volcanic Eruptions) : January 2013FakhraNo ratings yet
- Minggu 3 Klasifikasi, Bentuk Dan Struktur Gunung Api PDFDocument48 pagesMinggu 3 Klasifikasi, Bentuk Dan Struktur Gunung Api PDFeva aprillianaNo ratings yet