Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsFat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)
Fat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)
Uploaded by
Satyam AnandVitamins A, D, E, and K are fat soluble vitamins that require bile for proper absorption in the digestive system. They are stored in the liver and have a risk of toxicity if consumed in large amounts. Vitamin A supports vision and epithelial tissue integrity. Vitamin D works with calcium to support bone health. Vitamin E protects cell membranes from oxidative damage and supports reproduction. Vitamin K is required for blood clotting through the production of clotting proteins. Deficiencies of these vitamins can lead to diseases like night blindness, rickets, bleeding disorders, and neurological or reproductive issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartGerarld Immanuel Kairupan100% (1)
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument5 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartKaye Tubungbanua MatunogNo ratings yet
- GTG 43Document14 pagesGTG 43jhjgfNo ratings yet
- Nutrient ChartDocument7 pagesNutrient ChartDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- BCH 211 Lecture NoteDocument13 pagesBCH 211 Lecture NotemanomistephenNo ratings yet
- Vitamins MineralsDocument23 pagesVitamins Mineralsgenesis victorinoNo ratings yet
- Keratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's SpotsDocument3 pagesKeratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's SpotsNimish BajareNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument6 pagesVitamin and Mineral Chartsellitt ngNo ratings yet
- 12 Fat-Soluble Vitamins1Document44 pages12 Fat-Soluble Vitamins1Awab MohamedNo ratings yet
- Vitamins For BSC Nursing Students (PHARMACOLOGY) - By: BINI P SAMUEL, ASSISTANT PROFESSORDocument17 pagesVitamins For BSC Nursing Students (PHARMACOLOGY) - By: BINI P SAMUEL, ASSISTANT PROFESSORbinipsamuel25No ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument58 pagesVITAMINSRazvan DinuNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Pharmacology-34Document1 pageMidwifery Pharmacology-34georgeloto12No ratings yet
- NutrientDocument1 pageNutrientJazz Astucia AzarconNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument61 pagesVitamins and MineralsMackoy LoganNo ratings yet
- MOST Assign1 VitaminsDocument6 pagesMOST Assign1 VitaminsbubblingbrookNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument8 pagesVitamins & Mineralswardahmohammad2022No ratings yet
- Micronutrients 2020Document44 pagesMicronutrients 2020Arsyi ZahwaNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients - VitaminsDocument9 pagesMicronutrients - VitaminsKate SantosNo ratings yet
- Cielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADocument10 pagesCielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- 2.vitamin ADocument20 pages2.vitamin AdrmaseerkhanNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartJagan LogaiyaNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument23 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: Treatment of MalnutritionDocument4 pagesPediatrics: Treatment of Malnutritionapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Vitamins: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman Ph.D. M.D Medical BiochemistryDocument20 pagesVitamins: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman Ph.D. M.D Medical BiochemistryHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument2 pagesAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Vitamins TableDocument3 pagesVitamins Tableapi-512416839No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument5 pagesVitamins2n5pbr5598No ratings yet
- AppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFDocument7 pagesAppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFMaria Christina LagartejaNo ratings yet
- 105 Vitamins - Social Pharmacy D Pharm I Year Gyandeep Academy 9826672215 1Document5 pages105 Vitamins - Social Pharmacy D Pharm I Year Gyandeep Academy 9826672215 1Vikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument21 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsPragnesh BhalalaNo ratings yet
- Christine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument5 pagesChristine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy AY 2020-2021: VitaminsDocument3 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy AY 2020-2021: VitaminsToyour EternityNo ratings yet
- Nutrilite RefChartDocument4 pagesNutrilite RefChartgirishkumarhm50% (4)
- Nutrition and VitaminDocument70 pagesNutrition and VitaminTob JurNo ratings yet
- SM 6 NutritionDocument10 pagesSM 6 Nutritionrahul royNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminsHamas ArshadNo ratings yet
- 119 Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument33 pages119 Fat Soluble VitaminsEve TinirnacNo ratings yet
- 2012-09-07 VitaminsDocument22 pages2012-09-07 Vitaminsaltemsahvetmed.85No ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Part 2Document30 pagesHuman Nutrition Part 2Sbahat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficiency in FishesDocument40 pagesVitamin Deficiency in FishesDuong Vu TungNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument17 pagesVitaminsnicholaschungu24No ratings yet
- Presented By: DR - Eglal Hakeim &DR - Hoda SyaedDocument33 pagesPresented By: DR - Eglal Hakeim &DR - Hoda Syaedbobovovo bobovovoNo ratings yet
- The Vitamins: Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble VitaminsDocument66 pagesThe Vitamins: Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble VitaminsKennethTrucillaCortezNo ratings yet
- MCHN Week 1november-18Document46 pagesMCHN Week 1november-18cyrilperry1No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument8 pagesVitaminsecho tiongcoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Best Sources Functions Deficiency Symptoms: VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitamin Best Sources Functions Deficiency Symptoms: Vitaminsjenny gallegosNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A: A Pre-Formed Vitamin RETINOL and A Pro-Vitamin, Beta CaroteneDocument21 pagesVitamin A: A Pre-Formed Vitamin RETINOL and A Pro-Vitamin, Beta CarotenezuhaibjokhioNo ratings yet
- Dietary Guidelines For Different Population Groups: Subject: Human Nutrition and Dietetics Student: Isela MenjivarDocument27 pagesDietary Guidelines For Different Population Groups: Subject: Human Nutrition and Dietetics Student: Isela MenjivarIsela Menjivar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficiency DisordersDocument23 pagesVitamin Deficiency DisordersKibromWeldegiyorgisNo ratings yet
- Classification of VitaminsDocument26 pagesClassification of VitaminsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Lecture Notes Module 2 ContinuationDocument5 pagesNutrition Lecture Notes Module 2 ContinuationfallenNo ratings yet
- Vitamin: Sunny Yadav BPH, TuDocument47 pagesVitamin: Sunny Yadav BPH, TuSUNNY YADAVNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminsDeeksha GovilNo ratings yet
- Retinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin ADocument2 pagesRetinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin AsashellNo ratings yet
- Dietetic Guidelines Short VersionDocument22 pagesDietetic Guidelines Short VersionIsela Menjivar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- 2 4-LipidsDocument24 pages2 4-Lipidshero samilinNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Dr. Babiker Mohamed Ali RahamtallaDocument52 pagesVitamins: Dr. Babiker Mohamed Ali Rahamtallaعوض الكريمNo ratings yet
- VutaminDocument66 pagesVutamindyla nabillaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin MicronutrientsDocument11 pagesVitamin Micronutrientsprabhjot singhNo ratings yet
- The Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyDocument20 pagesThe Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyGerald Limo Arap ChebiiNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Gizi Mikro-3 MagnesiumDocument34 pagesMetabolisme Gizi Mikro-3 MagnesiumIndra punya ProjectNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K2 PaperDocument55 pagesVitamin K2 PapernbpravinNo ratings yet
- Circumcision On The 8th DayDocument2 pagesCircumcision On The 8th DayindeenikeNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue ANG B2b.indd MalyDocument42 pagesProduct Catalogue ANG B2b.indd MalyAlex NikolishviliNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Control Questions. Module 3Document3 pagesBiochemistry Control Questions. Module 3Valeriy MelnykNo ratings yet
- Not Owned SourceDocument3 pagesNot Owned SourceAlma CayapNo ratings yet
- Name Brand Names: International: SucralfateDocument10 pagesName Brand Names: International: Sucralfatenurul husnaNo ratings yet
- The Vitamins: Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble VitaminsDocument66 pagesThe Vitamins: Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble VitaminsSiti Diah Nur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Deficiencies Bariatric SurgeryDocument10 pagesDeficiencies Bariatric SurgeryYazen JoudehNo ratings yet
- 03 Modul SC T2-Bab3 (Csy4p) PDFDocument22 pages03 Modul SC T2-Bab3 (Csy4p) PDFSitiRohaizaMatYusoffNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document13 pagesLesson 10armin509No ratings yet
- Drugs For Coagulation DisordersDocument38 pagesDrugs For Coagulation DisordersAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument111 pagesAnimal NutritionOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDocument3 pagesVitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDeni Yuda Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug Interactions in Dentistry PDFDocument16 pagesAdverse Drug Interactions in Dentistry PDFAbhay KhannaNo ratings yet
- Proximate, Mineral and Vitamin Contents of Indian Major CarpDocument7 pagesProximate, Mineral and Vitamin Contents of Indian Major CarpIheti SamNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: IntroductionDocument16 pagesVitamins: IntroductionDarshan MishraNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K ResumeDocument1 pageVitamin K ResumeMegan MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- Emerging Issues in Vitamin K Research: Jennifer T. Truong, MD, MPH and Sarah L. Booth, PHDDocument7 pagesEmerging Issues in Vitamin K Research: Jennifer T. Truong, MD, MPH and Sarah L. Booth, PHDYustika Denanty SitorusNo ratings yet
- Masterjohn - Vit D Toxicity Redefined - Vit K Molecular MechanismDocument9 pagesMasterjohn - Vit D Toxicity Redefined - Vit K Molecular MechanismBradNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K Plasma Levels Determination in Human HealthDocument11 pagesVitamin K Plasma Levels Determination in Human HealthZackNo ratings yet
- 42 National Science Olympiad: 9 March 2006 Questions and Solutions: BiologyDocument55 pages42 National Science Olympiad: 9 March 2006 Questions and Solutions: Biologymartynapet100% (2)
- Biochemistry Week 10 - Vitamins and MineralsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Week 10 - Vitamins and MineralsMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- Slide 1: Slide 2Document4 pagesSlide 1: Slide 2kundagolNo ratings yet
- Department of Pharmacy: VitaminsDocument7 pagesDepartment of Pharmacy: Vitaminsraisul razaNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Mechanism of Action, Indications AtfDocument4 pagesWarfarin Mechanism of Action, Indications AtfAmir mohammad moori MohammadiNo ratings yet
- GCH VBVDocument2 pagesGCH VBVGilianne JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Infancy and NutritionDocument1 pageInfancy and NutritionGeneveive GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin D Vitamin KDocument28 pagesVitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin D Vitamin KSajanMaharjanNo ratings yet
Fat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)
Fat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)
Uploaded by
Satyam Anand0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageVitamins A, D, E, and K are fat soluble vitamins that require bile for proper absorption in the digestive system. They are stored in the liver and have a risk of toxicity if consumed in large amounts. Vitamin A supports vision and epithelial tissue integrity. Vitamin D works with calcium to support bone health. Vitamin E protects cell membranes from oxidative damage and supports reproduction. Vitamin K is required for blood clotting through the production of clotting proteins. Deficiencies of these vitamins can lead to diseases like night blindness, rickets, bleeding disorders, and neurological or reproductive issues.
Original Description:
Original Title
5_6055612306325242094
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentVitamins A, D, E, and K are fat soluble vitamins that require bile for proper absorption in the digestive system. They are stored in the liver and have a risk of toxicity if consumed in large amounts. Vitamin A supports vision and epithelial tissue integrity. Vitamin D works with calcium to support bone health. Vitamin E protects cell membranes from oxidative damage and supports reproduction. Vitamin K is required for blood clotting through the production of clotting proteins. Deficiencies of these vitamins can lead to diseases like night blindness, rickets, bleeding disorders, and neurological or reproductive issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageFat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)
Fat Soluble Vitamins: 1913 (Retinol, Retinal)
Uploaded by
Satyam AnandVitamins A, D, E, and K are fat soluble vitamins that require bile for proper absorption in the digestive system. They are stored in the liver and have a risk of toxicity if consumed in large amounts. Vitamin A supports vision and epithelial tissue integrity. Vitamin D works with calcium to support bone health. Vitamin E protects cell membranes from oxidative damage and supports reproduction. Vitamin K is required for blood clotting through the production of clotting proteins. Deficiencies of these vitamins can lead to diseases like night blindness, rickets, bleeding disorders, and neurological or reproductive issues.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
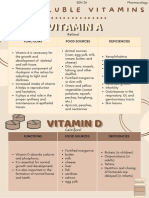
Fat soluble Vitamins
Vitamins Sources Functions Deficiency Disease Toxicity Symptoms Daily Allowances*
Vitamin A Animal Fish-liver oils Liver Bile necessary for absorption Stored in liver Night blindness, Fatigue; night sweats; vertigo; headache; Children:400-700 RE (2,000-3,300
1913; (Retinol, retinal) Butter, cream ,milk , cheeses, Egg Maintains integrity of muscosal epithelium, Keratomalacia dry and fissured skin; lips; IU)
yolk, green vegetables, yellow maintains visual acuity in dim light. hyperpigmentation; retarded growth; Men:1,000 RE(5,000 IU)
and orange coloured fruits, Large amounts are toxic bone pain; abdominal pain; vomiting; Women:800 RE (4,000 IU)
vegetables, red palm oil, fish and jaun- dice; hypercalcemia Pregnancy:1,000 RE (5,000 IU)
fish liver oil. Lactation: 1,200 RE (6,000 IU)
Vitamin D Fish-liver oils fortified milk Synthesized in skin by activity of ultraviolet Rickets and Abnormally high blood calcium Children 0-18 years: 10mg
1920; activated sterols Exposure to light, Liver synthesizes 25 (OH) D3, Kidney Osteomalacia (hypercalcemia), retarded growth, Adults 19-22 years 7.5 mg
Vitamin D2- sunlight Very small amounts in synthesizes 1,25 (OH)2D3. vomiting, nephrocalci- nosis Adults over 22 years: 5 mg
Ergocalciferol Vitamin D3 - butter, liver, egg yolk, salmon or Functions as steroid hormone to regulate calcium Pregnant/lactating women:+5mg
Cholecalciferol sardines fish and phosphorus absorption, mobilization and
(Antirachitic factor) mineralization of bone. Large amounts are toxic.
Vitamin E Plant tissues-vegetable oils; wheat
Not store in body to any extent. Sterility, Deficiency May interfere with vitamin K activity Infants: 3-4 mg
1922; germ, rice germ; green leafy (Related to action of selenium) is very rare; mild leading to prolonged clotting and Men:10 mg
Alpha-, beta-, gamma- vegetables; nuts; legumes ,animal 1. Humans: reduces oxidation of vitamin A, hemolytic anemiain bleeding time; in anemia, suppresses the Women:8 mg
tocopherol foods are poor sources carotenes, and polyunsaturated fatty acids newborn infants normal hematologic response to iron Pregnancy:10 mg
(Antisterility vitamin, (PUFA) Lactation:11 mg
Beauty vitamin) 2. Animals: normal reproduction; utilization of
sex hormones,cholesterol.
Vitamin K Green leaves such as alfalfa, Bile necessary for absorption, Formation of Hemophilia, Possible hemolytic anemia; hyper- Infants:10-20 mg
1929; Phylloquinone (K1), spinach, cabbage, liver, Synthesis prothrombin and other clotting proteins. Sulfa Bleeding diathesis bilirubinemia (jaundice) Adults: 70-140 mg
Menaquinone (K2) in intestine drugs and antibiotics interfere with absorption,
Large amounts are toxic
You might also like
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartGerarld Immanuel Kairupan100% (1)
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument5 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartKaye Tubungbanua MatunogNo ratings yet
- GTG 43Document14 pagesGTG 43jhjgfNo ratings yet
- Nutrient ChartDocument7 pagesNutrient ChartDanilo Clerigo Sr.No ratings yet
- BCH 211 Lecture NoteDocument13 pagesBCH 211 Lecture NotemanomistephenNo ratings yet
- Vitamins MineralsDocument23 pagesVitamins Mineralsgenesis victorinoNo ratings yet
- Keratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's SpotsDocument3 pagesKeratomalacia in Eyes: Xerophthalmia, Bitot's SpotsNimish BajareNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument6 pagesVitamin and Mineral Chartsellitt ngNo ratings yet
- 12 Fat-Soluble Vitamins1Document44 pages12 Fat-Soluble Vitamins1Awab MohamedNo ratings yet
- Vitamins For BSC Nursing Students (PHARMACOLOGY) - By: BINI P SAMUEL, ASSISTANT PROFESSORDocument17 pagesVitamins For BSC Nursing Students (PHARMACOLOGY) - By: BINI P SAMUEL, ASSISTANT PROFESSORbinipsamuel25No ratings yet
- VITAMINSDocument58 pagesVITAMINSRazvan DinuNo ratings yet
- Midwifery Pharmacology-34Document1 pageMidwifery Pharmacology-34georgeloto12No ratings yet
- NutrientDocument1 pageNutrientJazz Astucia AzarconNo ratings yet
- Vitamins and MineralsDocument61 pagesVitamins and MineralsMackoy LoganNo ratings yet
- MOST Assign1 VitaminsDocument6 pagesMOST Assign1 VitaminsbubblingbrookNo ratings yet
- Vitamins & MineralsDocument8 pagesVitamins & Mineralswardahmohammad2022No ratings yet
- Micronutrients 2020Document44 pagesMicronutrients 2020Arsyi ZahwaNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients - VitaminsDocument9 pagesMicronutrients - VitaminsKate SantosNo ratings yet
- Cielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADocument10 pagesCielo, Divina Gracia V. BSM-1 Vitamins Function RDA Sources Effects of Deficiency Symptoms of Excess ADivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- 2.vitamin ADocument20 pages2.vitamin AdrmaseerkhanNo ratings yet
- Vitamin and Mineral ChartDocument4 pagesVitamin and Mineral ChartJagan LogaiyaNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument23 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: Treatment of MalnutritionDocument4 pagesPediatrics: Treatment of Malnutritionapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Vitamins: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman Ph.D. M.D Medical BiochemistryDocument20 pagesVitamins: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman Ph.D. M.D Medical BiochemistryHUAWEI HUAWEINo ratings yet
- Any Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently ReceivingDocument2 pagesAny Up-Dates Are To Be Completed in Different Color Ink. The Student Is Expected To Document All Meds The Client Is Currently Receivinggeorgeloto12No ratings yet
- Vitamins TableDocument3 pagesVitamins Tableapi-512416839No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument5 pagesVitamins2n5pbr5598No ratings yet
- AppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFDocument7 pagesAppendixC - Nutrient Chart PDFMaria Christina LagartejaNo ratings yet
- 105 Vitamins - Social Pharmacy D Pharm I Year Gyandeep Academy 9826672215 1Document5 pages105 Vitamins - Social Pharmacy D Pharm I Year Gyandeep Academy 9826672215 1Vikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument21 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsPragnesh BhalalaNo ratings yet
- Christine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyDocument5 pagesChristine P. Salimbagat: BSN262 Nutrition and Diet TherapyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy AY 2020-2021: VitaminsDocument3 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy AY 2020-2021: VitaminsToyour EternityNo ratings yet
- Nutrilite RefChartDocument4 pagesNutrilite RefChartgirishkumarhm50% (4)
- Nutrition and VitaminDocument70 pagesNutrition and VitaminTob JurNo ratings yet
- SM 6 NutritionDocument10 pagesSM 6 Nutritionrahul royNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminsHamas ArshadNo ratings yet
- 119 Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument33 pages119 Fat Soluble VitaminsEve TinirnacNo ratings yet
- 2012-09-07 VitaminsDocument22 pages2012-09-07 Vitaminsaltemsahvetmed.85No ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Part 2Document30 pagesHuman Nutrition Part 2Sbahat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficiency in FishesDocument40 pagesVitamin Deficiency in FishesDuong Vu TungNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument17 pagesVitaminsnicholaschungu24No ratings yet
- Presented By: DR - Eglal Hakeim &DR - Hoda SyaedDocument33 pagesPresented By: DR - Eglal Hakeim &DR - Hoda Syaedbobovovo bobovovoNo ratings yet
- The Vitamins: Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble VitaminsDocument66 pagesThe Vitamins: Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble VitaminsKennethTrucillaCortezNo ratings yet
- MCHN Week 1november-18Document46 pagesMCHN Week 1november-18cyrilperry1No ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument8 pagesVitaminsecho tiongcoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Best Sources Functions Deficiency Symptoms: VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitamin Best Sources Functions Deficiency Symptoms: Vitaminsjenny gallegosNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A: A Pre-Formed Vitamin RETINOL and A Pro-Vitamin, Beta CaroteneDocument21 pagesVitamin A: A Pre-Formed Vitamin RETINOL and A Pro-Vitamin, Beta CarotenezuhaibjokhioNo ratings yet
- Dietary Guidelines For Different Population Groups: Subject: Human Nutrition and Dietetics Student: Isela MenjivarDocument27 pagesDietary Guidelines For Different Population Groups: Subject: Human Nutrition and Dietetics Student: Isela MenjivarIsela Menjivar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Deficiency DisordersDocument23 pagesVitamin Deficiency DisordersKibromWeldegiyorgisNo ratings yet
- Classification of VitaminsDocument26 pagesClassification of VitaminsRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Lecture Notes Module 2 ContinuationDocument5 pagesNutrition Lecture Notes Module 2 ContinuationfallenNo ratings yet
- Vitamin: Sunny Yadav BPH, TuDocument47 pagesVitamin: Sunny Yadav BPH, TuSUNNY YADAVNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument2 pagesVitaminsDeeksha GovilNo ratings yet
- Retinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin ADocument2 pagesRetinol in Animal Food: Milk,: Vitamin AsashellNo ratings yet
- Dietetic Guidelines Short VersionDocument22 pagesDietetic Guidelines Short VersionIsela Menjivar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- 2 4-LipidsDocument24 pages2 4-Lipidshero samilinNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: Dr. Babiker Mohamed Ali RahamtallaDocument52 pagesVitamins: Dr. Babiker Mohamed Ali Rahamtallaعوض الكريمNo ratings yet
- VutaminDocument66 pagesVutamindyla nabillaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin MicronutrientsDocument11 pagesVitamin Micronutrientsprabhjot singhNo ratings yet
- The Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyDocument20 pagesThe Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyGerald Limo Arap ChebiiNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Gizi Mikro-3 MagnesiumDocument34 pagesMetabolisme Gizi Mikro-3 MagnesiumIndra punya ProjectNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K2 PaperDocument55 pagesVitamin K2 PapernbpravinNo ratings yet
- Circumcision On The 8th DayDocument2 pagesCircumcision On The 8th DayindeenikeNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue ANG B2b.indd MalyDocument42 pagesProduct Catalogue ANG B2b.indd MalyAlex NikolishviliNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Control Questions. Module 3Document3 pagesBiochemistry Control Questions. Module 3Valeriy MelnykNo ratings yet
- Not Owned SourceDocument3 pagesNot Owned SourceAlma CayapNo ratings yet
- Name Brand Names: International: SucralfateDocument10 pagesName Brand Names: International: Sucralfatenurul husnaNo ratings yet
- The Vitamins: Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble VitaminsDocument66 pagesThe Vitamins: Fat Soluble Vitamins Water Soluble VitaminsSiti Diah Nur RohmahNo ratings yet
- Deficiencies Bariatric SurgeryDocument10 pagesDeficiencies Bariatric SurgeryYazen JoudehNo ratings yet
- 03 Modul SC T2-Bab3 (Csy4p) PDFDocument22 pages03 Modul SC T2-Bab3 (Csy4p) PDFSitiRohaizaMatYusoffNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document13 pagesLesson 10armin509No ratings yet
- Drugs For Coagulation DisordersDocument38 pagesDrugs For Coagulation DisordersAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument111 pagesAnimal NutritionOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDocument3 pagesVitamin K (Phytomenadione) 2016: Indication Action Drug Type Trade Name Presentation Dosage / IntervalDeni Yuda Adi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug Interactions in Dentistry PDFDocument16 pagesAdverse Drug Interactions in Dentistry PDFAbhay KhannaNo ratings yet
- Proximate, Mineral and Vitamin Contents of Indian Major CarpDocument7 pagesProximate, Mineral and Vitamin Contents of Indian Major CarpIheti SamNo ratings yet
- Vitamins: IntroductionDocument16 pagesVitamins: IntroductionDarshan MishraNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K ResumeDocument1 pageVitamin K ResumeMegan MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- Emerging Issues in Vitamin K Research: Jennifer T. Truong, MD, MPH and Sarah L. Booth, PHDDocument7 pagesEmerging Issues in Vitamin K Research: Jennifer T. Truong, MD, MPH and Sarah L. Booth, PHDYustika Denanty SitorusNo ratings yet
- Masterjohn - Vit D Toxicity Redefined - Vit K Molecular MechanismDocument9 pagesMasterjohn - Vit D Toxicity Redefined - Vit K Molecular MechanismBradNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K Plasma Levels Determination in Human HealthDocument11 pagesVitamin K Plasma Levels Determination in Human HealthZackNo ratings yet
- 42 National Science Olympiad: 9 March 2006 Questions and Solutions: BiologyDocument55 pages42 National Science Olympiad: 9 March 2006 Questions and Solutions: Biologymartynapet100% (2)
- Biochemistry Week 10 - Vitamins and MineralsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry Week 10 - Vitamins and MineralsMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- Slide 1: Slide 2Document4 pagesSlide 1: Slide 2kundagolNo ratings yet
- Department of Pharmacy: VitaminsDocument7 pagesDepartment of Pharmacy: Vitaminsraisul razaNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Mechanism of Action, Indications AtfDocument4 pagesWarfarin Mechanism of Action, Indications AtfAmir mohammad moori MohammadiNo ratings yet
- GCH VBVDocument2 pagesGCH VBVGilianne JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Infancy and NutritionDocument1 pageInfancy and NutritionGeneveive GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Vitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin D Vitamin KDocument28 pagesVitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin C Vitamin E Vitamin D Vitamin KSajanMaharjanNo ratings yet