Professional Documents
Culture Documents
For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Chlorine Nitrogen
For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Chlorine Nitrogen
Uploaded by
carlos mosqueraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Chlorine Nitrogen
For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Chlorine Nitrogen
Uploaded by
carlos mosqueraCopyright:
Available Formats
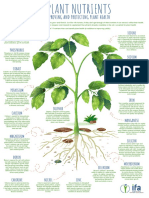
14 ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
FOR IMPROVING AND PROTECTING PLANT HEALTH
Plants need essential nutrients from the soil in order to grow and flourish.
Just like us, if they don’t get enough nutrients it can seriously affect their health. To coincide with the International Year of Plant Health in 2020,
here’s a look at how all 14 essential plant nutrients benefit plant health (in addition to improving yields):
NITROGEN CHLORINE
Nitrogen is an essential component of Chlorine improves plant productivity,
amino acids for building proteins, plays a role in photosynthesis and is
nucleic acids, and chlorophyll which needed for for osmosis and ionic
converts the sun’s energy into sugars. balance. It can help to minimize water
It is vital for plant metabolism, loss during stressful dry periods and
growth and health. enhance disease resistance.
PHOSPHORUS
Phosphorus is vital for energy storage
and transfer and membrane integrity
in plants. Particularly important in early
growth stages, it promotes tillering,
COPPER
root development, early flowering
and ripening.
Copper plays a key role in nitrogen
and hormone metabolism and is
POTASSIUM
needed for many enzyme activities
in plants, as well as for chlorophyll
Potassium has major functions in and seed production. Deficiencies can
enzyme activation, transpiration and lead to crop failure and increased
the transport of assimilates susceptibility to diseases such as ergot.
(the products of photosynthesis).
It helps plants to retain water during
droughts, provides strength to plant
IRON
cell walls and decreases
susceptibility to diseases
and insects.
Iron is another essential component
for creating chlorophyll and also
serves as a catalyst for cell division
which is central to plant growth.
Many plants also use iron for their
CALCIUM SULPHUR enzyme functions. A lack of iron
results in yellowing leaves and poor
Calcium is needed for biomembrane Sulphur is integral to all living plant fruit quality and quantity.
maintenance. It helps in cell wall cells and helps to produce amino acids
involved in chlorophyll production,
MANGANESE
stabilization as an enzyme activator, in
osmoregulation, and in the cation-anion proteins and vitamins. It contributes
balance and thus also plays important to plant growth and seed formation,
improves winter hardiness and helps Manganese plays a key role in a
roles in resistance to diseases and
plants resist diseases. variety of plant functions including
abiotic stresses such as drought,
photosynthesis, enzyme activation,
heat and cold.
respiration, and nitrogen assimilation.
Deficiencies can cause weaker
structural resistance against pathogens
and less tolerance to drought
MAGNESIUM
and heat stress.
Magnesium is central to the production
of chlorophyll which is needed for
photosynthesis and healthy green leaf
tissue. It reduces crop stress caused by
exposure to the sun and high
temperatures, while a deficit can often
cause stunted growth.
MOLYBDENUM
Molybdenum is used by plants to
reduce nitrates into usable forms and
BORON for biological nitrogen fixation by
certain species. Insufficient molybdenum
Boron is required for cell wall synthesis mean some plants can’t fix nitrogen
and cell expansion. Boron deficiency from the air to make proteins and can
disrupts reproductive growth, shoot and hinder normal plant growth.
root growth and pollen viability and
NICKEL ZINC
hence influences seed set and yield.
A lack of boron can result in deformed
leaves and poor quality of
harvested product. Nickel is important in plant seed Zinc participates in chlorophyll
germination, photosynthesis, enzyme formation, is needed to activate many
functions and nitrogen metabolism. enzymes in plants and is needed for
A deficiency affects plant growth, plant immune responses. As a result, it is
antioxidant systems and response important for increasing plant resistance
to stress. to diseases and pests.
You might also like
- Plants and Animals Nutrition General BiologyDocument11 pagesPlants and Animals Nutrition General Biologyjaira magbanuaNo ratings yet
- Paradigma Nutrición SustentableDocument24 pagesParadigma Nutrición Sustentablecarlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- GroveGreen ImperialismDocument8 pagesGroveGreen Imperialismdr_ardenNo ratings yet
- For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Nitrogen ChlorineDocument1 pageFor Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Nitrogen ChlorineRahmat SunaryaNo ratings yet
- For Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Nitrogen IodineDocument1 pageFor Improving and Protecting Plant Health: Nitrogen IodinePao Becerra ENo ratings yet
- Roles of The 16 Essential Nutrients inDocument4 pagesRoles of The 16 Essential Nutrients inAbas S. AcmadNo ratings yet
- Micronutrients and Macronutrients in PlantsDocument4 pagesMicronutrients and Macronutrients in Plantsashleyjade.sundiam.sccNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesBIOLOGYNadine PascuaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Secondary Nutrients in Plant Growth: by Kadiresan KadirDocument7 pagesThe Role of Secondary Nutrients in Plant Growth: by Kadiresan Kadirkadiresan2005No ratings yet
- Lemna SP ArmDocument16 pagesLemna SP ArmHanin Jaliyy100% (1)
- Nutrition: Animation 8.1: Nutrition Source & Credit: WikispaceDocument43 pagesNutrition: Animation 8.1: Nutrition Source & Credit: WikispaceAaa SssNo ratings yet
- Hellagrolip Nitrogenous Brochure enDocument2 pagesHellagrolip Nitrogenous Brochure enBashir A. SialNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Plant GrowthDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis and Plant GrowthzaivrkNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrients NoteDocument10 pagesPlant Nutrients NoteIbukun OlaitanNo ratings yet
- Mineral Nutrition in PlantsDocument32 pagesMineral Nutrition in PlantsSourabh DhanetiaNo ratings yet
- AndrewefsdfsdfDocument4 pagesAndrewefsdfsdfJep TacadaoNo ratings yet
- Anannya Banerjee (6th Sem, Presentation) .Document11 pagesAnannya Banerjee (6th Sem, Presentation) .Soham JashuNo ratings yet
- Plant Mineral Nutrition 2014 FinalpdfDocument7 pagesPlant Mineral Nutrition 2014 Finalpdfalhajifawaz77No ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 3abdullamalek339No ratings yet
- Basic Need of PlantDocument1 pageBasic Need of PlantMohamad Syafie Bin SamsirNo ratings yet
- Plant Mineral Nutrition: July 2014Document7 pagesPlant Mineral Nutrition: July 2014Abdul SalamNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 Horticulture 10 April 16 2024Document19 pagesQuarter 4 Horticulture 10 April 16 2024reyesmiguelpaolo516No ratings yet
- ClassNotes-Agricultural Science SSS2 First Term-1061635166839Document80 pagesClassNotes-Agricultural Science SSS2 First Term-1061635166839mauricechimeNo ratings yet
- Unit 8: Nutrition Short Questions: Q: Why Does An Organism Need Food?Document12 pagesUnit 8: Nutrition Short Questions: Q: Why Does An Organism Need Food?Ghulam Baqir MazariNo ratings yet
- Mineral NutritionDocument13 pagesMineral NutritionPranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Class-Vii Subject-Science: Nutrition in PlantsDocument25 pagesClass-Vii Subject-Science: Nutrition in PlantsNisha ShahNo ratings yet
- Mineral NutritionDocument13 pagesMineral NutritionMunna Salpama100% (1)
- 11.modes of Plant NutritionDocument8 pages11.modes of Plant NutritionRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- FSSAI Ebook Principles Basics Food ChemistryDocument12 pagesFSSAI Ebook Principles Basics Food ChemistrybalwanNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Foliar Feeding: Has AdvantagesDocument4 pagesNitrogen Foliar Feeding: Has Advantageszikra arahmanNo ratings yet
- NM2Document12 pagesNM2meiNo ratings yet
- Analisi Foliar (33 A 55)Document55 pagesAnalisi Foliar (33 A 55)José Lobato TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Nutrients RelatedDocument24 pagesAgriculture Nutrients RelatedBharat KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 09 PDFDocument13 pagesLesson 09 PDFMohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- 5 Life at Molecular Level OwnDocument56 pages5 Life at Molecular Level Ownapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Basic Botany - BIO 003-1Document49 pagesLecture Note - Basic Botany - BIO 003-1Lincoln JamesNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 08 New CompleteDocument27 pagesChapter No 08 New CompleteGhulam Baqir MazariNo ratings yet
- Module I - Soil 2Document6 pagesModule I - Soil 2cristine abridaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Contents: Methods To Study The Mineral Requirements of PlantsDocument28 pagesChapter Contents: Methods To Study The Mineral Requirements of Plantskrish masterjeeNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition NotesDocument4 pagesPlant Nutrition Notesvijend100% (1)
- Republic of The Philipppines Bulacan Agricultural State College Pinaod, San Ildefonso, Bulacan Institute of AgricultureDocument6 pagesRepublic of The Philipppines Bulacan Agricultural State College Pinaod, San Ildefonso, Bulacan Institute of AgricultureJojenNo ratings yet
- What's The Function of Phosphorus (P) in PlantsDocument1 pageWhat's The Function of Phosphorus (P) in PlantsJay TailorNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PBL 2Document17 pagesChemistry PBL 2Yu Han OngNo ratings yet
- Absorption by RootsDocument18 pagesAbsorption by RootsDebdeepNo ratings yet
- TTL InfographicDocument1 pageTTL InfographicAngeline SiaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry2 PapersDocument31 pagesBiochemistry2 PapersShamoon HaroonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants - Mind MapDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Nutrition in Plants - Mind MapHari Krishna KommiNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition: Primary (Macro) NutrientsDocument3 pagesPlant Nutrition: Primary (Macro) NutrientsPralex PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Hydroponics HandoutDocument10 pagesHydroponics HandoutMark Boxill100% (1)
- NutritionDocument10 pagesNutritionJerwin GarnaceNo ratings yet
- Topic: Plant Growth Regulators: Subject: Pharmacognosy Prepared By: Urooj UmerDocument4 pagesTopic: Plant Growth Regulators: Subject: Pharmacognosy Prepared By: Urooj UmerUrooj UmerNo ratings yet
- Macro and MicronutrientsDocument17 pagesMacro and Micronutrientsdwana148No ratings yet
- Role of Macro and Micronutrient in Development and Growth of PlantDocument3 pagesRole of Macro and Micronutrient in Development and Growth of PlantÁngeles AlbinoNo ratings yet
- Module 5. Maintain The Growth of CropsDocument98 pagesModule 5. Maintain The Growth of CropsMayco CabildoNo ratings yet
- Plant Lab ResearchDocument15 pagesPlant Lab ResearchAntoun LeonaNo ratings yet
- Function of Phosphorous in PlantsDocument2 pagesFunction of Phosphorous in PlantsSaHaar AhmAd ALiNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Adaptation by Plants RevDocument2 pagesNutritional Adaptation by Plants Revjessy silva (Lynsy)No ratings yet
- Lesson Five - Nutrient Requirements and TestingDocument45 pagesLesson Five - Nutrient Requirements and TestingBangjoNo ratings yet
- Roll of FertilizerDocument3 pagesRoll of FertilizerSunil ValandNo ratings yet
- The Flowerdaze Farm Regenerative Guide to Cannabis: A Season-Long Recipe Book for the Beyond-Organic GardenerFrom EverandThe Flowerdaze Farm Regenerative Guide to Cannabis: A Season-Long Recipe Book for the Beyond-Organic GardenerNo ratings yet
- Study of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.From EverandStudy of Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and Development.No ratings yet
- Roadmap April 2023Document1 pageRoadmap April 2023carlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- IFA - 2019 - 1.1.fertilizer Consumption - Historical COLOMBIADocument2 pagesIFA - 2019 - 1.1.fertilizer Consumption - Historical COLOMBIAcarlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- Nop Sustancias ProhibidasDocument13 pagesNop Sustancias Prohibidascarlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- Jas 2005Document9 pagesJas 2005carlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- 2016 - The - Role - of - Fertilizers - in - Climate-Smart - Agriculture (Edited)Document12 pages2016 - The - Role - of - Fertilizers - in - Climate-Smart - Agriculture (Edited)carlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- 2018 IFA Integrated Plant Nutrient Management HighlightsDocument9 pages2018 IFA Integrated Plant Nutrient Management Highlightscarlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- Coastal Gardens Web VersionDocument48 pagesCoastal Gardens Web VersionPonechor HomeNo ratings yet
- Grodan Gro-Guide 2019Document7 pagesGrodan Gro-Guide 2019Eric SteenNo ratings yet
- Tree Watering HandoutsDocument18 pagesTree Watering HandoutsΤΔΕ ΚύπροςNo ratings yet
- New Plant Cream of The Crop List 05082011Document3 pagesNew Plant Cream of The Crop List 05082011andrea2671No ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 6 Identification and Classification of Crop Pest Based On Morphological Traits and Damage Characteristics WorksheetDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 6 Identification and Classification of Crop Pest Based On Morphological Traits and Damage Characteristics WorksheetmmabejarNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants: Pre Fertilisation EventsDocument16 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants: Pre Fertilisation EventsYashwanth SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- The Academicians DecadeDocument55 pagesThe Academicians DecadeEvan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- Identification and Classification of Ornamental Crops: Cut FlowerDocument5 pagesIdentification and Classification of Ornamental Crops: Cut FlowerRandy OruaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Commercial Growing Media On Emergence, Growth and Development of Tomato SeedlingsDocument9 pagesEffect of Commercial Growing Media On Emergence, Growth and Development of Tomato SeedlingsMd Ashikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Nursery Propagation Technique of BagalungaDocument11 pagesNursery Propagation Technique of Bagalungasohalsingh1No ratings yet
- Basic Plant Tissue CultureDocument6 pagesBasic Plant Tissue Culturealphabetagama713085100% (1)
- Preliminary Taxonomic Survey of Aquatic Plants of Feni District, BangladeshDocument9 pagesPreliminary Taxonomic Survey of Aquatic Plants of Feni District, Bangladeshshuvo devNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Is The Way That Plants Make Food, Using Energy From The Light.Document18 pagesPhotosynthesis Is The Way That Plants Make Food, Using Energy From The Light.KaitheryNo ratings yet
- 07082023Document2 pages07082023Trung VietNo ratings yet
- Grade: XI Subject: Commercial Fruit Production andDocument2 pagesGrade: XI Subject: Commercial Fruit Production andNishad MallaNo ratings yet
- CPPS-PSR Report-January 2023 - FinalDocument30 pagesCPPS-PSR Report-January 2023 - FinalSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Nutrient Uptake and Nutrient-Use Efficiency of SRI and Conventional Rice Cultivation Methods in MadagascarDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Nutrient Uptake and Nutrient-Use Efficiency of SRI and Conventional Rice Cultivation Methods in Madagascarmote34No ratings yet
- Figure 1.9 (B)Document8 pagesFigure 1.9 (B)ichrak blfNo ratings yet
- Composition of Planting Media On Growth Banana Seeds (Musa Paradiciaca)Document5 pagesComposition of Planting Media On Growth Banana Seeds (Musa Paradiciaca)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- (30x3) Biology State Exam QuestionsDocument4 pages(30x3) Biology State Exam QuestionsbenabdulloevNo ratings yet
- Ryan International School: Holiday Homework SESSION 2022-23Document17 pagesRyan International School: Holiday Homework SESSION 2022-23Pranav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris 1-5 KALK II ALPHADocument15 pagesBahasa Inggris 1-5 KALK II ALPHAsatwiko2005No ratings yet
- Tom Watermelon - Crop Stage-Wise IPM - VikaspediaDocument3 pagesTom Watermelon - Crop Stage-Wise IPM - VikaspediaESTHER OGODONo ratings yet
- The Lycophytes, Monilophytes, and Gymnosperms of The Delmarva Peninsula, An Annotated Checklist William A. McAvoyDocument46 pagesThe Lycophytes, Monilophytes, and Gymnosperms of The Delmarva Peninsula, An Annotated Checklist William A. McAvoygothmoz2No ratings yet
- The OrchidDocument5 pagesThe Orchid04. Arum RamadinaNo ratings yet
- Basic 7 Agric SC 1ST Term E-NotesDocument17 pagesBasic 7 Agric SC 1ST Term E-Notessamuel joshua100% (1)
- Literature Review On AllelopathyDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Allelopathyeqcusqwgf100% (1)
- Rohan Ghadge Thesis HorticultureDocument137 pagesRohan Ghadge Thesis HorticulturePravinNo ratings yet
- Fossil Angiosperms-A General Account: by - Yogesh SharmaDocument9 pagesFossil Angiosperms-A General Account: by - Yogesh SharmayogeshNo ratings yet