Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Epidemiology and Stats - Screening
Epidemiology and Stats - Screening
Uploaded by
Wendy Sierra0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageEpidemiology and Stats - Screening
Epidemiology and Stats - Screening
Uploaded by
Wendy SierraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
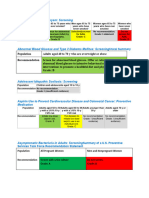
Epidemiology and Stats [SCREENING]
Screening is generally looking for cancer and medical disease.
Grading Scale
Cancers we screen for A = Definitely do this
Currently, there are only four cancers for which screening is B = Probably do this
recommended. Grade for practice is included in parentheses. C = Probably don’t do this
D = Don’t do this
I = Insufficient evidence
For colon cancer, a colonoscopy is the preferred screening tool.
Fecal immunochemical test (FIT) is more specific than guaiac-
based testing as it only detects globins that are present (not seen Cancer Age Screen
in foods and already digested in upper GI bleeds, but they’re Colon 50-75 yrs (A) Colonoscopy q10 yrs OR
effectively the same, FIT = FOBT for you. Flex Sig q5 + FOBT q3 yrs OR
Guaiac FOBT q1 yr
In 2016, breast cancer screening recommendations were
changed. Testing at 40 years is still an option (Grade C) after >75 If they’re doing great otherwise
discussion with patient (taking into account false positives,
>85 Stop no matter what
stress/anxiety of screen, family hx). The benefit of screening Breast Start 40 (C) Mammogram q1y
seems to be higher for those in their 50s and 60s. Start 50 (B) Mammogram q2y
Stop > 75yrs
Lung cancer screening with a low dose CT scan is a fairly new Cervical 21-65 yrs (A) Pap Smear q3 yrs
recommendation; it only applies to individuals with a 30 pack OR
HPV + Pap q5 yrs (over 30)
year cigarette history within the last 15 years.
65 If abnormal keep going
Cervical cancer continues to start screening at 21 even as that Lung 55-80 yrs + Low dose CT q1y
age group fills with women that have the HPV vaccine. Can space 30 py + Or
out to every 5 years if combined with HPV testing at age 30. Quit < 15 yrs 15y from quit
(B)
Cancers we don’t screen for
We don’t screen for other cancers because a) we don’t have a
Don’t routinely screen for these cancers
screening tool that is cost effective or b) improves mortality. Most
Grade D = ovarian, prostate, testicular,
notable is prostate cancer. It was previously screened annually
pancreatic
by PSA + digital rectal exam. However, the USPSTF changed its
Grade I = skin, bladder, oral
recommendation a few years back as there’s minimal benefit
given the potential harm. Most men die with prostate cancer – not
2015-2016 significant changes
from it. Another example is ovarian cancer in average risk
Thyroid dysfunction screening now Grade I
patients. The only screen we have finds it too late – at stage 3 or
Visual acuity screening in 65+ yrs now Grade I
worse – so there’s no benefit.
*These recommendations are based on the latest U.S. Preventive
Medical diseases we screen for
Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines as of 12/2016.
The table below has the medical diseases that are screened for. In
Everyone has different reqs, but standardize with these. We
order to get these questions right on the test, you have to identify
strive to keep this document up to date but all recs can be found
the person who needs the screen and how to do it. The most likely
here.
ones to show up are the one time screens: hepatitis C,
osteoporosis, and AAA.
Dz Age Screen
AAA ♂ 65-75 yrs + smoke One-time U/S of abdominal aorta
Osteoporosis ♀ 65 yrs (B) and ♂ DEXA scan (one-time if normal)
Hepatitis C Adults born between 1945-65 (B) One-time antibody screen
HIV 15-65 yrs (A) One-time rapid test, repeat if ↑ risk
Hypertension Everybody (A) Check BP (every time)
Diabetes HTN (B) A1c
Cholesterol ♀ 45 yrs (A) and ♂ 35 yrs (A) Fasting lipid panel q5 yrs
Start at 20 yrs for both if high risk (B)
Depression Everybody (B) PHQ, EPDS, etc.
© OnlineMedEd. http://www.onlinemeded.org
You might also like
- Clinical Internal Medicine Review 2023: For USMLE Step 2 CK and COMLEX-USA Level 2From EverandClinical Internal Medicine Review 2023: For USMLE Step 2 CK and COMLEX-USA Level 2Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Longevity Diet: Discover The New Science Behind Stem Cell Activation and Regeneration To Slow Aging, Fight Disease, and Optimize Weight - Valter LongoDocument5 pagesThe Longevity Diet: Discover The New Science Behind Stem Cell Activation and Regeneration To Slow Aging, Fight Disease, and Optimize Weight - Valter Longozyrybosi17% (6)
- Screening Case Study Exercises - Hannah TurnerDocument4 pagesScreening Case Study Exercises - Hannah Turnerapi-457299309100% (1)
- Biostats and EpidemiologyDocument24 pagesBiostats and Epidemiologyprakash poudelNo ratings yet
- Cancer ScreeningDocument37 pagesCancer ScreeningTomb RaiderNo ratings yet
- Online MedEd For Bioethics, Biostats, EtcDocument2 pagesOnline MedEd For Bioethics, Biostats, EtcjohntheuglyllamaNo ratings yet
- SketchyDocument3 pagesSketchybellNo ratings yet
- Oncology and Palliative Care 2023 FinalDocument99 pagesOncology and Palliative Care 2023 FinalBelinda ELISHANo ratings yet
- USPTFT Screening GuideDocument2 pagesUSPTFT Screening GuideAndrew McGowanNo ratings yet
- Preventive Services in Primary Health CareDocument19 pagesPreventive Services in Primary Health CareAhmad AltarefeNo ratings yet
- Health Maintenance: Guidelines For AdultsDocument6 pagesHealth Maintenance: Guidelines For AdultsgurneeNo ratings yet
- USPSTF Summary For ScreeningDocument22 pagesUSPSTF Summary For ScreeningEmirhan llkhanNo ratings yet
- Health Maintenance GuidelinesDocument2 pagesHealth Maintenance GuidelinesmtataNo ratings yet
- Do Cervical Cancer Screening Recommendations Differ Among Women at Different Age Groups?Document8 pagesDo Cervical Cancer Screening Recommendations Differ Among Women at Different Age Groups?Nico Angelo CopoNo ratings yet
- FM CasesDocument16 pagesFM CasesJameson87No ratings yet
- Acg CRC Deck - Final 2023Document121 pagesAcg CRC Deck - Final 2023DJMT EVENTSNo ratings yet
- Guidelines Screening USADocument2 pagesGuidelines Screening USAAyu RahmaNo ratings yet
- 12.14.11 Geriatric Immunization & ScreeningDocument6 pages12.14.11 Geriatric Immunization & ScreeningDiana HyltonNo ratings yet
- Pap Smear - Overview, Indications, PreparationDocument11 pagesPap Smear - Overview, Indications, PreparationBayu Surya DanaNo ratings yet
- 6 Primary HPV Screening - HuffDocument37 pages6 Primary HPV Screening - HuffJennyNo ratings yet
- Preventive Medicine (Cancer Screening & Immunizations) in AdultsDocument70 pagesPreventive Medicine (Cancer Screening & Immunizations) in Adultssmith197077No ratings yet
- A and B Recommendations United States Preventive Services TaskforceDocument7 pagesA and B Recommendations United States Preventive Services TaskforcejonNo ratings yet
- Smear Pap ResultDocument2 pagesSmear Pap ResultalienyyNo ratings yet
- Pap SmearDocument8 pagesPap Smearsmv2No ratings yet
- Nurses As Cancer InsurgentsDocument7 pagesNurses As Cancer InsurgentsNick RealinoNo ratings yet
- MAMOGRAFIADocument2 pagesMAMOGRAFIAFabián Alejandro Vargas VillalbaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening TestsDocument3 pagesCancer Screening TestsVijaya AcharNo ratings yet
- Cancer de Mama JAMA 2015 ScreeningDocument1 pageCancer de Mama JAMA 2015 ScreeningieoNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Prevention & Management of Pre-Malignant LesionsDocument41 pagesCervical Cancer Prevention & Management of Pre-Malignant LesionsMichaelNo ratings yet
- General Principles & Pathophysiology of Neoplastic DisordersDocument7 pagesGeneral Principles & Pathophysiology of Neoplastic DisordersAmina RichardsonNo ratings yet
- LSIL, HSIL, ColposDocument19 pagesLSIL, HSIL, Colposxt115283No ratings yet
- Screening For Female Genital Tract MalignancyDocument40 pagesScreening For Female Genital Tract MalignancyLili Uisa RahmasariNo ratings yet
- 2021 Adult Preventive Health GuidelinesDocument8 pages2021 Adult Preventive Health GuidelinesAnthony El HageNo ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B Recommendations: Topic Description GradeDocument3 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendations: Topic Description GradeSantiago AldayNo ratings yet
- Truth About Cancer Screening Nine Ways PDFDocument3 pagesTruth About Cancer Screening Nine Ways PDFSandro Marcelo Peirano GozalvezNo ratings yet
- The American Cancer Society Recommends The Following Guidelines For EarlyDocument2 pagesThe American Cancer Society Recommends The Following Guidelines For EarlyRatih Kusuma Dewi ArfaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening and PreventionDocument31 pagesCancer Screening and PreventionShadin SNo ratings yet
- Incidence of Cancer and Screening RecommendationsDocument12 pagesIncidence of Cancer and Screening RecommendationsSeba StiánNo ratings yet
- Handout For PatientsDocument4 pagesHandout For Patientsapi-640781324No ratings yet
- Pap Smear TestDocument27 pagesPap Smear TestZeeshan Yousuf100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Approach To The Patient - 30qDocument19 pagesUnit 1 - Approach To The Patient - 30qaeltee100% (1)
- CA CervixDocument54 pagesCA CervixsesiaNo ratings yet
- A and B Recommendations - United States Preventive Services TaskforceDocument7 pagesA and B Recommendations - United States Preventive Services TaskforceDavid CheNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening GuideDocument3 pagesCancer Screening Guidebond0071993No ratings yet
- Clinical Task ForceDocument13 pagesClinical Task ForcePriscillitapp JimenezNo ratings yet
- HMC Pap Guidelines November 2007Document1 pageHMC Pap Guidelines November 2007Nikki Mariz DepayNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet?: March 2010 Andrew M.D. Wolf, MD University of Virginia School of MedicineDocument48 pagesProstate Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet?: March 2010 Andrew M.D. Wolf, MD University of Virginia School of Medicineibrunom3No ratings yet
- Pap Smear TestDocument27 pagesPap Smear Testiangould12No ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Education12.29bDocument52 pagesCervical Cancer Education12.29bPoroh ManuelaNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner's Clinical Pocket GuideDocument283 pagesNurse Practitioner's Clinical Pocket GuideEribertoNo ratings yet
- Mqic Adult Preventive Services Ages 18 To 49 CPGDocument1 pageMqic Adult Preventive Services Ages 18 To 49 CPGjetiradoNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer ScreeningDocument1 pageCervical Cancer Screeningtavo823No ratings yet
- USPSTF A and B RecommendationsDocument4 pagesUSPSTF A and B Recommendationsstarblue265No ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer: DR - Ravichandra Varma SDocument35 pagesCervical Cancer: DR - Ravichandra Varma SJulianaGozaliNo ratings yet
- My Pap Smear Is Abnormal !Document70 pagesMy Pap Smear Is Abnormal !Alena JosephNo ratings yet
- 4 HPV Testing - DarraghDocument37 pages4 HPV Testing - DarraghJennyNo ratings yet
- Faq085-Ervical Cancer ScreeningDocument3 pagesFaq085-Ervical Cancer ScreeningTjoema AsriNo ratings yet
- 2019AdultPreventiveHealthGuidelines PDFDocument7 pages2019AdultPreventiveHealthGuidelines PDFvesvNo ratings yet
- Screeningforcancer: Whentostop?: A Practical Guide and Review of The EvidenceDocument14 pagesScreeningforcancer: Whentostop?: A Practical Guide and Review of The EvidenceMohamedRashadNo ratings yet
- Perspective: New England Journal MedicineDocument3 pagesPerspective: New England Journal MedicineYosua_123No ratings yet
- Prevention Case StudyDocument6 pagesPrevention Case StudyllukelawrenceNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening Guidelines: Prepared By: DR. Hanan AbbasDocument35 pagesCancer Screening Guidelines: Prepared By: DR. Hanan AbbashanfmhananfmhanNo ratings yet
- Divine Intervention Episode 54 Comprehensive UsmleDocument69 pagesDivine Intervention Episode 54 Comprehensive UsmleWendy SierraNo ratings yet
- Writing Task Sample Letters PDFDocument87 pagesWriting Task Sample Letters PDFWendy SierraNo ratings yet
- 2021 Song Mom Calendar 08 1Document1 page2021 Song Mom Calendar 08 1Wendy SierraNo ratings yet
- Metabolism - Glycolysis-2Document8 pagesMetabolism - Glycolysis-2Wendy SierraNo ratings yet
- 2021 Song Mom Calendar 09 1Document1 page2021 Song Mom Calendar 09 1Wendy SierraNo ratings yet
- Oet Writing Guide by E2Language 1Document6 pagesOet Writing Guide by E2Language 1Wendy SierraNo ratings yet
- NAME: Neema Tamang Roll No:-20 Subject:-Surgery Assignment Topic:-Pneumothorax Faculty: HA 2Document9 pagesNAME: Neema Tamang Roll No:-20 Subject:-Surgery Assignment Topic:-Pneumothorax Faculty: HA 2Shreekrishna BudhathokiNo ratings yet
- Current Senerio of Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Clinical Isolates in East Uttar Pradesh, IndiaDocument4 pagesCurrent Senerio of Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Clinical Isolates in East Uttar Pradesh, IndiaPraveen GautamNo ratings yet
- The Medically Important MycosesDocument8 pagesThe Medically Important MycosesNatasha JeanNo ratings yet
- Por Que Mi Paciente Tiene LeucocitosisDocument17 pagesPor Que Mi Paciente Tiene LeucocitosisOsnaider Andrés Cuello TorresNo ratings yet
- RRL e CigarettesDocument12 pagesRRL e CigarettesBalingatan RonalynNo ratings yet
- Chapter 54 Assessment and Management of Patients With Rheumatic DisordersDocument19 pagesChapter 54 Assessment and Management of Patients With Rheumatic DisordersMaryrose GestosoNo ratings yet
- Dissertation PsoriasisDocument7 pagesDissertation PsoriasisPayingSomeoneToWriteAPaperSingapore100% (1)
- 757 - Penyakit Ginjal KronikDocument30 pages757 - Penyakit Ginjal KronikPujhi Meisya SoniaNo ratings yet
- (Pandanus Conoideus) TERHADAP KADAR GLUKOSA DARAH Rattus Norvegicus) DIABETIKDocument6 pages(Pandanus Conoideus) TERHADAP KADAR GLUKOSA DARAH Rattus Norvegicus) DIABETIKagus sangkaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Decision Making: Putu Moda ArsanaDocument47 pagesClinical Decision Making: Putu Moda ArsanaVina Tri AdityaNo ratings yet
- HydronephrosisDocument2 pagesHydronephrosisStefan ZemoraNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Trauma - WaniDocument60 pagesGeriatric Trauma - WaniNurul Syazwani RamliNo ratings yet
- Effect of Toe-Spread-Out Exercise On Hallux Valgus Angle and Cross-Sectional Area of Abductor Hallucis Muscle in Subjects With Hallux ValgusDocument4 pagesEffect of Toe-Spread-Out Exercise On Hallux Valgus Angle and Cross-Sectional Area of Abductor Hallucis Muscle in Subjects With Hallux ValgusArchana MohantyNo ratings yet
- Health Daily News Healthmedicinet 2024-03-25Document5 pagesHealth Daily News Healthmedicinet 2024-03-25tuni santeNo ratings yet
- FASENRA - PFS To Pen Communication Downloadable PDFDocument2 pagesFASENRA - PFS To Pen Communication Downloadable PDFBrîndușa PetruțescuNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Research AssignmentDocument10 pagesDiabetes Research AssignmentDoris SanchezNo ratings yet
- Prescribing Antibiotics and Analgesics in ChildrenDocument4 pagesPrescribing Antibiotics and Analgesics in ChildrenPreetam PatnalaNo ratings yet
- Specific Language Impairment (SLI) (The Term Developmental Language Disorder Is Preferred byDocument2 pagesSpecific Language Impairment (SLI) (The Term Developmental Language Disorder Is Preferred byGrim ReaperNo ratings yet
- CEDH Syllabus - FinalDocument8 pagesCEDH Syllabus - Finaldipgang7174No ratings yet
- Couple More Ch.43 Fundamental of NursingDocument3 pagesCouple More Ch.43 Fundamental of NursingAnnette McdonaldNo ratings yet
- Piis1073874613000777 PDFDocument20 pagesPiis1073874613000777 PDFdrzana78No ratings yet
- DR Ken LiegnerDocument43 pagesDR Ken LiegnertonerangerNo ratings yet
- Acute Management of Hypocalcaemia in AdultsDocument1 pageAcute Management of Hypocalcaemia in Adultsaimi hj zulkipliNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 3 Tle 10Document2 pagesQuiz No 3 Tle 10Israel Marquez100% (1)
- Practice HPIDocument3 pagesPractice HPImedicalmatins100% (1)
- Congenital RubellaDocument15 pagesCongenital RubellaShanaz AlvikhaNo ratings yet
- SurveyDocument6 pagesSurveyFaustino, Jayreign MaeNo ratings yet
- Epispadias: PaperDocument14 pagesEpispadias: PaperJajangNo ratings yet