Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical Manual: Electrical Machine - I Lab
Practical Manual: Electrical Machine - I Lab
Uploaded by
HinaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- VM 2.5 ManualDocument49 pagesVM 2.5 Manualjeepfreak212185% (20)
- Practical Manual: Electrical Machine-I LabDocument5 pagesPractical Manual: Electrical Machine-I LabHinaNo ratings yet
- Magnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateDocument60 pagesMagnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateSuyash SinghNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2. Study of O.C.C of D.C. GeneratorDocument3 pagesExp - 2. Study of O.C.C of D.C. GeneratorMd KaziNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments: Sno Name of The Experiment Date SignatureDocument41 pagesList of Experiments: Sno Name of The Experiment Date SignatureRajeshKanchanaNo ratings yet
- Ee6461 Eecs Lab Manual (1) - 1Document113 pagesEe6461 Eecs Lab Manual (1) - 1Ajay GanesanNo ratings yet
- Dev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandDocument32 pagesDev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandRockstar RichNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine-II Laboratory Manual B.Tech, 3 Yr, 5 Semester, Electrical Engg. DeptDocument28 pagesElectrical Machine-II Laboratory Manual B.Tech, 3 Yr, 5 Semester, Electrical Engg. DeptMoumi PanditNo ratings yet
- BE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab Manual FINAL PDFDocument82 pagesBE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab Manual FINAL PDFBHUVANA ARUMUGAMNo ratings yet
- DC Machines and Transformers Lab Manual ModifiedDocument50 pagesDC Machines and Transformers Lab Manual ModifiedSuseel MenonNo ratings yet
- BE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab ManualDocument162 pagesBE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab ManualAntonio LeonNo ratings yet
- Retardation TestDocument53 pagesRetardation Testkiran_y2100% (9)
- Winsem2023-24 Beee215p Lo Ch2023240502403 Reference Material I Lab Manual Beee215pDocument25 pagesWinsem2023-24 Beee215p Lo Ch2023240502403 Reference Material I Lab Manual Beee215pshrinidhi.rm2022No ratings yet
- BE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab ManualDocument81 pagesBE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab ManualAntonio LeonNo ratings yet
- Otho Niversity Faculty of Engineering and Applied SciencesDocument15 pagesOtho Niversity Faculty of Engineering and Applied Scienceskobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- OCC Magnetization CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesOCC Magnetization CharacteristicsAbhipsha PatroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Session 5 Magnetization Curve of A DC GeneratorDocument7 pagesLaboratory Session 5 Magnetization Curve of A DC GeneratorNatan Bravo GarridoNo ratings yet
- All 2 Marks emDocument54 pagesAll 2 Marks emSathishNo ratings yet
- M.A.M School of Engineering TRICHY - 621 105Document97 pagesM.A.M School of Engineering TRICHY - 621 105Preethi RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualDocument36 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory Manualprathap kumarNo ratings yet
- EM-I LAB-finalDocument114 pagesEM-I LAB-finalHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory ManualDocument36 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory Manualjith16No ratings yet
- Acc ManualDocument44 pagesAcc ManualDevendra VelhalNo ratings yet
- 9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorDocument4 pages9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Em-Ii ExperimentDocument19 pagesEm-Ii Experimentprince rajNo ratings yet
- ECE Electrical Engineering 2 Marks PDFDocument22 pagesECE Electrical Engineering 2 Marks PDFsivagamiNo ratings yet
- Rotating Electrical Machine Lab: B.E. 5 SemesterDocument33 pagesRotating Electrical Machine Lab: B.E. 5 SemesterSuma Rani GNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document9 pagesExp 10Vamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Eee ELECTRICAL MACHINES-I DC LAB MANUAL 10122019 PDFDocument68 pagesEee ELECTRICAL MACHINES-I DC LAB MANUAL 10122019 PDFSwaraj KaushkikNo ratings yet
- Cycle 1 Experiment No. 4 Study of The Steady State Performance of A Separately Excited DC GeneratorDocument4 pagesCycle 1 Experiment No. 4 Study of The Steady State Performance of A Separately Excited DC GeneratorVIJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-I Lab Manual R16 Modified PDFDocument83 pagesElectrical Machines-I Lab Manual R16 Modified PDFsk ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual: Electrical Machine LabDocument4 pagesPractical Manual: Electrical Machine LabSurajMauryaNo ratings yet
- Ec-I Lab MannualDocument30 pagesEc-I Lab Mannualsmaran247017No ratings yet
- Lab-4 - Name - IDDocument11 pagesLab-4 - Name - IDMOSAED MOSAED ALLOGMANINo ratings yet
- 9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorDocument4 pages9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotormanishNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab Manual R19Document25 pagesBee Lab Manual R19Sudharshan ChennupalliNo ratings yet
- DCM Lab Manual - 0 PDFDocument45 pagesDCM Lab Manual - 0 PDFVenkata HemanthNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document4 pagesExp 2Avneesh KarNo ratings yet
- (4 Rsted: Seent SpeesDocument3 pages(4 Rsted: Seent SpeesRahul RNo ratings yet
- OCC of DC GeneratorDocument8 pagesOCC of DC GeneratorShoeb Mohammed Ziauddin100% (1)
- Exp. 2 - OCC and Load Test On AlternatorDocument7 pagesExp. 2 - OCC and Load Test On AlternatorKailash Jagarwal100% (1)
- Swinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)Document24 pagesSwinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Total 363 Lab ManualDocument67 pagesTotal 363 Lab ManualBisal Sarker JoyNo ratings yet
- Em-1 LabDocument32 pagesEm-1 LabM Pavankumar PavanNo ratings yet
- D.C. Machines and Transformers LabDocument41 pagesD.C. Machines and Transformers Labsrinivas gangishettiNo ratings yet
- EE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFDocument67 pagesEE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFkrishnandrk100% (2)
- EE6352 Electrical Engineering and InstruDocument27 pagesEE6352 Electrical Engineering and InstruSaravanan ArulmaniNo ratings yet
- Control System Lab EE-324-FDocument45 pagesControl System Lab EE-324-FBalraj SinghNo ratings yet
- EM-I LAB-finalDocument111 pagesEM-I LAB-finalHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNo ratings yet
- 1 Characterstics of DC DC Shunt Gen PDFDocument2 pages1 Characterstics of DC DC Shunt Gen PDFRedwan Ahmad MuidNo ratings yet
- DCMT - Amin ManualDocument56 pagesDCMT - Amin ManualAmin KharadiNo ratings yet
- Emc611s Lab 4, 2023Document9 pagesEmc611s Lab 4, 2023DimphoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.6 The DC Shunt Motor RatingDocument7 pagesExperiment No.6 The DC Shunt Motor RatingMounta1n DewNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringDocument21 pagesElectrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringSreerag Kunnathu SugathanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits (EME-306) Lab 1: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits (EME-306) Lab 1: ObjectiveAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Using The Cockroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier Design in Hanheld DevicesDocument5 pagesUsing The Cockroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier Design in Hanheld Devicesja632271100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 03 Student NotesDocument4 pagesExperiment 03 Student NotesJane DoeNo ratings yet
- Galvaniska CellerDocument8 pagesGalvaniska Cellerapi-25888481No ratings yet
- 5E Lesson Plan: Engagement: Day 1 &2Document3 pages5E Lesson Plan: Engagement: Day 1 &2api-240269666No ratings yet
- Baby Lock BLE3ATW Sewing Machine Service ManualDocument18 pagesBaby Lock BLE3ATW Sewing Machine Service ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- What Is PhilosophyDocument4 pagesWhat Is PhilosophyLetlie Zoilo SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Methods. Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesElectrochemical Methods. Fundamentals and ApplicationsJustin WareNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behavioral TheoryDocument28 pagesCognitive Behavioral TheoryAngela CabasNo ratings yet
- WellComm ToolkitDocument1 pageWellComm ToolkitpfsheldrakeNo ratings yet
- Stack SpecDocument10 pagesStack SpecHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
- All About Numbers 1-10 Student Booklet: Number SenseDocument8 pagesAll About Numbers 1-10 Student Booklet: Number Sensealana reneNo ratings yet
- Scan Barcode 220812Document1,230 pagesScan Barcode 220812Rommy firmansyahNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 19: Harth, II Et Al. 11 Patent Number: 5,661,241 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 1997Document16 pagesUnited States Patent 19: Harth, II Et Al. 11 Patent Number: 5,661,241 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 1997TYO WIBOWONo ratings yet
- Bassin Du Gharb GeophysiqueDocument9 pagesBassin Du Gharb GeophysiqueKarim El MorabitiNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Offshore Refuelling Rev 0Document9 pagesRisk Assessment For Offshore Refuelling Rev 0ringbolt100% (1)
- Activity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsDocument84 pagesActivity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsMuhammad MishbahurrizqiNo ratings yet
- JETIR1907J03Document5 pagesJETIR1907J03Iram KhanNo ratings yet
- HRD and Organizational ChangeDocument10 pagesHRD and Organizational ChangeYaso TharNo ratings yet
- Quality Control & Quality AssuranceDocument75 pagesQuality Control & Quality Assurancemuhammad omerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SlabsDocument12 pagesChapter 8 Slabsmike smith100% (1)
- Çalışma Soruları - 1Document6 pagesÇalışma Soruları - 1emreasker22No ratings yet
- Fluent-Intro 15.0 WS08b Vortex SheddingDocument39 pagesFluent-Intro 15.0 WS08b Vortex Sheddingmatteo_1234No ratings yet
- EY Re Engineering The Supply Chain For The Omni Channel of Tomorrow PDFDocument39 pagesEY Re Engineering The Supply Chain For The Omni Channel of Tomorrow PDFjunaid madniNo ratings yet
- International Ego State Therapy Bibliography Sept 2014Document35 pagesInternational Ego State Therapy Bibliography Sept 2014RudolfSianto100% (1)
- Educational Institutions Have A Responsibility To Dissuade Students From Pursuing Fields of Study in Which They Are Unlikely To SucceedDocument2 pagesEducational Institutions Have A Responsibility To Dissuade Students From Pursuing Fields of Study in Which They Are Unlikely To SucceedsusmithaNo ratings yet
- Inspection of Emergency ExitsDocument1 pageInspection of Emergency ExitsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (51) : Class XDocument5 pagesMathematics (51) : Class XdhruvNo ratings yet
- Event-Calender For 75 Years CelebrationDocument4 pagesEvent-Calender For 75 Years Celebrationrajiv kumarNo ratings yet
- Mba ZC415 Course HandoutDocument11 pagesMba ZC415 Course HandoutareanNo ratings yet
- PlaygroundDocument16 pagesPlaygroundpaduuNo ratings yet
Practical Manual: Electrical Machine - I Lab
Practical Manual: Electrical Machine - I Lab
Uploaded by
HinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical Manual: Electrical Machine - I Lab
Practical Manual: Electrical Machine - I Lab
Uploaded by
HinaCopyright:
Available Formats
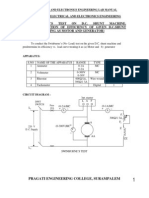
KIET/EN/EMEC-1st /01
PRACTICAL MANUAL
Electrical Machine –I Lab
To Obtain Magnetization Characteristic of D.C. Shunt
Generator.
SIGNATURE OF (H. O. D.) SIGNATURE OF LAB IN-CHARGE
KIET/EN/EMEC-1st /01
Experiment No. – 1
Object: -
To obtain magnetization characteristic of a D.C. shunt generator.
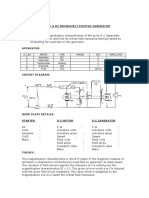
Equipment Required: -
S. No Equipments Type Specification/Range/Rating Quantity
1. Ammeter MC 0-2 Amp DC 1 No.
2. Voltmeter MC 0-300 V DC 1 No.
3. Rheostat 272 Ω, 1.7 A 2 No.
4. Tachometer Digital 0-2000 r.p.m. 1 No.
5. D.C. Motor, Shunt 5 HP, 1500 r.p.m., 16.7 A, 220 Volt 1 No.
6. D.C. Generator Shunt 3 KW, 1500 r.p.m., 13 A, 220 Volt 1 No.
DC
Theory: -
The e.m.f. generated in the armature winding of a d.c. generator under no load
operation is given by –
Eg = (PφNZ)/ 60 A
Eg = Generated e.m.f
P = No. of poles
Φ = Flux per pole
N = speed in r.p.m.
Z = Total no. of conductors in the armature
A = No. of parallel paths
Hence, at constant speed, no load e.m.f. Eg is directly proportional to the flux per pole φ,
which depends upon the field current I f. The characteristic showing the relationship
between field current If, and the generated e.m.f. Eg, at no load and at a constant speed is
known as ‘Magnetization characteristic’ or open circuit characteristic (O.C.C.) of d.c.
Generator. A small e.m.f. hardly of the order of 10-15 V is generated, even when the field
current is zero, which is due to the residual magnetism in the poles. Critical resistance
of the field can be obtained by drawing a tangent to the initial portion of the
magnetization characteristic, the slope of which gives the critical resistance, as shown in
fig:1.
SIGNATURE OF (H. O. D.) SIGNATURE OF LAB IN-CHARGE
KIET/EN/EMEC-1st /01
Circuit diagram: -
Procedure: -
1. Connect the circuit as shown in fig.1.
2. Ensure that the resistance in the field circuit of motor is reduced to zero value.
3. Set the potential divider feeding the field circuit of the generator for zero input
voltage.
4. Adjust the motor speed using field rheostat.
5. Record the generated e.m.f. due to residual magnetism.
6. Switch on the d.c. supply across the field circuit of the generator.
7. Vary the field current of generator in steps and record its value and the
corresponding generated e.m.f. of the generator. Observations should be taken up
to the generated voltage 25% higher that the rated voltage of the generator.
8. Switch-off the d.c. supply to stop the motor.
SIGNATURE OF (H. O. D.) SIGNATURE OF LAB IN-CHARGE
KIET/EN/EMEC-1st /01
Observations Table: -
S. No. Field current If (A) Generated e.m.f. Eg(Volts)
Result: - The output voltage corresponding to different excitation currents of the
generator are obtained and tabulated above. The variation of output voltage with respect
to excitation current is also plotted and attached
Precaution:-
1. All connections should be tight and clean.
2. The instruments and rheostats used should be of proper ratings.
3. If the dc shunt generator fails to build up voltage due to absence of the residual
magnetism, the generator should be run as a separately excited generator for some
time and then this experiment should be performed.
4. While performing experiment, the instrument readings should not exceed the
ratings of the machine under test.
5. During this experiment ensure that the speed of the prime mover does not fall
down beyond 10% of the rated value or no load value.
Viva Questions:-
1. How is the voltage build-up of dc generator affected by the variation of speed of the
prime-mover?
2. What does the name-plate of dc generator generally indicates?
3. What is the most essential condition for voltage build-up for a dc shunt generator?
4. What are the different types of self-excited dc generators?
5. Why brush drop is taken as constant?
Industrial application:-
The magnetization characteristics are used to find the value of excitation current required
to generate a particular voltage.
SIGNATURE OF (H. O. D.) SIGNATURE OF LAB IN-CHARGE
You might also like
- VM 2.5 ManualDocument49 pagesVM 2.5 Manualjeepfreak212185% (20)
- Practical Manual: Electrical Machine-I LabDocument5 pagesPractical Manual: Electrical Machine-I LabHinaNo ratings yet
- Magnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateDocument60 pagesMagnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateSuyash SinghNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2. Study of O.C.C of D.C. GeneratorDocument3 pagesExp - 2. Study of O.C.C of D.C. GeneratorMd KaziNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments: Sno Name of The Experiment Date SignatureDocument41 pagesList of Experiments: Sno Name of The Experiment Date SignatureRajeshKanchanaNo ratings yet
- Ee6461 Eecs Lab Manual (1) - 1Document113 pagesEe6461 Eecs Lab Manual (1) - 1Ajay GanesanNo ratings yet
- Dev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandDocument32 pagesDev Bhoomi Institute Chakrata Road, Navgaoun Manduwala, UttarakhandRockstar RichNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine-II Laboratory Manual B.Tech, 3 Yr, 5 Semester, Electrical Engg. DeptDocument28 pagesElectrical Machine-II Laboratory Manual B.Tech, 3 Yr, 5 Semester, Electrical Engg. DeptMoumi PanditNo ratings yet
- BE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab Manual FINAL PDFDocument82 pagesBE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab Manual FINAL PDFBHUVANA ARUMUGAMNo ratings yet
- DC Machines and Transformers Lab Manual ModifiedDocument50 pagesDC Machines and Transformers Lab Manual ModifiedSuseel MenonNo ratings yet
- BE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab ManualDocument162 pagesBE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab ManualAntonio LeonNo ratings yet
- Retardation TestDocument53 pagesRetardation Testkiran_y2100% (9)
- Winsem2023-24 Beee215p Lo Ch2023240502403 Reference Material I Lab Manual Beee215pDocument25 pagesWinsem2023-24 Beee215p Lo Ch2023240502403 Reference Material I Lab Manual Beee215pshrinidhi.rm2022No ratings yet
- BE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab ManualDocument81 pagesBE8161-Basic Electrical Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering Lab ManualAntonio LeonNo ratings yet
- Otho Niversity Faculty of Engineering and Applied SciencesDocument15 pagesOtho Niversity Faculty of Engineering and Applied Scienceskobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- OCC Magnetization CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesOCC Magnetization CharacteristicsAbhipsha PatroNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Session 5 Magnetization Curve of A DC GeneratorDocument7 pagesLaboratory Session 5 Magnetization Curve of A DC GeneratorNatan Bravo GarridoNo ratings yet
- All 2 Marks emDocument54 pagesAll 2 Marks emSathishNo ratings yet
- M.A.M School of Engineering TRICHY - 621 105Document97 pagesM.A.M School of Engineering TRICHY - 621 105Preethi RanganathanNo ratings yet
- Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory ManualDocument36 pagesJawaharlal Nehru Engineering College: Laboratory Manualprathap kumarNo ratings yet
- EM-I LAB-finalDocument114 pagesEM-I LAB-finalHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory ManualDocument36 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory Manualjith16No ratings yet
- Acc ManualDocument44 pagesAcc ManualDevendra VelhalNo ratings yet
- 9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorDocument4 pages9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Em-Ii ExperimentDocument19 pagesEm-Ii Experimentprince rajNo ratings yet
- ECE Electrical Engineering 2 Marks PDFDocument22 pagesECE Electrical Engineering 2 Marks PDFsivagamiNo ratings yet
- Rotating Electrical Machine Lab: B.E. 5 SemesterDocument33 pagesRotating Electrical Machine Lab: B.E. 5 SemesterSuma Rani GNo ratings yet
- Exp 10Document9 pagesExp 10Vamsi RamNo ratings yet
- Eee ELECTRICAL MACHINES-I DC LAB MANUAL 10122019 PDFDocument68 pagesEee ELECTRICAL MACHINES-I DC LAB MANUAL 10122019 PDFSwaraj KaushkikNo ratings yet
- Cycle 1 Experiment No. 4 Study of The Steady State Performance of A Separately Excited DC GeneratorDocument4 pagesCycle 1 Experiment No. 4 Study of The Steady State Performance of A Separately Excited DC GeneratorVIJAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-I Lab Manual R16 Modified PDFDocument83 pagesElectrical Machines-I Lab Manual R16 Modified PDFsk ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual: Electrical Machine LabDocument4 pagesPractical Manual: Electrical Machine LabSurajMauryaNo ratings yet
- Ec-I Lab MannualDocument30 pagesEc-I Lab Mannualsmaran247017No ratings yet
- Lab-4 - Name - IDDocument11 pagesLab-4 - Name - IDMOSAED MOSAED ALLOGMANINo ratings yet
- 9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotorDocument4 pages9 Speed Control of DC Shunt MotormanishNo ratings yet
- Bee Lab Manual R19Document25 pagesBee Lab Manual R19Sudharshan ChennupalliNo ratings yet
- DCM Lab Manual - 0 PDFDocument45 pagesDCM Lab Manual - 0 PDFVenkata HemanthNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document4 pagesExp 2Avneesh KarNo ratings yet
- (4 Rsted: Seent SpeesDocument3 pages(4 Rsted: Seent SpeesRahul RNo ratings yet
- OCC of DC GeneratorDocument8 pagesOCC of DC GeneratorShoeb Mohammed Ziauddin100% (1)
- Exp. 2 - OCC and Load Test On AlternatorDocument7 pagesExp. 2 - OCC and Load Test On AlternatorKailash Jagarwal100% (1)
- Swinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)Document24 pagesSwinburne'S Test ON D.C. Shunt Machine. (Predetermination of Efficiency of Given D.C.Shunt Machine Working As Motor and Generator)pragatinareshNo ratings yet
- Total 363 Lab ManualDocument67 pagesTotal 363 Lab ManualBisal Sarker JoyNo ratings yet
- Em-1 LabDocument32 pagesEm-1 LabM Pavankumar PavanNo ratings yet
- D.C. Machines and Transformers LabDocument41 pagesD.C. Machines and Transformers Labsrinivas gangishettiNo ratings yet
- EE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFDocument67 pagesEE8311 Electrical Machines Lab - 1 Manual PDFkrishnandrk100% (2)
- EE6352 Electrical Engineering and InstruDocument27 pagesEE6352 Electrical Engineering and InstruSaravanan ArulmaniNo ratings yet
- Control System Lab EE-324-FDocument45 pagesControl System Lab EE-324-FBalraj SinghNo ratings yet
- EM-I LAB-finalDocument111 pagesEM-I LAB-finalHarimadhavareddy YenireddyNo ratings yet
- 1 Characterstics of DC DC Shunt Gen PDFDocument2 pages1 Characterstics of DC DC Shunt Gen PDFRedwan Ahmad MuidNo ratings yet
- DCMT - Amin ManualDocument56 pagesDCMT - Amin ManualAmin KharadiNo ratings yet
- Emc611s Lab 4, 2023Document9 pagesEmc611s Lab 4, 2023DimphoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.6 The DC Shunt Motor RatingDocument7 pagesExperiment No.6 The DC Shunt Motor RatingMounta1n DewNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringDocument21 pagesElectrical and Electronics Lab Manual For Mechanical EngineeringSreerag Kunnathu SugathanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits (EME-306) Lab 1: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits (EME-306) Lab 1: ObjectiveAhmed SayedNo ratings yet
- Using The Cockroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier Design in Hanheld DevicesDocument5 pagesUsing The Cockroft-Walton Voltage Multiplier Design in Hanheld Devicesja632271100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 03 Student NotesDocument4 pagesExperiment 03 Student NotesJane DoeNo ratings yet
- Galvaniska CellerDocument8 pagesGalvaniska Cellerapi-25888481No ratings yet
- 5E Lesson Plan: Engagement: Day 1 &2Document3 pages5E Lesson Plan: Engagement: Day 1 &2api-240269666No ratings yet
- Baby Lock BLE3ATW Sewing Machine Service ManualDocument18 pagesBaby Lock BLE3ATW Sewing Machine Service ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- What Is PhilosophyDocument4 pagesWhat Is PhilosophyLetlie Zoilo SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Methods. Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesElectrochemical Methods. Fundamentals and ApplicationsJustin WareNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Behavioral TheoryDocument28 pagesCognitive Behavioral TheoryAngela CabasNo ratings yet
- WellComm ToolkitDocument1 pageWellComm ToolkitpfsheldrakeNo ratings yet
- Stack SpecDocument10 pagesStack SpecHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
- All About Numbers 1-10 Student Booklet: Number SenseDocument8 pagesAll About Numbers 1-10 Student Booklet: Number Sensealana reneNo ratings yet
- Scan Barcode 220812Document1,230 pagesScan Barcode 220812Rommy firmansyahNo ratings yet
- United States Patent 19: Harth, II Et Al. 11 Patent Number: 5,661,241 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 1997Document16 pagesUnited States Patent 19: Harth, II Et Al. 11 Patent Number: 5,661,241 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 26, 1997TYO WIBOWONo ratings yet
- Bassin Du Gharb GeophysiqueDocument9 pagesBassin Du Gharb GeophysiqueKarim El MorabitiNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Offshore Refuelling Rev 0Document9 pagesRisk Assessment For Offshore Refuelling Rev 0ringbolt100% (1)
- Activity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsDocument84 pagesActivity Analysis, Cost Behavior, and Cost Estimation: Answers To Review QuestionsMuhammad MishbahurrizqiNo ratings yet
- JETIR1907J03Document5 pagesJETIR1907J03Iram KhanNo ratings yet
- HRD and Organizational ChangeDocument10 pagesHRD and Organizational ChangeYaso TharNo ratings yet
- Quality Control & Quality AssuranceDocument75 pagesQuality Control & Quality Assurancemuhammad omerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SlabsDocument12 pagesChapter 8 Slabsmike smith100% (1)
- Çalışma Soruları - 1Document6 pagesÇalışma Soruları - 1emreasker22No ratings yet
- Fluent-Intro 15.0 WS08b Vortex SheddingDocument39 pagesFluent-Intro 15.0 WS08b Vortex Sheddingmatteo_1234No ratings yet
- EY Re Engineering The Supply Chain For The Omni Channel of Tomorrow PDFDocument39 pagesEY Re Engineering The Supply Chain For The Omni Channel of Tomorrow PDFjunaid madniNo ratings yet
- International Ego State Therapy Bibliography Sept 2014Document35 pagesInternational Ego State Therapy Bibliography Sept 2014RudolfSianto100% (1)
- Educational Institutions Have A Responsibility To Dissuade Students From Pursuing Fields of Study in Which They Are Unlikely To SucceedDocument2 pagesEducational Institutions Have A Responsibility To Dissuade Students From Pursuing Fields of Study in Which They Are Unlikely To SucceedsusmithaNo ratings yet
- Inspection of Emergency ExitsDocument1 pageInspection of Emergency ExitsScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (51) : Class XDocument5 pagesMathematics (51) : Class XdhruvNo ratings yet
- Event-Calender For 75 Years CelebrationDocument4 pagesEvent-Calender For 75 Years Celebrationrajiv kumarNo ratings yet
- Mba ZC415 Course HandoutDocument11 pagesMba ZC415 Course HandoutareanNo ratings yet
- PlaygroundDocument16 pagesPlaygroundpaduuNo ratings yet