Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M1 Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology
M1 Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology
Uploaded by
Meteor 8580 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
404 views4 pagesThis document provides an introduction to human anatomy and physiology. It defines anatomy as the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts, while physiology is the study of how the body and its parts work and function. There are 11 organ systems that work together to carry out necessary life functions like maintaining homeostasis, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, and growth. Key organ systems discussed include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Original Description:
Original Title
M1 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an introduction to human anatomy and physiology. It defines anatomy as the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts, while physiology is the study of how the body and its parts work and function. There are 11 organ systems that work together to carry out necessary life functions like maintaining homeostasis, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, and growth. Key organ systems discussed include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
404 views4 pagesM1 Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology
M1 Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology
Uploaded by
Meteor 858This document provides an introduction to human anatomy and physiology. It defines anatomy as the study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts, while physiology is the study of how the body and its parts work and function. There are 11 organ systems that work together to carry out necessary life functions like maintaining homeostasis, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, and growth. Key organ systems discussed include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
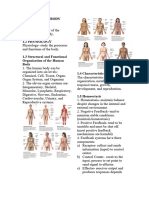
M1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Anatomy - secrete regulatory hormones Survival Needs
- Study of the structure and shape of the -growth, reproduction, metabolism 1.) Nutrients
body and its parts 6.) Cardiovascular system - chemicals for energy and cell-building
- transport nutrients via blood pumped - carbohydrates, lipids, minerals, etc.
2 Levels of Anatomy
by heart 2.) Oxygen
Gross Anatomy (Macroscopic)
- heart, blood vessels, blood - needed for chemical reactions
- deals with large structures
7.) Lymphatic system - we need this to live
- easily observable
- for immunity 3.) Water
Microscopic Anatomy
- returns fluids - 60-80% of our weight
- very small structures
- cleanses the blood - for metabolic reactions
- requires microscope
8.) Respiratory system 4.) Stable body temperature
Physiology - keeps blood supplied with oxygen - ranges form 36.5-37.5 Celsius
- study of how the body and its parts - oxygen removes carbon and is
Homeostasis
work and function essential to our bodies
- dynamic state of equilibrium
9.) Digestive system
Level of Structural Organization - maintenance of a stable internal
- break down food
1.) Chemical level environment
- for nutrient absorption
- atom combine to form molecules - needed for normal body function and
- eliminates substances
2.) Cellular level sustain life
10.) Urinary system
- cell are made up of molecules - eliminates nitrogenous substances Homeostatic Balance
3.) Tissue level - maintains acid-base balance - disturbance in the homeostasis of the
- consist of similar cells - regulates water and electrolytes body
4.) Organ level 11.) Reproductive system - results in disease
- made up of different tissues - for producing offspring
5.) Organ System level Maintaining Homeostasis
- consist of different organs working Necessary Life Functions - through hormonal (endocrine) and
together closely 1.) Maintain boundaries neural system (nervous)
6.) Organismal level - set limits - Receptor
- made up of many organ structures. 2.) Movement : responds to changes in the
- locomotion environment
11 Organ Systems - movement of substances : sends information to control center
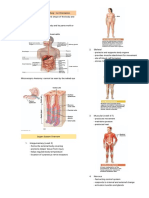
1.) Integumentary system - circulation of oxygen and blood - Control center
- form external cover 3.) Responsiveness : determines set point
- protect deeper tissues from injury - ability to sense changes in the : analyzes information
- helps regulate body temperature environment : determines response
- location of cutaneous nerve receptors 4.) Digestion
- Effector
2.) Skeletal system - break down and absorption of : means for response of stimulus
- does not produce movement but nutrients
attachments for muscles 5.) Metabolism Negative Feedback
- stores mineral - chemical reactions in our body - includes most homeostatic control
- cartilage, joints, bones - produces energy mechanism
3.) Muscular system - makes body structure - shuts off original stimulus/ reduces its
- produces movement 6.) Excretion intensity
- produces heat - eliminates waste from metabolic - works like a household thermostat
4.) Nervous system reactions Positive Feedback
- fast acting (rapid) system 7.) Reproduction - increase the original stimulus to push
- internal and external - for offspring variable further
- activates glands and muscles 8.) Growth - occurs during blood clotting and
- brain, spinal cord, nerves - increase of cell size and number. childbirth
5.) Endocrine system
M1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
M1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
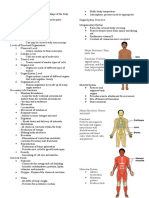
Regional Terms
Body Planes and Sections
M1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Abdominopelvic Regions Abdominopelvic Quadrants
Abdominopelvic Major Organs Body Cavities
You might also like
- At Q Short Form Scoring UpdatedDocument12 pagesAt Q Short Form Scoring UpdatedArunKumar100% (1)
- The Human Body OrientationDocument6 pagesThe Human Body OrientationHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- M1: CDU-CN BSN Program Outcomes of The BSN CurriculumDocument8 pagesM1: CDU-CN BSN Program Outcomes of The BSN CurriculumMeteor 858No ratings yet
- Anaphysio Midterm ReviewerDocument63 pagesAnaphysio Midterm Reviewer쥬얼이No ratings yet
- Anaphysio Midterm ReviewerDocument63 pagesAnaphysio Midterm ReviewerElaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesAnaphysio Lecture NotesJune Suzete RubioNo ratings yet
- Anaphy NotesDocument13 pagesAnaphy NotesMARIANNE ADEVANo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology LectureDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology LectureER TradoNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY ANG PHYSIOLOGY The Human OrganismDocument9 pagesANATOMY ANG PHYSIOLOGY The Human OrganismBugayong Manzon BethNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology IntroductionDocument19 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Introductionkdh yjmNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Intro-TissueDocument19 pagesAnaPhy Intro-Tissuekdh yjmNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyFiona Aaronica Hope LibrandaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy With Pathophysiology - Orientation of The Human BodyDocument11 pagesAnaphy With Pathophysiology - Orientation of The Human Bodyrichardgalvano45No ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer PrelimsDocument5 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Prelimskristine dadorNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology W/ Human PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology W/ Human PathophysiologyJuliana CostinianoNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerDocument11 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerMarmie Babaran GallibuNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerDocument11 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Reviewerjoyce.feir03No ratings yet
- Into" Because It Implies The Dissection of Cadavers.: Khaye Dela Cruz (1 MT - R) Anatomy and Physiology 1 (8/7/19)Document7 pagesInto" Because It Implies The Dissection of Cadavers.: Khaye Dela Cruz (1 MT - R) Anatomy and Physiology 1 (8/7/19)Mow LesterNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 The Human Organism GRRRDocument5 pagesLesson1 The Human Organism GRRRqueen grazildaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Ana Physio RBLDocument69 pagesIntro To Ana Physio RBLHades HadesNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY LEC PRELIMS NOTES by NOVERO KEN BMLS2 1Document55 pagesANAPHY LEC PRELIMS NOTES by NOVERO KEN BMLS2 1Marcus Randielle FloresNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterm ReviewerDocument14 pagesAnaphy Midterm ReviewerCarmela Jane SonzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsDocument16 pagesChapter 1 - The Human Body: Notes: From Atoms To OrganismsIssa AvenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: An Introduction To The Human BodyDocument7 pagesChapter 1: An Introduction To The Human BodyShyra EntradaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyDanielle AguilaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerNathaniel FerrerNo ratings yet
- 1&2 Homeostasis&basicchem PDocument20 pages1&2 Homeostasis&basicchem PMandyNo ratings yet
- RUNNNDocument18 pagesRUNNNNathaniel FerrerNo ratings yet
- HOMEOSTASIE DLG GDocument44 pagesHOMEOSTASIE DLG Gsheila.nandjomNo ratings yet
- Correche HA12 Unit1NotesDocument9 pagesCorreche HA12 Unit1NotesleiannbellecorrecheNo ratings yet
- Anaphy MidtermDocument5 pagesAnaphy MidtermSamantha LiberatoNo ratings yet
- 2e Partie BIO 2054 HoméostasieDocument53 pages2e Partie BIO 2054 HoméostasieMassaou Blama RapataNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY REVIEWER - PRELIMS ZZ PDFDocument10 pagesANATOMY REVIEWER - PRELIMS ZZ PDFKarol OpenianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Anaphy MariebDocument26 pagesChapter 1 Anaphy MariebKeanna ZurriagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDocument6 pagesChapter 1 AnaPhy Notes - ReviewerDanielle LeighNo ratings yet
- MC1 REVIEWER (Introduction To AnaPhy)Document7 pagesMC1 REVIEWER (Introduction To AnaPhy)Francine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Complete Study NotesDocument99 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology 1 Complete Study NotesSamuels JosepNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument141 pagesAnaphy ReviewerStar ChainzNo ratings yet
- Overview (Advance)Document8 pagesOverview (Advance)GuenNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 and 2Document20 pagesChapters 1 and 2GuenNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument3 pagesBody SystemsA R F I J U LNo ratings yet
- HAPP Reviewer 1Document4 pagesHAPP Reviewer 1Alianna Irish ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Ana1n2 - First Quiz ReviewerDocument4 pagesAna1n2 - First Quiz ReviewerJacinth ManuelNo ratings yet
- Anph111 Prelims (Intro To Anaphy)Document9 pagesAnph111 Prelims (Intro To Anaphy)Maria Clarisse ReyesNo ratings yet
- Intro To Ana Physio RBLDocument69 pagesIntro To Ana Physio RBLAirish AmboniNo ratings yet
- Anaphy PrelimDocument17 pagesAnaphy Prelimnero.keishareignc17No ratings yet
- ANPATHDocument23 pagesANPATHmwah mwahNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Rev1Document6 pagesAnaphy Rev1antonettevegamia3No ratings yet
- Life Processes in Plants & Animals: Lecture 1: IntroductionDocument5 pagesLife Processes in Plants & Animals: Lecture 1: Introductiongod ryujinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: An Introduction To Human Body: 1.1 Anatomy and Physiology DefinedDocument2 pagesChapter 1: An Introduction To Human Body: 1.1 Anatomy and Physiology DefinedKatelinne DabucolNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Transes 1stYear1stSemDocument42 pagesAnaphy Transes 1stYear1stSemzyrenejoy.motita.mnlNo ratings yet
- New SasDocument133 pagesNew SasUNKNOWN ANGELNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerKyNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Week 23Document8 pagesANAPHY Week 23Trisha Mae BalladNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Midterm ReviewerDocument8 pagesAnaphy Midterm ReviewerHazelle CarpioNo ratings yet
- ZooLec Reviewer February 24Document2 pagesZooLec Reviewer February 24Charles GuillermoNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 1Document4 pagesPHYSIOLOGY Chapter 1HUBERT JOHN RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Intro Anaphy Lec Reviewer - Camasin - LongDocument4 pagesIntro Anaphy Lec Reviewer - Camasin - LongJelou LumakinNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chap1 Lec Handout 1Document3 pagesAnaphy Chap1 Lec Handout 1psyche.ladicaNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerDocument8 pagesGENERAL PHYSIOLOGY ReviewerCherrie AnneNo ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- F3: Interpersonal Relationship: de Los Reyes - BSN 1DDocument7 pagesF3: Interpersonal Relationship: de Los Reyes - BSN 1DMeteor 858No ratings yet
- ETHICS MidtermDocument5 pagesETHICS MidtermMeteor 858No ratings yet
- Biochem 1st Year College ReviewerDocument16 pagesBiochem 1st Year College ReviewerMeteor 858100% (3)
- M2F Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesM2F Cardiovascular SystemMeteor 858No ratings yet
- Communication SkillDocument125 pagesCommunication SkillVivek PalNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics Quiz 10 QuestionsDocument2 pagesGeriatrics Quiz 10 QuestionsBrian Strauss100% (4)
- TASTE AND SMEL Note - 014427Document15 pagesTASTE AND SMEL Note - 014427Esosa OdighizuwaNo ratings yet
- Sensory DeprivationDocument25 pagesSensory DeprivationPrabhjot Singh67% (3)
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 4 - Module 1D PDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 4 - Module 1D PSyrine Myles Sullivan100% (1)
- Eals ReviewerDocument12 pagesEals ReviewerEms TeopeNo ratings yet
- Posner 1997 Pragmatics in Semiotik 01 de GruyterDocument28 pagesPosner 1997 Pragmatics in Semiotik 01 de GruyterJavi IbacetaNo ratings yet
- Virtual Lab JournalDocument2 pagesVirtual Lab Journalapi-325089664100% (2)
- MCATPrep Practice MCAT Test 2-Mcat2Document39 pagesMCATPrep Practice MCAT Test 2-Mcat2anc2061100% (4)
- Febi's Thesis Proposal-5 April 2021Document44 pagesFebi's Thesis Proposal-5 April 2021Riko Wijaya PBSNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisHT (Copy)Document14 pagesHomeostasisHT (Copy)jane byersNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Herbal Medicine: Phytochemical Screening and Analgesic Activity of "Kantkari"Document10 pagesInternational Journal of Herbal Medicine: Phytochemical Screening and Analgesic Activity of "Kantkari"ArmanNo ratings yet
- Belisle Stanley Dixon 2017Document11 pagesBelisle Stanley Dixon 2017cristian vargasNo ratings yet
- Extra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 PurposeDocument35 pagesExtra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 Purposelengers poworNo ratings yet
- Sensors & TransducersDocument5 pagesSensors & TransducersSachith Praminda RupasingheNo ratings yet
- Consumption Journal Presentation Nescafé Cold Coffee (Muhammad Asad Bin Faruq)Document20 pagesConsumption Journal Presentation Nescafé Cold Coffee (Muhammad Asad Bin Faruq)mabf89No ratings yet
- Proprioceptors and Their Contribution To Somatosensory Mapping: Complex Messages Require Complex Processing'Document9 pagesProprioceptors and Their Contribution To Somatosensory Mapping: Complex Messages Require Complex Processing'Francisco Vicent PachecoNo ratings yet
- MCQ Test Sheet PSYPDocument93 pagesMCQ Test Sheet PSYPHarshil DaveNo ratings yet
- Pain Gate MechanismDocument9 pagesPain Gate MechanismKaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Nerve Muscle PhysiologyDocument18 pagesNerve Muscle PhysiologyDr P N N Reddy100% (2)
- Saint Augustine Seminary Suqui Calapan City, Oriental Mindoro General Psychology (Final Examination)Document4 pagesSaint Augustine Seminary Suqui Calapan City, Oriental Mindoro General Psychology (Final Examination)Neri ErinNo ratings yet
- CNS PDFDocument412 pagesCNS PDFSami Juggy G100% (1)
- Animal Research ERQDocument2 pagesAnimal Research ERQSckerroNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Anatomy and Physiology An Integrative Approach 2nd Edition Mckinley Solutions Manual PDFDocument32 pagesDwnload Full Anatomy and Physiology An Integrative Approach 2nd Edition Mckinley Solutions Manual PDFgurlstocker9ucvp100% (22)
- Coordination and Response IGCSE NotesDocument11 pagesCoordination and Response IGCSE NotesDrRemyaranjith Menon100% (1)
- Soalan Science PMR Kertas 1 2006Document21 pagesSoalan Science PMR Kertas 1 2006Azim SufieNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Notes ControlcoordinationDocument6 pagesClass 10 Notes ControlcoordinationVijayasimha rao RavooriNo ratings yet
- 10.5 Speed of The Nerve ImpulseDocument23 pages10.5 Speed of The Nerve ImpulsequinNo ratings yet
- Body Coordination 2023Document73 pagesBody Coordination 2023AbbygailNo ratings yet