Professional Documents
Culture Documents
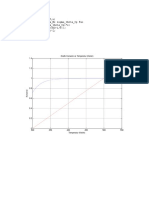
Thermopile Test
Thermopile Test
Uploaded by
EdmundJun0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesThis Arduino sketch measures temperature using a thermopile and thermistor. It defines constants for the thermistor temperature calculation and thermopile voltage calculation. In setup, it initializes the serial port. In loop, it reads the thermopile and thermistor values, calculates the ambient and object temperatures using those readings and constants, and prints the results to serial.
Original Description:
Thermopile test
Original Title
Thermopile test
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis Arduino sketch measures temperature using a thermopile and thermistor. It defines constants for the thermistor temperature calculation and thermopile voltage calculation. In setup, it initializes the serial port. In loop, it reads the thermopile and thermistor values, calculates the ambient and object temperatures using those readings and constants, and prints the results to serial.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesThermopile Test
Thermopile Test
Uploaded by
EdmundJunThis Arduino sketch measures temperature using a thermopile and thermistor. It defines constants for the thermistor temperature calculation and thermopile voltage calculation. In setup, it initializes the serial port. In loop, it reads the thermopile and thermistor values, calculates the ambient and object temperatures using those readings and constants, and prints the results to serial.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
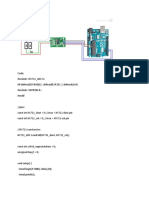
// Thermopile test
// pins used
#define THERMOPILE A0
#define THERMISTOR A1
// constants for the thermistor calculations
const float a = -412.6;
const float b = 140.41;
const float c = 0.00764;
const float d = -0.0000000000000000625;
const float e = -0.00000000000000000000000115;
// constants for the thermopile calculation
const float k = 0.004313;
const float delta = 2.468;
const float reftemp = 25; // reference temperature is 25C
const float shiftv = 0.6; // amount to shift thermopile voltage for negative V values in range
const float verr = 0.6; // voltage error introduced to thermopile by circuit
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
void loop() {
float thermopileValue = analogRead(THERMOPILE);
float thermistorValue = analogRead(THERMISTOR);
// work out thermistor temp from reading
float v1 = (thermistorValue / 1024) * 5; // source voltage is 5v so reading is fraction of that
float r = -(v1*1000)/(v1-5); // to get the resistance
float ambtemp = a + b * sqrt(1+c*r) + d*pow(r,5) + e*pow(r,7); // ambient temp
float comp = k * (pow(ambtemp,4-delta)-pow(reftemp,4-delta)); // equivalent thermopile V for
amb temp
// calculate the thermopile temp
float v2 = (thermopileValue / 1024) * 5 + comp - verr - shiftv; // thermopile voltage
float objtemp = pow((v2+k*pow(ambtemp,4-delta))/k, 1/(4-delta)); // object temp
Serial.print("thermopile value = ");
Serial.println(thermopileValue);
Serial.print("thermistor value = ");
Serial.println(thermistorValue);
Serial.print("ambient temp = ");
Serial.println(ambtemp);
Serial.print("object temp = ");
Serial.println(objtemp);
Serial.println();
delay(2000);
You might also like
- Code ArduinoDocument1 pageCode ArduinoAdil BentamouchNo ratings yet
- Pid Temperatura ArduinoDocument3 pagesPid Temperatura ArduinoFernando GomezNo ratings yet
- Arduino Voltage Sensor1Document3 pagesArduino Voltage Sensor1samantharathnasiriNo ratings yet
- Codigo ADocument4 pagesCodigo AIgnacioMartíNo ratings yet
- Arduino Sensor Datasheets and Circuit DiagramDocument8 pagesArduino Sensor Datasheets and Circuit DiagramSugarNo ratings yet
- Arduino Wattmeter v1Document34 pagesArduino Wattmeter v1Viena Mae MaglupayNo ratings yet
- TemperatureDocument5 pagesTemperatureEltierry SoaresNo ratings yet
- Arduino Voltage Sensor2Document3 pagesArduino Voltage Sensor2samantharathnasiriNo ratings yet
- C ProgramsDocument41 pagesC ProgramshlvijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Conversao de TemperaturaDocument2 pagesConversao de TemperaturaAnderson CastroNo ratings yet
- Project of Java 4Document6 pagesProject of Java 4Gemechis GurmesaNo ratings yet
- LM35 Temp Sensor Arduino CodeDocument3 pagesLM35 Temp Sensor Arduino CodeSisayDesalegnNo ratings yet
- Access Analog PinDocument1 pageAccess Analog Pinkarnikrathva200No ratings yet
- Arduino Fuel Gauge & Warning Lights SketchDocument4 pagesArduino Fuel Gauge & Warning Lights SketchAnonymous 6N7hofVNo ratings yet
- 07 - Reading A ThermistorDocument2 pages07 - Reading A ThermistorAl InalNo ratings yet
- Automated Hydro 5 Pumps 5-21-23Document9 pagesAutomated Hydro 5 Pumps 5-21-23Kenny HebertNo ratings yet
- Arduino Pellet Boiler Data Logger v1 My Nerd StuffDocument36 pagesArduino Pellet Boiler Data Logger v1 My Nerd StuffmyEbooks0% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0013468622005618 mmc1Document124 pages1 s2.0 S0013468622005618 mmc1Guilherme H. De MarchiNo ratings yet
- Code DumpDocument17 pagesCode DumpGameplay OrIgInAlINo ratings yet
- Psychrometrics FormulaeDocument5 pagesPsychrometrics Formulaetmy3dataNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1 (ES Lab)Document3 pagesExperiment - 1 (ES Lab)shubhamgarna.ytNo ratings yet
- Padhoz Rail 16F628A.hDocument6 pagesPadhoz Rail 16F628A.hPéter KovácsNo ratings yet
- Código em MATLAB 6Document4 pagesCódigo em MATLAB 6SOST HUMAPNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document4 pagesExperiment 3Sankar SorenNo ratings yet
- SDA SCL: //wire - Begin //connects I2C // Serial - Begin (9600)Document6 pagesSDA SCL: //wire - Begin //connects I2C // Serial - Begin (9600)Lisa EllisNo ratings yet
- Ec and Water Temperature CodeDocument6 pagesEc and Water Temperature CodeYusra AmeenNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Sample Scripts: Shameer A KoyaDocument12 pagesMATLAB Sample Scripts: Shameer A Koyadivya1587No ratings yet
- ParametersDocument5 pagesParametersDrSachin GuptaNo ratings yet
- VERILOG Code For Up and Down Counter of Varying FrequencyDocument11 pagesVERILOG Code For Up and Down Counter of Varying FrequencyKartik VermaNo ratings yet
- A. Koding: 1. Response of An RC CircuitDocument7 pagesA. Koding: 1. Response of An RC CircuitSartika Dewi HutabaratNo ratings yet
- KGYT5E4WXDocument3 pagesKGYT5E4WXAnisaNo ratings yet
- Openfoam Course Final Assignment: Tutorial For Natural Convection Boundary LayerDocument11 pagesOpenfoam Course Final Assignment: Tutorial For Natural Convection Boundary LayerdidNo ratings yet
- VoiDocument8 pagesVoiPanje DarlingtonNo ratings yet
- LoadcellDocument9 pagesLoadcellHarsh DaharwalNo ratings yet
- KIRCHHOFF'S Law 1-1Document10 pagesKIRCHHOFF'S Law 1-1alebelkinde81No ratings yet
- Codigo PWM 1Document3 pagesCodigo PWM 1André AleixoNo ratings yet
- Ty Man V ACDocument17 pagesTy Man V AC10 Joshua MasterNo ratings yet
- FA21 - Lec21 - 2021-12-01 - Relay, Optoisolators and Stepper MotorDocument27 pagesFA21 - Lec21 - 2021-12-01 - Relay, Optoisolators and Stepper MotorMahreenNo ratings yet
- Project 2Document3 pagesProject 2Vallabh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Matlab CodeDocument2 pagesMatlab CodeEddieLohNo ratings yet
- Adapter PatternDocument5 pagesAdapter PatternShivam AroraNo ratings yet
- Latih 8 Nama: Oggy Riza Erlangga NIM: A22.2018.02682: Membuat Konversi Suhu Celcius, Fahrenheit, Reamur, Dan KelvinDocument6 pagesLatih 8 Nama: Oggy Riza Erlangga NIM: A22.2018.02682: Membuat Konversi Suhu Celcius, Fahrenheit, Reamur, Dan KelvinOggy Riza ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- Psych As Raw TextDocument7 pagesPsych As Raw Textpkg6466No ratings yet
- LSU EE 3755 - Fall 2012 - Computer Organization Verilog Notes 3 - DelayDocument8 pagesLSU EE 3755 - Fall 2012 - Computer Organization Verilog Notes 3 - DelayMerupu DebbaNo ratings yet
- Fa20-Bee-150 MP Lab Report - 07Document5 pagesFa20-Bee-150 MP Lab Report - 07Saadat KhanNo ratings yet
- LAB 1 Circuit CirculationDocument4 pagesLAB 1 Circuit CirculationKevin OmesNo ratings yet
- VLSI Lab 9Document33 pagesVLSI Lab 9Umar AyubNo ratings yet
- Afl AmibrokerDocument7 pagesAfl AmibrokershilpaNo ratings yet
- Thermistor Temperature Sensor in LabVIEWDocument26 pagesThermistor Temperature Sensor in LabVIEWEfrain Parra QuispeNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Dual Axis ProgramDocument12 pagesEnhanced Dual Axis ProgramLENKAI—254No ratings yet
- Max - Power Transfer Theorem Verification by Using CDocument2 pagesMax - Power Transfer Theorem Verification by Using CSuketNo ratings yet
- Fa20-Bee-150 MP Lab Report - 07Document5 pagesFa20-Bee-150 MP Lab Report - 07Saadat KhanNo ratings yet
- Experiment:-7 Aim: To Study The Operation of Resistance Firing Circuit Using R, RC & UJT Firing Module. ApparatusDocument6 pagesExperiment:-7 Aim: To Study The Operation of Resistance Firing Circuit Using R, RC & UJT Firing Module. ApparatusNikhil BindalNo ratings yet
- Generalized StepsDocument4 pagesGeneralized StepsHimanshuNo ratings yet
- Httpsforum Arduino Cctenergy-Moniotr629438Document3 pagesHttpsforum Arduino Cctenergy-Moniotr629438hddhanushkaNo ratings yet
- EeDocument12 pagesEepriyaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Temperature Using An NTC Thermistor Using An Abbreviated Lookup TableDocument11 pagesMeasuring Temperature Using An NTC Thermistor Using An Abbreviated Lookup TablehuynhghinaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual For Data Structures With Java: John R. Hubbard Anita HurayDocument190 pagesSolutions Manual For Data Structures With Java: John R. Hubbard Anita HurayDiman IonutNo ratings yet
- How To Measure Ac Voltage Using Ampt101bDocument3 pagesHow To Measure Ac Voltage Using Ampt101bRafiul mulkNo ratings yet