Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7.3 SRAM Data Memory: Figure 7-2
7.3 SRAM Data Memory: Figure 7-2
Uploaded by
salar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageThe document summarizes the SRAM data memory organization of the ATmega328P microcontroller. The SRAM memory is made up of 32 registers, 64 I/O registers, 160 extended I/O registers, and 2048 bytes of internal data SRAM. It can be accessed using direct, indirect with displacement, indirect, indirect with pre-decrement, and indirect with post-increment addressing modes. Data access to the internal SRAM takes place over two clock cycles, with address computation in the first cycle and data valid in the second.
Original Description:
a
Original Title
Atmel_0018
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the SRAM data memory organization of the ATmega328P microcontroller. The SRAM memory is made up of 32 registers, 64 I/O registers, 160 extended I/O registers, and 2048 bytes of internal data SRAM. It can be accessed using direct, indirect with displacement, indirect, indirect with pre-decrement, and indirect with post-increment addressing modes. Data access to the internal SRAM takes place over two clock cycles, with address computation in the first cycle and data valid in the second.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 page7.3 SRAM Data Memory: Figure 7-2
7.3 SRAM Data Memory: Figure 7-2
Uploaded by
salarThe document summarizes the SRAM data memory organization of the ATmega328P microcontroller. The SRAM memory is made up of 32 registers, 64 I/O registers, 160 extended I/O registers, and 2048 bytes of internal data SRAM. It can be accessed using direct, indirect with displacement, indirect, indirect with pre-decrement, and indirect with post-increment addressing modes. Data access to the internal SRAM takes place over two clock cycles, with address computation in the first cycle and data valid in the second.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
7.
3 SRAM Data Memory
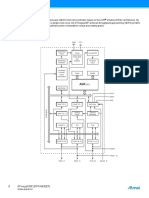
Figure 7-2 shows how the ATmega328P SRAM memory is organized.
The ATmega328P is a complex microcontroller with more peripheral units than can be supported within the 64 locations
reserved in the opcode for the IN and OUT instructions. For the extended I/O space from 0x60 - 0xFF in SRAM, only the
ST/STS/STD and LD/LDS/LDD instructions can be used.
The lower 2303 data memory locations address both the register file, the I/O memory, extended I/O memory, and the
internal data SRAM. The first 32 locations address the register file, the next 64 location the standard I/O memory, then 160
locations of extended I/O memory, and the next 2048 locations address the internal data SRAM.
The five different addressing modes for the data memory cover: Direct, indirect with displacement, indirect, indirect with
pre-decrement, and indirect with post-increment. In the register file, registers R26 to R31 feature the indirect addressing
pointer registers.
The direct addressing reaches the entire data space.
The indirect with displacement mode reaches 63 address locations from the base address given by the Y- or Z-register.
When using register indirect addressing modes with automatic pre-decrement and post-increment, the address registers X,
Y, and Z are decremented or incremented.
The 32 general purpose working registers, 64 I/O registers, 160 extended I/O registers, and the 2048 bytes of internal data
SRAM in the ATmega328P are all accessible through all these addressing modes. The register file is described in
Section 6.4 “General Purpose Register File” on page 12.
Figure 7-2. Data Memory Map
Data Memory
32 Registers 0x0000 - 0x001F
64 I/O Registers 0x0020 - 0x005F
160 Ext I/O Registers 0x0060 - 0x00FF
0x0100
Internal SRAM
(1048 x 8)
0x08FF
7.3.1 Data Memory Access Times
This section describes the general access timing concepts for internal memory access. The internal data SRAM access is
performed in two clkCPU cycles as described in Figure 7-3.
Figure 7-3. On-chip Data SRAM Access Cycles
T1 T2 T3
clkCPU
Address Compute Address Address valid
Data
Write
WR
Data
Read
RD
Memory Access Instruction Next Instruction
18 ATmega328P [DATASHEET]
7810D–AVR–01/15
You might also like
- Note Ông VinhDocument2 pagesNote Ông VinhNguyễn TàiNo ratings yet
- 1990 Fujitsu Channelless Gate ArraysDocument1,140 pages1990 Fujitsu Channelless Gate ArraysvpsampathNo ratings yet
- 1-32-Bit Microprocessor - Intel 80386Document37 pages1-32-Bit Microprocessor - Intel 80386afzal_a67% (3)
- Atmega 2560 Ingles (031-060)Document30 pagesAtmega 2560 Ingles (031-060)Yovan MamaniNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics 4Document7 pagesMechatronics 4Ab AnNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Notes PDFDocument68 pagesUnit 3 Notes PDFPadmanaban MNo ratings yet
- AVR MicrocontrollerDocument10 pagesAVR Microcontroller23mz41No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Memory HeirarchyDocument16 pagesUnit 4 Memory Heirarchyvivek kumarNo ratings yet
- Interfacing Devices Memory Devices and Interfacing Interfacing DevicesDocument14 pagesInterfacing Devices Memory Devices and Interfacing Interfacing DevicesShilpa ShettyNo ratings yet
- L24C32Document14 pagesL24C32mpapamicNo ratings yet
- LectEPE1301 3 RegistersRAMMemory AddressMappingAndDecoding1Document25 pagesLectEPE1301 3 RegistersRAMMemory AddressMappingAndDecoding1Bryan KekNo ratings yet
- 8051Document161 pages805121wh1a0487No ratings yet
- Lec 03 Internal Micro ArchitectureDocument24 pagesLec 03 Internal Micro ArchitecturePaarth JamwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 PDFDocument44 pagesUnit 2 PDFprashantvlsiNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Hardware Interfacing With Intel 8085Document44 pagesUnit Ii Hardware Interfacing With Intel 8085Basheer V.PNo ratings yet
- L9 Understanding Atmega328PExraDocument15 pagesL9 Understanding Atmega328PExraVIGHNESH AIYANo ratings yet
- L9 Understanding Atmega328P 2Document15 pagesL9 Understanding Atmega328P 2VIGHNESH AIYANo ratings yet
- Memory InterfaceDocument42 pagesMemory InterfacezemikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Arduino Uno AVR, Registers, RAM, Architecture Input & OutputDocument27 pagesChapter 2 Arduino Uno AVR, Registers, RAM, Architecture Input & OutputthandowatersonmpilaNo ratings yet
- ATmega Memory MapDocument1 pageATmega Memory MapshapouryNo ratings yet
- Peripherai Interface Microprocessor 68000Document40 pagesPeripherai Interface Microprocessor 68000Alfi Muhammad Akbar BariaNo ratings yet
- MICROPS 6 Memory InterfaceDocument44 pagesMICROPS 6 Memory InterfaceKyle GambalaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor By, Er. Swapnil V. KawareDocument55 pagesMicroprocessor By, Er. Swapnil V. KawareswapnilNo ratings yet
- Architecture OF MC-1Document33 pagesArchitecture OF MC-1Unique ProNo ratings yet
- CH02Document53 pagesCH02GemechuBGNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv: Advanced Microprocessors: Salient Features of 80386Document14 pagesUnit - Iv: Advanced Microprocessors: Salient Features of 80386Swamy NallabelliNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 80286 80386 80486 MicroproseccorsDocument91 pagesArchitecture of 80286 80386 80486 MicroproseccorsYash Mistry100% (1)
- Module 1Document95 pagesModule 1rishikesh tpNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument21 pagesNotesShinisg Vava50% (2)
- Advanced ProcessorDocument85 pagesAdvanced ProcessorRenit AntoNo ratings yet
- Architecture of Tms320c5xDocument32 pagesArchitecture of Tms320c5xUjwal Patil100% (1)
- G MPMC U4 Rit 150 CopiesDocument19 pagesG MPMC U4 Rit 150 CopiesBobby SatyaNo ratings yet
- Atmega ArchitectureDocument18 pagesAtmega ArchitecturevigneshthegreatNo ratings yet
- Intel 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument5 pagesIntel 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureFaheem Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Object Counting ConveyorDocument42 pagesObject Counting ConveyorMayilai AshokNo ratings yet
- Avr A & A: Rchitecture SsemblyDocument45 pagesAvr A & A: Rchitecture SsemblyFengxing ZhuNo ratings yet
- 20 سؤال معماريةDocument23 pages20 سؤال معماريةمصطفى شاكر محمودNo ratings yet
- MICRO133 Prelim Lecture 3 Intel 80286 and 80386 Microprocessor Protected Mode Addressing v2Document60 pagesMICRO133 Prelim Lecture 3 Intel 80286 and 80386 Microprocessor Protected Mode Addressing v2John Vinz CustodioNo ratings yet
- Intel: Term Paper On 80486 MicroprocessorDocument8 pagesIntel: Term Paper On 80486 MicroprocessorLALRAZNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document43 pagesUnit 1Aditya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 80286Document4 pagesMicroprocessor 80286xorxorxorNo ratings yet
- MP-MC R16 - Unit-4Document14 pagesMP-MC R16 - Unit-4satyanarayana12No ratings yet
- AMI CHP 1 32bit 80386 FinalDocument59 pagesAMI CHP 1 32bit 80386 FinalAliNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument16 pages8085 MicroprocessorVinay FelixNo ratings yet
- Microsad Q2Document66 pagesMicrosad Q2John Railey P. PamintuanNo ratings yet
- 8086 Min Max Mode Operations ModifiedDocument78 pages8086 Min Max Mode Operations ModifiedRitu RathiNo ratings yet
- R20 MPMC Unit IiiDocument25 pagesR20 MPMC Unit IiiMaddineni TejaNo ratings yet
- 8086 Memory & Interfacing PDFDocument39 pages8086 Memory & Interfacing PDFAnnamalai SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- U3 8086 MicroprocessorDocument10 pagesU3 8086 MicroprocessorNishant Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Advanced+MicroprocesorDocument66 pages2 Advanced+MicroprocesorMilind KhanderaoNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 80386Document17 pagesMicroprocessor 80386gujusNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 80486Document6 pagesMicroprocessor 80486Gaurav BisaniNo ratings yet
- 184 Pin 512mb 1g Unbuffered DDR Dimm Pc3200 DsDocument9 pages184 Pin 512mb 1g Unbuffered DDR Dimm Pc3200 DsKiran VeesamNo ratings yet
- 8-Bit Microcontroller With 4K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash AT90S4414 PreliminaryDocument10 pages8-Bit Microcontroller With 4K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash AT90S4414 PreliminaryYerson CrespoNo ratings yet
- Writing To Flash and Eeprom On The Tinyavr 1-Series: Application NoteDocument11 pagesWriting To Flash and Eeprom On The Tinyavr 1-Series: Application NoteanilNo ratings yet
- 4 SHARC MicroprocessorDocument31 pages4 SHARC MicroprocessorAshokkumar ManickamNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument46 pagesMicroprocessor Architecture'Jaspreet SandhuNo ratings yet
- INTEL 8086 MicroprocessorDocument85 pagesINTEL 8086 MicroprocessorsaiNo ratings yet
- 3 Microprocessor 8086Document27 pages3 Microprocessor 8086Munazza FatmaNo ratings yet
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationFrom EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- 8.2 Clock Sources: 8.1.4 Asynchronous Timer Clock - CLKDocument1 page8.2 Clock Sources: 8.1.4 Asynchronous Timer Clock - CLKsalarNo ratings yet
- 8.3 Low Power Crystal Oscillator: Figure 8-2Document1 page8.3 Low Power Crystal Oscillator: Figure 8-2salarNo ratings yet
- System Clock and Clock OptionsDocument1 pageSystem Clock and Clock OptionssalarNo ratings yet
- 7.6 Register Description: 7.5.1 General Purpose I/O RegistersDocument1 page7.6 Register Description: 7.5.1 General Purpose I/O RegisterssalarNo ratings yet
- Figure 8-3. Crystal Oscillator ConnectionsDocument1 pageFigure 8-3. Crystal Oscillator ConnectionssalarNo ratings yet
- Oscillator Source / Power Conditions Start-Up Time From Power-Down and Power-Save Additional Delay From Reset (V 5.0V) Cksel0 SUT1..0Document1 pageOscillator Source / Power Conditions Start-Up Time From Power-Down and Power-Save Additional Delay From Reset (V 5.0V) Cksel0 SUT1..0salarNo ratings yet
- Sbic RJMP: Wait For Completion of Previous WriteDocument1 pageSbic RJMP: Wait For Completion of Previous WritesalarNo ratings yet
- Eepm1 Eepm0 Programming Time Operation: Table 7-1. EEPROM Mode BitsDocument1 pageEepm1 Eepm0 Programming Time Operation: Table 7-1. EEPROM Mode BitssalarNo ratings yet
- 8.5 Low Frequency Crystal Oscillator: Table 8-7Document1 page8.5 Low Frequency Crystal Oscillator: Table 8-7salarNo ratings yet
- Avr Memories: Figure 7-1. Program Memory Map Atmega328PDocument1 pageAvr Memories: Figure 7-1. Program Memory Map Atmega328PsalarNo ratings yet
- 7.4 EEPROM Data Memory: Section 27. "Memory Programming" On Page 241Document1 page7.4 EEPROM Data Memory: Section 27. "Memory Programming" On Page 241salarNo ratings yet
- 6.6 Instruction Execution Timing: 6.5.1 SPH and SPL - Stack Pointer High and Stack Pointer Low RegisterDocument1 page6.6 Instruction Execution Timing: 6.5.1 SPH and SPL - Stack Pointer High and Stack Pointer Low RegistersalarNo ratings yet
- Atmel 0013Document1 pageAtmel 0013salarNo ratings yet
- In Cli Sbi Sbi Out: Store SREG ValueDocument1 pageIn Cli Sbi Sbi Out: Store SREG ValuesalarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Pin Descriptions: Atmega328P (Datasheet) 4Document1 page1.1 Pin Descriptions: Atmega328P (Datasheet) 4salarNo ratings yet
- 6.3.1 SREG - AVR Status Register: - Bit 7 - I: Global Interrupt EnableDocument1 page6.3.1 SREG - AVR Status Register: - Bit 7 - I: Global Interrupt EnablesalarNo ratings yet
- 7 Atmega328P (Datasheet) : 7810D-Avr-01/15Document1 page7 Atmega328P (Datasheet) : 7810D-Avr-01/15salarNo ratings yet
- 6.4 General Purpose Register File: Figure 6-2Document1 page6.4 General Purpose Register File: Figure 6-2salarNo ratings yet
- Figure 2-1. Block DiagramDocument1 pageFigure 2-1. Block DiagramsalarNo ratings yet
- Pin Configurations: Figure 1-1. PinoutDocument1 pagePin Configurations: Figure 1-1. PinoutsalarNo ratings yet
- Digital Systems DesignDocument7 pagesDigital Systems DesignaminhdlNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 PDFDocument6 pagesLab 4 PDFAhsan Murtaza MalikNo ratings yet
- Quartus II TrainingDocument91 pagesQuartus II TrainingRodrigo CorreaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC - 1 MicroprocessorDocument38 pagesTOPIC - 1 MicroprocessorPrevenaManiamNo ratings yet
- To Describe The Procedures For Using Qsys Software and Design of Basic Nios II Based Embedded SystemDocument11 pagesTo Describe The Procedures For Using Qsys Software and Design of Basic Nios II Based Embedded SystemMuhammad MoinNo ratings yet
- Mosfet 2 3Document55 pagesMosfet 2 3Dr EramNo ratings yet
- 3-Wire LCD Driver For CCS PIC C CompilerDocument6 pages3-Wire LCD Driver For CCS PIC C CompilerJonathan LazoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Performance of The New Generation of 32-Bit Microcontrollers For IoT and Big Data ApplicationDocument7 pagesAnalysis of The Performance of The New Generation of 32-Bit Microcontrollers For IoT and Big Data Applicationsnri0da9No ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet # 10Document5 pagesLab Worksheet # 10Khawaja Bilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Finite State Machine ExamplesDocument55 pagesFinite State Machine ExamplesDionisio De Zolt100% (2)
- Tutorial 4 Combinational Logic Circuit Design and K-Map: C C C C D C D C D C CDDocument2 pagesTutorial 4 Combinational Logic Circuit Design and K-Map: C C C C D C D C D C CDMustafidzul MustaphaNo ratings yet
- ZX Spectrum 48K Service Manual (PDFDrive)Document67 pagesZX Spectrum 48K Service Manual (PDFDrive)ionut76733No ratings yet
- Unit-5 DSP ProcessorDocument28 pagesUnit-5 DSP ProcessorCCE notesNo ratings yet
- SOC Architecture and Design: - System-On-Chip (SOC) - SOC Covers Many TopicsDocument32 pagesSOC Architecture and Design: - System-On-Chip (SOC) - SOC Covers Many TopicschaitanyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Blind Via PCBDocument10 pagesWhat Is Blind Via PCBjackNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual ElectronicsDocument57 pagesLab Manual ElectronicsNaveen Rockzz Bhavans100% (2)
- ARM Arch (Compatibility Mode)Document56 pagesARM Arch (Compatibility Mode)『HW』 DOBBYNo ratings yet
- Lista de Precios Yim S.A.C. 21-12-20 (20+4)Document27 pagesLista de Precios Yim S.A.C. 21-12-20 (20+4)ivelha publicidadNo ratings yet
- Cadence Tutorial 3Document17 pagesCadence Tutorial 3Ian PressNo ratings yet
- Atmel 29C256 MemoryDocument17 pagesAtmel 29C256 MemoryYoseth Jose Vasquez ParraNo ratings yet
- PCB Layout Recommendations For Bga PackagesDocument75 pagesPCB Layout Recommendations For Bga PackagesPedroNo ratings yet
- RISC-V Lab Project PDFDocument21 pagesRISC-V Lab Project PDFAli ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Lab1 5 PDFDocument63 pagesLab1 5 PDFasadNo ratings yet
- Logic To PLC Ladder DiagramDocument4 pagesLogic To PLC Ladder DiagramNikhil S NairNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Synthesis - Part 2 2022Document86 pagesLecture 4 - Synthesis - Part 2 2022Shay SamiaNo ratings yet
- Final Revision LogicDocument66 pagesFinal Revision LogicKirillus MaherNo ratings yet
- Pic16c7x Micro Controller Data SheetDocument289 pagesPic16c7x Micro Controller Data SheetguttajimmyNo ratings yet
- Avr Risc PDFDocument3 pagesAvr Risc PDFMaheshKulkarniNo ratings yet
- Real Mode MicroprocessorDocument3 pagesReal Mode MicroprocessorSaqib RaoNo ratings yet