Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12 PermeabilityAnisotropy Solutions
12 PermeabilityAnisotropy Solutions
Uploaded by
SohaibSeidCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12 PermeabilityAnisotropy Solutions
12 PermeabilityAnisotropy Solutions
Uploaded by
SohaibSeidCopyright:
Available Formats
12--Permeability Anisotropy
Exercise 12-1—Vertical Well In Anisotropic Reservoir
You have just drilled a well in a new reservoir. There is evidence that the reservoir is
naturally fractured, with kx = 40 md parallel to the direction of the natural fractures and ky
= 5 md perpendicular to the direction of the natural fractures.
A. If the field were developed on 40 acre spacing with each well at the center of a 40
acre square, what would the permeability and drainage area dimensions of the well
spacing for the equivalent isotropic system be? Assume the sides of the 40-acre square
are aligned with the principal axes of permeability.
k = k xk y = (40 )(5) = 14.1 md
x = y = 43,560 A = (43,560 )(40 ) = 1,320 ft
x' =
k
x=
14.1
(1,320 ) = 784 ft
kx 40
y' =
k
y=
14.1
(1,320 ) = 2,217 ft
ky 5
B. What would the apparent skin factor be?
1 ⎡⎢⎛ k y ⎞ ⎛ kx ⎞ ⎤
1
⎡⎛ 5 ⎞ 4 ⎛ 40 ⎞ 4 ⎤
1 4 1 1
4
1
s = − ln ⎜⎜ ⎟⎟ + ⎜ ⎟ ⎥ = ln ⎢⎜ ⎟ + ⎜ ⎟ ⎥ = −0.129
2 ⎢⎝ k x ⎠ ⎜k ⎟ ⎥ 2 ⎢⎣⎝ 40 ⎠ ⎝ 5 ⎠ ⎥⎦
⎣ ⎝ y⎠ ⎦
C. What would the area of investigation be for a 24 hour test, if the viscosity were 0.75
cp, the porosity were 20%, and the total compressibility were 1.5×10-6 psi-1?
xi =
k xt
=
(40)(24 ) = 2,120
(948)(0.2 )(0.75)(1.5 × 10 −6 )
ft
948φµct
yi =
k yt
=
(5)(24 ) = 750
(948)(0.2 )(0.75)(1.5 × 10 −6 )
ft
948φµct
Ai = πxi yi = π (2,120)(750) = 115 acre
9/1/06 © 2006, Phoenix Reservoir Engineering 17
12--Permeability Anisotropy
(This page intentionally left blank)
18 © 2006, Phoenix Reservoir Engineering 9/1/06
12--Permeability Anisotropy
Exercise 12-2—Hydraulically Fractured Well In Anisotropic
Reservoir
You have just drilled and fractured a well in a new reservoir. The well does not appear to
be as stimulated as it should be if the reservoir were isotropic. The fracture was designed
to have a half-length of 500 feet and a fracture conductivity of 1,000 md-ft. If the
hydraulic fracture followed the path of existing natural fractures, and the reservoir had a
permeability kx of 0.4 md along the natural fractures and a permeability ky of 0.025 md
perpendicular to the natural fractures, what would the equivalent isotropic system be?
Solution:
k = kxk y = (0.4)(0.025) = 0.1 md
′
Lf =
k
Lf =
0.1
(500) = 250 ft
kx 0.4
⎛ ⎞⎛ k ⎛ 0.1 ⎞⎛ 0.1 ⎞
(wk )′ = ⎜⎜ ⎟⎜ k f ⎞⎟ =
⎟⎝ 0.4 ⎟⎠(1,000) = 500 md ⋅ ft
k k k
wf wk f = ⎜⎜ ⎟⎜
f
⎟⎜⎝ k x ⎟⎠
⎝ ky ⎠ ky kx ⎝ 0.025 ⎠
FcD
′
=
(wk )
′
f
=
500
= 20
kLf
′ (0.1)(250)
9/1/06 © 2006, Phoenix Reservoir Engineering 27
12--Permeability Anisotropy
(This page intentionally left blank)
28 © 2006, Phoenix Reservoir Engineering 9/1/06
12--Permeability Anisotropy
Exercise 12-3—Horizontal Well In Anisotropic Reservoir
Find the equivalent isotropic system for a horizontal well with a 5,000 ft lateral in a
reservoir with kx = 50 md, ky = 400 md, and kz = 1 md. The wellbore radius is 0.25 ft, and
the reservoir dimensions are h = 25 ft, xe = 10,000 ft, and ye = 3,000 ft.
Solution:
k ′ = k = 3 k x k y k z = 3 (50)(400)(1) = 27.1 md
L′ =
k
L=
27.1
(5,000) = 3,684 ft
kx 50
h′ =
k
h=
27.1
(25) = 130 ft
kz 1
′
xe =
k
xe =
27.1
(10,000) = 7,368 ft
kx 50
′
ye =
k
ye =
27.1
(3,000) = 781 ft
ky 400
aw =
k
rw =
27.1
(0.25) = 1.3 ft
kz 1
bw =
k
rw =
27.1
(0.25) = 0.065 ft
ky 400
′ a + bw 1.3 + 0.065
rw = w = = 0.6825 ft
2 2
9/1/06 © 2006, Phoenix Reservoir Engineering 37
12--Permeability Anisotropy
(This page intentionally left blank)
38 © 2006, Phoenix Reservoir Engineering 9/1/06
You might also like
- An Interview With Elon MuskDocument2 pagesAn Interview With Elon MuskGiselle Medina Maximiano67% (3)
- Solution Real Analysis Folland Ch5Document35 pagesSolution Real Analysis Folland Ch5ksNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis SolutionsDocument43 pagesFunctional Analysis SolutionsOlulolo100% (1)
- EbooksHouse Super Earth Encyclopedia - DKDocument210 pagesEbooksHouse Super Earth Encyclopedia - DKRaj100% (6)
- Exercise 2-1-Calculate Time To Reach Radius of InvestigationDocument12 pagesExercise 2-1-Calculate Time To Reach Radius of InvestigationSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- Rossby Waves in The Ocean (Part 1) : Stephen Riser, University of WashingtonDocument50 pagesRossby Waves in The Ocean (Part 1) : Stephen Riser, University of WashingtonAntonio Martinez MarreroNo ratings yet
- Appendix PDFDocument6 pagesAppendix PDFAnonymous 2rlcHIpCkwNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing DesignDocument7 pagesIsolated Footing DesignRamadanNo ratings yet
- Exercise1 QDocument2 pagesExercise1 QBin ChristianNo ratings yet
- Construction Management Chapter 2Document92 pagesConstruction Management Chapter 2thapitcherNo ratings yet
- Div Class Title On Certain Sequence Spaces DivDocument8 pagesDiv Class Title On Certain Sequence Spaces DivKarthikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nanomaterials and Devices - 2011 - Manasreh - Appendix A Derivation of Heisenberg Uncertainty PrincipleDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Nanomaterials and Devices - 2011 - Manasreh - Appendix A Derivation of Heisenberg Uncertainty Principleabhaypal617No ratings yet
- Functional AnalysisDocument37 pagesFunctional AnalysisCarlos RogerNo ratings yet
- MMAT5340 Sol1Document5 pagesMMAT5340 Sol1Love SmithNo ratings yet
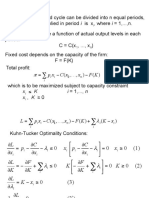
- 3rd LE-Nonlinear Programming - 30april2019Document12 pages3rd LE-Nonlinear Programming - 30april2019Mayumi VillavicencioNo ratings yet
- L4-1 KalmanDocument24 pagesL4-1 Kalmanhu jackNo ratings yet
- Fuid Dynamics FinalDocument318 pagesFuid Dynamics FinalPrateek ParashariNo ratings yet
- Example On Design of Biaxial Column With Design EccecntricitiessDocument10 pagesExample On Design of Biaxial Column With Design EccecntricitiessweynNo ratings yet
- Functional Analysis3Document6 pagesFunctional Analysis3Raja DuttaNo ratings yet
- Single Footing - US UnitsDocument26 pagesSingle Footing - US UnitsA.K.M Shafiq MondolNo ratings yet
- Determinar El Desplazamiento Horizontal en El Punto "D". E 29,000 I 600 in Ksi 4Document6 pagesDeterminar El Desplazamiento Horizontal en El Punto "D". E 29,000 I 600 in Ksi 4Amado JimenezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Normed Spaces: 5.1.1 Equivalence of NormsDocument6 pagesLecture 5: Normed Spaces: 5.1.1 Equivalence of NormsBabiiMuffinkNo ratings yet
- Course 3: 15.10.2020 Chapter 2 Vector SpacesDocument5 pagesCourse 3: 15.10.2020 Chapter 2 Vector SpacesPop RobertNo ratings yet
- Winkler FoundationDocument18 pagesWinkler Foundationdandy imam fauziNo ratings yet
- 852 2010hw12 SolutionsDocument8 pages852 2010hw12 Solutionshusneya salahatNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 24.1Document3 pagesEjercicio 24.1Mario Antonio Gomez CruzNo ratings yet
- P-Adic Analysis Compared To Real, Lecture 1 - F. Hensel, W. Lederle, S. MontemezzaniDocument11 pagesP-Adic Analysis Compared To Real, Lecture 1 - F. Hensel, W. Lederle, S. Montemezzanipeter.eggerNo ratings yet
- L4-2 MheDocument23 pagesL4-2 Mhehu jackNo ratings yet
- FA 15 16 Ex4 solHWDocument11 pagesFA 15 16 Ex4 solHWboris peñaNo ratings yet
- Maths TopicDocument2 pagesMaths Topicamitkathuria023_6245No ratings yet
- Taylor Series: Chapter ElevenDocument7 pagesTaylor Series: Chapter ElevenRhea GoelNo ratings yet
- Z TransformsDocument10 pagesZ TransformsSahil SinghNo ratings yet
- Lectura 3 1Document5 pagesLectura 3 1Santiago MoralesNo ratings yet
- 22 2 Continuity Operator NormDocument5 pages22 2 Continuity Operator NormDmitri ZaitsevNo ratings yet
- MIT6 641s09 Sol Exam2008Document9 pagesMIT6 641s09 Sol Exam2008Omwami LenoxNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2Elaine XieNo ratings yet
- Answers 2 ADocument24 pagesAnswers 2 AMarc Samper SeguraNo ratings yet
- Sheet01 H LSGDocument6 pagesSheet01 H LSGAusten Meusel100% (1)
- 02.01a Ch1 HW Solutions Update 21 May 2019Document17 pages02.01a Ch1 HW Solutions Update 21 May 2019EnriqueNo ratings yet
- CH E 441 Q5 Spring 05Document1 pageCH E 441 Q5 Spring 05Jhon Barzola PalominoNo ratings yet
- Math 551: Applied PDE and Complex Vars Fall 2017: Rφ φ σ dx = (0 j 6= k 1 j = kDocument1 pageMath 551: Applied PDE and Complex Vars Fall 2017: Rφ φ σ dx = (0 j 6= k 1 j = kAlexander BennettNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures Design and Behavior 5th Edition Salmon Solutions ManualDocument3 pagesSteel Structures Design and Behavior 5th Edition Salmon Solutions Manualkhuehang4k0deo100% (24)
- PropagateDocument11 pagesPropagateMichel Rodrigues AndradeNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus - Grade 12: Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Sarah BlythDocument34 pagesDifferential Calculus - Grade 12: Rory Adams Free High School Science Texts Project Sarah Blythcivilndlovu13No ratings yet
- Integer Programming Models - ProofsDocument5 pagesInteger Programming Models - ProofsNengke LinNo ratings yet
- Capacidad de Carga Última HANSEN - Sesión VivoDocument2 pagesCapacidad de Carga Última HANSEN - Sesión VivoJorge Luis ChuraNo ratings yet
- 6 Band Theory of SolidsDocument38 pages6 Band Theory of SolidsRavi Teja100% (2)
- ArmjiroDocument5 pagesArmjiroPedroSoucasauxNo ratings yet
- Analysis Epi Sheet5Document3 pagesAnalysis Epi Sheet5Tom BombardeNo ratings yet
- Newton-Raphson Method: Numerical AnalysisDocument14 pagesNewton-Raphson Method: Numerical Analysisنورالهدى سعيد عبدNo ratings yet
- Invese Scattering Problem For Perturbed Bi Harmonic OperatorDocument5 pagesInvese Scattering Problem For Perturbed Bi Harmonic OperatorAsim AsrarNo ratings yet
- (Power) Series: Solved Problems Phabala 2010Document6 pages(Power) Series: Solved Problems Phabala 2010alvinNo ratings yet
- Soln 11005Document1 pageSoln 11005fabmorenoNo ratings yet
- Model Answer Mid2-Mth462 - 2023-2024Document3 pagesModel Answer Mid2-Mth462 - 2023-2024rafatshaabNo ratings yet
- 2-03-Hilbert SpaceDocument16 pages2-03-Hilbert SpaceMalik Haseeb Malik HaseebNo ratings yet
- U20ma301 Tpde Model Set 1Document4 pagesU20ma301 Tpde Model Set 1PriyankaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Academy: Branch: Civil Engineering ESE-Offline Test Series - 2015 (Mock I Paper 2) SolutionsDocument20 pagesEngineering Academy: Branch: Civil Engineering ESE-Offline Test Series - 2015 (Mock I Paper 2) Solutionssaxenaarpita41No ratings yet
- Test Practice Exam Questions and Answers Solow ModelDocument5 pagesTest Practice Exam Questions and Answers Solow ModelFiranbek BgNo ratings yet
- GEC 210 Part 1 - Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesGEC 210 Part 1 - Tutorial QuestionsIfiok UsoroNo ratings yet
- GEC 210 Part 1 - Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesGEC 210 Part 1 - Tutorial QuestionsIfiok UsoroNo ratings yet
- VibrationsDocument13 pagesVibrationsSharon DouglasNo ratings yet
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)From EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)No ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical Models of Metal Surfaces and Nanoparticles Ebook3000Document104 pagesQuantum Mechanical Models of Metal Surfaces and Nanoparticles Ebook3000SohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- Chemical Electrostatics: Fernando Galembeck Thiago A. L. BurgoDocument237 pagesChemical Electrostatics: Fernando Galembeck Thiago A. L. BurgoSohaibSeid100% (1)
- Manual On The General ChemistryDocument268 pagesManual On The General ChemistrySohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- Surface and Interface AnalysisDocument316 pagesSurface and Interface AnalysisSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- Interfacial Phenomena On Biological Membranes: Manoranjan Arakha Suman JhaDocument156 pagesInterfacial Phenomena On Biological Membranes: Manoranjan Arakha Suman JhaSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- ,!7IB3B5-ijgibg!: Polyurethane Foam Sorbents in Separation ScienceDocument228 pages,!7IB3B5-ijgibg!: Polyurethane Foam Sorbents in Separation ScienceSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- 16 EstimatingAverageReservoirPressure SolutionsDocument4 pages16 EstimatingAverageReservoirPressure SolutionsSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- 13 NaturallyFracturedReservoirs SolutionsDocument8 pages13 NaturallyFracturedReservoirs SolutionsSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- 17 WellTestDesign SolutionsDocument2 pages17 WellTestDesign SolutionsSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6-1-Analyze Drawdown Test Well in Long, Narrow ReservoirDocument10 pagesExercise 6-1-Analyze Drawdown Test Well in Long, Narrow ReservoirSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2-1-Calculate Time To Reach Radius of InvestigationDocument12 pagesExercise 2-1-Calculate Time To Reach Radius of InvestigationSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3-1-Analyze Drawdown TestDocument4 pagesExercise 3-1-Analyze Drawdown TestSohaibSeidNo ratings yet
- DVP-10SX PLC DeltaDocument2 pagesDVP-10SX PLC Deltawilfredomolina100% (1)
- United International University: EEE 424: Microprocessor and Interfacing Laboratory Experiment#5Document7 pagesUnited International University: EEE 424: Microprocessor and Interfacing Laboratory Experiment#5Nura Alam ProtikNo ratings yet
- Beverage Purchasing ControlDocument51 pagesBeverage Purchasing ControlMoses Mwah Muraya100% (2)
- Symmetry: Multinode M2150 Intelligent ControllerDocument6 pagesSymmetry: Multinode M2150 Intelligent Controlleradela sampayoNo ratings yet
- Product NewsDocument112 pagesProduct Newsnunes999No ratings yet
- Discuss Vision StatementDocument4 pagesDiscuss Vision StatementAKINDE DAMILOLANo ratings yet
- STS1 1Document42 pagesSTS1 1Peter Paul Rebucan PerudaNo ratings yet
- Indian ArchitectsDocument14 pagesIndian ArchitectsNabeel KTNo ratings yet
- Ideal Op-Amp Equivalent CircuitDocument20 pagesIdeal Op-Amp Equivalent CircuitPiyush DubeyNo ratings yet
- General Pre Stress and ElasticDocument28 pagesGeneral Pre Stress and ElasticJorge Nickolai NavalesNo ratings yet
- Selective Red Cell Variables in Chippiparai Hound Breeds of Tamil Nadu - A Pilot Study in 30 DogsDocument6 pagesSelective Red Cell Variables in Chippiparai Hound Breeds of Tamil Nadu - A Pilot Study in 30 DogsIndian Journal of Veterinary and Animal Sciences RNo ratings yet
- Gis PortefolioDocument12 pagesGis PortefolioruimauricioferreiraNo ratings yet
- Freudian Revolution 2020Document6 pagesFreudian Revolution 2020Faith Vica Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- My CVDocument4 pagesMy CVSaifKhalidNo ratings yet
- 6003 Series 6403 and 6603 Tractors Mexico South Africa and Asian Edition Replacement Parts GuideDocument3 pages6003 Series 6403 and 6603 Tractors Mexico South Africa and Asian Edition Replacement Parts GuidePedro ValerioNo ratings yet
- Maths (Standard) Class - X - SET-1 (English Version)Document7 pagesMaths (Standard) Class - X - SET-1 (English Version)shanmugan rajNo ratings yet
- VAMP 125: Unit For Flexible Arc Flash ProtectionDocument12 pagesVAMP 125: Unit For Flexible Arc Flash Protectionuday chaurasiaNo ratings yet
- 10 Atypical PneumoniaDocument4 pages10 Atypical PneumoniaKevinTevesYupanquiNo ratings yet
- About Maths 8: AnswersDocument43 pagesAbout Maths 8: AnswersSean GongNo ratings yet
- WASS Form Proposal Adriana Ressiore Questions UpdatedDocument19 pagesWASS Form Proposal Adriana Ressiore Questions UpdatedMaria Fernanda MatosNo ratings yet
- Danby Dac12507ee User ManualDocument13 pagesDanby Dac12507ee User ManualElla MariaNo ratings yet
- Optimizing HPLC Methods 1684601740Document46 pagesOptimizing HPLC Methods 1684601740AlexandreLuizdeSouzaNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary HSC 22 PDFDocument28 pagesVocabulary HSC 22 PDFMadara Uchiha83% (6)
- Medicine Buddha SadhanaDocument4 pagesMedicine Buddha SadhanaMonge Dorj100% (2)
- KS3 Africa 5ghanafactsheetDocument3 pagesKS3 Africa 5ghanafactsheetSandy SaddlerNo ratings yet
- Carrier Air Cooled Liquid Chillers 30GH GZ Series DatasheetDocument16 pagesCarrier Air Cooled Liquid Chillers 30GH GZ Series DatasheetQazertNo ratings yet
- Calculate The Wetted Surface Area of Pressure VesselsDocument7 pagesCalculate The Wetted Surface Area of Pressure VesselsHsein WangNo ratings yet
- Pallas Athena in AstrologyDocument1 pagePallas Athena in AstrologyMoraru Mariana0% (1)