Professional Documents
Culture Documents
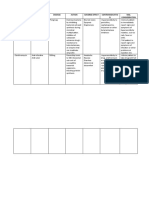
Drug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification Contraindication
Drug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification Contraindication
Uploaded by
Mel Izhra N. MargateCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Language of Change Elements of TherapeuticDocument2 pagesThe Language of Change Elements of Therapeuticnafiz0% (1)
- Pen G Drug StudyDocument1 pagePen G Drug Studyjean therese100% (1)
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument35 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologytoobanaeemNo ratings yet
- 1 LIVGBIntro OverviewDocument28 pages1 LIVGBIntro Overviewapi-3719759100% (1)
- Esi BenefitsDocument91 pagesEsi BenefitsAmey Vartak83% (6)
- NavapashanamDocument9 pagesNavapashanamcantuscantus0% (1)
- Drug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDan Dan Soi T50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument25 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- Emnc 4 North Drug StudyDocument12 pagesEmnc 4 North Drug StudyFrancesca Aurea MagumunNo ratings yet
- Final Drug Study NafldDocument10 pagesFinal Drug Study Nafld1A MARCOS, Ma. Alisa S.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyDana AlvaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaNo ratings yet
- DRUGDocument2 pagesDRUGEdissa PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern SamarDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern SamarTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Batmc GeriaDocument3 pagesDrug Study Batmc GeriaLeslee Amor EspirituNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRisha Ethel BerondoNo ratings yet
- Drugs MaleDocument4 pagesDrugs MaleJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument9 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeRio Ramon HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykakienz100% (7)
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyyyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyyyAlleinad BarracasNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibiliti EsDocument12 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibiliti EsdeliejoyceNo ratings yet
- PiptazDocument2 pagesPiptazZyrah Ziska Zafra100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY - CopdDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - CopdMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Drug-Study GaloloDocument3 pagesAmoxicillin Drug-Study Galolo40-GALOLO ANDREA PAULINENo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY pt1 DraftDocument8 pagesDRUG STUDY pt1 Draftjean samsonNo ratings yet
- Drug-Tabulation (2) For CHN IndiDocument5 pagesDrug-Tabulation (2) For CHN IndiKANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyLA GomezNo ratings yet
- DS ObDocument7 pagesDS ObZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: College of NursingDocument3 pagesRUG Tudy: College of NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinChristine NocomuraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NurseryDocument2 pagesDrug Study Nurseryjulesubayubay54280% (1)
- Name of The DrugsDocument1 pageName of The DrugsJake SmithNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJanika BecieraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format and SampleDocument6 pagesDrug Study Format and SampleA.No ratings yet
- Piptaz DSDocument4 pagesPiptaz DSArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study CefepimeDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Cefepimeprince gonzalesNo ratings yet
- DG1 CefuroximeDocument1 pageDG1 CefuroximeEkusu Yu ShunNo ratings yet
- DRUG TABULATION EditedDocument7 pagesDRUG TABULATION EditedAlexa Nicole GayosoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Threatened AbortionDocument7 pagesDrug Study Threatened AbortionKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug 101Document12 pagesDrug 101Alyzza DagoyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyAsh Moore MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Amoxicillin Suspension Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Amoxicillin Suspension Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilityNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis Drug Classification Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Action Side Effects/adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis Drug Classification Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Action Side Effects/adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesCarmela VargasNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Dosage/ Frequency /route Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Dosage/ Frequency /route Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLouisse Angeli AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4 Drug StudyDocument9 pagesCase Study 4 Drug StudyMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin TazobactamDocument2 pagesPiperacillin TazobactamLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime 260 MG Ivttq 8 HRS AnstDocument2 pagesCefuroxime 260 MG Ivttq 8 HRS AnstKate TergaNo ratings yet
- Or Drug StudyDocument19 pagesOr Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studystephanie valerioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY BudenosideDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY BudenosideJan Jiv Sanchez MedalloNo ratings yet
- Ndrug Ana Grand CaseDocument4 pagesNdrug Ana Grand CaseDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: BudesonideDocument8 pagesGeneric Name: BudesonidemeangelmeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyfortunelobsterNo ratings yet
- JD Drug-1-2Document2 pagesJD Drug-1-2RON PEARL ANGELIE CADORNANo ratings yet
- JD DrugDocument6 pagesJD DrugRON PEARL ANGELIE CADORNANo ratings yet
- Ampicillin+sulbactam, Irbesartan, Atorvastatin, Spironolactone, Losartan, ParacetamolDocument8 pagesAmpicillin+sulbactam, Irbesartan, Atorvastatin, Spironolactone, Losartan, ParacetamolDani DaniNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPedia Drug StudyTyn TynNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Manual: A Guide to commonly used antimicrobialsFrom EverandAntibiotics Manual: A Guide to commonly used antimicrobialsNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Symposium Article: Psychological Aspects of Depression in Cancer Patients: An UpdateDocument4 pagesSymposium Article: Psychological Aspects of Depression in Cancer Patients: An UpdateMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDocument4 pagesA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Almon D: AlmondDocument28 pagesAlmon D: AlmondMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- FNCP (Cigarette Smoking, Faulty Eating Habits and Alcohol Drinking) BuiuibDocument4 pagesFNCP (Cigarette Smoking, Faulty Eating Habits and Alcohol Drinking) BuiuibMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Principles of Pathophysiology - Bullock, ShaneDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Pathophysiology - Bullock, ShaneMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Significant: BullousDocument6 pagesSignificant: BullousMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Causes of Morbidity in Barangay 98 Camansihay, Tacloban CityDocument6 pagesCauses of Morbidity in Barangay 98 Camansihay, Tacloban CityMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Malaria: Control ProgramDocument40 pagesMalaria: Control ProgramMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goal Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Impaired Physical Mobility Related ToDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goal Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Impaired Physical Mobility Related ToMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Philippine Reproductive HealthDocument14 pagesPhilippine Reproductive HealthMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument1 pageOsteoarthritisMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Excreta and Sewage DisposalDocument51 pagesExcreta and Sewage DisposalMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- BALANITISDocument2 pagesBALANITISMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- 3ros & PeDocument4 pages3ros & PeMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- DMNCP - Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocument1 pageDMNCP - Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Oral MoniliasisDocument16 pagesOral MoniliasisMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Hookworm Diseases: (Ancylostomiasis /Miner'S Disease/Egyptian Chlorisis)Document21 pagesHookworm Diseases: (Ancylostomiasis /Miner'S Disease/Egyptian Chlorisis)Mel Izhra N. Margate100% (1)
- 08-Implant Surgery PDFDocument15 pages08-Implant Surgery PDFalkhalijia dentalNo ratings yet
- Paraneoplastic DermatosesDocument57 pagesParaneoplastic DermatosesMohamed Riyaz100% (1)
- Polio Physiotherapy NotesDocument6 pagesPolio Physiotherapy NotesyigoNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Beating Cancer NaturallyDocument9 pages7 Steps To Beating Cancer NaturallyRajak Mohamed100% (6)
- Maklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsDocument1 pageMaklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination Detailschandralekha kalaimutoNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Rubric - Neurology - Head - 2021 StudentDocument4 pagesPhase 1 Rubric - Neurology - Head - 2021 StudentEvan CheeNo ratings yet
- Palliative CareDocument106 pagesPalliative CarePadaaka AjiNo ratings yet
- Preview On MedicinesDocument3 pagesPreview On MedicinesafvxfNo ratings yet
- Narrow TopicDocument9 pagesNarrow TopicShabna MohanNo ratings yet
- GerdDocument19 pagesGerdMuhammad HafizdNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument36 pagesQuality ManagementMohammed Hussien100% (5)
- XDocument237 pagesXsigmundmaharaja2368No ratings yet
- Paediatric Drug Computation: Prepared By: Nursing Education Al Rayan HospitalDocument43 pagesPaediatric Drug Computation: Prepared By: Nursing Education Al Rayan HospitalDyan AmisolaNo ratings yet
- HA Checklist Mouth Nose ThoraxDocument9 pagesHA Checklist Mouth Nose ThoraxGemmalene PaclebNo ratings yet
- Mission Vision DohDocument3 pagesMission Vision DohCharlene MedranoNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument8 pagesCellulitisTricia Llorin100% (1)
- Clinical Practice Guideline For Adult Hypertension - Prevention, Screening, Counseling and ManagementDocument6 pagesClinical Practice Guideline For Adult Hypertension - Prevention, Screening, Counseling and ManagementHeppyMeiNo ratings yet
- Rhythm ECG Characteristics Strip Example: ECG Rhythms and Other Helpful ToolsDocument6 pagesRhythm ECG Characteristics Strip Example: ECG Rhythms and Other Helpful ToolsJohnildy MatiasNo ratings yet
- Health Care EnvironmentDocument17 pagesHealth Care EnvironmentrockheartyNo ratings yet
- Altering Occlusal Vertical Dimension in FunctionalDocument8 pagesAltering Occlusal Vertical Dimension in FunctionalDavid ColonNo ratings yet
- Insert Hep B Engerix-BDocument16 pagesInsert Hep B Engerix-BshifanahmedNo ratings yet
- Msds NH4ClDocument6 pagesMsds NH4Cl2imaNo ratings yet
- Uterin InversionDocument8 pagesUterin InversionZahra AlSaif100% (1)
- Measurement Properties of OakhqolDocument6 pagesMeasurement Properties of OakhqolRita RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pain FinalDocument87 pagesPathophysiology of Pain FinalKhushboo Rana A ScientistNo ratings yet
Drug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification Contraindication
Drug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification Contraindication
Uploaded by
Mel Izhra N. MargateOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification Contraindication
Drug Study: Classification Contraindication Classification Contraindication
Uploaded by
Mel Izhra N. MargateCopyright:
Available Formats
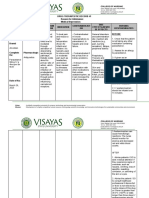
DRUG STUDY
NAME OF CLASSIFICATION SPECIFIC INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE
ADVERSE NURSING
NURSINGRESPONSIBILITIES
RESPONSIBILITIES
DRUG ACTION EFFECTS
EFFECTS
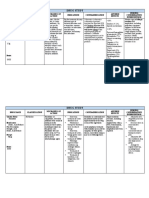
Cefuroxime750m
Piperacillin+Taz Therapeutic Class:
Anti-Infective Beta- Inhibits cell-wall
Anti-bacterial Surgical
Prophylaxis Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivitytoto Headache
Phlebitis Determine
Obtain historyhistory
of hypersensitivity
of
gobactam
IVTT q 8hrs Lactam Antibiotic;
Antibiotics combination
synthesis, against microbial
prophylaxis cephalosporins
piperacillin, and Insomia
Thrombophlebitis to penicillins, cephalosporins,
hypersensitivity reactions to or
Antipseudomonal product consisting
promoting osmotic activity or
reducing related
tazobactam,
antibiotics. Fever
penicillins, Diarrhea other drugs priorpenicillins
cephalosporins, to and
Dose: 750mg
4.5 mg Penicillin
Pharmacological of the
instability; usually eliminating Seizures
cephalosporins, or beta- Pseudomembrano administration.
history of allergies, particularly to
Route: IVTT Class: Second semisynthetic and
bactericidal. infection. lactamase inhibitors Agitation
us colitis drugs,
Considerbefore
the 12therapy
Rightsisofinitiated.
Frequency: q 8hrs generation the beta-lactamase such as clavulanic acid Dizziness
Nausea administering medication
ANST cephalosporins inhibitor and sulbactam. Chestpain
Anorexia Consider
Lab Tests:the C&S12 Rights
prior tooffirst dose
tazobactam, Edema
Vomiting of the drug; start
administering medication
drug pending
Tazobactam Contraindicated in Hypertension
Hemolytic anemia results.
component does patients hypersensitive Tachycardia
Thrombocytopeni Inspect
MonitorIV hematologic
injection sites
status with
NAME OF GENERAL not decrease the to the drug or other Diarrhea
a prolonged therapy
frequently for signs(Hctof phlebitis
and Hgb,
SPECIFIC
activity ofACTION
the INDICATION CONTRAINDICATIO
penicillins. ADVERSE
Constipation
Macupapular and NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
CBC with differential and platelet
DRUG ACTION
piperacillin N NauseaEFFECTS rash Monitor
erythematous count) signs and symptoms of
component Vomiting superinfection
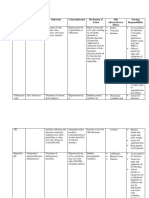
Omeprazole Therapeutic Inhibits proton against
pump Short term Contraindicated with
Urticaria
Headache
Monitor patientand carefully
Consider the 12 Rights of
diarrhea.
during
susceptible Dyspnea
Pain the first 30mins after initiation of
40mg IVTT OD Class: Antiulcer activity by binding to treatment of hypersensitivity to Asthenia administering medication
organisms. Dyspepsia
Anaphylaxis Advise
the infusion
patientfortosigns
report
of
drugs hydrogen-potassium active duodenal omeprazole or it’s Vertigo
Pseudomembranous
Hypersensitivity hypersensitivity.
discomfort at IV insertion site
adenosine and ileal ulcer components Colitis
Insomnia Verify doctor’s written
reaction Report rash, itching, or other
Pharmacological triphosphatase, located Use cautiously in prescription
Skin
Apatahy
SerumRash
sickness Document
signs of hypersensitivity
that drug was given
Class: Proton at secretory surface of Short term patients with
Pruritus
Anxiety immediately.
Pump Inhibitors gastric parietal cells, treatment of hypokalemia Inform
to suppress gastric Hypersensitivity
Paresthesia Report client about the
loose stools adverse as
or diarrhea
active benign Reactions
Dream effects of the drug
acid secretion. these may indicate
gastric ulcer abnormalities
Phlebitis at IV site pseudomembranous colitis.
Rash Report severe
Tell patient toheadache,
report any adverse
Urticaria worsening
reactions of symptoms, fever,
Pruritus chillss severetodiarrhea
Tell patient report discomfort
Dry skin at IV site
Tell patientthat
Document to report signsgiven
drug was and
Diarrhea
symptoms of low magnesium
Nausea
DRUG STUDY
Vomiting Dosage adjustment maybe
Abdominal pain necessary in Asians and patients
Constipation with hepatic impairement
Cough
Drug increases it’s own
bioavailability with repeated
doses. Drug is unstable in gastric
acid; less drug is lost to hydrolysis
because drug increases gastric pH.
Document that drug was given
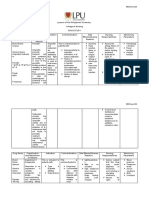
NAME OF CLASSIFICATION SPECIFIC INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
DRUG ACTION EFFECTS
Metronidazole Therapeutic Class: Direct-acting To prevent Contraindicate in patients Headache Consider the 12 Rights of
50mg IVTT q 8hrs Antiprotozoals trichomonicide post-operative hypersensitive to drug or Seizures administering medication
Pharmacological and amebicide that infection other nitroimidazoles. Fever
Class: works inside and To prevent Vertigo Observe patient for edema
Nitroimidazoles outside of the bacterial Use cautiously in patients Iritability
intestine. It’s infection with history of retinal or Edema Monitor LFT results carefully.
thought to enter visual field changes.
Rhinitis
the cells of Don’t give IV push
Sinusitis
mnicroorganisms Use cautiously in patients
that contain nitro who take hepatotoxic drugs Pharyngitis
Don’t refrigerate neutralized
reductase, forming or have hepatic disease or Nausea
Abdominal pain diluted solution precipitation may
unstable alcoholism. occur
compounds that Stomatitis
DRUG STUDY
bind to DNA and Anorexia Record number and chracter of
inhibit synthesis, Diarrhea stools when drug is used
causing cell death. Drymouth
Darkened urine Tell patient to avoid alcohol and
Polyuria alcohol containing drugs during
Dysuria and for atleast 3 days after
Transient joint treatment course
pains
URTI Tell patient to report to prescriber
Rash immediately any neurologic
symptoms such as seizures, and
General pruritus
peripheral neuropathy
Document that drug was given
DRUG STUDY
DRUG STUDY
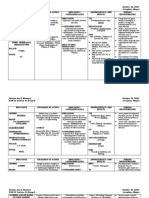
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
DRUG ACTION EFFECTS
Paracetamol Analgesics; Thought to produce For pain Contraindicated in Agitation Consider the 12 Rights of
600mg IVTT q Para- amalgesia by patients hypersensitive to Anxiety administering medication
6hrs x7 doses for aminophenol inhibiting drug IV form is Fatigue
pain derivatives prostaglandin and contraindicated in Headache Monitor vital signs before
other substances that patients with severe Insomnia and after administration.
sensitize pain hepatic impairement or Abdominal pain
receptors. Drugs may severe active liver Caution patient to contact
Constipation
relieve fever throught disease. healthcare provider if signs
central action in the and symptoms of liver
hypothalamic heat- damage occur
regulating center
Expect to reduce dosage for
patients with renal
dysfunction
Document that drug was
given
.
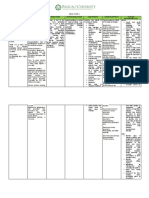
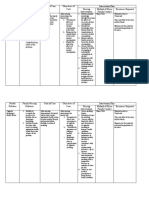
NAME OF GENERAL SPECIFIC ACTION INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
DRUG ACTION EFFECTS
Tramadol 50mg Therapeutic Binds to opiate Managemet of Hypersensitivity to Dizziness Consider the 12 Rights of
IV q 12hrs PRN Class: receptors in the CNS pain in the tramadol, opiods, or any Headache administering medication
for pain Analgesics causing inhibition of operation site component of the Seizures Reassess patient’s level of pain
Pharmacologica ascending pain formulation, opiod at least 30 mins after
Asthenia
l Class: pathways, altering the dependent patients; acute administration.
Sleep disorder Monitor CV and respiratory
Synthetic perception of and intoxication with alcohol,
DRUG STUDY
centrally active response to pain; also centrally acting Vasodilation status. Withold dose and notify
analgesics inhibits the reuptake of analgesics, opiods, or Visual disturbances prescriber if respirations are
norepinephrine and psychotropic drugs shallow or rate is below 12
Constipation
serotonin, which also bpm.
Nausea Monitor bowel and bladder
modifies the ascending Use cautiously in patients Vomiting
function. Monitor daily pattern
pain pathway with or at risk for acute Abdominal pain of bowel activity, stool
abdominal conditions,
Anorexia consistency.
renal or hepatic
Diarrhea Anticipate need for stimulant
impairement. laxative.
Dry mouth
Urine retention For better analgesic effect, give
drug before onset of intense
Hypertonia pain
Diaphoresis Monitor pulse, blood pressure,
Pruritus renal/hepatic function. Assist
Rash with ambulation if dizziness,
vertigo occurs.
Monitor patient for drug
dependence similar to that of
codeine and thus has potential
for abuse.
Withdrawal symptoms may
occur if drug is stopped
abruptly. Reduce dosage
gradually.
Assess for clinical
improvement, record onset of
relief of pain.
Document that drug was
given
You might also like
- The Language of Change Elements of TherapeuticDocument2 pagesThe Language of Change Elements of Therapeuticnafiz0% (1)
- Pen G Drug StudyDocument1 pagePen G Drug Studyjean therese100% (1)
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument35 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologytoobanaeemNo ratings yet
- 1 LIVGBIntro OverviewDocument28 pages1 LIVGBIntro Overviewapi-3719759100% (1)
- Esi BenefitsDocument91 pagesEsi BenefitsAmey Vartak83% (6)
- NavapashanamDocument9 pagesNavapashanamcantuscantus0% (1)
- Drug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Cefazolin DoxycyclineDan Dan Soi T50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument25 pagesDrug StudyRoland YusteNo ratings yet
- Emnc 4 North Drug StudyDocument12 pagesEmnc 4 North Drug StudyFrancesca Aurea MagumunNo ratings yet
- Final Drug Study NafldDocument10 pagesFinal Drug Study Nafld1A MARCOS, Ma. Alisa S.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyDana AlvaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaNo ratings yet
- DRUGDocument2 pagesDRUGEdissa PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern SamarDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern SamarTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Batmc GeriaDocument3 pagesDrug Study Batmc GeriaLeslee Amor EspirituNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRisha Ethel BerondoNo ratings yet
- Drugs MaleDocument4 pagesDrugs MaleJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument9 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeRio Ramon HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug Studykakienz100% (7)
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyyyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyyyAlleinad BarracasNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibiliti EsDocument12 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindicatio N Side Effects Nursing Responsibiliti EsdeliejoyceNo ratings yet
- PiptazDocument2 pagesPiptazZyrah Ziska Zafra100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY - CopdDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - CopdMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Drug-Study GaloloDocument3 pagesAmoxicillin Drug-Study Galolo40-GALOLO ANDREA PAULINENo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY pt1 DraftDocument8 pagesDRUG STUDY pt1 Draftjean samsonNo ratings yet
- Drug-Tabulation (2) For CHN IndiDocument5 pagesDrug-Tabulation (2) For CHN IndiKANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyLA GomezNo ratings yet
- DS ObDocument7 pagesDS ObZheyrille A. ArevaloNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: College of NursingDocument3 pagesRUG Tudy: College of NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinChristine NocomuraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NurseryDocument2 pagesDrug Study Nurseryjulesubayubay54280% (1)
- Name of The DrugsDocument1 pageName of The DrugsJake SmithNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJanika BecieraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format and SampleDocument6 pagesDrug Study Format and SampleA.No ratings yet
- Piptaz DSDocument4 pagesPiptaz DSArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study CefepimeDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Cefepimeprince gonzalesNo ratings yet
- DG1 CefuroximeDocument1 pageDG1 CefuroximeEkusu Yu ShunNo ratings yet
- DRUG TABULATION EditedDocument7 pagesDRUG TABULATION EditedAlexa Nicole GayosoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Threatened AbortionDocument7 pagesDrug Study Threatened AbortionKceey CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug 101Document12 pagesDrug 101Alyzza DagoyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyAsh Moore MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument24 pagesDrug StudyRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Amoxicillin Suspension Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Amoxicillin Suspension Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing ResponsibilityNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis Drug Classification Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Action Side Effects/adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis Drug Classification Indication Contraindication Mechanism of Action Side Effects/adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesCarmela VargasNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Dosage/ Frequency /route Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Dosage/ Frequency /route Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLouisse Angeli AbucejoNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4 Drug StudyDocument9 pagesCase Study 4 Drug StudyMontero, Ma. Cecilia - BSN 3-BNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin TazobactamDocument2 pagesPiperacillin TazobactamLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime 260 MG Ivttq 8 HRS AnstDocument2 pagesCefuroxime 260 MG Ivttq 8 HRS AnstKate TergaNo ratings yet
- Or Drug StudyDocument19 pagesOr Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studystephanie valerioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study QIDocument8 pagesDrug Study QImaeDonitaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY BudenosideDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY BudenosideJan Jiv Sanchez MedalloNo ratings yet
- Ndrug Ana Grand CaseDocument4 pagesNdrug Ana Grand CaseDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: BudesonideDocument8 pagesGeneric Name: BudesonidemeangelmeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyfortunelobsterNo ratings yet
- JD Drug-1-2Document2 pagesJD Drug-1-2RON PEARL ANGELIE CADORNANo ratings yet
- JD DrugDocument6 pagesJD DrugRON PEARL ANGELIE CADORNANo ratings yet
- Ampicillin+sulbactam, Irbesartan, Atorvastatin, Spironolactone, Losartan, ParacetamolDocument8 pagesAmpicillin+sulbactam, Irbesartan, Atorvastatin, Spironolactone, Losartan, ParacetamolDani DaniNo ratings yet
- Pedia Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPedia Drug StudyTyn TynNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics Manual: A Guide to commonly used antimicrobialsFrom EverandAntibiotics Manual: A Guide to commonly used antimicrobialsNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Symposium Article: Psychological Aspects of Depression in Cancer Patients: An UpdateDocument4 pagesSymposium Article: Psychological Aspects of Depression in Cancer Patients: An UpdateMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDocument4 pagesA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Almon D: AlmondDocument28 pagesAlmon D: AlmondMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- FNCP (Cigarette Smoking, Faulty Eating Habits and Alcohol Drinking) BuiuibDocument4 pagesFNCP (Cigarette Smoking, Faulty Eating Habits and Alcohol Drinking) BuiuibMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Principles of Pathophysiology - Bullock, ShaneDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Pathophysiology - Bullock, ShaneMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Significant: BullousDocument6 pagesSignificant: BullousMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Causes of Morbidity in Barangay 98 Camansihay, Tacloban CityDocument6 pagesCauses of Morbidity in Barangay 98 Camansihay, Tacloban CityMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Malaria: Control ProgramDocument40 pagesMalaria: Control ProgramMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goal Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Impaired Physical Mobility Related ToDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Goal Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Impaired Physical Mobility Related ToMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Philippine Reproductive HealthDocument14 pagesPhilippine Reproductive HealthMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument1 pageOsteoarthritisMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Excreta and Sewage DisposalDocument51 pagesExcreta and Sewage DisposalMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- BALANITISDocument2 pagesBALANITISMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- 3ros & PeDocument4 pages3ros & PeMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- DMNCP - Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDocument1 pageDMNCP - Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Oral MoniliasisDocument16 pagesOral MoniliasisMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Hookworm Diseases: (Ancylostomiasis /Miner'S Disease/Egyptian Chlorisis)Document21 pagesHookworm Diseases: (Ancylostomiasis /Miner'S Disease/Egyptian Chlorisis)Mel Izhra N. Margate100% (1)
- 08-Implant Surgery PDFDocument15 pages08-Implant Surgery PDFalkhalijia dentalNo ratings yet
- Paraneoplastic DermatosesDocument57 pagesParaneoplastic DermatosesMohamed Riyaz100% (1)
- Polio Physiotherapy NotesDocument6 pagesPolio Physiotherapy NotesyigoNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Beating Cancer NaturallyDocument9 pages7 Steps To Beating Cancer NaturallyRajak Mohamed100% (6)
- Maklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsDocument1 pageMaklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination Detailschandralekha kalaimutoNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Rubric - Neurology - Head - 2021 StudentDocument4 pagesPhase 1 Rubric - Neurology - Head - 2021 StudentEvan CheeNo ratings yet
- Palliative CareDocument106 pagesPalliative CarePadaaka AjiNo ratings yet
- Preview On MedicinesDocument3 pagesPreview On MedicinesafvxfNo ratings yet
- Narrow TopicDocument9 pagesNarrow TopicShabna MohanNo ratings yet
- GerdDocument19 pagesGerdMuhammad HafizdNo ratings yet
- Quality ManagementDocument36 pagesQuality ManagementMohammed Hussien100% (5)
- XDocument237 pagesXsigmundmaharaja2368No ratings yet
- Paediatric Drug Computation: Prepared By: Nursing Education Al Rayan HospitalDocument43 pagesPaediatric Drug Computation: Prepared By: Nursing Education Al Rayan HospitalDyan AmisolaNo ratings yet
- HA Checklist Mouth Nose ThoraxDocument9 pagesHA Checklist Mouth Nose ThoraxGemmalene PaclebNo ratings yet
- Mission Vision DohDocument3 pagesMission Vision DohCharlene MedranoNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument8 pagesCellulitisTricia Llorin100% (1)
- Clinical Practice Guideline For Adult Hypertension - Prevention, Screening, Counseling and ManagementDocument6 pagesClinical Practice Guideline For Adult Hypertension - Prevention, Screening, Counseling and ManagementHeppyMeiNo ratings yet
- Rhythm ECG Characteristics Strip Example: ECG Rhythms and Other Helpful ToolsDocument6 pagesRhythm ECG Characteristics Strip Example: ECG Rhythms and Other Helpful ToolsJohnildy MatiasNo ratings yet
- Health Care EnvironmentDocument17 pagesHealth Care EnvironmentrockheartyNo ratings yet
- Altering Occlusal Vertical Dimension in FunctionalDocument8 pagesAltering Occlusal Vertical Dimension in FunctionalDavid ColonNo ratings yet
- Insert Hep B Engerix-BDocument16 pagesInsert Hep B Engerix-BshifanahmedNo ratings yet
- Msds NH4ClDocument6 pagesMsds NH4Cl2imaNo ratings yet
- Uterin InversionDocument8 pagesUterin InversionZahra AlSaif100% (1)
- Measurement Properties of OakhqolDocument6 pagesMeasurement Properties of OakhqolRita RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pain FinalDocument87 pagesPathophysiology of Pain FinalKhushboo Rana A ScientistNo ratings yet