Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 2 Atoms, Molecules, & Ions
Lesson 2 Atoms, Molecules, & Ions
Uploaded by
Rachel VillasisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 2 Atoms, Molecules, & Ions
Lesson 2 Atoms, Molecules, & Ions
Uploaded by
Rachel VillasisCopyright:
Available Formats
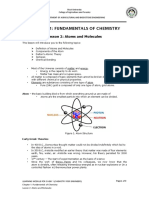
GENERAL CHEMISTRY 1: LESSON 2 ATOMS,
MOLECULES AND IONS
Atomic Theory: John Dalton
1. Each element is composed of extremely small
particles called atoms.
2. All atoms of a given element are identical; the atoms
of different elements are different and have different
properties (including masses)
3. Atoms of an element are not changed into different
types of atoms by chemical reactions; atoms are
neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions.
4. Compounds are formed when atoms of more than
one element combine; a given compound always
Classification of Matter has the same relative number and kind of atoms.
• According to its physical state, as a gas, liquid and *Atom are the basic building blocks of matter
solid *they are the smallest particles of an element that retain
• According to its composition as an element, the chemical identity of the element.
compound or mixture.
State of Matter
• A sample of matter can be solid, liquid or gas.
• These three forms of matter are called the state of
matter.
• These states of matter differ in some of their simple
observable properties.
The Discovery of Atomic Structure
The Modern View of Atomic Structure
1. Cathode Rays and Electrons
A high voltage produces radiation within the
tube.
It originated from the negative electrode or
cathode.
Important rule regarding the behavior of these
charges: like charges repels each other; unlike ! Atom consists of 3 subatomic particles:
charges attract.
Proton - a type of subatomic particle with
2. Radioactivity a positive charge
The spontaneous emission of radiation. Electronic charge: 1.602x10−19 C
Marie Sklodowska Curie (1867 -1934): Two Mass: 1.0073 amu
elements were discovered: polonium and
radium. Electron – a type of subatomic particle with a
negative charge
3. The Nuclear Atom: Plum-Pudding Electronic charge: - 1.602x10 −19
C
Ernest Rutherford Mass: 5.486x10 amu
−4
He revealed the three types of radiation: Alpha (
∝), beta (βγ), and gamma (γ) radiation.
Each type differs in its response to an electric Neutron - a subatomic particle of about the same
field. mass as a proton but without an electric charge
Electronic charge: Neutral
Mass: 1.0087 amu
Isotopes, Atomic Numbers and Mass Numbers
Isotopes – atoms of the same elements that
differ only in their number of neutrons.
Atomic & Mass
1. Atomic Number
The number of protons.
The atomic number of each element is listed
with the name and symbol of the element on
the front inside cover of the text.
2. Atomic Mass
The total number of protons plus neutrons in the
atom.
Sample exercise
1. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are
in an atom of Au197?
2. How many protons, neutrons and electrons are
in a K 39?
You might also like
- Chem Lec ReviewerDocument42 pagesChem Lec ReviewerMaryashlyn NableaNo ratings yet
- AtomicStructure 1Document41 pagesAtomicStructure 1Pankaj AroteNo ratings yet
- Chap 03Document22 pagesChap 03AmandaNo ratings yet
- AtomicStructure 1Document41 pagesAtomicStructure 1Juned AlamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gen ChemDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Gen ChemJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- 新chapter 02auDocument57 pages新chapter 02aurunshiguNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDocument3 pagesUnit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDanyel Rodriguez RomeraNo ratings yet
- HDF 111: Physical ChemistryDocument33 pagesHDF 111: Physical ChemistryachsanuddinNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Lesson 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry Lesson 2Andrea Marie LaquiñaNo ratings yet
- 2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument6 pages2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument57 pagesAtomic StructureMary Rose JasminNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryDocument4 pagesLesson - Atomic Structure: Scientist DiscoveryKokkilaa ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Eastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Document3 pagesEastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Isaac PiaoNo ratings yet
- MLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyDocument15 pagesMLS12101: Foundations of Chemistry 1. Matter and EnergyfuckyouNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Electron Proton NeutronDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure: Electron Proton NeutronTalao, Angelie Rei S.No ratings yet
- 03 Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument56 pages03 Atoms Molecules and Ionslhianne.bernalNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 1 LESSON 2 Atom Ions and MoleculesDocument60 pagesQUARTER 1 LESSON 2 Atom Ions and MoleculesMichelle De VillaNo ratings yet
- VI - Chemistry (Vol-III) Olympiad Class Work Book: Narayana Group of SchoolsDocument11 pagesVI - Chemistry (Vol-III) Olympiad Class Work Book: Narayana Group of SchoolsRita Tripathi100% (1)
- Intellectual Revolutions in The History of ScienceDocument5 pagesIntellectual Revolutions in The History of ScienceJustine Alyssa PardoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument19 pagesLecture 2 Atoms, Molecules and IonsHani TamimiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2Document24 pagesChemistry Unit 2Auvan HilarioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology: 2.1 Atoms: Fundamental Building Blocks of All Matter in The UniverseDocument50 pagesChapter 2: The Chemistry of Biology: 2.1 Atoms: Fundamental Building Blocks of All Matter in The UniverseShemmy Delotina DadulaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science MidtermsDocument4 pagesPhysical Science MidtermsKimberly MedranoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Chemistry: Lesson 2: Atoms and MoleculesDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Fundamentals of Chemistry: Lesson 2: Atoms and MoleculesKristine Cris VenusNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 01 3 Cont.Document52 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE Chapter 01 3 Cont.Think Before You ClickNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Module 3, Lesson 1: Atomic TheoryKeano GelmoNo ratings yet
- CH - 22 - LGDocument41 pagesCH - 22 - LGThaw ThawNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Model of An AtomSoumya Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 pagesPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaNo ratings yet
- Chem I Chapter 02Document9 pagesChem I Chapter 02M GNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Outline Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter ChapterDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Outline Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter ChapterTomás Monzón100% (1)
- ICSE Class 8 ChemistryDocument5 pagesICSE Class 8 ChemistryDoel Sen100% (1)
- Atoms Molecules IonsDocument36 pagesAtoms Molecules IonsGraciella Anne LandichoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Lesson Notes 2 - Atoms Molecules IonsDocument7 pages2023 Lesson Notes 2 - Atoms Molecules Ionsfanqi.xu10No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Study NotesDocument16 pagesAtomic Structure - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- The History of AtomDocument13 pagesThe History of AtomKylizzle xxNo ratings yet
- Unit4 - Matter and EenergyDocument21 pagesUnit4 - Matter and EenergyMiguel VintimillaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document18 pagesGeneral Physics 2Nea Faith L. LEMERICNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Document7 pagesGrade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Antonita100% (1)
- Academic Year 2020-21 Sub: Chemistry GRADE - 8: Learning ObjectivesDocument9 pagesAcademic Year 2020-21 Sub: Chemistry GRADE - 8: Learning Objectivesanish kanthethiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Three Types of Chemical Bonds: 1Document5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: Three Types of Chemical Bonds: 1Chris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Atomic Structure and Periodic TableDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Atomic Structure and Periodic TableAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Bab 2 (Material Science)Document11 pagesBab 2 (Material Science)Muhd AriffNo ratings yet
- Atoms: 1. Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesAtoms: 1. Atomic Structurecherry shane abanesNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument7 pagesGeneral ChemistryJeremiah DinioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry 9Document37 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry 9Kobie Loraine PonioNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Atomic Theory Part 1: Recall: NotesDocument11 pagesTopic 3: Atomic Theory Part 1: Recall: NotesniloNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Matter & Atomic StructureDocument12 pagesChap 2 Matter & Atomic StructureXr NightNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Material Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument33 pagesChapter 2 - Material Structure and Interatomic BondingamraqstnaNo ratings yet
- Partical of MatterDocument7 pagesPartical of MatterAinina DheotaNo ratings yet
- Second Grading Notes (NC)Document2 pagesSecond Grading Notes (NC)Lian VergaraNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Chemistry 2023 2Document60 pagesYr 9 Chemistry 2023 2mkkit2105No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument80 pagesAtomic Structureshelley guptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Complete Lecture 4x4Document17 pagesChapter 2 Complete Lecture 4x4michaelaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Form 2Document70 pagesChemistry Notes For Form 2Charles OtienoNo ratings yet
- Bohr's Model of AtomDocument22 pagesBohr's Model of AtomArsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- Carpentry 10Document5 pagesCarpentry 10Loejan ManlapasNo ratings yet
- Electron Theory: Level 1 EASA Part 66 Training ManualDocument35 pagesElectron Theory: Level 1 EASA Part 66 Training ManualAndy AlmineNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Lesson 10 Global CityDocument5 pagesLesson 10 Global CityRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Globalization For ReligionDocument6 pagesLesson 9 Globalization For ReligionRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Functions of ArtDocument3 pagesLesson 4 Functions of ArtRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Classification of ArtsDocument3 pagesLesson 3 Classification of ArtsRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Global DividesDocument5 pagesLesson 6 Global DividesRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Physical State Composition Pure Substance or MixturesDocument3 pagesPhysical State Composition Pure Substance or MixturesRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Assumptions and Nature of ArtsDocument4 pagesLesson 2 Assumptions and Nature of ArtsRachel Villasis0% (1)
- Lesson 3 Atomic Structure ModelDocument3 pagesLesson 3 Atomic Structure ModelRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Humanities and Nature of ArtsDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Humanities and Nature of ArtsRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Type of ErrorsDocument3 pagesLesson 4 Type of ErrorsRachel Villasis100% (1)
- ANA - 1 - History and Introduction To AnatomyDocument7 pagesANA - 1 - History and Introduction To AnatomyRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 Choosing Myself and The OtherDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 Choosing Myself and The OtherRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 4 AnswerDocument2 pagesWorksheet 4 AnswerRachel VillasisNo ratings yet
- Pnabx861 PDFDocument145 pagesPnabx861 PDFBindu ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Mardina A PDFDocument4 pagesMardina A PDFAdib YusofNo ratings yet
- Tropical Green BuildingDocument17 pagesTropical Green BuildingNeyl AwitanNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument42 pagesWork Energy and PowerKryschan CaditeNo ratings yet
- Industrial Energy Audit GuidebookDocument91 pagesIndustrial Energy Audit GuidebookBabar SaleemNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Review Hidrogeologi PertambanganDocument3 pages1.1 Review Hidrogeologi PertambanganDevina DianmahendraNo ratings yet
- MRS and Etc Microproject TopicDocument6 pagesMRS and Etc Microproject TopicShivam BhivgadeNo ratings yet
- Primary Drying: The Sublimation of Ice: 8.1 Principles of Coupled Heat and Mass TransferDocument16 pagesPrimary Drying: The Sublimation of Ice: 8.1 Principles of Coupled Heat and Mass TransferLIZETH YULIANA FAJARDO CENDALESNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/13Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/13annwong85No ratings yet
- Control Valve SizingDocument5 pagesControl Valve SizingMostafa SharafNo ratings yet
- Book ListDocument18 pagesBook ListazizbinnaserNo ratings yet
- 100 Magic Weather and Storms - DndspeakDocument6 pages100 Magic Weather and Storms - DndspeakThaoreoesNo ratings yet
- Direction: Analyze and Answer Carefully The Following Questions. Choose The BestDocument5 pagesDirection: Analyze and Answer Carefully The Following Questions. Choose The BestGener ToledoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 / 1 Week The Technology of FireDocument28 pagesChapter 1 / 1 Week The Technology of FireFEI RIENo ratings yet
- Oxo AQA16 P101 pr01 XxaannDocument6 pagesOxo AQA16 P101 pr01 XxaannAlenNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING PHYSICS Problem Set 1 - MidtermDocument2 pagesENGINEERING PHYSICS Problem Set 1 - MidtermShieNo ratings yet
- Approved List of Models and Manufacturers ALMM 1633167831Document21 pagesApproved List of Models and Manufacturers ALMM 1633167831srsinghal223No ratings yet
- Earthing Single Chamber PDFDocument2 pagesEarthing Single Chamber PDFNaim RoniNo ratings yet
- Soal Tes Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesSoal Tes Bahasa Inggrisskybladeline100% (6)
- Reines and Cowan Experiment: Iit Delhi EPL 332Document10 pagesReines and Cowan Experiment: Iit Delhi EPL 332Nitish RanjanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure-EngDocument49 pagesAtomic Structure-EngUğurörengülNo ratings yet
- SED 312 ISO Course Syllabus in Geology and AstronomyDocument6 pagesSED 312 ISO Course Syllabus in Geology and AstronomyRomel Christian Zamoranos MianoNo ratings yet
- 1 Activity: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A Disaster Risk ReductionDocument2 pages1 Activity: Ganilyn D. Ponciano. Stem 12 - A Disaster Risk ReductionGanilyn PoncianoNo ratings yet
- Astm G 113 2005 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm G 113 2005 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTANo ratings yet
- Your PDF - IELTS Vocabulary & Ideas About The EnvironmentDocument9 pagesYour PDF - IELTS Vocabulary & Ideas About The EnvironmentMARCOS PRIETO RICONo ratings yet
- Energy Savings Calculator For Boiler ReplacementsDocument14 pagesEnergy Savings Calculator For Boiler ReplacementsSanjeev KachharaNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy EssayDocument6 pagesRenewable Energy Essayapi-639009097No ratings yet
- U3 Vocabulary ExtensionDocument2 pagesU3 Vocabulary ExtensionLorena GCNo ratings yet
- June 2021 (v2) QP - Paper 4 CIE Physics IGCSEDocument16 pagesJune 2021 (v2) QP - Paper 4 CIE Physics IGCSEManya PunjabiNo ratings yet