Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan: Angeles University Foundation College of Nursing
Nursing Care Plan: Angeles University Foundation College of Nursing
Uploaded by
Rey Ann PangilinanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan: Angeles University Foundation College of Nursing
Nursing Care Plan: Angeles University Foundation College of Nursing
Uploaded by
Rey Ann PangilinanCopyright:
Available Formats
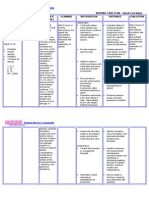
ANGELES UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION
COLLEGE OF NURSING
NURSING CARE PLAN
NAME OF STUDENT: Rey Ann M. Pangilinan PATIENTS PSEUDONAME: Anton
YEAR/SECTION II-G DIAGNOSIS: Risk for noncompliance with prophylactic drug therapy
GROUP NO. 26 AGE AND SEX:
DATE: 05/17/2021
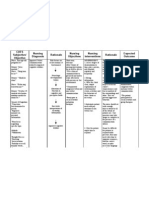
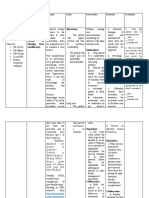
ASSESSMENT NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EXPECTED OUTCOME
EXPLANATION
Subjective: Risk for noncompliance Rheumatic fever Short term: Independent: Short term:
Parents reported that with prophylactic drug necessitates prophylactic After 3 hours of nursing After 3 hours of nursing
the boy refused to take therapy related to treatment to avoid interventions: 1. Establish trust and rapport 1. Developing a therapeutic interventions:
antibiotics burden of lifelong recurrence of the infection, The patient will with the child relationship with the patient The patient shall
therapy which may require long-term develop trust with encourages expression of be able to develop
Objective: care. The patient may be too the nurse patient’s feelings and trust with the nurse
Further review of the overwhelmed by the burden The patient will thoughts The patient shall
patient’s history of of lifelong therapy because express his express his
present illness he was discharged with thoughts or the 2. Assess the child’s 2. Each patient's perspective thoughts or the
revealed instructions to continue reason for his understanding of his and reasons for refusal of reason for his
noncompliance with taking his medications for noncompliance condition and the medical treatment differ. noncompliance
previously prescribed the next 10 years. As a with the drug significance of health care This method will serve as a with the drug
treatment result, the patient may not therapy basis for future care therapy prescribed.
adhere with the prescribed prescribed. planning. The patient shall
treatment regimen, The patient will be able to gain an
preventing him from fully gain an 3. Examine the patient's 3. According to the Health understanding of
recovering from the disease understanding of viewpoint and willingness Belief Model, a patient's the benefits of
or illness. There may be the benefits of to follow the treatment perceived susceptibility to complying with his
underlying reasons why a complying with his plan and severity of disease, as drug regimen and
patient refuses to take drug regimen and well as perceived benefits the complications
prescribed medications, the complications from sticking to a treatment that may occur
which must be thoroughly that may occur plan, all influence
investigated in order to compliance.
properly address the Long term: Long term:
problem and assist the After 2 days of nursing 4. Assess the factors that the 4. This enables the corrective After 2 days of nursing
patient in adhering to drug interventions, the patient patient believes are plan to be tailored to the interventions, the patient
therapy. will demonstrate hindering compliance. individual. shall be able to
willingness to adhere to demonstrate willingness to
the prophylactic drug 5. Evaluate the patient's 5. To address reasons that adhere to the prophylactic
therapy insight, worries, or might interfere with the drug therapy
misconceptions about the ability of the patient to
medication regimen. comply
6. Instruct the mother to keep 6. The patient's significant
an eye on the patient until others can provide
the patient's compliance supervision as needed that
improves. can be tapered as
appropriate.
7. Encourage the mother to 7. Rewards provides positive
establish a reward system reinforcements for
with the patient based on compliant behavior.
successful compliance.
8. Using simple words, 8. This raises awareness of
explain to the patient the the importance of following
benefits of sticking to the through with the treatment
medication regimen and plan. It increases the
the potential complications likelihood of treatment
that could arise if he compliance.
continues to refuse to take
his medications.
Dependent:
1. Discuss with the physician 1. Patients who are involved in
to see if the timing of the the planning of their care are
medication regimen can be more likely to stick to the
adjusted to fit the patient's regimen because it gives them
lifestyle and activities. a sense of control.
Interdependent:
1. Explore community 1. Such groups may assist the
resources available, or provide patient in better understanding
social support through the the advantages of treatment
child’s family and self-help adherence.
groups
You might also like
- 3-In-1 40K Ultrasonic Cavitaton Machine User ManualDocument26 pages3-In-1 40K Ultrasonic Cavitaton Machine User ManualJosé Emmanuel Chacón Chavarría100% (1)
- Case Studies On Major Concepts: NeurologicalDocument37 pagesCase Studies On Major Concepts: NeurologicalJek Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NCP GDMDocument5 pagesNCP GDMShaina Millan100% (1)
- Valdez Reflective-Questions PDFDocument3 pagesValdez Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Marijuana Research ReportDocument42 pagesMarijuana Research ReportMichael HamoudiNo ratings yet
- The Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseFrom EverandThe Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPAnne De VeraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementio N EvaluationAndrew James Javier Quidez100% (1)
- Diagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiagnosis Analysis Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Nursing Care PlanMartin Lєtmaku EspinaNo ratings yet
- Nusing CareplanDocument3 pagesNusing Careplanardec_143No ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPMelissa David100% (1)
- Subjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective:: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationAyra PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Brain Surgery Post Op NCPDocument6 pagesBrain Surgery Post Op NCPunnamed personNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument84 pagesCancerKaruna KumariNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients in Emergency Situation 2Document108 pagesNursing Care of Clients in Emergency Situation 2Mary Joy FrancoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPHuzzain PangcogaNo ratings yet
- Process RecordingDocument1 pageProcess RecordingJuko Fernandez0% (1)
- Med-Surg Care PlanDocument13 pagesMed-Surg Care Planapi-520453750No ratings yet
- Nursing TheoristDocument22 pagesNursing TheoristG a i l R i c h w e l lNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- Geriatric NursingDocument6 pagesGeriatric NursingMadelaine Mary Rose GarciaNo ratings yet
- X. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesX. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Bsn309 NeriDocument3 pagesCase Analysis Bsn309 NeriAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Premenstrual Dysphoric DisorderDocument11 pagesPremenstrual Dysphoric Disorderapi-3764215No ratings yet
- Psych NCPDocument1 pagePsych NCPEliza Joy Franco RNNo ratings yet
- Process Recording (PR) GuidelinesDocument2 pagesProcess Recording (PR) Guidelinesmrda9228No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationLi Luren Raphaelle TanNo ratings yet
- 6 Nursing Care Plan 1Document2 pages6 Nursing Care Plan 1Denise Louise PoNo ratings yet
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- MAHILOM NCP Risk For FallDocument2 pagesMAHILOM NCP Risk For Fallkasandra dawn BerisoNo ratings yet
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2ampalNo ratings yet
- ScriptDocument12 pagesScriptWaleed Nadeem50% (2)
- NCP Acute PainDocument5 pagesNCP Acute PainEzra TuanNo ratings yet
- Process Recording Sample Copy FormatDocument25 pagesProcess Recording Sample Copy FormatteuuuuNo ratings yet
- Pontine BleedingDocument99 pagesPontine BleedingJeffrey Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interview Guide To Collect Subjective Data From The Client Questions RationaleDocument19 pagesNursing Interview Guide To Collect Subjective Data From The Client Questions RationaleKent Rebong100% (1)
- CHN 1 Reg 8 HEALTH TEACHING PLAN FORMATDocument2 pagesCHN 1 Reg 8 HEALTH TEACHING PLAN FORMATChristine SaliganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PainDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Painjanmarc goreroNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- Qi NCPDocument5 pagesQi NCPJesse Israel TadenaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Acute ConfusionDocument4 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Acute Confusionasmika danaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument3 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryDan Leo UnicoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Physical Mobility Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationSheril Sularte CasanesNo ratings yet
- Tonsilitis NCPDocument2 pagesTonsilitis NCPFATIMA MARYAMA USMANNo ratings yet
- Jenninngs Disaster Nursing Management Model Annotated BibliographyDocument2 pagesJenninngs Disaster Nursing Management Model Annotated BibliographyEmergencyPlanning101No ratings yet
- FNCP On Elevated Blood Pressure 2Document4 pagesFNCP On Elevated Blood Pressure 2Aaron EspirituNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objective S Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objective S Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationJhun GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Oral CareDocument3 pagesOral CareLucy CenizaNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Sample CHN Teaching Learning GuideDocument3 pagesSample CHN Teaching Learning GuideSUREEN MAY ANG REGULARNo ratings yet
- Group 9 Sickle Cell Anemia Case Study ActivityDocument4 pagesGroup 9 Sickle Cell Anemia Case Study ActivityJuliaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Coping NCPDocument4 pagesIneffective Coping NCPFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- F Discharge Plan 2019Document1 pageF Discharge Plan 2019Besael BaccolNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNCP Drug StudyAndrea JoyaNo ratings yet
- FractureDocument4 pagesFractureRaveen mayiNo ratings yet
- CamileDocument42 pagesCamilebabypauNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Short Term: Independent: Short TermMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Anxiety NCPDocument2 pagesAnxiety NCPmitzi019No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: OSTEOPOROSIS DateDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: OSTEOPOROSIS DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNo ratings yet
- Prognosis and Discharge Plan - MaiaDocument12 pagesPrognosis and Discharge Plan - Maiajia88100% (1)
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument11 pagesPHARMACOLOGYadrianleet18No ratings yet
- HIV-related Stigma and DiscriminationDocument11 pagesHIV-related Stigma and DiscriminationRey Ann PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Normal Values UrinalysisDocument4 pagesNormal Values UrinalysisRey Ann PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Normal ValuesDocument3 pagesNormal ValuesRey Ann PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Normal Values UrinalysisDocument3 pagesNormal Values UrinalysisRey Ann PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management GLDocument11 pagesMarketing Management GLSaravanan VaradharajanNo ratings yet
- Intoxication Assessment Tool S C A B: Sober Influenced IntoxicatedDocument1 pageIntoxication Assessment Tool S C A B: Sober Influenced IntoxicatedFawxse YTNo ratings yet
- Reflective Journal 4Document2 pagesReflective Journal 4api-350779667No ratings yet
- Anomalias Dentarias2Document76 pagesAnomalias Dentarias2daruNo ratings yet
- M788 SDSDocument15 pagesM788 SDSYusuf Emre ÇABUKOĞLUNo ratings yet
- Single Institution Study On The Management of Childhood Bladder and Prostate RhabdomyosarcomaDocument5 pagesSingle Institution Study On The Management of Childhood Bladder and Prostate RhabdomyosarcomaIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- OIS-91 Basic H S TrainingDocument33 pagesOIS-91 Basic H S TrainingTej PalNo ratings yet
- Social Anxiety (CASE STUDY)Document7 pagesSocial Anxiety (CASE STUDY)Angel DIMACULANGANNo ratings yet
- DiarrheaDocument8 pagesDiarrheagautami charingiaNo ratings yet
- FirstWord Lists - Pharma's Biggest Product Growth Drivers - Q3 - FirstWord PharmaDocument3 pagesFirstWord Lists - Pharma's Biggest Product Growth Drivers - Q3 - FirstWord PharmamagicianchemistNo ratings yet
- Understanding Behavior: A Review of Influences On Health and Illness BehaviorsDocument23 pagesUnderstanding Behavior: A Review of Influences On Health and Illness BehaviorsOsama AlhumisiNo ratings yet
- Aim Global Approved Product Prescription-8Document9 pagesAim Global Approved Product Prescription-8ZION SIONNo ratings yet
- Sample Examination Paper 1: Photosynthesis. Below Is An Outline of The Procedure The Students UsedDocument4 pagesSample Examination Paper 1: Photosynthesis. Below Is An Outline of The Procedure The Students UsedCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Claim Procedure: Prepared by Aon Vietnam Limited - Proprietary & ConfidentialDocument32 pagesClaim Procedure: Prepared by Aon Vietnam Limited - Proprietary & ConfidentialGolden SaladinNo ratings yet
- Correction of Severe Crouch Gait in Patients With Spastic Diplegia With Use of Multilevel Orthopaedic SurgeryDocument12 pagesCorrection of Severe Crouch Gait in Patients With Spastic Diplegia With Use of Multilevel Orthopaedic Surgeryyarimar hoyosNo ratings yet
- 5 Love & Other Drugs.Document59 pages5 Love & Other Drugs.yosoylailaNo ratings yet
- Soal SMA Kelas 12 Bahasa Inggris SulitDocument10 pagesSoal SMA Kelas 12 Bahasa Inggris SulitsssssNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: 5 - Nucleotidase Kit Abbreviated Name: 5 - NT Order Information Cat. No. Package SizeDocument30 pagesGeneric Name: 5 - Nucleotidase Kit Abbreviated Name: 5 - NT Order Information Cat. No. Package SizeSharom Zelene Cordova RomanNo ratings yet
- Hagiwara, 2017Document13 pagesHagiwara, 2017luccafcms56No ratings yet
- Caloss2013 PDFDocument221 pagesCaloss2013 PDFsriwahyuutamiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Nateglinide On The Incidence of DiabetesDocument31 pagesEffect of Nateglinide On The Incidence of Diabetesfred opinionNo ratings yet
- History Taking and Examination For SurgeryDocument68 pagesHistory Taking and Examination For Surgerytayiba.m1995No ratings yet
- Clinical Bacteriology Lecture (W01)Document3 pagesClinical Bacteriology Lecture (W01)nicholehernandez05No ratings yet
- Interventions For Replacing Missing Teeth - Antibiotics at Dental Implant Placement To Prevent Complications - Esposito (2013)Document29 pagesInterventions For Replacing Missing Teeth - Antibiotics at Dental Implant Placement To Prevent Complications - Esposito (2013)Jorge Ampuero MelipillanNo ratings yet
- Dela Peña NCP 3Document2 pagesDela Peña NCP 3Mark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- O&G EMQsDocument10 pagesO&G EMQsV SugrimNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Surgery: Prospective Cohort StudyDocument7 pagesInternational Journal of Surgery: Prospective Cohort StudyAkbar Adrian RamadhanNo ratings yet