Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HL Answers To Rate Expression Questions: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, Inthinking
HL Answers To Rate Expression Questions: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, Inthinking
Uploaded by
aurennos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
233 views1 pageOriginal Title
Answers to Rate Expression
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
233 views1 pageHL Answers To Rate Expression Questions: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, Inthinking
HL Answers To Rate Expression Questions: © DR Geoffrey Neuss, Inthinking
Uploaded by
aurennosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
HL
Answers to Rate expression questions
1. In terms of units, rate = concentrationx
k
mol dm-3 s-1 = mol3 dm-9 = (mol dm-3)3 = concentration3
dm6 mol-2 s-1
Hence the units of the rate constant show that the reaction is third order overall
2. (a) From experiments 3 and 1, doubling [CH3COCH3(aq)] causes the rate to double hence
the order of the reaction with respect to propanone is one.
(b) From experiments 1 and 2 doubling [Br2(aq)] has no effect on the initial rate hence
the order of the reaction with respect to bromine is zero.
(c) From experiments 3 and 4, doubling [H+(aq)] causes the rate to double hence
the order of the reaction with respect to hydrogen ions is one.
(d) The overall order is two, i.e. a second order reaction.
(e) rate = k[CH3COCH3(aq)][H+(aq)]
(f) Substituting the values from experiment 4 into the rate expression
5.0 x 10-5 mol dm-3 s-1 = k x (1.0 x 10-1 mol dm-3) x (10-1 mol dm-3)
k = 5.0 x 10-3 mol-1 dm3 s-1
(Note: You can use any of experiments 1 to 4 to give the same result.)
(g) rate = 5.0 x 10-3 x (1.7 x 10-1) x (2.9 x 10-1) = 2.5 x 10-4 mol dm-3 s-1
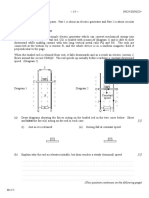
3. (a)
The graph of concentration of reactant against time (i)
will show the straight line sloping downwards as the
reactant is used up.
The graph of rate of reaction against concentration of
reactant (ii) will show the straight line staying at the same
(i) (ii)
level as the rate is independent of the concentration.
(b) rate = k, so units of k = mol dm-3 s-1
4. (a) For a first order reaction (left) the line slopes downwards and
the time is constant each time the concentration is halved.
The slope is even steeper for a second order reaction.
(b)
(i) first order reaction: rate = k x concentration so units of k = s-1
(ii) second order reaction: rate = k x concentration 2,
so units of k = dm3 mol-1 s-1
Dr Geoffrey Neuss, InThinking
©
http://www.thinkib.net/chemistry 1
You might also like
- Physics Paper 3 TZ1 SL MarkschemeDocument20 pagesPhysics Paper 3 TZ1 SL MarkschemeOnur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- Planning and Process For The TOK Exhibition Written Commentary Stage 1: Planning IA PromptDocument5 pagesPlanning and Process For The TOK Exhibition Written Commentary Stage 1: Planning IA Promptaurennos100% (4)
- Astro - All - 2023Document53 pagesAstro - All - 2023KaptainxdNo ratings yet
- November 2017 Chemistry H1 Paper 3 MarkschemeDocument38 pagesNovember 2017 Chemistry H1 Paper 3 MarkschemeArti Chamoli100% (1)
- Physics Paper 2 TZ1 SL MarkschemeDocument13 pagesPhysics Paper 2 TZ1 SL MarkschemeJoseph LAU [11D]No ratings yet
- Annotated HL P1Document11 pagesAnnotated HL P1Ruth Hilton100% (1)
- Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches Practice HL Paper 3 QuestionsDocument10 pagesMathematics: Analysis and Approaches Practice HL Paper 3 QuestionsRuth HiltonNo ratings yet
- HL Topic 5 & 15: Energetics/Thermochemistry (2nd Test)Document1 pageHL Topic 5 & 15: Energetics/Thermochemistry (2nd Test)aurennosNo ratings yet
- DP1 Practice 2: MarkschemeDocument17 pagesDP1 Practice 2: MarkschemeaurennosNo ratings yet
- This Content Downloaded From 162.247.5.10 On Tue, 08 Jun 2021 06:50:40 UTCDocument10 pagesThis Content Downloaded From 162.247.5.10 On Tue, 08 Jun 2021 06:50:40 UTCaurennosNo ratings yet
- Displacement and Velocity: ©chris HamperDocument9 pagesDisplacement and Velocity: ©chris HamperParth BhangaleNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Structured 1Document75 pages7.2 Structured 1Anonymous Fspcb0No ratings yet
- 6-7. Solve Problems Using Ratio & ProportionDocument5 pages6-7. Solve Problems Using Ratio & ProportionDaisydonut TVNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 QDocument19 pagesTopic 9 QIndraneel BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 3 TZ1 SL MarkschemeDocument18 pagesPhysics Paper 3 TZ1 SL MarkschemeRita ChtNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Higher Level Paper 2: Instructions To CandidatesDocument24 pagesChemistry Higher Level Paper 2: Instructions To CandidatesAleksander ZiolkowskiNo ratings yet
- Topic - 5.1 - Formative Physics IbDocument2 pagesTopic - 5.1 - Formative Physics Iblogeshraj raja0% (1)
- Specimen Papers 2021 - English PDFDocument122 pagesSpecimen Papers 2021 - English PDFsohamNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Acids and Bases SLDocument11 pagesTopic 8 Acids and Bases SLoscarbec0% (1)
- Four Seasons Leisure: Exam Practice QuestionDocument1 pageFour Seasons Leisure: Exam Practice QuestionLissa MontielNo ratings yet
- Ib Physics SL - Unit 4 ReviewDocument46 pagesIb Physics SL - Unit 4 ReviewMax HudgenesNo ratings yet
- Chem T6 HLQDocument26 pagesChem T6 HLQStefanieNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 3 TZ1 SL PDFDocument24 pagesPhysics Paper 3 TZ1 SL PDFAnonymous G1foKjNo ratings yet
- Physics IADocument2 pagesPhysics IAPriyam SarkarNo ratings yet
- Georgia Tech Civil and Environmental Engineering Annual ReportDocument44 pagesGeorgia Tech Civil and Environmental Engineering Annual ReportjesshuntNo ratings yet
- Aahl1 Unit 7: Further Algebra: Complex Numbers IB Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesAahl1 Unit 7: Further Algebra: Complex Numbers IB Practice ProblemsOrisa THANAJARONo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument44 pagesElectromagnetic InductionEdgardo LeysaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Measurement and Uncertainties - IB PhysicsDocument9 pagesTopic 1 - Measurement and Uncertainties - IB PhysicsAzzahra Yeasmin SaikaNo ratings yet
- Organisation Structure: Activity 12.1 (Page 214) : Penang Valley Cars LTDDocument7 pagesOrganisation Structure: Activity 12.1 (Page 214) : Penang Valley Cars LTDNguyễn QuânNo ratings yet
- Mechanics SLDocument30 pagesMechanics SLMartin DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Vectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsDocument4 pagesVectors Review IB Paper 2 QuestionsJasmine YimNo ratings yet
- Calculus Paper 2Document25 pagesCalculus Paper 2Vincents Genesius EvansNo ratings yet
- 086 - 2004 Nov O Level Physics (5052) P1 P2 - Suggested Answers (PDF Library)Document4 pages086 - 2004 Nov O Level Physics (5052) P1 P2 - Suggested Answers (PDF Library)McDonald Whites JonesNo ratings yet
- AAHL Sample Paper 3 AgnesiDocument2 pagesAAHL Sample Paper 3 Agnesiannaageeva118No ratings yet
- Mathematical Studies Standard Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesDocument24 pagesMathematical Studies Standard Level Paper 1: Instructions To CandidatesDEMNo ratings yet
- Physics Standard Level Paper 2: Instructions To CandidatesDocument20 pagesPhysics Standard Level Paper 2: Instructions To CandidatesKevin HuNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Review - Electrostatics and FieldsDocument7 pagesIB Physics Review - Electrostatics and Fieldsballer5556No ratings yet
- Physics Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument17 pagesPhysics Paper 2 SL MarkschemeYoutube ForoauNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Topic 2-4 Paper 1 ProblemsDocument20 pagesIB Physics Topic 2-4 Paper 1 Problemswonjunlim0819No ratings yet
- IB Chem Energetics HandoutsDocument17 pagesIB Chem Energetics HandoutsNguyenHoangMinhDucNo ratings yet
- Option E - Astrophysics Self Study 10Document9 pagesOption E - Astrophysics Self Study 10sudkNo ratings yet
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Functions)Document17 pages2017 H2 Prelim (Functions)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Paper II - Reading MarkScheme - HLDocument5 pagesPaper II - Reading MarkScheme - HLGulumser MencikNo ratings yet
- Quantum and Nuclear Questions and AnswersDocument43 pagesQuantum and Nuclear Questions and AnswersemilyNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 3 TZ2 SL Markscheme PDFDocument18 pagesPhysics Paper 3 TZ2 SL Markscheme PDFjumanachiNo ratings yet
- Calculus Holiday FunDocument10 pagesCalculus Holiday FunLaislee CirlandeNo ratings yet
- Topic 16 Past Paper Questions 2011Document15 pagesTopic 16 Past Paper Questions 2011nadia sykesNo ratings yet
- Physics HL Paper 1 TZ1Document18 pagesPhysics HL Paper 1 TZ1Rishab ParuchuriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Extension 2: Assessment Task 1Document4 pagesMathematics Extension 2: Assessment Task 1AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Mechanics - IB PhysicsDocument23 pagesTopic 2 - Mechanics - IB PhysicsAzzahra Yeasmin Saika100% (1)
- Analysis and Approaches Standard November 2021 Paper 2 MSDocument20 pagesAnalysis and Approaches Standard November 2021 Paper 2 MSYewah Nzali Guy KyleNo ratings yet
- Topic 5.1 - Electric Fields Formative Assessment NAMEDocument2 pagesTopic 5.1 - Electric Fields Formative Assessment NAMEfelaso9354No ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 3 SLDocument28 pagesChemistry Paper 3 SLsilagulec9No ratings yet
- Linear Regression - 1: Answers Included)Document3 pagesLinear Regression - 1: Answers Included)凛音No ratings yet
- Worksheets On Maxima & Minima (22!09!15)Document1 pageWorksheets On Maxima & Minima (22!09!15)ib elite tutorNo ratings yet
- Markscheme: Trigonometry Worksheet 3 With Mark Scheme (Graphs of Trig. Functions) 1a. (2 Marks)Document11 pagesMarkscheme: Trigonometry Worksheet 3 With Mark Scheme (Graphs of Trig. Functions) 1a. (2 Marks)Ella JonasNo ratings yet
- Galileo's Accelerated Motion Lab PDFDocument3 pagesGalileo's Accelerated Motion Lab PDFGhostlyBot 16No ratings yet
- Wave Practice 2Document24 pagesWave Practice 2Soyoko U.No ratings yet
- 07-Chemical EquilibriumDocument66 pages07-Chemical EquilibriumRiyan FatchurahmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2 HL MarkschemeDocument23 pagesChemistry Paper 2 HL MarkschemeEthan LamNo ratings yet
- Spacimen Paper - 1, 2 and 3 For HL and SL - Analysis and Approaches 1 To 5Document5 pagesSpacimen Paper - 1, 2 and 3 For HL and SL - Analysis and Approaches 1 To 5Mohammad Fazlur Rahman0% (1)
- Theory: Name: Onkar Pardeshi Roll - No: 12 P.R.N: 12011027 Batch-B1Document6 pagesTheory: Name: Onkar Pardeshi Roll - No: 12 P.R.N: 12011027 Batch-B1Onkar BhosleNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 12th SubejctiveDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRY 12th SubejctiveVivek SanwalNo ratings yet
- Final Exam CRIM ADGEDocument9 pagesFinal Exam CRIM ADGEBernard Agcanas FelipeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 and 16 Revision: (104 Marks)Document26 pagesChapter 15 and 16 Revision: (104 Marks)aurennosNo ratings yet
- TOK Exhibition Revisited - 5.6-5.7Document26 pagesTOK Exhibition Revisited - 5.6-5.7aurennosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 and 6 Questions: (58 Marks)Document21 pagesChapter 5 and 6 Questions: (58 Marks)aurennosNo ratings yet
- Rules For Selection For Philosophy, Politics and Economics 2021-2022Document3 pagesRules For Selection For Philosophy, Politics and Economics 2021-2022aurennosNo ratings yet
- Example 21: Gabriel Dawe S Rainbow Coloured Curves-Student WorkDocument12 pagesExample 21: Gabriel Dawe S Rainbow Coloured Curves-Student WorkaurennosNo ratings yet
- English Department Procedures For 2021-22: Student Allocations & TransfersDocument3 pagesEnglish Department Procedures For 2021-22: Student Allocations & TransfersaurennosNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IA TemplateDocument6 pagesChemistry IA TemplateaurennosNo ratings yet
- Sample 3 EE Grade ADocument30 pagesSample 3 EE Grade AaurennosNo ratings yet
- Stage 6 1st Formal Reflection Session: Interpretation of This StageDocument2 pagesStage 6 1st Formal Reflection Session: Interpretation of This StageaurennosNo ratings yet
- Who Voted For The Nazis. GearyDocument5 pagesWho Voted For The Nazis. GearyaurennosNo ratings yet
- Geo Factsheet: An Idiot's Guide To Bid RentDocument2 pagesGeo Factsheet: An Idiot's Guide To Bid RentaurennosNo ratings yet
- (更新)顾瑞2021线上大学游 Updated Virtual TourDocument5 pages(更新)顾瑞2021线上大学游 Updated Virtual TouraurennosNo ratings yet
- Diploma Equivalency ListDocument3 pagesDiploma Equivalency ListaurennosNo ratings yet
- Energetics: To Entropy On Next Page To Spontaneous Reactions On Next PageDocument2 pagesEnergetics: To Entropy On Next Page To Spontaneous Reactions On Next PageaurennosNo ratings yet
- Using The Conjugate Of: 1 (A) (M1) EitherDocument5 pagesUsing The Conjugate Of: 1 (A) (M1) EitheraurennosNo ratings yet
- Maths Example 12 Comm enDocument1 pageMaths Example 12 Comm enaurennosNo ratings yet
- 6.1.2 Collision Theory: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pages6.1.2 Collision Theory: Learning ObjectivesaurennosNo ratings yet
- 6.1.0 Chemical KineticsDocument14 pages6.1.0 Chemical KineticsaurennosNo ratings yet
- The Discovery of The Radical Superoxide: Linus PaulingDocument2 pagesThe Discovery of The Radical Superoxide: Linus PaulingAna-Maria DucuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - UV-Visible Molecular Absorption SpectrophotometryDocument59 pagesChapter 13 - UV-Visible Molecular Absorption SpectrophotometryaNo ratings yet
- Reactions in Aqueous Solutions II: CalculationsDocument39 pagesReactions in Aqueous Solutions II: CalculationsSantiago Gonzalez BogotaNo ratings yet
- US EPA Method 26ADocument13 pagesUS EPA Method 26AputtipongtanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction TableDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction TableKristineNo ratings yet
- Analysis 5 Yrs PaperDocument8 pagesAnalysis 5 Yrs PaperHILAL AHMAD DASSNo ratings yet
- Yanet Becerra - Molecular Polarity PhET LabDocument3 pagesYanet Becerra - Molecular Polarity PhET LabYanet BecerraNo ratings yet
- Proposal On WastewaterDocument6 pagesProposal On WastewaterChukwu SolomonNo ratings yet
- What Is A Mole?: Calculate How Many Molecules Are in 5.5 Moles of Glucose (C H O) ?Document5 pagesWhat Is A Mole?: Calculate How Many Molecules Are in 5.5 Moles of Glucose (C H O) ?Bea Dacillo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Wetting and WettabilityDocument11 pagesWetting and WettabilityDuc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- CH 44 Organic Reactions - Supp Ex 1 (Updated)Document4 pagesCH 44 Organic Reactions - Supp Ex 1 (Updated)伊貝P-No ratings yet
- 〈401〉 FATS AND FIXED OILSDocument13 pages〈401〉 FATS AND FIXED OILSgrace_febiantyNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms in The Deterioration and Preservation of Cultural HeritageDocument364 pagesMicroorganisms in The Deterioration and Preservation of Cultural HeritageCao Minh TríNo ratings yet
- 2. اسید نیتریک ۳۳۳۳۳Document170 pages2. اسید نیتریک ۳۳۳۳۳Ashkan AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Phosphoric Acid (MSDS)Document9 pagesPhosphoric Acid (MSDS)Barry ParkinNo ratings yet
- PPT, Indicator and Acid StrengthDocument20 pagesPPT, Indicator and Acid StrengthZUNINo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Chemistry Salt Analysis 12th CbseDocument5 pagesCheat Sheet Chemistry Salt Analysis 12th CbseHKNo ratings yet
- Disperse Dyes For Polyester Dyeing MethodDocument3 pagesDisperse Dyes For Polyester Dyeing Methodwalter_higginsNo ratings yet
- Energy: SciencedirectDocument8 pagesEnergy: SciencedirectclaudiacarranzafNo ratings yet
- Coll OidsDocument37 pagesColl OidsPoonam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Molygraph-General EngineeringDocument6 pagesMolygraph-General Engineeringkominthitsar7474No ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals Practice PacketDocument22 pagesRocks and Minerals Practice PacketJosé SuárezNo ratings yet
- Symbol of Some Hazardous ChemicalsDocument2 pagesSymbol of Some Hazardous ChemicalsRiza AbdillahNo ratings yet
- PT Ions PDFDocument1 pagePT Ions PDFAdarshNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Chemical EquationsDocument8 pages2.2 Chemical EquationsPBL MOMOSNo ratings yet
- Tirtratable Acidity DanielleDocument7 pagesTirtratable Acidity DanielleDCRUZNo ratings yet
- 1 - Identificación de ProductoDocument7 pages1 - Identificación de ProductoAlexis GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 12 Respiration - CAIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument1 pageDefinitions - Topic 12 Respiration - CAIE Biology IGCSE PDFeric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology (BUFT)Document27 pagesBGMEA University of Fashion & Technology (BUFT)Hassan Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Chem 2 Homework 5Document3 pagesChem 2 Homework 5Albert YanNo ratings yet