Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Superconductivity.: The Meissner Effect
Superconductivity.: The Meissner Effect
Uploaded by
ayush0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views3 pagesSuperconductivity is a phenomenon where certain materials exhibit zero electrical resistance and expel interior magnetic fields when cooled below a critical temperature. This critical temperature is called the critical temperature (Tc). Below this temperature, known as the superconducting transition, the materials become perfect superconductors and exhibit the Meissner effect where they spontaneously expel all magnetic fields. Potential applications of superconductors include more efficient power systems, magnetic propulsion for satellites, high-speed levitating trains, and transmission lines with no current loss.
Original Description:
Original Title
Phy Proj
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSuperconductivity is a phenomenon where certain materials exhibit zero electrical resistance and expel interior magnetic fields when cooled below a critical temperature. This critical temperature is called the critical temperature (Tc). Below this temperature, known as the superconducting transition, the materials become perfect superconductors and exhibit the Meissner effect where they spontaneously expel all magnetic fields. Potential applications of superconductors include more efficient power systems, magnetic propulsion for satellites, high-speed levitating trains, and transmission lines with no current loss.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views3 pagesSuperconductivity.: The Meissner Effect
Superconductivity.: The Meissner Effect
Uploaded by
ayushSuperconductivity is a phenomenon where certain materials exhibit zero electrical resistance and expel interior magnetic fields when cooled below a critical temperature. This critical temperature is called the critical temperature (Tc). Below this temperature, known as the superconducting transition, the materials become perfect superconductors and exhibit the Meissner effect where they spontaneously expel all magnetic fields. Potential applications of superconductors include more efficient power systems, magnetic propulsion for satellites, high-speed levitating trains, and transmission lines with no current loss.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Superconductivity.
What is superconductivity?
Superconductivity is a phenomenon occurring in certain materials
generally at very low temperatures characterized by exactly 0 electrical
resistance and the exclusion of the interior magnetic field
In simple words for some materials the resistivity vanish is at some low
temperature they become superconducting such materials are called
superconductors
The temperature at which electrical resistance is zero is called the Critical
temperature (Tc) .
The cooling of the material can be achieved using liquid nitrogen or liquid
helium for even more lower temperature.
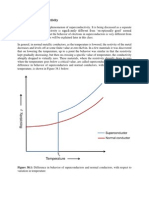
The Meissner Effect
The limit of external magnetic field strength at which a superconductor can
exclude the field is known as the critical field strength, Hc. In 1920
Meissner discovered not only did superconductors exhibit zero resistance
but also spontaneous expel all magnetic flux when cooled through the
superconducting transition , that is they are also perfect dimagnets . We call
this the Meissner effect
Applications
Superconductors form the basis of energy saving power systems,
namely the superconducting generators, smaller in size and weight, in
comparison with conventional generators.
Superconducting magnetic propulsion systems may be used to launch
satellites into orbits directly from the earth without the use of rockets.
Superconducting magnets have been used to levitate trains above its
rails. They can be driven at high speed with minimal expenditure of
energy
Superconducting wire can be used for transmission lines as the
current can flow without any change in magnitude.
You might also like
- Storage Emulated 0 Android Data Com - Cv.docscanner Cache Unit 2Document12 pagesStorage Emulated 0 Android Data Com - Cv.docscanner Cache Unit 2anil23hr1a0547No ratings yet
- Super ConductivityDocument16 pagesSuper Conductivitymanisha.e08No ratings yet
- Uperconductivity: Presented by Thejasree PrabhakaranDocument16 pagesUperconductivity: Presented by Thejasree PrabhakaranThejasreeprabhakaran100% (1)
- SuperconductorDocument33 pagesSuperconductorCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document5 pagesDocument 1Tahira ShujatNo ratings yet
- Nano SuperconductivityDocument26 pagesNano Superconductivity2018 01403No ratings yet
- Active Learning Assignment On: Gandhinagar Institute of TechnologyDocument28 pagesActive Learning Assignment On: Gandhinagar Institute of TechnologyRakesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Super Conductive Materials - 231216 - 163337Document18 pagesSuper Conductive Materials - 231216 - 163337engahmednasser58No ratings yet
- Superconductivity 2Document20 pagesSuperconductivity 2Ritu KlairNo ratings yet
- SuperconductivityDocument25 pagesSuperconductivityyusuf230395bhimaniNo ratings yet
- SUPERCONDUCTIVITYDocument14 pagesSUPERCONDUCTIVITYJeromeDelCastilloNo ratings yet
- WaheguruDocument2 pagesWaheguruAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity: Superconductivity Is A Phenomenon of Exactly ZeroDocument11 pagesSuperconductivity: Superconductivity Is A Phenomenon of Exactly Zero回覧するサティヤムNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Superconductor... NanomaterialsDocument10 pagesUNIT 5 Superconductor... Nanomaterialssantoshdevi9758No ratings yet
- Advanced Morden Solid State Physics 7Document23 pagesAdvanced Morden Solid State Physics 7Edge of ScenesNo ratings yet
- Essay: Undergraduate 1-2Document10 pagesEssay: Undergraduate 1-2FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Essay: Undergraduate 1-2Document10 pagesEssay: Undergraduate 1-2showmelocalNo ratings yet
- CH 16 ScienceDocument2 pagesCH 16 ScienceAditi AllianceNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity and Optical Fibers: Who Can Use This?Document12 pagesSuperconductivity and Optical Fibers: Who Can Use This?rockingjoeNo ratings yet
- Super Conductor2Document4 pagesSuper Conductor2pranavabaascaranNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity: Aqeel A. Al-TaieDocument25 pagesSuperconductivity: Aqeel A. Al-TaieshrutiNo ratings yet
- Prof. Harvinder Kaur Govt College For GirlsDocument15 pagesProf. Harvinder Kaur Govt College For GirlsRaj PaulNo ratings yet
- Superconductors and Applications-2Document20 pagesSuperconductors and Applications-2vismayaprasadvismayaprasadNo ratings yet
- SuperconductivityDocument11 pagesSuperconductivitysurya_220880No ratings yet
- Microwave SuperconductivityDocument23 pagesMicrowave Superconductivityhareesh64kumarNo ratings yet
- Rio Andika Putra - Superkonduktor Tipe IIDocument28 pagesRio Andika Putra - Superkonduktor Tipe IIRio AndikaNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity: Name:Sandeep Kumar Prusty REGD - NO:0801214249Document14 pagesSuperconductivity: Name:Sandeep Kumar Prusty REGD - NO:0801214249Dev KumarNo ratings yet
- SUPERCONDUCTIVITYDocument30 pagesSUPERCONDUCTIVITYgeethikamuraliNo ratings yet
- Superconductors - Properties Technology and ApplicationsDocument448 pagesSuperconductors - Properties Technology and ApplicationsJosé Ramírez100% (1)
- SuperconductivityDocument2 pagesSuperconductivityHafiztayyab AliNo ratings yet
- Chap 4. SuperconductorDocument8 pagesChap 4. SuperconductorAbu Talha TalhaNo ratings yet
- S2634: Physique de La Matière Condensée & Nano-Objets: SuperconductivityDocument24 pagesS2634: Physique de La Matière Condensée & Nano-Objets: SuperconductivityShradhananda GhadeiNo ratings yet
- Institute of Technology and Management: Super ConductorsDocument20 pagesInstitute of Technology and Management: Super ConductorsAkash TripathiNo ratings yet
- Superconductors and SupercapacitorsDocument12 pagesSuperconductors and SupercapacitorsjameshrclassesNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity Referat, Translation NeededDocument7 pagesSuperconductivity Referat, Translation NeededDaria CulaghinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document52 pagesLecture 1Lokendra AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity Research PaperDocument3 pagesSuperconductivity Research PaperHitanshNo ratings yet
- SuperconductivityDocument13 pagesSuperconductivityRachel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- MATERIAL May FinalDocument17 pagesMATERIAL May FinalMajier MakeerNo ratings yet
- Note - Superconductivity 2023Document4 pagesNote - Superconductivity 2023Mani devassyNo ratings yet
- SuperconductorDocument25 pagesSuperconductoranisghaniNo ratings yet
- SuperconductorsDocument11 pagesSuperconductorspranavabaascaran100% (1)
- Ultra ConductorDocument22 pagesUltra Conductoramit patilNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 12A (Lina) PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics Project 12A (Lina) PDFlina atyaniNo ratings yet
- Superconductive MaterialsDocument14 pagesSuperconductive Materials6732771fb7No ratings yet
- Superconductors 31.8.18Document9 pagesSuperconductors 31.8.18BullShit signupNo ratings yet
- 2 SolidstatePhysDocument14 pages2 SolidstatePhysKunal WaghNo ratings yet
- Module V NotesDocument18 pagesModule V NotesSURESH BABU M PhyNo ratings yet
- Super ConductivityDocument26 pagesSuper ConductivityAFTABALI SALIM MAMTULAYNo ratings yet
- Lecture 38Document5 pagesLecture 38Chayon MondalNo ratings yet
- Question & Answer of SuperconducatorDocument9 pagesQuestion & Answer of SuperconducatorSai Printers100% (3)
- Praxis Business SchoolDocument16 pagesPraxis Business SchoolSubhodeep Kumar DeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Superconductivity: 4.2K He Named The New Phenomenon-SuperconductivityDocument28 pagesChapter-3: Superconductivity: 4.2K He Named The New Phenomenon-SuperconductivityberhaneNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity in Bilayer GrapheneDocument5 pagesSuperconductivity in Bilayer GrapheneScience BrainsNo ratings yet
- Superconductive MaterialsDocument14 pagesSuperconductive Materials6732771fb7No ratings yet
- Superconductors TheoryDocument2 pagesSuperconductors Theorykashyap_cherukuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document10 pagesChapter 3aregawi weleabezgiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note EEE 3515 Stenza 8Document7 pagesLecture Note EEE 3515 Stenza 8Farid RahmanNo ratings yet