Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fitt Recommendations For Hypertension - Update
Fitt Recommendations For Hypertension - Update
Uploaded by
shwetaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fitt Recommendations For Hypertension - Update
Fitt Recommendations For Hypertension - Update
Uploaded by
shwetaCopyright:
Available Formats
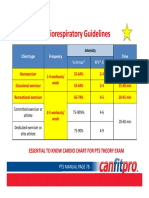
Table.
The New ACSM FITT Recommendations for Hypertension (adapted from 6, 9)
The New ACSM
Aerobic and/or Resistance Neuromotor** Flexibility FITT Exercise
Recommendations
Frequency >2-3 sessions per
week
>2-3 sessions per
week
>2-3 session per week >2-3 sessions per
week with daily being
***On most, preferably
all, days of the week
most effective
Intensity *Moderate (i.e., 40%
- 59% VO2R or HRR;
Moderate (i.e., 60%
- 70% 1-RM; may
Low to Moderate Stretch to the point of
feeling tightness or
Low, Moderate, or
Vigorous with an
RPE 12-13 on a 6–20 progress to 80% slight discomfort emphasis on Moderate
scale to Vigorous (i.e., 1-RM. For older
60% - 80% VO2R or adults and novice
HRR; RPE 14-16 on a exercisers begin with
6–20 scale) 40-50% 1RM)
Time >20-30 min per
session of continuous
2-4 sets of 8-12
repetitions of 8-10
>20-30 min per
session
Hold static stretch
for 10-30 s with 2-4
>20 to 30 min per
day to total >90 to
or accumulated resistance exercises repetitions of each 150+ min per week
exercise of any of each of the major exercise targeting the of continuous or
duration muscle groups per major muscle tendon accumulated exercise
session to total >20 units to total 60 s of of any duration
min per session with total stretching time
rest days interspersed for each exercise; <10
depending on the min per session
muscle groups being
exercised
Type Prolonged, rhythmic
activities using large
Resistance machines,
free weights,
Exercise involving
motor skills and/or
Static, dynamic, and/
or proprioceptive
An emphasis on
aerobic or resistance
muscle groups (e.g., resistance bands, and/ functional body weight neuromuscular exercise alone or
walking, cycling, or functional body and flexibility exercise facilitation combined in addition
swimming) weight exercise such as yoga, pilates, to neuromotor and
and tai chi flexibility depending
on personal preference
VO2R=oxygen uptake reserve; HRR= heart rate reserve; RPE=rating of perceived exertion; 1-RM=one repetition maximum.
* The magnitude of the BP reductions resulting from aerobic exercise are directly proportional to intensity such that the greatest BP reductions
occur after vigorous intensity exercise if the patient/client is willing and able to perform vigorous intensity exercise (4).
** Neuromotor functional body weight exercise can be substituted for resistance exercise, and depending on the amount of flexibility exercise
integrated into a session, neuromotor flexibility exercise can be substituted for flexibility exercise depending on patient/client preference. The
evidence is promising but limited for neuromotor exercise to be recommended alongside aerobic and resistance exercise as a primary exercise
modality at this time (6).
*** The frequency recommendation is made due to the immediate blood pressure lowering effects of exercise, termed
postexercise hypotension (4).
You might also like
- Case Study, Chapter 70, Management of Patients WithOncologic or Degenerative Neurologic DisordersDocument1 pageCase Study, Chapter 70, Management of Patients WithOncologic or Degenerative Neurologic Disordersclyde i am100% (1)
- Jake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersDocument8 pagesJake Yvan Dizon Case Study, Chapter 49, Assessment and Management of Patients With Hepatic DisordersJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPJose CousinsNo ratings yet
- NCP On DyspneaDocument5 pagesNCP On DyspneaDizzy BualanNo ratings yet
- Group 9 Sickle Cell Anemia Case Study ActivityDocument4 pagesGroup 9 Sickle Cell Anemia Case Study ActivityJuliaNo ratings yet
- Date and Time Focus Data Action Response 12/10/21Document2 pagesDate and Time Focus Data Action Response 12/10/21ANGEL AKIRA TORRESNo ratings yet
- Drug PepcidDocument2 pagesDrug PepcidSrkocher0% (1)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityAbdelhafiz SusmiranNo ratings yet
- NCP Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNCP Drug StudyAndrea JoyaNo ratings yet
- NCP For COPDDocument3 pagesNCP For COPDcy belNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Name: Oyardo Cherilyn BED NO.: 408 Attending Physician: DR - Baldovino Diet: Diet As Tolerated Diagnosis: Post-PartumDocument7 pagesName: Oyardo Cherilyn BED NO.: 408 Attending Physician: DR - Baldovino Diet: Diet As Tolerated Diagnosis: Post-PartumshinloNo ratings yet
- NCP ImmobiltyDocument4 pagesNCP ImmobiltyAlizza Therese Severo AnzanoNo ratings yet
- NCP High Risk PregnancyDocument7 pagesNCP High Risk PregnancyRica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- NCP FeverDocument1 pageNCP FeverJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Yayin Ob: - Slightly CompromisedDocument2 pagesYayin Ob: - Slightly CompromisedYayin PestañoNo ratings yet
- Sleep Pattern DisturbanceDocument1 pageSleep Pattern DisturbanceNik Rose ElNo ratings yet
- NCP On Preterm LaborDocument2 pagesNCP On Preterm LaborAngelica Malacay RevilNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesAcute Pain Nursing Care PlanSiafei RabeNo ratings yet
- Exercise Prescription For Health & Fittness For Patients With ObesityDocument1 pageExercise Prescription For Health & Fittness For Patients With ObesityWasemBhatNo ratings yet
- Family Service and Progress Record: Daughter SeptemberDocument29 pagesFamily Service and Progress Record: Daughter SeptemberKathleen Kae Carmona TanNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Related To Faulty Eating Habits As Evidence My Blood Pressure of 13080.Document2 pagesHypertension Related To Faulty Eating Habits As Evidence My Blood Pressure of 13080.Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Code Green Introduction Reviewer - RedDocument4 pagesCode Green Introduction Reviewer - RedJamieNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Community-Health-Survey-11aDocument8 pages2.0 Community-Health-Survey-11aCassey CuregNo ratings yet
- NCP Altered Bowel EleminationDocument2 pagesNCP Altered Bowel EleminationDianna RoseNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing and Allied Medical Sciences: WesleyanPrince Juzzel Banag100% (1)
- Risk For Falls As Evidence by Loss of BalanceDocument4 pagesRisk For Falls As Evidence by Loss of BalanceAlexandrea MayNo ratings yet
- NCP ThoracostomyDocument3 pagesNCP ThoracostomyMark Zedrix MediarioNo ratings yet
- (Original Article) Assessment of The Role of Community Health Volunteers in Delivering Primary Health Care in Manila, The PhilippinesDocument11 pages(Original Article) Assessment of The Role of Community Health Volunteers in Delivering Primary Health Care in Manila, The Philippinesalfeo AlfecheNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument35 pagesCHFNurayunie Abd HalimNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications & Contraindications Side Effects & Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument1 pageDrug Dosage Mechanism of Action Indications & Contraindications Side Effects & Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilityAthena SaturdayNo ratings yet
- NCP - Hygiene and ComfortDocument3 pagesNCP - Hygiene and ComfortJaella EpeNo ratings yet
- Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPDocument7 pagesNgo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCPAMIEL SIMON NGONo ratings yet
- Ncp-Drug Induced-PsychosisDocument3 pagesNcp-Drug Induced-PsychosisMeryville Jacildo100% (1)
- Coma - Types, Causes, Treatments, PrognosisDocument3 pagesComa - Types, Causes, Treatments, PrognosisgcsNo ratings yet
- NCP Hip FractureDocument5 pagesNCP Hip FractureCherry Ann BalagotNo ratings yet
- Guide in Making The FCA 1Document18 pagesGuide in Making The FCA 1Zedrake CaraanNo ratings yet
- Course Task - Traction BARTOLOME, JANIZE KHATEDocument2 pagesCourse Task - Traction BARTOLOME, JANIZE KHATEKhate BartolomeNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument2 pagesNCP FormatGeraldine BirowaNo ratings yet
- NCP AnxietyDocument6 pagesNCP AnxietyRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Case Study No. 1 NCP Fdar Drug Study CompilationDocument8 pagesCase Study No. 1 NCP Fdar Drug Study CompilationRosemarie R. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Circulating Nurse ScriptDocument1 pageCirculating Nurse Scriptmaga.abigail.bsnNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PDFDocument14 pagesDrug Study PDFsretirado02No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsDocument6 pagesNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan PrioritizationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan PrioritizationKASIA SyNo ratings yet
- Rafin NCP and Drug StudyDocument7 pagesRafin NCP and Drug StudyCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN - Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDaniel Andre S. SomorayNo ratings yet
- NCP ReviseDocument7 pagesNCP ReviseRhobic ManansalaNo ratings yet
- EsophagomyotomyDocument3 pagesEsophagomyotomySamVelascoNo ratings yet
- Silliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesDocument8 pagesSilliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesRyan Robert V. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Document10 pagesEctopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Lobectomy and IsthmusectomyDocument12 pagesThyroid Lobectomy and IsthmusectomyAgustina100% (1)
- NCP - Format Spina BifidaDocument2 pagesNCP - Format Spina Bifidaamal abdulrahman100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- RM 11-FM: FITT Principle Guidelines: Fitness And/or Health Benefit Variables F I T TDocument1 pageRM 11-FM: FITT Principle Guidelines: Fitness And/or Health Benefit Variables F I T Tmarielle motelNo ratings yet
- 11 FMDocument1 page11 FMHoniel PagoboNo ratings yet
- Cardio & Resistance Charts ExamDocument2 pagesCardio & Resistance Charts ExamalexNo ratings yet
- Sets F.I.T.T. Goals: Lesson 3Document8 pagesSets F.I.T.T. Goals: Lesson 3JaysonMananquilLabsanNo ratings yet
- First Year Final OSCE EXAM 2018 2019Document4 pagesFirst Year Final OSCE EXAM 2018 2019محمد المنصورNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Study GuideDocument5 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Study Guiderr5633No ratings yet
- Practical Guide and Atlas For The Diagnosis of Fungal InfectionsDocument68 pagesPractical Guide and Atlas For The Diagnosis of Fungal Infectionsasfwegere100% (1)
- Animal Bite GuildlinesDocument7 pagesAnimal Bite GuildlinesHari Pawan Kishore GarimellaNo ratings yet
- Khodayari, 2011Document5 pagesKhodayari, 2011KharismaNisaNo ratings yet
- Difference: Making ADocument24 pagesDifference: Making AlonmtNo ratings yet
- ERAS Quality Symposium Poster 2021Document1 pageERAS Quality Symposium Poster 2021Baptist Memorial Health CareNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Medicine Technician or MedicalDocument2 pagesNuclear Medicine Technician or Medicalapi-79207760No ratings yet
- How To Use This MedicineDocument2 pagesHow To Use This MedicinelelaniaNo ratings yet
- Trauma-Sensitive Yoga - Principles, Practice and ResearchDocument6 pagesTrauma-Sensitive Yoga - Principles, Practice and ResearchRichard Guerra100% (1)
- Community MedicineDocument7 pagesCommunity MedicinePavithra S 1 8 2001No ratings yet
- Product Datasheet: MCM7 Antibody NBP1-85721Document5 pagesProduct Datasheet: MCM7 Antibody NBP1-85721JoaoNo ratings yet
- Post Abortion CareDocument35 pagesPost Abortion CareNatukunda DianahNo ratings yet
- Patient 1 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPatient 1 Drug StudyCharlyn JenselNo ratings yet
- Effect of The Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drop (Ripasudil) On Corneal Endothelial Wound HealingDocument9 pagesEffect of The Rho-Associated Kinase Inhibitor Eye Drop (Ripasudil) On Corneal Endothelial Wound HealingRaúl Plasencia SaliniNo ratings yet
- Siberia Medical TrainDocument1 pageSiberia Medical TrainSantiago CarreñoNo ratings yet
- Ok Ii: DPJP: Dr. Kulsum, SP - An 5 Rencana AnestesiDocument28 pagesOk Ii: DPJP: Dr. Kulsum, SP - An 5 Rencana AnestesiAbrar PoetehNo ratings yet
- Child Health Nursing NotesDocument9 pagesChild Health Nursing NotesBindhu RaniNo ratings yet
- Miniguia de EstudosDocument6 pagesMiniguia de EstudosMaykom LiraNo ratings yet
- MOLINA, CHRISTINE JOY BSN 2B Nursing Informatics Assignment1Document3 pagesMOLINA, CHRISTINE JOY BSN 2B Nursing Informatics Assignment1Christine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Anemia 130809044630 Phpapp01Document21 pagesAnemia 130809044630 Phpapp01Siddharth Das100% (1)
- The Bigger The Bulge The Better - Rayner & Smale PDFDocument4 pagesThe Bigger The Bulge The Better - Rayner & Smale PDFItai IzhakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cystic FibrosisDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Cystic FibrosisMariana DariiNo ratings yet
- Tyrosinemia Type 1Document8 pagesTyrosinemia Type 1Muhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Collagenase For Enzymatic Debridement A.2Document8 pagesCollagenase For Enzymatic Debridement A.2Agung GinanjarNo ratings yet
- MCQ THDocument200 pagesMCQ THarushrushNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic LaparosDocument11 pagesDiagnostic LaparosDr-Shadi MeteirNo ratings yet
- BDS Syllabus Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesBDS Syllabus Lesson PlanDr. Pooja NakumNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer WorksheetDocument3 pagesAlzheimer WorksheetRoberto Queiroz GomesNo ratings yet
- OBAT PrintDocument43 pagesOBAT PrintSelempang RaniNo ratings yet