Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Batch 2017 4th Semester CSE
Batch 2017 4th Semester CSE
Uploaded by
Azeem KhanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Batch 2017 4th Semester CSE
Batch 2017 4th Semester CSE
Uploaded by
Azeem KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
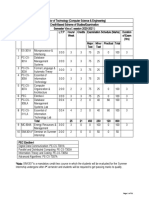
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
4th Semester
Subject Subjec
S.No Subject Name L T P INT EXT Total Cr.
Code t Type
1 Soft Skill TDP-251 DC 0 0 2 60 40 100 1
System Analysis and CST-278
2 DC 2 0 0 40 60 100 2
Design
Database Management CST-279
3 DC 2 0 0 40 60 100 2
Systems
CST-281
4 System Programming DC 3 0 0 40 60 100 3
Microprocessor and CST-282
5 DC 2 0 0 40 60 100 2
interfacing
CST-283
6 Computer Networks DC 3 0 0 40 60 100 3
Microprocessor and CSP-257
7 DC 0 0 2 60 40 100 1
Interfacing Lab
CSP-284
8 Computer Networks Lab DC 0 0 2 60 40 100 1
9 Python Programming Lab CSP-285 DC 0 0 4 60 40 100 2
CSR-260
10 Project PR. 0 0 4 60 40 100 2
Database Management CSP-286
11 DC 0 0 2 60 40 100 1
Systems Lab
CST-287
PROBABILITY & 60
12 DC 3 1 0 40 100 4
STATISTICS
Total 15 1 16 24
Life Skills and Mentoring- UCY-296
13 MNG 0 1 0 0 0 0 0.5
2
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
CHANDIGARH UNIVERSITY
GHARUAN
Syllabus
B.E. (Computer Science & Engineering)
4th Semester
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
4th Semester
Chandigarh University, Gharuan
Database Management Systems L T P C
Subject Code
Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
CST-279/ITT-279
Common to all Specializations of CSE 2nd 2 0 0 2
Year
Marks-100
Internal-40 External-60
Course Objectives
To have good understanding of database system concepts and design databases for
different applications.
To learn how to use a DBMS and RDBMS.
To implement and understand different types of DDL, DML and DCL statements.
To understand transaction concepts related to databases and recovery/backup techniques
required for the proper storage of data.
Unit Course Outcomes
Be familiar with a commercial relational database system (Oracle) by writing SQL
using the system.
I.
Be familiar with the relational database theory, and be able to write relational algebra
expressions for queries
Be familiar with basic database storage structures and access techniques: file and page
II. organizations, indexing methods including B‐tree, and hashing.
III. Be familiar with the basic issues of transaction processing and concurrency control.
Contents of the Syllabus
UNIT-I [15h]
Overview of Databases: Database concepts, DBMS, Data Base System Architecture (Three
Level ANSI-SPARC Architecture), Advantages and Disadvantages of DBMS, Data
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Independence, DBA and Responsibilities of DBA, Relational Data Structure, Keys, Relations,
Attributes, Schema and Instances, Referential integrity, Entity integrity.
Data Models: Relational Model, Network Model, Hierarchical Model, ER Model: Design,
issues, Mapping constraints, ER diagram, Comparison of Models.
Relational Algebra & Relational Calculus: Introduction, Syntax, Semantics, Additional
operators, Grouping and Ungrouping, Relational comparisons, Tuple Calculus, Domain
Calculus, Calculus Vs Algebra, Computational capabilities.
UNIT-II [15h]
Functional dependencies and Normalization: Functional dependencies, Decomposition, Full
Functional Dependency (FFD), Transitive Dependency (TD), Join Dependency (JD), Multi-
valued Dependency (MVD), Normal Forms (1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF), De-normalization.
Database Security: Introduction, Threats, Counter Measures.
Control Structures: Introduction to conditional control, Iterative control and sequential control
statements, Cursors, Views.
UNIT-III [15h]
Package, Procedures and Triggers: Parts of procedures, Parameter modes, Advantages of
procedures, Syntax for creating triggers, Types of triggers, package specification and package
body, developing a package, Bodiless package, Advantages of packages.
Transaction Management and Concurrency Control: Introduction to Transaction Processing,
Properties of Transactions, Serializability and Recoverability, Need for Concurrency Control,
Locking Techniques, Time Stamping Methods, Optimistic Techniques and Granularity of Data
items.
Database Recovery of database: Introduction, Need for Recovery, Types of errors, Recovery
Techniques.
Text Books:
1. Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe, “Fundamentals of Database System”, The
Benjamin / Cummings Publishing Co.
2. Korth and Silberschatz Abraham, “Database System Concepts”, McGraw Hall.
3. Pratt,” DBMS”, Cengage Learning.
Reference Books:
1. C.J.Date, “An Introduction to Database Systems”, Addison Wesley.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
2. Thomas M. Connolly, Carolyn & E. Begg, “Database Systems: A Practical Approach to
Design, Implementation and Management”, 5/E, University of Paisley, Addison-Wesley.
3. Rob,” Database Principal Fundamental Design, Cengage Learning.
Instructions for the paper-setter
Please go through these instructions thoroughly and follow the same pattern while setting the
paper as the students have been prepared according to this format.
Maximum Marks = 60 Time: 3 Hrs
The syllabus has been divided into three equal units. The paper setter is required to set ten
questions in all, three questions from each unit and a compulsory question consisting of five sub
parts and based on the whole syllabus. The candidate will be required to attempt six questions
including the compulsory question number no 1 and not more than two questions from each unit.
Course Code
CST-279/ITT-279 Database Management Systems
Department
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Teaching the Subject
Program Outcome a b c d E f g h i j
Mapping of Course
outcome with I,II,III
Program outcome
BS ES PD PC PE OE Project/Training
Category
X
Approval Date of meeting of the Board of Studies
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Chandigarh University, Gharuan
SYSTEM PROGRAMMING L T P C
Subject Code
Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
CST-281/ITT-281
Common to all Specializations of CSE 2nd 3 0 0 3
Year
Marks-100
Internal-40 External-60
Course Objectives
Design, write, and test moderately complicated low-level programs using a systems
programming language.
Proficiently use a preprocessor to implement code that is portable between different
computing platforms.
Implement routines that read and write structured binary fies such as word processing
documents, index systems, or serialized hierarchical data
Unit Course Outcomes
To understand the execution process of HLL programs.
I.
To understand the working of scanners and parsers
II. To understand the basic design of various system software.
III. To implement various system software.
Contents of the Syllabus
UNIT-I [15h]
Editors: Line editor, Full screen editor and multi window editor. Case study MS-Word, DOS
Editor and vi editor.
Assemblers: First pass and second pass of assembler and their algorithms. Assemblers for CISC
Machines: case study x85 & x86 machines.
.
UNIT-II [15h]
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Compilers: Introduction to various translators, Various phases of compiler, Introduction to
Grammars and finite automata, Bootstrapping for compilers, Lexical Analysis and syntax
analysis, Intermediate Code Generation, Code optimization techniques, Code generation, Case
study :LEXX and YACC, Design of a compiler in C++ as Prototype.
Debuggers: Introduction to various debugging techniques, Case Study: - Debugging in Turbo
C++ IDE.
UNIT-III [15h]
Linkers and Loaders: Concept of linking, Case study of Linker in x86 machines, loading of various loading
schemes.
Operating System: Booting techniques and sub-routines, Design of kernel and various management for OS,
Design of Shell and other utilities.
Text Books:
1. Donovan J.J., Systems Programming, New York, Mc-Graw Hill, 1972.
2. Dhamdhere, D.M., Introduction to Systems Software, Tata Mc-Graw Hill 1996.
3.
Reference Books:
1. Aho A.V. and J.D. Ullman Principles of compiler Design Addison Wesley/ Narosa
1985.
Subject Code
CST-281/ITT-281
SYSTEM PROGRAMMING
Department
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Teaching the Subject
Program Outcome a b c d E f g h i j
Mapping of Course
outcome with Program I,II,III
outcome
BS ES PD PC PE OE Project/Training
Category
X
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
CHANDIGARH UNIVERSITY, GHARUAN
Subject Microprocessors and Interfacing L T P C
Code Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
2 0 0 2
CST- Common to all Specializations of CSE 2rd Year
282/ITT-282
Prerequisite: Studied Computer Architecture & Basics of Computers in Previous
semesters
Marks-100
Internal-40 External-60
Course Objectives
To understand the architecture, components, flags and instruction set of 8085 and 8086.
To design interfacing circuits using 8085 and 8086.
To gain familiarity with 8255(PPI), 8253(Programmable interval timer), 8259 ( PIC),
8237(DMA) and advanced microprocessor chips.
Unit Course Outcome
Identify the basic element and functions of microprocessor.
I Describe the architecture of microprocessor and its peripheral devices.
Demonstrate fundamental understanding on the operation between the
II microprocessor and its interfacing devices.
Apply the programming techniques in developing the assembly language
III program for microprocessor application.
Contents of the Syllabus
Unit-I [15h]
Introduction: Review of Hardwired Logic v/s Flexible Logic, Tri State Logic. Introduction to
microprocessor, Difference between microprocessor and microcomputer, Basic components of a
microprocessor, system bus: address, data and control buses.
8085 microprocessor: Architecture, pin diagram, flags, addressing modes, instruction set and
assembly language programming, timing diagrams, interrupt structure of 8085.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Memory Interfacing: Interfacing memory- Interfacing SRAM, DRAM, EPROM etc.
Unit-II [15h]
Interfacing devices:
Architecture, Block Diagram, Control words, Modes and working of 8255.
Architecture, Block Diagram and working of8251
Architecture, Block Diagram and working of 8253
Architecture, Block Diagram and working of 8259
Architecture, Block Diagram and working of 8237
Unit-III [15h]
8086 Microprocessor: Architecture, block diagram and pin diagram of 8086, operating modes
of 8086, details of sub-blocks such as EU, BIU; memory segmentation and physical address
computations, program relocation, addressing modes.
Advanced microprocessors: Introduction to 80186, 80286, 80386, 80486, Pentium
microprocessors.
Text Books:
1. Gaonkar, Ramesh S., “Microprocessor Architecture, Programming & Applications with
8085”, Wiley Eastern Ltd.
2. Ayala, “The 8086 Microprocessor: Programming & Interfacing the PC” , Cengage
Learning.
3. Bhurchandi, K.M, Ray, A.K, “Advanced microprocessors and peripherals”, TMH.
Reference Books:
1. Brey, “The Intel Microprocessors 8086- Pentium processor”, PHI.
2. Triebel and Singh, Avtar, “The 8088 & 8086 Microprocessors-Programming,
interfacing, Hardware & Applications”, PHI
3. Liu, Yu-Chang &Gibson, Glenn A, “Microcomputer systems: The 8086/8088 Family:
architecture, Programming & Design”, PHI.
4. Antonakos, James L., “The Pentium processor”, Pearson.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
CST-282/ITT-282
Microprocessors and Interfacing
Department Teaching
Department of CSE
the Subject
a b c d e f g h i j k
Program Outcome
Mapping of Course
outcome with Program
outcome
Project/
BS ES PD PC PE OE
Category Training
Approval Date of meeting of the Board of Studies……..
Instructions for the Paper-Setter
Please go through these instructions thoroughly and follow the same pattern while setting the
paper as the students have been prepared according to this format.
Maximum Marks = 60 Time: 3 Hrs
Weight age per unit = 20 marks (excluding over attempt weight age)
1. Question Paper will consist of ten questions.
2. Section A of question paper is compulsory, containing five parts each of 2 marks covering the
whole syllabus (short answer type- total 10 marks)
3. Set three questions from each unit I, II and III. Students will attempt 5 questions selecting at
least one question from sections B, C & D. Each question carries 10 marks. Questions of Section
B will be from unit I, Questions of Section C from unit II and Questions of section D from unit
III.
4. In the question paper, distribution of the questions should be by considering 30 % numerical
part and 70 % conceptual.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Chandigarh University, Gharuan
Subject Code Computer Networks L T P C
CST- Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
283/ITT-283 3 0 0 3
Common to all Specializations of CSE 2nd Year
Marks-100
Internal-40 External-60
Course Objectives
To understand Data Communication , it’s components & network types
To understand and Compare models, signals, multiplexing, switching & transmission
media.
Unit Course Outcome
Successfully participate in higher level Data Communication and Networking
classes
I.
Troubleshoot simple Data Communication problems
Design moderately complex networks using appropriate network architectures and
II. hardware
III. To understand various network terminologies.
Contents of the Syllabus
UNIT-I [15h]
Introduction: Introduction to network, types of transmission technologies, Network Categories:
LAN, MAN, WAN (Wireless /Wired), Network Software: Concept of Layers, Protocols,
interfaces and services. Reference Models: OSI, TCP/IP and comparison.
Physical Layer: Bit rate, Baud rate, Bandwidth, Transmission Impairments: Attenuation,
Distortion, Noise; Data rate limits: Nyquist formula, Shannon Formula, Modulation & modems;
Transmission Modes, Multiplexing: Frequency Division, Time Division, Wavelength Division;
Concept of Topologies, Transmission Media: Twisted pair, coaxial, fiber optics, Wireless
Transmission (radio, microwave & infrared);Message switching, Circuit Switching & Packet
Switching.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
UNIT-II [15h]
Data Link Layer: Design issues, Error Detection & Correction; Flow control & Error Control;
Sliding Window Protocols, ARQ: Stop & Wait , Go Back n, Selective Repeat ; Examples of
DLL protocols – HDLC, PPP; Medium Access Sub layer: Channel Allocation; Random Access:
ALOHA, CSMA protocols; Controlled Access: Polling, Reservation, Token Passing; Examples
of IEEE 802.2,802.3,802.4, 802.5,802.11 standards.
Network Layer: Design issues, Logical Addressing: IPv4 & IPv6; Packet Formats & their
comparison IPv4 & IPv6; Routing Algorithms: Distance Vector, Link State, Hierarchical, Super
netting and sub Netting; Congestion Control: Principles of congestion control; Congestion
prevention policies, Leaky bucket & Token Bucket Algorithms.
UNIT-III [15h]
Transport Layer: Services provided to upper layers, Elements of Transport protocols.
Addressing, Flow Control & buffering; Example Transport protocols: TCP, SCTCP & UDP.
Application Layer: Network security, Domain Name System, Simple Network Management
Protocol, Electronic Mail, World Wide Web.
Text Books:
1. Forouzan, Behrouz A.: “Data Communications & networking”, 4th edition TataMcgraw
Hill.
2. Tanenbaum, Andrew S: “Computer networks”, 4th Edition, Pearson education.
Reference Books:
1. Stallings, William : “Data and computer communications”, 8th edition,Pearson
Education.
2. Ross, Kurose,“Computer Networking: A top down Approach”, 2nd edition, Pearson
Education.
3. Coomer,Douglas E.: “Internet working with TCP/IP” , 2 nd edition, Pearson Education
4. Dave ,” Computer Networks, Cengage Learning.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Course Code-
CST-283/ITT-283 Computer Networks
Department
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Teaching the Subject
Program Outcome a b c d E f g h i j
Mapping of Course
outcome with I,II,III
Program outcome
BS ES PD PC PE OE Project/Training
Category
X
Approval Date of meeting of the Board of Studies
Instructions for the paper-setter
Please go through these instructions thoroughly and follow the same pattern while setting the
paper as the students have been prepared according to this format.
Maximum Marks = 60 Time: 3 Hrs
The syllabus has been divided into three equal units. The paper setter is required to set ten
questions in all, three questions from each unit and a compulsory question consisting of five sub
parts and based on the whole syllabus. The candidate will be required to attempt six questions
including the compulsory question number no 1 and not more than two questions from each unit.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Chandigarh University, Gharuan
Scheme PROBABILITY & STATISTICS L T P C
Version 2018- Applicable to branches (CSE/IT/EE/ECE/CSE Hons)
19 3 1 0 4
(2nd semester)
Subject Code Prerequisite: Knowledge of Mathematics up to senior
Total hours =45
CST-287/ITT- secondary level.
287
Objectives
The objective of this course is to familiarize the students with statistical
techniques.
It aims to equip the students with standard concepts and tools at an
intermediate to advanced level that will serve them well towards tackling
various problems in the discipline.
Subject Outcome
Students will be able to understand
The ideas of probability and random variables and various discrete and
1
continuous probability distributions and their properties.
The basic ideas of statistics including measures of central tendency,
2
correlation and regression.
3 The statistical methods of studying data samples
The content of the Syllabus
Unit-I
Basic Statistics:
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Measures of Central tendency: Moments, skewness and Kurtosis – Random Variable : Discrete and
Continuous.Probability distributions: Binomial, Poisson and Normal - evaluation of statistical parameters
for these three distributions.
[15H]
Unit-II
Applied Statistics:
Curve fitting by the method of least squares- fitting of straight lines, second degree Parabola and more
general curves. Test of significance: Large sample test for single proportion, difference of proportions,
single mean, difference of means, and difference of standard deviations.
[15H]
Unit-III
Bivariate Distributions:
Bivariate distributions and their properties, distribution of sums and quotients, conditional densities,
Bayes' rule.
Correlation and regression – Rank correlation.
Small samples:
Test for single mean, difference of means and correlation coefficients, test for ratio of variances - Chi-
square test for goodness of fit and independence of attributes.
[15H]
TEXT BOOKS
1. H.K Dass., Higher Engineering Mathematics, S. Chand Publishers, 3rd revised edition .2014.
2. B.S.Grewal, Higher Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publishers, 42th ed.2013, New Delhi.
3. N.P. Bali and Manish Goyal, A text book of Engineering Mathematics, Laxmi Publications, Reprint,
2008.
Reference Material:
1. R.K. Jain, and S.R.K. lyengar,Advanced Engineering Mathematics, 3rd Edition Narosa Publishing
House, 2004, New Delhi.
2. B.V. Ramana Advanced Engineering Mathematics, McGraw Hill, July 2006, New Delhi.
3. S.P. Gupta, Statistical Methods, S. Chand & Sons, 2017, New Delhi, ISBN 9789351610281
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
The Students outcomes are:
a) An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, and engineering.
b) An ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data.
c) An ability to design a system, component or process to meet desired needs within realistic
constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety,
manufacturability, and sustainability.
d) An ability to function on multidisciplinary teams.
e) An ability to identify, formulates, and solves engineering problems.
f) An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility.
g) An ability to communication effectively.
h) The board education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in global,
economic, environmental, and societal context.
i) Recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning.
j) Knowledge of contemporary issues.
k) An ability to use the techniques skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering
practice
Subject outcome
Subject
a b c d e f g h i j k
Outcome
Subject
mapping
√
S.nit
I,II,III I,II,III I,II,III I,II,III I,II,III
Mapping UC B/F DC DE UO MNG
HONS PROJEC BW PRACTICAL TRAINING SEMINAR
Category T
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Instructions for the paper-setter:
Please go through these instructions thoroughly and follow the same pattern while
setting the paper as the students have been prepared according to this format.
Maximum Marks= 60 Time: 3 Hours
Weightage per unit = 20 marks (excluding over attempt weightage)
1. Question Paper will consist of ten questions.
2. Section A of question paper is compulsory, containing five parts each of 2 marks covering the
whole syllabus (total 10 marks)
3. Section B, C, D contains 9 questions in total, 3 from each Unit I, II, III respectively.
Attempt any five questions from Section B, C, D taking at least one question from each
section but not more than two questions from Section-B, C, D. (Total 50 marks).
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
CHANDIGARH UNIVERSITY, GHARUAN
Subject Code Microprocessors & Interfacing Lab L T P C
CSP-257/ITP- Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
0 0 2 1
257 Common to all Specializations of CSE 3rd Year
Prerequisite: Studied Computer Architecture & Basics of Computers
Marks-100
Internal-60 External-40
Course Objectives
To get familiarization with 8085 kit and simulator.
To implement basic programs using 8085 kit/simulator.
Unit Course Outcomes
learn how the hardware and software components of a microprocessor-
based system work together to implement system-level features;
I learn both hardware and software aspects of integrating digital devices
(such as memory and I/O interfaces) into microprocessor-based systems;
learn the operating principles of, and gain hands-on experience with,
common microprocessor peripherals such as UARTs, timers, and analog-
II
to-digital and digital-to-analog converters;
Get practical experience in applied digital logic design and assembly-
III language programming.
List of Experiments
UNIT-I
1. To study 8085-microprocessor trainer kit.
2. Addition of two 8-bit numbers; sum 8 bits
3. Addition of two 16 bit number; sum 16- bits.
4. Subtraction of two 8-bit numbers; result 8 bits.
5. Subtraction of two-16 bit numbers; sum 16 bits.
UNIT-II
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
6. Find one’s complement of an 8-bit number.
7. Find one’s complement of a 16-bit number.
8. Find two’s complement of a 8-bit number.
9. Find two’s complement of a 16- bit number.
10. Shift an 8 -bit number to left by 1- bit.
11. Shift an 8-bit number to left by 2-bits.
12. Shift a 16 -bit number to left by 1- bit.
13. Shift a 16-bit number to left by 2- bits.
UNIT-III
14. Mask of least significant 4 bits of an 8-bit number.
15. Mask of most significant 4 bits of an 8-bit number.
16. Find the smaller out of two numbers.
17. Find the smaller number in a data array
18. Find the larger out of two numbers.
19. Find the largest number from data array.
Subject Code
CSP-257/ITP-257 Microprocessors & Interfacing Lab
Department Teaching
Department of CSE
the Subject
a b c d e f g h i j k
Program Outcome
Mapping of Course
outcome with Program
outcome
Project/
BS ES PD PC PE OE
Category Training
Approval Date of meeting of the Board of Studies……..
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
CHANDIGARH UNIVERSITY, GHARUAN
Computer Network Lab L T P C
Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
Subject Code
Common to all Specializations of CSE 2nd 0 0 2 1
CSP-284/ITP-284
Year
Prerequisite: Studied C/C++ in previous semesters
Marks-100
Internal-60 External-40
Course Objectives
To understand Computer Hardware and networking.
Unit Course Outcomes
Understand the structure and organization of computer networks; including the division
into network layers
I.
Understand the basic concepts of application layer protocol design; including
client/server models
Understand the basic concepts of link layer properties; including error-detection and
II. correction techniques
III. Understand the basic concepts of network security concepts; including authentication
List of Experiments
UNIT I
1. Familiarization with Computer Hardware & write specifications of latest desktops and laptops.
2. Installation Process of various operating systems.
3. Study of LAN Components.
UNIT-II
4. Preparing straight and cross cables.
5. Familiarization with transmission media viz. coaxial cable, twisted pairs, optical fibre
networking, wireless networking, connectors etc.
6. Creation of different topologies.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
UNIT III
7. Sharing of resources with two connected nodes.
8. Configuration of TCP/IP Protocols.
9. Network troubleshooting.
Subject Code
CSP-284/ITP-284 Computer Network Lab
Department
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Teaching the Subject
Program Outcome a b c d E f g h i j
Mapping of Course
outcome with I,II,III
Program outcome
BS ES PD PC PE OE Project/Training
Category
X
Approval Date of meeting of the Board of Studies
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
CHANDIGARH UNIVERSITY, GHARUAN
Python Programming - Lab L T P C
Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
Subject Code Common to all Specializations of CSE 2nd 0 0 4 2
CSP-285/ITP-285 Year
Marks-100
Internal-60 External-40
Course Objectives
To understand the concepts of object oriented and develop these skills using Python
Programming.
To be able to work on projects using File Handling.
Unit Course Outcomes
I. Knowledge of the structure and model of the Python programming language
Use the Java programming language for various programming technologies
II.
III. Develop software in the Java programming language, (application) .
List of Experiments
UNIT I
1. Writing python programs in various modes and printing and assigning values assigned to the
variables.
2. Program to demonstrate the use of if, if-else, while, for, break and continue
3. Program to demonstrate the use o functions and passing different types of arguments to
functions.
UNIT II
4. Program to demonstrate the various kind of operations that can be applied to the string.
5. Program to demonstrate creation and accessing of lists and apply different kinds of operations
on them.
6. Program to demonstrate creation and accessing of dictionary and apply different kinds of
operations on them.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
7. Program to demonstrate creation and accessing of tuples and apply different kinds of
operations on them.
8. Program to implement various kinds of searching and sorting algorithms
UNIT III
9. Program to implement concepts of Object Oriented Programming such as classes, inheritance
and polymorphism.
10. Program to demonstrate read and write data to the file in various modes.
Subject Code
CSP-285/ITP-285 Python Programming - Lab
Department
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Teaching the Subject
Program Outcome a b c d E f g h i j
Mapping of Course
outcome with I,II,III
Program outcome
BS ES PD PC PE OE Project/Training
Category
X
Approval Date of meeting of the Board of Studies
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
CHANDIGARH UNIVERSITY, GHARUAN
Database Management Systems Lab L T P C
Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
Subject Code
Common to all Specializations of CSE 0 0 2 1
CSP-286/ITP-286
2nd Year
Prerequisite: Studied C/C++ in previous semesters
Marks-100
Internal-60 External-40
Course Objectives
To enable students to retrieve and update data from relational databases.
To implement programs using procedural language structure.
To have good understanding of implementation and use of cursors, procedures,
packages, triggers etc.
Unit Course Outcomes
Brief knowledge about SQL Fundamentals.
I.
Unary & Binary table operations.
II. Able to handle with different Data Base languages.
III. Table View, Log & Triggers.
List of Experiments
UNIT-I
1. To implement different types of DDL, DML, DCL queries.
2. To explore “SELECT” clause using where, order by, between, like, group by, having etc.
UNIT-II
3. Introduction and implementation of programs using
a. Block Structure and Variables
b. To write programs using control structures of
i. If-else statements.
c. To write programs using loops like
i. For
ii. Do-while
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
iii. while
d. Cursors
e. Views
UNIT-III
4. Introduction and implementation of programs of
a. Procedures
b. Packages
c. Triggers
Subject Code
CSP-286/ITP-286 Database Management Systems Lab
Department
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Teaching the Subject
Program Outcome a b c d E f g h i j
Mapping of Course
outcome with I,II,III
Program outcome
BS ES PD PC PE OE Project/Training
Category
X
Approval Date of meeting of the Board of Studies
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Subject Code System Analysis and Design L T P C
CST-278/ITT-278 Total Contact Hours : 45Hours
2 0 0 2
nd
Common to all Specializations of CSE 2 Year
Marks-100
Internal-40 External-60
Course Objectives
To understand to provide a solid foundation of systems principles
To understand how business function, while heightening students to the issues
analysts face daily.
Unit Course Outcome
Be familiar with how to specify the requirement of the system
I
II Be familiar with design system components and environment
Be familiar with how to design database for data storage and a user interface
III for data input and output, as well as controls to protect the system and its
data
Contents of the Syllabus
UNIT-I [15h]
System definition and concepts: Characteristics and types of system, Manual and automated
Systems, Real-life Business sub-systems: Production, Marketing, Personal, Material,
Finance, Systems models types of models: Systems environment and boundaries, Real-time
and distributed systems, Basic principles of successful systems.
Systems analyst :Role and need of systems analyst ,Qualifications and responsibilities
,Systems Analyst as an agent of change, Introduction to systems development life cycle
(SDLC), Various phases of development :Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation,
Maintenance
Systems documentation considerations: Principles of systems documentation, Types of
documentation and their importance, enforcing documentation discipline in an organization.
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
UNIT-II [15h]
System Planning: Data and fact gathering techniques: Interviews, Group communication,
Presentations, Site visits, Feasibility study and its importance, Types of feasibility reports,
System Selection plan and proposal Prototyping, Cost-Benefit and analysis: Tools and
techniques
Systems Design and modeling: Process modeling, Logical and physical design, Design
representation, Systems flowcharts and structured charts, Data flow diagrams, Common
diagramming conventions and guidelines using DFD and ERD diagrams. Data Modeling and
systems analysis, designing the internals: Program and Process design, Designing Distributed
Systems.
Input and Output: Classification of forms: Input/output forms design, User-interface
design, Graphical interfaces
UNIT-III [15h]
System Implementation and Maintenance: Planning considerations, Conversion methods,
producers and controls, System acceptance Criteria, System evaluation and performance,
Testing and validation, Systems qualify Control and assurance, Maintenance activities and
issues.
System Audit and Security: Computer system as an expensive resource: Data and Strong
media, Procedures and norms for utilization of computer equipment, Audit of computer
system usage, Audit trails, Types of threats to computer system and control measures: Threat
to computer system and control measures, Disaster recovery and contingency planning
Object Oriented Analysis and design: Introduction to Object Oriented Analysis and design
life cycle, object modeling: Class Diagrams, Dynamic modeling: state diagram, Dynamic
modeling: sequence diagramming.
Text Books:
1. Elias M.Awad ” Systems Analysis and Design” 2nd Edition Galgotia Publications.
Reference Books:
1. Perry Edwards “System analysis and design “
2. James A.Senn “Analysis and design of information systems “
Instructions for the paper-setter
University Institute of Engineering
Department of Computer Science & Engineering
Please go through these instructions thoroughly and follow the same pattern while setting
the paper as the students have been prepared according to this format.
Maximum Marks = 60 Time: 3 Hrs
The syllabus has been divided into three equal units. The paper setter is required to set
ten questions in all, three questions from each unit and a compulsory question consisting
of five sub parts and based on the whole syllabus. The candidate will be required to
attempt six questions including the compulsory question number no 1 and not more than
two questions from each unit.
Course Code
CST-278/ITT-278 System Analysis and Design
Department
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Teaching the Subject
Program Outcome a b c d E f g h i j
Mapping of Course
outcome with I,II,III
Program outcome
BS ES PD PC PE OE Project/Training
Category
X
Approval Date of meeting of the Board of Studies
University Institute of Engineering
You might also like
- CENTRALIGN Utra Standard Operating Handbook ALI 9 849 02 12 en WebversionDocument44 pagesCENTRALIGN Utra Standard Operating Handbook ALI 9 849 02 12 en WebversionCésar Rodrigo Puentes ArriagadaNo ratings yet
- Scheme & Syllabus: Be Cse Batch 2018 - 2022Document23 pagesScheme & Syllabus: Be Cse Batch 2018 - 2022Ritik GoyalNo ratings yet
- SOP For LabsolutionDocument6 pagesSOP For Labsolutionmsr_roni83% (6)
- Scheme& Syllabus IOT (CS207) - 1Document26 pagesScheme& Syllabus IOT (CS207) - 1Břïjëšh PinderNo ratings yet
- BE CSE 5th Semester Batch 2017Document32 pagesBE CSE 5th Semester Batch 2017Ritik GoyalNo ratings yet
- 3rd YEARDocument31 pages3rd YEARAD THE GR8No ratings yet
- BTECH CSE 5th 6th Sem 2020 21Document29 pagesBTECH CSE 5th 6th Sem 2020 21Rahul GoyalNo ratings yet
- KUK CSE 3rd Yr - SYDocument30 pagesKUK CSE 3rd Yr - SYsanchit1222368No ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology, RaipurDocument11 pagesNational Institute of Technology, RaipurAjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Cse - 3rd Sem SyllabusDocument51 pagesCse - 3rd Sem SyllabusVikasNo ratings yet
- CSE 3yr Syllabus 240920Document40 pagesCSE 3yr Syllabus 240920RekhasreeGoneNo ratings yet
- BCA Sem-II SyllabusDocument16 pagesBCA Sem-II SyllabusDivyanshuNo ratings yet
- R18B Tech CSE (SoftwareEngineering) IIYearSyllabus1Document34 pagesR18B Tech CSE (SoftwareEngineering) IIYearSyllabus1David JesusNo ratings yet
- R18 B.TECH CSE II Year Syllabus PDFDocument33 pagesR18 B.TECH CSE II Year Syllabus PDFHemima RachelNo ratings yet
- CSD - III & IV Sem MR-21 SyllabusDocument48 pagesCSD - III & IV Sem MR-21 SyllabusrishaNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem SyllabusDocument10 pages5th Sem SyllabusdMAX GamingNo ratings yet
- AIML 2022 23 PEOs PSOs III and IV Sem SyllabusDocument36 pagesAIML 2022 23 PEOs PSOs III and IV Sem SyllabusRam babuNo ratings yet
- Batch 2017 3rd Semester CSEDocument27 pagesBatch 2017 3rd Semester CSEAnkur GiriNo ratings yet
- Diploma CS III SEMDocument18 pagesDiploma CS III SEMManik SinghNo ratings yet
- BSC CBCS Computer-ScienceDocument21 pagesBSC CBCS Computer-Scienceaniruddha shimpaleNo ratings yet
- R18B Tech CSE (CyberSecurity) IIYearSyllabusDocument34 pagesR18B Tech CSE (CyberSecurity) IIYearSyllabusFareedNo ratings yet
- 4thyearsyllabuslucknowuniversityDocument25 pages4thyearsyllabuslucknowuniversitySuryansh MishraNo ratings yet
- R18 B.Tech 3-2 CSE SyllabusDocument26 pagesR18 B.Tech 3-2 CSE SyllabusNishanth NishiNo ratings yet
- R18 B.TECH CSE II Year SyllabusDocument33 pagesR18 B.TECH CSE II Year SyllabusDivyaThalankiVenkataNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 3Document63 pagesSyllabus 3Nikita SaxenaNo ratings yet
- 25th August MCA New First Year Syllabus 2020Document24 pages25th August MCA New First Year Syllabus 2020Satyarth PundirNo ratings yet
- Info Tech V SEM 2023-24Document13 pagesInfo Tech V SEM 2023-24Maximus AranhaNo ratings yet
- Dept Elective MTECH - EC - VLSI - EVEN 2023Document13 pagesDept Elective MTECH - EC - VLSI - EVEN 2023Amit TufaniNo ratings yet
- B.Tech CSE 3 4 Semester Session 2021-22 Scheme SyllabusDocument28 pagesB.Tech CSE 3 4 Semester Session 2021-22 Scheme SyllabusDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Cbcs III IV 27.09.19Document51 pagesSyllabus Cbcs III IV 27.09.19हर्ष सौदर्शनNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer Science & Engg: Principles of Artificial IntelligenceDocument5 pagesDepartment of Computer Science & Engg: Principles of Artificial IntelligenceAditya ShankerNo ratings yet
- IT Syllabus SASTRA 2019 OnwardsDocument40 pagesIT Syllabus SASTRA 2019 OnwardsstarNo ratings yet
- R18B Tech CSE (Networks) IIYearSyllabus1Document34 pagesR18B Tech CSE (Networks) IIYearSyllabus1kethavath srinuNo ratings yet
- 3 Sem Mtech Cad Cam MpccetDocument5 pages3 Sem Mtech Cad Cam MpccetEL-Sayed HamedNo ratings yet
- Ladoke Akintola University of Technology, OgbomosoDocument9 pagesLadoke Akintola University of Technology, OgbomosoJames JacklynNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Technology CseDocument8 pagesBachelor of Technology CseNaveen Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- R18B Tech CSE (IoT) IIYearSyllabus1Document34 pagesR18B Tech CSE (IoT) IIYearSyllabus1Kedar KedarNo ratings yet
- Computer Science & Engineering-4th Sem 2020-21 B.tech. CSEDocument11 pagesComputer Science & Engineering-4th Sem 2020-21 B.tech. CSEbeastboy00077No ratings yet
- 4th Sem SyllabusDocument10 pages4th Sem SyllabusAdil Hassan Mir 8720105No ratings yet
- BCA 2 Year Syllabus-1Document21 pagesBCA 2 Year Syllabus-1Anuj ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Mca - Semester System - 3 Years - CbcegsDocument44 pagesMca - Semester System - 3 Years - CbcegsKaranvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Punjab Technical University: Scheme & Syllabus of B. Tech. Computer Science & Engineering (CSE)Document57 pagesPunjab Technical University: Scheme & Syllabus of B. Tech. Computer Science & Engineering (CSE)nehachoudhryNo ratings yet
- MCA First Year SyllabusDocument24 pagesMCA First Year Syllabusdixitachal284No ratings yet
- Evaluation Scheme & Syllabus For B. Tech. Third Year (Information Technology)Document22 pagesEvaluation Scheme & Syllabus For B. Tech. Third Year (Information Technology)Lion YtNo ratings yet
- Sem 320Document14 pagesSem 320sg7365818621No ratings yet
- Btech 4th Sem SyllabusDocument14 pagesBtech 4th Sem Syllabusramandubey69No ratings yet
- BoS Circular-12.03.2024Document2 pagesBoS Circular-12.03.2024chidambaram SNo ratings yet
- IIT SyllabusDocument20 pagesIIT Syllabusritesh_necNo ratings yet
- CSE 4 NotesDocument22 pagesCSE 4 NotesCSE SSGINo ratings yet
- Big DataDocument28 pagesBig DatajaijohnkNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. (IT) FIRST YEAR (SEMESTER I & II) 2020-21 AND 2021-22Document23 pagesM.Sc. (IT) FIRST YEAR (SEMESTER I & II) 2020-21 AND 2021-22Harmanpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Batch 2018 3rd Semester CSEDocument20 pagesBatch 2018 3rd Semester CSERitik GoyalNo ratings yet
- Shri Ramdeobaba College of Engineering and Management, NAGPUR - 440013Document94 pagesShri Ramdeobaba College of Engineering and Management, NAGPUR - 440013NABEEL KHANNo ratings yet
- B.tech r20 III Year Cse Syllabus Final WsDocument52 pagesB.tech r20 III Year Cse Syllabus Final Wsgnaneshgnani16662No ratings yet
- MCA _SyllabusDocument25 pagesMCA _SyllabusphaimlNo ratings yet
- MSD Bos CseDocument40 pagesMSD Bos Csepravin2mNo ratings yet
- MCA Two Years 1st Year K Series Syllabus EFS 2020 21Document24 pagesMCA Two Years 1st Year K Series Syllabus EFS 2020 21kimog66911No ratings yet
- Unit3 - AMIT YADAV COADocument89 pagesUnit3 - AMIT YADAV COAmayankrajput13626No ratings yet
- Cse - 5thDocument46 pagesCse - 5thSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- IV Sem - SchemeDocument2 pagesIV Sem - SchemeAMNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Quantum Computing & Machine Learning Technologies: 1, #1From EverandIntroduction to Quantum Computing & Machine Learning Technologies: 1, #1No ratings yet
- DBMS Module-IVDocument9 pagesDBMS Module-IVSivaNo ratings yet
- Libra II Release Notes V 2.1.20Document6 pagesLibra II Release Notes V 2.1.20Bryan NadimpallyNo ratings yet
- And Hadoop: Integration of Data and AnalyticsDocument7 pagesAnd Hadoop: Integration of Data and AnalyticsrsearchNo ratings yet
- 9775c Bistro2 - Service Manual PDFDocument47 pages9775c Bistro2 - Service Manual PDFdanielradu27No ratings yet
- All in One Cracking Guide PDocument88 pagesAll in One Cracking Guide Pacermichel3No ratings yet
- Paul Wachira: Calculus IiiDocument50 pagesPaul Wachira: Calculus IiiBrian NyagaNo ratings yet
- q2 Week 2 Arts 10 Activities 1Document11 pagesq2 Week 2 Arts 10 Activities 1SalomeNo ratings yet
- Game Exploratorium Rapid RouterDocument14 pagesGame Exploratorium Rapid Routerapi-678195305No ratings yet
- Cancer Treatment Healthcare Center by SlidesgoDocument50 pagesCancer Treatment Healthcare Center by SlidesgotaridaNo ratings yet
- C vs. C++ Programming Under VxworksDocument24 pagesC vs. C++ Programming Under VxworksjackNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Abdullah CH: Carrier ObjectiveDocument3 pagesMuhammad Abdullah CH: Carrier ObjectiveAbdullah ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- New Media Module HandbookDocument17 pagesNew Media Module HandbookMelvin SalibaNo ratings yet
- Service - Connect 607Document82 pagesService - Connect 607Sherin SalimNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rates For Everyone EbookDocument10 pagesExchange Rates For Everyone EbookmovizepNo ratings yet
- NA Contemporary Part 6 GuideDocument7 pagesNA Contemporary Part 6 GuidekooloNo ratings yet
- ICT Grade 11-ExamDocument10 pagesICT Grade 11-ExamEndash HaileNo ratings yet
- Developing A Global Vision Through Marketing ResearchDocument16 pagesDeveloping A Global Vision Through Marketing ResearchManju KengannarNo ratings yet
- Inp314t-4d (3in1) - DB-2P (12-48VDC) QigDocument3 pagesInp314t-4d (3in1) - DB-2P (12-48VDC) QigNatan Genao HdezNo ratings yet
- Block Chain Technology For Secure Land RegistrationDocument12 pagesBlock Chain Technology For Secure Land RegistrationSpandana KundarapuNo ratings yet
- OIML R 50-1: Nternational EcommendationDocument51 pagesOIML R 50-1: Nternational EcommendationWilliam GómezNo ratings yet
- About Page Generate Bug Template - JSPDocument3 pagesAbout Page Generate Bug Template - JSPnani2003No ratings yet
- AI Lab11 TaskDocument21 pagesAI Lab11 TaskEngr Aftab AminNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Saleem IqbalNo ratings yet
- DNS ProblemDocument19 pagesDNS ProblemNayem Hossain HemuNo ratings yet
- A - The Legal 500 and The in House Lawyer Comparative Legal GuideDocument13 pagesA - The Legal 500 and The in House Lawyer Comparative Legal GuideharshNo ratings yet
- Configuration Manual Lantek Expert CutDocument194 pagesConfiguration Manual Lantek Expert CutPeterNo ratings yet
- Long Range ReaderDocument6 pagesLong Range Readerabd el hamid atefNo ratings yet
- Book-2 Cad Cam Cae by NK ChouguleDocument124 pagesBook-2 Cad Cam Cae by NK Chouguletherashijain16No ratings yet