Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intro To Psych Exam 3 - Brody Flashcards - PT 1
Intro To Psych Exam 3 - Brody Flashcards - PT 1
Uploaded by
Emily CallerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro To Psych Exam 3 - Brody Flashcards - PT 1
Intro To Psych Exam 3 - Brody Flashcards - PT 1
Uploaded by
Emily CallerCopyright:
Available Formats
Intro to Psych Exam 3 - Brody
Terms in this set (73)
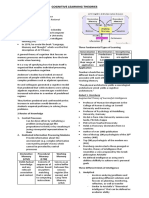
2 types:
1) automatic → implicit memories (without conscious
recall) → processed in cerebellum and basal ganglia
→ space, time, frequency (ex: where you ate dinner
yesterday)
List and describe the levels of → motor and cognitive skills (ex: riding a bike)
memory processing → classical conditioning (ex: reaching an office)
2) effortful → explicit memories (with conscious recall) →
processed in hippocampus and frontal lobe
→ semantic memory: facts and general knowledge (ex:
concepts from a textbook) → episodic memory:
personally experienced events (ex: family holidays)
Memory researcher who studied how emotions and other
variables affected Ebbinghaus' forgetting curve
Trailblazer for Native American scholars
1st in her community to leave reservation and pursue a
college education
Marigold Linton
Despite being an extraordinary student, she was plagued
with self-doubt because of her token status
Founder of SACNAS, an organization created to address
the lack of diversity in the scientific community (now >
6,000 members)
Intro to Psych Exam 3 - Brody
Facing stress, women may have a tend-and-befriend
response; men may withdraw socially, turn to alcohol, or
Shelley Taylor
become aggressive
Attempted to assess intellectual intelligence (1884)
Found no correlation between measures
Believed in the inheritance of genius (discussed in his
book Hereditary Genius)
Francis Galton
Coined the term "eugenics" & promoted racist ideas in the
name of science
Galton's influence on the shameful history of American
eugenics
Tended toward environmental explanation of intelligence
differences
Assumed all children follow the same course, but not the
same rate, of intellectual development
Measured each child's mental age
Alfred Binet
Tested a variety of reasoning and problem-solving
questions that predicted how well French children would
do in school
Binet started the modern intelligence testing movement in
France in 1904, when he developed questions to help
predict children's future progress in the Paris school
system
Intro to Psych Exam 3 - Brody
Revised Binet's test for wider use in the United States
Revision was called the Stanford-Binet
Theorized intelligence tests reveal intelligence with which
person is born
Eugenicist who abused tests to help make case for 1924
Lewis Terman Immigration law (Binet would have been rolling over in his
grave)
intelligence quotient (IQ): Defined originally as the ratio of
mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca) multiplied by
100 (thus, IQ = ma/ca × 100). On contemporary intelligence
tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned
a score of 100.
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) and Wechsler's
tests for children
Created the most widely used intelligence test today
Yields an overall intelligence score and separate scores
David Wechsler
for verbal comprehension, perceptual organization,
working memory, and processing speed
Wechsler's tests differ from their predecessors in the way
they offer an overall intelligence score as well as scores
for various verbal and performance areas.
Intro to Psych Exam 3 - Brody
recall: retrieving information that is not currently in your
conscious awareness but that was learned at an earlier
time.
EX: A fill-in-the-blank question tests your recall.
recognition: identifying items previously learned. EX: A
List and describe the three
multiple-choice question tests your recognition.
measures of retention
relearning: learning something more quickly when you
learn it a second or later time.
EX: When you study for a final exam or engage a
language used in early childhood, you will relearn the
material more easily than you did initially.
encoding get information into our brain
storage retain that information
retrieval later get the information back out
consolidation neural storage for long-term memory
Upgrade to remove ads Only $3.99/month
associations activated without our awareness resulting in
priming
predisposing one's perception, memory, or response
an increase in a cell's firing potential after brief, rapid
long-term potentiation
stimulation; a neural basis for learning and memory
Intro to Psych Exam 3 - Brody
working memory: a newer understanding of short-term
memory that adds conscious, active processing of
incoming auditory and visual information, and of
information retrieved from long-term memory
Explain the roles that working
memory, short-term memory, and short-term memory: activated memory that holds a few
long-term memory play in
items briefly, before the information is stored or forgotten
memory processing
long-term memory: the relatively permanent and limitless
storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge,
skills, and experiences
effortful processing: encoding that requires attention and
constant effort
Compare and contrast effortful
processing and automatic
automatic processing: unconscious encoding of incidental
processing
information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of
well-learned information, such as word meanings.
chunking: organizing items into familiar, manageable units
mnemonics: memory aids, especially those that use vivid
imagery and organizational devices
List and describe three effortful
the spacing effect: the tendency for distributed study or
processing strategies
practice to yield better long-term retention than is
achieved through massed study or practice
hierarchies: broad divided and subdivided into narrower
concepts and facts
iconic memory: a momentary sensory memory of visual
stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting
no more than a few tenths of a second
Compare and contrast iconic
memory and echoic memory
echoic memory: a momentary sensory memory of
auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and
Intro to Psych Exam 3 - Brody words can still be recalled within 3 or 4 seconds
You might also like
- Developmental Psychology ReviewerDocument3 pagesDevelopmental Psychology ReviewerJavee Gamboa50% (2)
- Melissam021004 AP Psychology CH 6 10 Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesMelissam021004 AP Psychology CH 6 10 Cheat SheetHanie OriginalNo ratings yet
- Neurobiology of Learning and MemoryDocument7 pagesNeurobiology of Learning and MemoryKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Day 1 - Intelligence SDocument18 pagesDay 1 - Intelligence SAma De SilvaNo ratings yet
- ResultsDocument2 pagesResultsJuan PedroNo ratings yet
- Intelligence NobaDocument1 pageIntelligence NobaLaura LaraNo ratings yet
- Middle Childhood 1Document24 pagesMiddle Childhood 1Ray Sophia CuberoNo ratings yet
- $RV681SVDocument14 pages$RV681SVRyan BastiampillaiNo ratings yet
- Edelman EmbodimentMind 2006Document11 pagesEdelman EmbodimentMind 2006Fernanda PioNo ratings yet
- Cog Psych MOdule 1Document4 pagesCog Psych MOdule 1Alexander DavadillaNo ratings yet
- Magazine: What Is Cognition?Document8 pagesMagazine: What Is Cognition?Edwin Yahir GalvisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document1 pageLesson 2marinemaisonnNo ratings yet
- File 9Document11 pagesFile 9Malek ElgmatiNo ratings yet
- 2ND DevpsyDocument8 pages2ND DevpsyKEITH MORGAN OLAZONo ratings yet
- " Intelligence" and TestingDocument18 pages" Intelligence" and Testing123 AbcNo ratings yet
- Intelligence: Controversy Over Definition: ©john Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e)Document28 pagesIntelligence: Controversy Over Definition: ©john Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2007 Huffman: Psychology in Action (8e)anisha batraNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Learning Theories: Anderson's Model of Intelligence Adaptive Control of Thought - Rational (ACT-R)Document9 pagesCognitive Learning Theories: Anderson's Model of Intelligence Adaptive Control of Thought - Rational (ACT-R)lanNo ratings yet
- Assessing Intelligence in A Cultural Context: Lisa A. Suzuki, Samar Naqvi, and Jill S. HillDocument20 pagesAssessing Intelligence in A Cultural Context: Lisa A. Suzuki, Samar Naqvi, and Jill S. Hillgogicha mariNo ratings yet
- UTS ReviewerDocument8 pagesUTS Reviewerjmamaglalang.studentNo ratings yet
- Psych Assessment Trans Lec1Document3 pagesPsych Assessment Trans Lec1ALYANAH DALE MAGNONo ratings yet
- Final+Review FADocument82 pagesFinal+Review FAsara mirzaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 The Nature and History of PsychologyDocument8 pagesLesson 1 The Nature and History of PsychologyAllison MaañoNo ratings yet
- Mid Tri NotesDocument35 pagesMid Tri NotesJamila TangaNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022-CompleteDocument17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022-Completeapi-681360617No ratings yet
- Combined Activity 2 - 230803 - 200223Document3 pagesCombined Activity 2 - 230803 - 200223beatrizoyarzo15No ratings yet
- Prologue: The Story of PsychologyDocument25 pagesPrologue: The Story of PsychologyLana AlsalemNo ratings yet
- U1 Class Note OutlinesDocument13 pagesU1 Class Note OutlinesTiffany AustinNo ratings yet
- Intelligence and The Assessment of Intelligence - Lecture 7Document18 pagesIntelligence and The Assessment of Intelligence - Lecture 7Faraz Ali Khan100% (1)
- HISTORICAL, CULTURAL, AND LEGAL or ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONSDocument3 pagesHISTORICAL, CULTURAL, AND LEGAL or ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONSjesperlaheyNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document4 pagesActivity 3Saitama SenseiNo ratings yet
- Note Introduction To PsychologyDocument3 pagesNote Introduction To PsychologyLinh MaiNo ratings yet
- Prologue - The Story of PsychologyDocument28 pagesPrologue - The Story of PsychologyCooper BullNo ratings yet
- Intelligence 1Document6 pagesIntelligence 1aiyswaryaajNo ratings yet
- The Unbearable Automaticity of BeingDocument18 pagesThe Unbearable Automaticity of BeingSebastian Gonzalez MazoNo ratings yet
- PSYCH 431 Slides For IQ TestingDocument73 pagesPSYCH 431 Slides For IQ TestingOmar WazedNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer in INTROPSYDocument14 pagesMidterm Reviewer in INTROPSYFrances Rein TacusalmeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1nerlynpar04No ratings yet
- Intelligence: Suellen Concessio FernandesDocument19 pagesIntelligence: Suellen Concessio FernandesSueNo ratings yet
- PS1012 & PS1014 Approaches To PsychologyDocument48 pagesPS1012 & PS1014 Approaches To PsychologyArnab BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Psychology, Sociology, and AnthropologyDocument29 pagesPsychology, Sociology, and AnthropologyArviNo ratings yet
- zf11437 HBP 20230308 HistoryDocument14 pageszf11437 HBP 20230308 HistorySnow ANo ratings yet
- WestraCarruthers TheoryofmindDocument8 pagesWestraCarruthers Theoryofmindimroah339No ratings yet
- Intelligence PDFDocument13 pagesIntelligence PDFShaista KhattakNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022-1 1Document16 pagesGo To Page Word 2022-1 1api-678689506No ratings yet
- Intelligence, Artificial Intelligence and Other Forms ofDocument75 pagesIntelligence, Artificial Intelligence and Other Forms ofZoha MerchantNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document3 pagesUnit 1patrickNo ratings yet
- DialoguesClinNeurosci 14 19Document9 pagesDialoguesClinNeurosci 14 19epfaNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Learning 2022 1Document53 pagesFacilitating Learning 2022 1Nezza PeterNo ratings yet
- Theory of Mind in Nonhuman Primates: C. M. HeyesDocument48 pagesTheory of Mind in Nonhuman Primates: C. M. HeyesJunyuZhuNo ratings yet
- CAD ReportingDocument60 pagesCAD ReportingRodel YapNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 1 Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesProf Ed 1 Midterm ReviewervelardecrazelleNo ratings yet
- (Basilan) Dissociation Between Language and General IntelligentDocument11 pages(Basilan) Dissociation Between Language and General IntelligentMampusti MarlojaykeNo ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022-3Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022-3api-747550850No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 2022-1 Use This OneDocument17 pagesGo To Page Word 2022-1 Use This Oneapi-673836743No ratings yet
- Go To Page Word 12252023Document17 pagesGo To Page Word 12252023api-717832207No ratings yet
- Choose One of The Following SubjectsDocument5 pagesChoose One of The Following SubjectsNana jaberNo ratings yet
- Saying Seeing and ActingDocument206 pagesSaying Seeing and ActingLamiaa GhamriNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology Prelim and Finals Reviewer - CompressDocument31 pagesDevelopmental Psychology Prelim and Finals Reviewer - CompressGlory Mae ProllesNo ratings yet
- History of Intelligence: What Makes Us Intelligent or Not So IntelligentDocument18 pagesHistory of Intelligence: What Makes Us Intelligent or Not So IntelligentShams JhugrooNo ratings yet
- Intelligence: Theories about Psychology, Signs, and StupidityFrom EverandIntelligence: Theories about Psychology, Signs, and StupidityNo ratings yet
- EMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 1Document4 pagesEMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 1Emily CallerNo ratings yet
- NREMT Terms Flashcards PT 1Document3 pagesNREMT Terms Flashcards PT 1Emily CallerNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Conditions (Chapter 15) Flashcards - QuizletDocument4 pagesRespiratory Conditions (Chapter 15) Flashcards - QuizletEmily CallerNo ratings yet
- EMT HESI Prep Flashcards - PT 2Document4 pagesEMT HESI Prep Flashcards - PT 2Emily CallerNo ratings yet
- EMT HESI Prep Flashcards PT 1Document4 pagesEMT HESI Prep Flashcards PT 1Emily Caller100% (1)
- EMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 2Document2 pagesEMT Chapter 10 Vocabulary Flashcards - PT 2Emily CallerNo ratings yet
- Example Identification (Type of Long Term Memory) JustificationDocument2 pagesExample Identification (Type of Long Term Memory) JustificationHadia AamirNo ratings yet
- Human) MemoryDocument23 pagesHuman) MemoryYanpinginbkkNo ratings yet
- Working Memory BaddeleyDocument20 pagesWorking Memory BaddeleycyrtamoNo ratings yet
- ความจำระยะสั้นและความจำระยะยาวDocument20 pagesความจำระยะสั้นและความจำระยะยาวsaminNo ratings yet
- Memory:: EncodingDocument4 pagesMemory:: EncodingNoor Ul Ain ZareefNo ratings yet
- PSY 206 - 6. Hafta - Working Memory IDocument38 pagesPSY 206 - 6. Hafta - Working Memory IFatma Zehra AkarsuNo ratings yet
- Class 11 CH 7Document9 pagesClass 11 CH 7Varun DhawanNo ratings yet
- PsychSim 5 Trusting Your MemoryDocument2 pagesPsychSim 5 Trusting Your MemoryFrancoAVasquezNo ratings yet
- Is Working Memory Still WorkingDocument31 pagesIs Working Memory Still WorkingMarcela ZárateNo ratings yet
- Pedagogy-Remembering and ForgettingDocument25 pagesPedagogy-Remembering and ForgettinggengkapakNo ratings yet
- Memory Booklet Part ONEDocument35 pagesMemory Booklet Part ONEatuna joeNo ratings yet
- The Working Memory ModelDocument67 pagesThe Working Memory ModelRand HannaNo ratings yet
- Sistemas de MemoriaDocument9 pagesSistemas de MemoriaLorena VergaraNo ratings yet
- 3 - Definisi Human ErrorDocument26 pages3 - Definisi Human ErrorSandy KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Memory Definition & Types of Memory: How We Form MemoriesDocument4 pagesMemory Definition & Types of Memory: How We Form Memoriessaman safdar0% (1)
- Bartosz Czekala How To Learn Faster and Rediscover Joy of LearningDocument14 pagesBartosz Czekala How To Learn Faster and Rediscover Joy of LearningAnchieNo ratings yet
- Psychology Chapter 7: Human MemoryDocument26 pagesPsychology Chapter 7: Human MemoryZubaidahNo ratings yet
- Why We Forget and How To RememberDocument6 pagesWhy We Forget and How To RememberTope Georges-Emmanuel100% (1)
- Memory in Psychology: Lecturer: Thaddues Hostetler Course: Psychology Name: Nguyen Thi Ha Class: SNHU20E2Document18 pagesMemory in Psychology: Lecturer: Thaddues Hostetler Course: Psychology Name: Nguyen Thi Ha Class: SNHU20E2Hà BeNo ratings yet
- Psychology (Memory)Document8 pagesPsychology (Memory)Shariq Ghouri100% (1)
- Unit 7 Module 31 Studying and Building Memories PowerpointDocument24 pagesUnit 7 Module 31 Studying and Building Memories Powerpointapi-300762638No ratings yet
- Theories of ForgettingDocument7 pagesTheories of Forgettingshubhamsilawat100% (2)
- 2004 - Wixted - Psychology and Neuroscience of ForgettingDocument38 pages2004 - Wixted - Psychology and Neuroscience of ForgettingMa Kristine Bernadette SiatrizNo ratings yet
- Cornell Notes Template - Memory Summary HomeworkDocument4 pagesCornell Notes Template - Memory Summary HomeworkLaura SánchezNo ratings yet
- 學習&記憶Document67 pages學習&記憶Peter ChangNo ratings yet
- Memory: Sta. Teresa CollegeDocument4 pagesMemory: Sta. Teresa Collegeaudree d. aldayNo ratings yet
- Class 11 CH 7Document9 pagesClass 11 CH 7Varun DhawanNo ratings yet
- TB1 Chapter 8 - Study Guide Progress Test 1Document5 pagesTB1 Chapter 8 - Study Guide Progress Test 1MonicaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PsychologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Psychologynimra rafiNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University of Rizal System Rodriguez, Rizal Graduate SchoolDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University of Rizal System Rodriguez, Rizal Graduate SchoolJennifer OriolaNo ratings yet