Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Yuhbnb 1
Yuhbnb 1
Uploaded by
Saroj GautamCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Marketing and Retail Analytics ProjectDocument17 pagesMarketing and Retail Analytics ProjectManish Verma100% (1)
- GM CropsDocument17 pagesGM CropsShankho BaghNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Specifications Nestle PDFDocument24 pagesMicrobiological Specifications Nestle PDFmadiha altafNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Marketing ManagementDocument18 pagesAgricultural Marketing ManagementTapesh AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Codes and Standards With Government Involvement: Management of Production Problems in Tropical Fruit CropsDocument1 pageCodes and Standards With Government Involvement: Management of Production Problems in Tropical Fruit CropswidagdoNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Food Quality and Safety and FAO Technical AssistanceDocument8 pagesEnsuring Food Quality and Safety and FAO Technical AssistanceJuan Gonzalez FernandezNo ratings yet
- AGSC 55 Module 4 Lesson 2Document39 pagesAGSC 55 Module 4 Lesson 2KIM GRACE BANZUELONo ratings yet
- Benefits of GAP Will Accrue To:: Alimentarius, The Agricultural Sector Lacks A UnifyingDocument1 pageBenefits of GAP Will Accrue To:: Alimentarius, The Agricultural Sector Lacks A UnifyingwidagdoNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest ManagemtentDocument11 pagesIntegrated Pest ManagemtentAli SaliuNo ratings yet
- Day3 Symp AIASDocument34 pagesDay3 Symp AIASHanaw MohammadNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Management of Mango Trees For Better QualityDocument7 pagesSustainable Management of Mango Trees For Better QualityWeb ResearchNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified CropsDocument16 pagesGenetically Modified CropsSandesh Kumar Gangwar100% (1)
- STS 4Document10 pagesSTS 4apriljoytraballoNo ratings yet
- Good Agricultural Practices: For BananasDocument5 pagesGood Agricultural Practices: For BananasMuslimNo ratings yet
- Syngenta RPM Case Study 021721 MO 002 1Document13 pagesSyngenta RPM Case Study 021721 MO 002 1jahidulislambizdevNo ratings yet
- UMK Chapter 12 Sem 2Document44 pagesUMK Chapter 12 Sem 2Rina Abigail CarterNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dairy - 1Document15 pagesPrinciples of Dairy - 1zarqa zulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Rules On Transgenic PlantDocument25 pagesRules On Transgenic Plantoryzasativa26No ratings yet
- FINAL PROJECTdjjffjfkkfrokffnDocument41 pagesFINAL PROJECTdjjffjfkkfrokffnmishraravihbk136No ratings yet
- 2 CEFS Insect Management On Organic Farms PDFDocument37 pages2 CEFS Insect Management On Organic Farms PDFScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- Insectmgmtfinaljan09 PDFDocument37 pagesInsectmgmtfinaljan09 PDFLucky TraderNo ratings yet
- Ishita InternshipDocument25 pagesIshita InternshipSabrm Rpcau PusaNo ratings yet
- PF ReviewerDocument1 pagePF ReviewerVanessa BaguiNo ratings yet
- AGROCERT PPT - Vol.1Document13 pagesAGROCERT PPT - Vol.1Kumar PradeepNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Principles and Practices in Plant BreedingDocument28 pagesLecture 1 Principles and Practices in Plant BreedingChenie Rose GaNo ratings yet
- Application of BiotechnologyDocument1 pageApplication of BiotechnologyscribsunilNo ratings yet
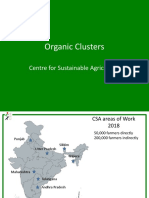
- Organic Clusters: Centre For Sustainable AgricultureDocument41 pagesOrganic Clusters: Centre For Sustainable AgricultureRamanjaneyulu GVNo ratings yet
- NICRADocument14 pagesNICRAkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food Safety and Good Agricultural PracticesDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Food Safety and Good Agricultural Practicesroyporter473No ratings yet
- Principles & Practices For Sustainable Fruit Production: SAI Platform Fruit Working GroupDocument14 pagesPrinciples & Practices For Sustainable Fruit Production: SAI Platform Fruit Working GroupLeinad IbregNo ratings yet
- Monsanto Trait QA Requirements2010Document20 pagesMonsanto Trait QA Requirements2010shavsrNo ratings yet
- Intro Pre BreedingDocument16 pagesIntro Pre BreedingRamavtar MêéñãNo ratings yet
- SGS AGRI PPR Services A4 EN 11Document20 pagesSGS AGRI PPR Services A4 EN 11Mahmoud DomourNo ratings yet
- IPM IntroductionDocument148 pagesIPM IntroductionJerzon VillacencioNo ratings yet
- FARMING ACTIVITIES - March 23, 2021Document12 pagesFARMING ACTIVITIES - March 23, 2021Jaibel Borbe0% (1)
- Silage Note 5 Factors Affecting The Quality Fandf Quantity of Forage Harvested For SilageDocument2 pagesSilage Note 5 Factors Affecting The Quality Fandf Quantity of Forage Harvested For SilageArun T YltpNo ratings yet
- Oxfam Guide Agriculture 2014 EngDocument20 pagesOxfam Guide Agriculture 2014 EngOrville JamesNo ratings yet
- Ashish Malik - Opportunity Green Conference 2010 - Fast Growth, The Business of Organics, Food Systems and AgricultureDocument13 pagesAshish Malik - Opportunity Green Conference 2010 - Fast Growth, The Business of Organics, Food Systems and AgricultureOpportunity Green ConferenceNo ratings yet
- DR Mahendra SharmaDocument39 pagesDR Mahendra Sharmasumana86_ghoshNo ratings yet
- Operator'S Guidelines: General Requirements For Organic Certification For All Categories of OperatorsDocument10 pagesOperator'S Guidelines: General Requirements For Organic Certification For All Categories of OperatorsLucky TraderNo ratings yet
- HACCP Application & Implementation TrainingDocument92 pagesHACCP Application & Implementation Trainingalexander.bigreddotNo ratings yet
- AIM Assignment: Market Structure of Pesticides IndustryDocument20 pagesAIM Assignment: Market Structure of Pesticides IndustryMegaAppleNo ratings yet
- GMP, Ssop, HaccpDocument74 pagesGMP, Ssop, HaccpsbelodoNo ratings yet
- Organic 2Document20 pagesOrganic 2aq3398237No ratings yet
- Fs 26chemicalDocument2 pagesFs 26chemicalLady BirdNo ratings yet
- E. Vadivel and V. PanimalarDocument1 pageE. Vadivel and V. PanimalarwidagdoNo ratings yet
- PGPSM07011 Sustainable AgricultureDocument6 pagesPGPSM07011 Sustainable AgricultureAbhijeet kohatNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Pertanian OrganikDocument37 pagesPrinsip Pertanian Organikelyani-eLNo ratings yet
- Achm PDFDocument61 pagesAchm PDFAnnNo ratings yet
- GAP PengertianDocument59 pagesGAP PengertiansudarmadipNo ratings yet
- General Background On Food Standards: A. Cassava Local StandardsDocument4 pagesGeneral Background On Food Standards: A. Cassava Local StandardsHenry KaweesaNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Standards Recommended Practices - Felicilda and Dahan ReportDocument70 pagesPhilippine National Standards Recommended Practices - Felicilda and Dahan ReportRena bellsNo ratings yet
- Code of Gap PhilgapDocument10 pagesCode of Gap PhilgapgildesenganioNo ratings yet
- Aman Kumar - 19020242004 GramophoneDocument4 pagesAman Kumar - 19020242004 GramophoneAman KumarNo ratings yet
- What Are Confined Field Trials - and Why Are They Needed?: Environmental Biosafety WorkshopDocument25 pagesWhat Are Confined Field Trials - and Why Are They Needed?: Environmental Biosafety WorkshopwafiyyatunnufusNo ratings yet
- Animal Science 2 Dairy ProductionDocument24 pagesAnimal Science 2 Dairy ProductionimanhuwelNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest Management L 429Document2 pagesIntegrated Pest Management L 429PoopNo ratings yet
- Kraft Allergen Management ForumDocument63 pagesKraft Allergen Management ForumDavid100% (1)
- TOPIC 1 Zainab, Mariam, Nadine, Katia - 2Document25 pagesTOPIC 1 Zainab, Mariam, Nadine, Katia - 2Mohammed RafiNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Good Agricultural Practices for Commercial Production of Ginger under Field Conditions in JamaicaFrom EverandA Guide to Good Agricultural Practices for Commercial Production of Ginger under Field Conditions in JamaicaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- DOS Instruction ManualsDocument1 pageDOS Instruction ManualsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Section #1: Getting AcquaintedDocument1 pageSection #1: Getting AcquaintedSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Oilcakes: Nutrient Content of Important Organic ManuresDocument1 pageOilcakes: Nutrient Content of Important Organic ManuresSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing FertilizersDocument1 pageNutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing FertilizersSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- I. Package of Practices - BananaDocument1 pageI. Package of Practices - BananaSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrient Microorganism Crops Benefited NitrogenDocument1 pagePlant Nutrient Microorganism Crops Benefited NitrogenSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Different Fertilizers and Their Nutrient Content: A. Soil Analysis: Key To A Successful Nutrient Management PlanDocument1 page2.5. Different Fertilizers and Their Nutrient Content: A. Soil Analysis: Key To A Successful Nutrient Management PlanSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Vermi-Compost:: Organic FertilizersDocument1 pageVermi-Compost:: Organic FertilizersSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Boron (B) - Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageBoron (B) - Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Soil Sampling: An IllustrationDocument1 pageSoil Sampling: An IllustrationSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Calcium (Ca) - Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageCalcium (Ca) - Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Zinc (ZN) Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageZinc (ZN) Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Carbon - Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio)Document1 pageCarbon - Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio)Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 2.4. Deficiency Symptoms of Nutrients in PlantsDocument1 page2.4. Deficiency Symptoms of Nutrients in PlantsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.8. Cropping SystemsDocument1 page1.8. Cropping SystemsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Salient Features: Subsidy PatternDocument1 pageSalient Features: Subsidy PatternSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Recommendation of Seed Treatment For Different Crops Contiued..Document1 pageRecommendation of Seed Treatment For Different Crops Contiued..Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3. Drainage: Eligibility Area of OperationDocument1 page1.6.3. Drainage: Eligibility Area of OperationSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- At Low Rate Over A Long Period of Time. at Frequent Intervals Directly Into The Plant's Root ZoneDocument1 pageAt Low Rate Over A Long Period of Time. at Frequent Intervals Directly Into The Plant's Root ZoneSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.7. Seed: Functions of SeedsDocument1 page1.7. Seed: Functions of SeedsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Layout of Micro Irrigation System: Name of The Crop Critical Stages Oil SeedsDocument1 pageLayout of Micro Irrigation System: Name of The Crop Critical Stages Oil SeedsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Vegetation and Vegetative Management: Zero TillageDocument1 pageVegetation and Vegetative Management: Zero TillageSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation: A Typical Drip Irrigation System Consists of The Following ComponentsDocument1 pageDrip Irrigation: A Typical Drip Irrigation System Consists of The Following ComponentsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Drip Irrigation Over Surface Irrigation Continued...Document1 pageBenefits of Drip Irrigation Over Surface Irrigation Continued...Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Penambahan Santan Pada Susu Kambing Etawa (Capra: Aegagrus Hircus) Terhadap Kadar Protein SusuDocument5 pagesPengaruh Penambahan Santan Pada Susu Kambing Etawa (Capra: Aegagrus Hircus) Terhadap Kadar Protein SusuIdris FaturrohmanNo ratings yet
- Pickling Cucumbers Worked PowerpointDocument12 pagesPickling Cucumbers Worked Powerpointric bolNo ratings yet
- Eco Digester PDFDocument1 pageEco Digester PDFeaang55No ratings yet
- Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMP)Document15 pagesProject Procurement Management Plan (PPMP)Jonath M GelomioNo ratings yet
- Scarlet Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesScarlet Lesson PlanScarlet Elgamo GalantoNo ratings yet
- Narrative PHT3Document3 pagesNarrative PHT3Jericho Basmayor SajulanNo ratings yet
- Raj Pavilion MenuDocument2 pagesRaj Pavilion Menuapi-2528277980% (1)
- Silk Food Ramadan PromoDocument4 pagesSilk Food Ramadan PromotariNo ratings yet
- Sts Final Research AaaaaaaDocument13 pagesSts Final Research AaaaaaaDunston Chi EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Post Harvest Management Value Addition of Fruits Vegetable PDFDocument145 pagesPost Harvest Management Value Addition of Fruits Vegetable PDFMãnéešh TűtîķäNo ratings yet
- A Research Study On Control Blood Sugar With Jackfruit365 Green Jackfruit FloorDocument11 pagesA Research Study On Control Blood Sugar With Jackfruit365 Green Jackfruit FloorAbhinave PatilNo ratings yet
- Amalia Rahma Firdaus - A320200183 - Comparison and Contrast EssayDocument2 pagesAmalia Rahma Firdaus - A320200183 - Comparison and Contrast Essay183Amalia Rahma FirdausNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian-Vegan Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesVegetarian-Vegan Brochure PDFAmy SNo ratings yet
- MALNUTRITIONDocument6 pagesMALNUTRITIONEndah FitriNo ratings yet
- CST USEN 17373332 MealBuilder Veg PDFDocument1 pageCST USEN 17373332 MealBuilder Veg PDFTC Serhan UçarNo ratings yet
- Millet Tribe - KEM Cooking WorkshopDocument16 pagesMillet Tribe - KEM Cooking Workshopayanah.jeelani12No ratings yet
- Charlie and The Chocolate Factory-Dahl RoaldDocument161 pagesCharlie and The Chocolate Factory-Dahl Roaldapi-254239238100% (2)
- Sibo Gut Healing Protocol PDFDocument2 pagesSibo Gut Healing Protocol PDFLee Ming Hin100% (1)
- A, An, Some, Any 01Document3 pagesA, An, Some, Any 01Maite ChimboNo ratings yet
- Brine Curing and MarinadeDocument13 pagesBrine Curing and MarinadeArunkumar KPNo ratings yet
- Foods 1 2.05.adjusting RecipesDocument8 pagesFoods 1 2.05.adjusting RecipesGeorgette YarboroughNo ratings yet
- Melon HerbaZestDocument1 pageMelon HerbaZestCla RenceNo ratings yet
- Share It Student Book Level2 Unit 4 SpreadDocument8 pagesShare It Student Book Level2 Unit 4 Spreaddemo presentationsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Diet Nutrients and Dental CariesDocument9 pagesLecture 6 Diet Nutrients and Dental CariesNasser DabiNo ratings yet
- Development of A Sweetened Beverage Tax, PhilippinesDocument7 pagesDevelopment of A Sweetened Beverage Tax, PhilippinesRochelle GamboaNo ratings yet
- Glosario Ingles Ii / Lengua Ii: Ingles: Tema 1: Estilos de VidaDocument7 pagesGlosario Ingles Ii / Lengua Ii: Ingles: Tema 1: Estilos de VidaAndrea SalazarNo ratings yet
- R-732 Microwave Oven With Grill Operation Manual With CookbookDocument27 pagesR-732 Microwave Oven With Grill Operation Manual With Cookbookulvah imuetzNo ratings yet
- Why To Choose AgricultureDocument7 pagesWhy To Choose Agricultureapi-344405949No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 ProtienDocument8 pagesLesson Plan 3 Protienapi-270183943No ratings yet
Yuhbnb 1
Yuhbnb 1
Uploaded by
Saroj GautamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Yuhbnb 1
Yuhbnb 1
Uploaded by
Saroj GautamCopyright:
Available Formats
General Conditions for Cultivation of Crops
1.10. Good Agricultural Practices GAP related to crop protection
(GAP) • Use resistant cultivars and varieties.
G
• Crop sequences, associations and cultural prac-
ood Agricultural Practices (GAP) are "prac-
tices.
tices that address environmental, economic and
• Biological prevention of pests and diseases.
social sustainability for on-farm processes, and which
• Maintain regular and quantitative assessment
result in safe and quality food and non-food agricul-
of the balance status between pests and diseases
tural products".
and beneficial organisms of all crops.
• Adopt organic control practices where and
What are GAP codes, standards and when applicable.
regulations? • Apply pest and disease forecasting techniques
where available.
Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) codes, stand- • Determine interventions following considera-
ards and regulations are guidelines which have tion of all possible methods and their short and
been developed in recent years by the food industry, long-term effects on farm productivity and en-
producers' organizations, governments and NGOs vironmental implications. This will allow the
aiming to codify agricultural practices at farm level minimizing of agrochemicals, in particular, to
for a range of commodities. promote Integrated Pest Management (IPM).
• Store and use agrochemicals according to le-
Why do GAP codes, standards and gal requirements of registration for individual
regulations exist? crops, rates, timings, and pre-harvest intervals
• Ensure that agrochemicals are only applied by
These GAP codes, programmes or standards exist specially trained and knowledgeable persons.
because of: • Ensure that equipment used for the handling
and application of agrochemicals complies with
• Growing concerns about food quality and safe-
established safety and maintenance standards.
ty worldwide.
• Maintain accurate records of agrochemical use.
• Fulfilment of trade and government regulatory
• Identify the GAP in each protection method.
requirements.
• Specific requirements especially for niche mar- Crop rotation systems
kets. • Sequence crops by selecting pest host relation.
• Selected crop for rotation in order to break the
Objectives
life cycle of pest (Jowar should be rotated with
• Ensuring safety and quality of produce in the
pulses to combat striga weed).
food chain.
• The selected crop for rotation should not be the
• Capturing new market advantages by modify-
food of previous crop pest.
ing supply chain governance.
• To select appropriate crops for rotation:
• Improving natural resources used, workers'
• Analyze the pest habitat
health and working conditions to creating new
• Follow forecasts
market opportunities for farmers and exporters
• Monitor pest and natural enemies
in developing countries.
The benefits of GAP codes Privilege resistant species
• Cultivate plant varieties which are less prone to
• Standards and regulations are numerous, in-
pest attack.
cluding food quality and safety improvement.
• The resistant varieties reduce production cost.
• Facilitation of market access.
• Pest resistant transgenic crops developed for
• Reduction in non-compliance risks regarding
specific pest can be used. This is new avenue for
permitted pesticides, Maximum Residue Limits
reducing pesticide load.
(MRLs) and other contamination hazards.
30 Farmer’s Handbook on Basic Agriculture
You might also like
- Marketing and Retail Analytics ProjectDocument17 pagesMarketing and Retail Analytics ProjectManish Verma100% (1)
- GM CropsDocument17 pagesGM CropsShankho BaghNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Specifications Nestle PDFDocument24 pagesMicrobiological Specifications Nestle PDFmadiha altafNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Marketing ManagementDocument18 pagesAgricultural Marketing ManagementTapesh AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Codes and Standards With Government Involvement: Management of Production Problems in Tropical Fruit CropsDocument1 pageCodes and Standards With Government Involvement: Management of Production Problems in Tropical Fruit CropswidagdoNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Food Quality and Safety and FAO Technical AssistanceDocument8 pagesEnsuring Food Quality and Safety and FAO Technical AssistanceJuan Gonzalez FernandezNo ratings yet
- AGSC 55 Module 4 Lesson 2Document39 pagesAGSC 55 Module 4 Lesson 2KIM GRACE BANZUELONo ratings yet
- Benefits of GAP Will Accrue To:: Alimentarius, The Agricultural Sector Lacks A UnifyingDocument1 pageBenefits of GAP Will Accrue To:: Alimentarius, The Agricultural Sector Lacks A UnifyingwidagdoNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest ManagemtentDocument11 pagesIntegrated Pest ManagemtentAli SaliuNo ratings yet
- Day3 Symp AIASDocument34 pagesDay3 Symp AIASHanaw MohammadNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Management of Mango Trees For Better QualityDocument7 pagesSustainable Management of Mango Trees For Better QualityWeb ResearchNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified CropsDocument16 pagesGenetically Modified CropsSandesh Kumar Gangwar100% (1)
- STS 4Document10 pagesSTS 4apriljoytraballoNo ratings yet
- Good Agricultural Practices: For BananasDocument5 pagesGood Agricultural Practices: For BananasMuslimNo ratings yet
- Syngenta RPM Case Study 021721 MO 002 1Document13 pagesSyngenta RPM Case Study 021721 MO 002 1jahidulislambizdevNo ratings yet
- UMK Chapter 12 Sem 2Document44 pagesUMK Chapter 12 Sem 2Rina Abigail CarterNo ratings yet
- Principles of Dairy - 1Document15 pagesPrinciples of Dairy - 1zarqa zulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Rules On Transgenic PlantDocument25 pagesRules On Transgenic Plantoryzasativa26No ratings yet
- FINAL PROJECTdjjffjfkkfrokffnDocument41 pagesFINAL PROJECTdjjffjfkkfrokffnmishraravihbk136No ratings yet
- 2 CEFS Insect Management On Organic Farms PDFDocument37 pages2 CEFS Insect Management On Organic Farms PDFScarlet VillamorNo ratings yet
- Insectmgmtfinaljan09 PDFDocument37 pagesInsectmgmtfinaljan09 PDFLucky TraderNo ratings yet
- Ishita InternshipDocument25 pagesIshita InternshipSabrm Rpcau PusaNo ratings yet
- PF ReviewerDocument1 pagePF ReviewerVanessa BaguiNo ratings yet
- AGROCERT PPT - Vol.1Document13 pagesAGROCERT PPT - Vol.1Kumar PradeepNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Principles and Practices in Plant BreedingDocument28 pagesLecture 1 Principles and Practices in Plant BreedingChenie Rose GaNo ratings yet
- Application of BiotechnologyDocument1 pageApplication of BiotechnologyscribsunilNo ratings yet
- Organic Clusters: Centre For Sustainable AgricultureDocument41 pagesOrganic Clusters: Centre For Sustainable AgricultureRamanjaneyulu GVNo ratings yet
- NICRADocument14 pagesNICRAkrishnaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food Safety and Good Agricultural PracticesDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Food Safety and Good Agricultural Practicesroyporter473No ratings yet
- Principles & Practices For Sustainable Fruit Production: SAI Platform Fruit Working GroupDocument14 pagesPrinciples & Practices For Sustainable Fruit Production: SAI Platform Fruit Working GroupLeinad IbregNo ratings yet
- Monsanto Trait QA Requirements2010Document20 pagesMonsanto Trait QA Requirements2010shavsrNo ratings yet
- Intro Pre BreedingDocument16 pagesIntro Pre BreedingRamavtar MêéñãNo ratings yet
- SGS AGRI PPR Services A4 EN 11Document20 pagesSGS AGRI PPR Services A4 EN 11Mahmoud DomourNo ratings yet
- IPM IntroductionDocument148 pagesIPM IntroductionJerzon VillacencioNo ratings yet
- FARMING ACTIVITIES - March 23, 2021Document12 pagesFARMING ACTIVITIES - March 23, 2021Jaibel Borbe0% (1)
- Silage Note 5 Factors Affecting The Quality Fandf Quantity of Forage Harvested For SilageDocument2 pagesSilage Note 5 Factors Affecting The Quality Fandf Quantity of Forage Harvested For SilageArun T YltpNo ratings yet
- Oxfam Guide Agriculture 2014 EngDocument20 pagesOxfam Guide Agriculture 2014 EngOrville JamesNo ratings yet
- Ashish Malik - Opportunity Green Conference 2010 - Fast Growth, The Business of Organics, Food Systems and AgricultureDocument13 pagesAshish Malik - Opportunity Green Conference 2010 - Fast Growth, The Business of Organics, Food Systems and AgricultureOpportunity Green ConferenceNo ratings yet
- DR Mahendra SharmaDocument39 pagesDR Mahendra Sharmasumana86_ghoshNo ratings yet
- Operator'S Guidelines: General Requirements For Organic Certification For All Categories of OperatorsDocument10 pagesOperator'S Guidelines: General Requirements For Organic Certification For All Categories of OperatorsLucky TraderNo ratings yet
- HACCP Application & Implementation TrainingDocument92 pagesHACCP Application & Implementation Trainingalexander.bigreddotNo ratings yet
- AIM Assignment: Market Structure of Pesticides IndustryDocument20 pagesAIM Assignment: Market Structure of Pesticides IndustryMegaAppleNo ratings yet
- GMP, Ssop, HaccpDocument74 pagesGMP, Ssop, HaccpsbelodoNo ratings yet
- Organic 2Document20 pagesOrganic 2aq3398237No ratings yet
- Fs 26chemicalDocument2 pagesFs 26chemicalLady BirdNo ratings yet
- E. Vadivel and V. PanimalarDocument1 pageE. Vadivel and V. PanimalarwidagdoNo ratings yet
- PGPSM07011 Sustainable AgricultureDocument6 pagesPGPSM07011 Sustainable AgricultureAbhijeet kohatNo ratings yet
- Prinsip Pertanian OrganikDocument37 pagesPrinsip Pertanian Organikelyani-eLNo ratings yet
- Achm PDFDocument61 pagesAchm PDFAnnNo ratings yet
- GAP PengertianDocument59 pagesGAP PengertiansudarmadipNo ratings yet
- General Background On Food Standards: A. Cassava Local StandardsDocument4 pagesGeneral Background On Food Standards: A. Cassava Local StandardsHenry KaweesaNo ratings yet
- Philippine National Standards Recommended Practices - Felicilda and Dahan ReportDocument70 pagesPhilippine National Standards Recommended Practices - Felicilda and Dahan ReportRena bellsNo ratings yet
- Code of Gap PhilgapDocument10 pagesCode of Gap PhilgapgildesenganioNo ratings yet
- Aman Kumar - 19020242004 GramophoneDocument4 pagesAman Kumar - 19020242004 GramophoneAman KumarNo ratings yet
- What Are Confined Field Trials - and Why Are They Needed?: Environmental Biosafety WorkshopDocument25 pagesWhat Are Confined Field Trials - and Why Are They Needed?: Environmental Biosafety WorkshopwafiyyatunnufusNo ratings yet
- Animal Science 2 Dairy ProductionDocument24 pagesAnimal Science 2 Dairy ProductionimanhuwelNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest Management L 429Document2 pagesIntegrated Pest Management L 429PoopNo ratings yet
- Kraft Allergen Management ForumDocument63 pagesKraft Allergen Management ForumDavid100% (1)
- TOPIC 1 Zainab, Mariam, Nadine, Katia - 2Document25 pagesTOPIC 1 Zainab, Mariam, Nadine, Katia - 2Mohammed RafiNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Good Agricultural Practices for Commercial Production of Ginger under Field Conditions in JamaicaFrom EverandA Guide to Good Agricultural Practices for Commercial Production of Ginger under Field Conditions in JamaicaRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- DOS Instruction ManualsDocument1 pageDOS Instruction ManualsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Section #1: Getting AcquaintedDocument1 pageSection #1: Getting AcquaintedSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Oilcakes: Nutrient Content of Important Organic ManuresDocument1 pageOilcakes: Nutrient Content of Important Organic ManuresSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing FertilizersDocument1 pageNutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing FertilizersSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- I. Package of Practices - BananaDocument1 pageI. Package of Practices - BananaSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrient Microorganism Crops Benefited NitrogenDocument1 pagePlant Nutrient Microorganism Crops Benefited NitrogenSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Different Fertilizers and Their Nutrient Content: A. Soil Analysis: Key To A Successful Nutrient Management PlanDocument1 page2.5. Different Fertilizers and Their Nutrient Content: A. Soil Analysis: Key To A Successful Nutrient Management PlanSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Vermi-Compost:: Organic FertilizersDocument1 pageVermi-Compost:: Organic FertilizersSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Boron (B) - Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageBoron (B) - Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Soil Sampling: An IllustrationDocument1 pageSoil Sampling: An IllustrationSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Calcium (Ca) - Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageCalcium (Ca) - Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Zinc (ZN) Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageZinc (ZN) Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Carbon - Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio)Document1 pageCarbon - Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio)Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 2.4. Deficiency Symptoms of Nutrients in PlantsDocument1 page2.4. Deficiency Symptoms of Nutrients in PlantsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.8. Cropping SystemsDocument1 page1.8. Cropping SystemsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Salient Features: Subsidy PatternDocument1 pageSalient Features: Subsidy PatternSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Recommendation of Seed Treatment For Different Crops Contiued..Document1 pageRecommendation of Seed Treatment For Different Crops Contiued..Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3. Drainage: Eligibility Area of OperationDocument1 page1.6.3. Drainage: Eligibility Area of OperationSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- At Low Rate Over A Long Period of Time. at Frequent Intervals Directly Into The Plant's Root ZoneDocument1 pageAt Low Rate Over A Long Period of Time. at Frequent Intervals Directly Into The Plant's Root ZoneSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.7. Seed: Functions of SeedsDocument1 page1.7. Seed: Functions of SeedsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Layout of Micro Irrigation System: Name of The Crop Critical Stages Oil SeedsDocument1 pageLayout of Micro Irrigation System: Name of The Crop Critical Stages Oil SeedsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Vegetation and Vegetative Management: Zero TillageDocument1 pageVegetation and Vegetative Management: Zero TillageSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation: A Typical Drip Irrigation System Consists of The Following ComponentsDocument1 pageDrip Irrigation: A Typical Drip Irrigation System Consists of The Following ComponentsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Drip Irrigation Over Surface Irrigation Continued...Document1 pageBenefits of Drip Irrigation Over Surface Irrigation Continued...Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Penambahan Santan Pada Susu Kambing Etawa (Capra: Aegagrus Hircus) Terhadap Kadar Protein SusuDocument5 pagesPengaruh Penambahan Santan Pada Susu Kambing Etawa (Capra: Aegagrus Hircus) Terhadap Kadar Protein SusuIdris FaturrohmanNo ratings yet
- Pickling Cucumbers Worked PowerpointDocument12 pagesPickling Cucumbers Worked Powerpointric bolNo ratings yet
- Eco Digester PDFDocument1 pageEco Digester PDFeaang55No ratings yet
- Project Procurement Management Plan (PPMP)Document15 pagesProject Procurement Management Plan (PPMP)Jonath M GelomioNo ratings yet
- Scarlet Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesScarlet Lesson PlanScarlet Elgamo GalantoNo ratings yet
- Narrative PHT3Document3 pagesNarrative PHT3Jericho Basmayor SajulanNo ratings yet
- Raj Pavilion MenuDocument2 pagesRaj Pavilion Menuapi-2528277980% (1)
- Silk Food Ramadan PromoDocument4 pagesSilk Food Ramadan PromotariNo ratings yet
- Sts Final Research AaaaaaaDocument13 pagesSts Final Research AaaaaaaDunston Chi EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Post Harvest Management Value Addition of Fruits Vegetable PDFDocument145 pagesPost Harvest Management Value Addition of Fruits Vegetable PDFMãnéešh TűtîķäNo ratings yet
- A Research Study On Control Blood Sugar With Jackfruit365 Green Jackfruit FloorDocument11 pagesA Research Study On Control Blood Sugar With Jackfruit365 Green Jackfruit FloorAbhinave PatilNo ratings yet
- Amalia Rahma Firdaus - A320200183 - Comparison and Contrast EssayDocument2 pagesAmalia Rahma Firdaus - A320200183 - Comparison and Contrast Essay183Amalia Rahma FirdausNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian-Vegan Brochure PDFDocument2 pagesVegetarian-Vegan Brochure PDFAmy SNo ratings yet
- MALNUTRITIONDocument6 pagesMALNUTRITIONEndah FitriNo ratings yet
- CST USEN 17373332 MealBuilder Veg PDFDocument1 pageCST USEN 17373332 MealBuilder Veg PDFTC Serhan UçarNo ratings yet
- Millet Tribe - KEM Cooking WorkshopDocument16 pagesMillet Tribe - KEM Cooking Workshopayanah.jeelani12No ratings yet
- Charlie and The Chocolate Factory-Dahl RoaldDocument161 pagesCharlie and The Chocolate Factory-Dahl Roaldapi-254239238100% (2)
- Sibo Gut Healing Protocol PDFDocument2 pagesSibo Gut Healing Protocol PDFLee Ming Hin100% (1)
- A, An, Some, Any 01Document3 pagesA, An, Some, Any 01Maite ChimboNo ratings yet
- Brine Curing and MarinadeDocument13 pagesBrine Curing and MarinadeArunkumar KPNo ratings yet
- Foods 1 2.05.adjusting RecipesDocument8 pagesFoods 1 2.05.adjusting RecipesGeorgette YarboroughNo ratings yet
- Melon HerbaZestDocument1 pageMelon HerbaZestCla RenceNo ratings yet
- Share It Student Book Level2 Unit 4 SpreadDocument8 pagesShare It Student Book Level2 Unit 4 Spreaddemo presentationsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Diet Nutrients and Dental CariesDocument9 pagesLecture 6 Diet Nutrients and Dental CariesNasser DabiNo ratings yet
- Development of A Sweetened Beverage Tax, PhilippinesDocument7 pagesDevelopment of A Sweetened Beverage Tax, PhilippinesRochelle GamboaNo ratings yet
- Glosario Ingles Ii / Lengua Ii: Ingles: Tema 1: Estilos de VidaDocument7 pagesGlosario Ingles Ii / Lengua Ii: Ingles: Tema 1: Estilos de VidaAndrea SalazarNo ratings yet
- R-732 Microwave Oven With Grill Operation Manual With CookbookDocument27 pagesR-732 Microwave Oven With Grill Operation Manual With Cookbookulvah imuetzNo ratings yet
- Why To Choose AgricultureDocument7 pagesWhy To Choose Agricultureapi-344405949No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3 ProtienDocument8 pagesLesson Plan 3 Protienapi-270183943No ratings yet