Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing Fertilizers
Nutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing Fertilizers
Uploaded by
Saroj GautamCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Dash 8 QRH PDFDocument142 pagesDash 8 QRH PDFjohn heath50% (4)
- CES Wrong Answer Summary 1e18da38 A505 48c1 b100 8cddd2b264e7Document4 pagesCES Wrong Answer Summary 1e18da38 A505 48c1 b100 8cddd2b264e7Sridharan Narasingan75% (4)
- Calculation of Fertilizers DoseDocument4 pagesCalculation of Fertilizers Dosevigyanashram90% (50)
- Module 1 (Database Management in Construction)Document42 pagesModule 1 (Database Management in Construction)MARTHIE JASELLYN LOPENANo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Computation - CONSUELO - DOMINIC BSA3J2Document6 pagesFertilizer Computation - CONSUELO - DOMINIC BSA3J2Whel DeLima ConsueloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 How To Calculate Rertiliser Rates and CostsDocument16 pagesChapter 14 How To Calculate Rertiliser Rates and CostssuggyNo ratings yet
- Rock PhosphateDocument2 pagesRock PhosphateGrignionNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument40 pagesIlovepdf MergedDhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- Fertiliser CalculationsDocument2 pagesFertiliser CalculationsadithyaNo ratings yet
- Factsheet Product Ammonium Sulphate FINAL 22052018Document4 pagesFactsheet Product Ammonium Sulphate FINAL 22052018Haider AlIraqiNo ratings yet
- Ijas DK 678-680Document3 pagesIjas DK 678-680Dinesh Kumar JajoriaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Effectiveness of TSP and DapDocument3 pagesComparative Study of Effectiveness of TSP and DapEl Mahjoub LAGRININo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY SHEET - Fertilizer ComputationDocument3 pagesACTIVITY SHEET - Fertilizer ComputationAllivasor SiugomaNo ratings yet
- Learner'S Home Task in Technology and Livelihood EducationDocument6 pagesLearner'S Home Task in Technology and Livelihood EducationRonald Matias CristobalNo ratings yet
- NPK Production Technologies Fertilizer FocusDocument6 pagesNPK Production Technologies Fertilizer FocusELIO BARRIOS IBARRANo ratings yet
- Typical Process in The MillDocument4 pagesTypical Process in The MillFauzan MuzakkiNo ratings yet
- Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R From Aqueous Solution by Pirina Pretreated With Nitric Acid and Commercial Activated CarbonDocument15 pagesRemoval of Remazol Brilliant Blue R From Aqueous Solution by Pirina Pretreated With Nitric Acid and Commercial Activated Carbonceo.didansiNo ratings yet
- MAss Balance of Phosphoric AcidDocument6 pagesMAss Balance of Phosphoric Acidwhãts brøNo ratings yet
- AGRO 234 KC Chart-1 PDFDocument1 pageAGRO 234 KC Chart-1 PDFDhage Shubham0% (2)
- Dept of Agronamy Kharip Crop - Guided by - Prof Inamke.T.D: Botanical NameDocument1 pageDept of Agronamy Kharip Crop - Guided by - Prof Inamke.T.D: Botanical NameSachin BudhwantNo ratings yet
- Palestra EROS - IPNI - SolubilddFosfatosDocument18 pagesPalestra EROS - IPNI - SolubilddFosfatosTania SouzaNo ratings yet
- Energies: Increasing Profits in Food Waste Biorefinery - A Techno-Economic AnalysisDocument14 pagesEnergies: Increasing Profits in Food Waste Biorefinery - A Techno-Economic AnalysisDevson PauloNo ratings yet
- Weights MeasuresDocument2 pagesWeights MeasuresDerek MukokanwaNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer CalculationDocument8 pagesFertilizer CalculationAmir MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2. Fertilizer for RubberDocument11 pages2. Fertilizer for Rubberlab1284uNo ratings yet
- 2017-02-15 Brochure Ammonium Sulfate Plants SCRDocument8 pages2017-02-15 Brochure Ammonium Sulfate Plants SCRSya Fitri MarsellaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 PDFDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 PDFKami TazuNo ratings yet
- Kharip Crop ChartDocument1 pageKharip Crop ChartShaikh SahilNo ratings yet
- Unit2a AcidDocument19 pagesUnit2a AcidKarthik TNo ratings yet
- Fertiliser CalculationsDocument2 pagesFertiliser CalculationsIqbal HussainNo ratings yet
- Fertilization Guide For CoconutsDocument2 pagesFertilization Guide For CoconutsTrade goalNo ratings yet
- Stefanus Johan Biogas Future and Opportunities-R2Document15 pagesStefanus Johan Biogas Future and Opportunities-R2Bimo Nuswantoro SugardoNo ratings yet
- Tarif Analisa EMU Lab (2016) - 1Document1 pageTarif Analisa EMU Lab (2016) - 1Andiko Putro SuryotomoNo ratings yet
- FINAL Phosphate Flow MapDocument2 pagesFINAL Phosphate Flow MapSamuel IliffeNo ratings yet
- NPK FertilizerDocument11 pagesNPK FertilizermajidNo ratings yet
- Technology, Energy Efficiency and Environmental Externalities in The Pulp and Paper Industry - AIT, ThailandDocument140 pagesTechnology, Energy Efficiency and Environmental Externalities in The Pulp and Paper Industry - AIT, ThailandVishal Duggal100% (1)
- Pulses Production (Rabi-2013-14) IN BIHAR: Department of Agriculture Government of BiharDocument13 pagesPulses Production (Rabi-2013-14) IN BIHAR: Department of Agriculture Government of BiharviewpawanNo ratings yet
- Lamberte, Joshua Paul - Exercise 3Document10 pagesLamberte, Joshua Paul - Exercise 3lambertejoshuapaulNo ratings yet
- FERTILIZERSDocument8 pagesFERTILIZERSAdios ANo ratings yet
- Questions Visit Coments SolidaridadDocument10 pagesQuestions Visit Coments SolidaridadcarlosisazaNo ratings yet
- NPK FertilizerDocument11 pagesNPK FertilizerShivaniNo ratings yet
- 03graph01 1055Document5 pages03graph01 1055arulprakashf.sdcNo ratings yet
- TXRF Application Note XRF 460 Rapid Ultra Trace Analysis of Arsenic in Rice by TXRF Spectroscopy EN BRUKERDocument4 pagesTXRF Application Note XRF 460 Rapid Ultra Trace Analysis of Arsenic in Rice by TXRF Spectroscopy EN BRUKERArif SumonNo ratings yet
- 6 ReCiPe111Document1,518 pages6 ReCiPe111Krishan AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Studies On Complete and Partial Acidulation of Eppawela ApatiteDocument17 pagesStudies On Complete and Partial Acidulation of Eppawela ApatiteThusith WijayawardenaNo ratings yet
- Mubarak 2013Document10 pagesMubarak 2013Ahmed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Agronomy: 3.1 Long-Term Fertility Experiment On Cropping Systems Involving Rapeseed-MustardDocument23 pagesAgronomy: 3.1 Long-Term Fertility Experiment On Cropping Systems Involving Rapeseed-MustardManvendra Singh InaniyaNo ratings yet
- Chemcom SIDocument5 pagesChemcom SIRoja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Composite Fish Culture PDFDocument2 pagesComposite Fish Culture PDFHanumant JagtapNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Recycling Agent Dosage in Hot Mix Recycled AsphaltDocument37 pagesOptimization of Recycling Agent Dosage in Hot Mix Recycled AsphaltSAlil GuPtaNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Production Economics: Chapter 17 Two Inputs and Two OutputsDocument39 pagesAgricultural Production Economics: Chapter 17 Two Inputs and Two OutputsHusseinNo ratings yet
- Soil Health Card Number - PB/2017-18/135123536/1 Farmer's Details Sukhwinder SinghDocument2 pagesSoil Health Card Number - PB/2017-18/135123536/1 Farmer's Details Sukhwinder SinghManish BokadiyaNo ratings yet
- Resep Pulvis 1-46Document2 pagesResep Pulvis 1-46Nonori TataNo ratings yet
- ResinDocument14 pagesResinrlharasvityaNo ratings yet
- DR Block C 01, C03, C04 - 20240211 - Cycle 3Document79 pagesDR Block C 01, C03, C04 - 20240211 - Cycle 3ares try putra handrahNo ratings yet
- Mxdfertilizer PPAH PDFDocument4 pagesMxdfertilizer PPAH PDFASDFG21No ratings yet
- Ammonia and Urea Cash Cost - Yara InternationalDocument2 pagesAmmonia and Urea Cash Cost - Yara InternationalPriya VahinipathiNo ratings yet
- DOS Instruction ManualsDocument1 pageDOS Instruction ManualsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Section #1: Getting AcquaintedDocument1 pageSection #1: Getting AcquaintedSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Oilcakes: Nutrient Content of Important Organic ManuresDocument1 pageOilcakes: Nutrient Content of Important Organic ManuresSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- I. Package of Practices - BananaDocument1 pageI. Package of Practices - BananaSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Vermi-Compost:: Organic FertilizersDocument1 pageVermi-Compost:: Organic FertilizersSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrient Microorganism Crops Benefited NitrogenDocument1 pagePlant Nutrient Microorganism Crops Benefited NitrogenSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Boron (B) - Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageBoron (B) - Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Soil Sampling: An IllustrationDocument1 pageSoil Sampling: An IllustrationSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 2.4. Deficiency Symptoms of Nutrients in PlantsDocument1 page2.4. Deficiency Symptoms of Nutrients in PlantsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Zinc (ZN) Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageZinc (ZN) Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Different Fertilizers and Their Nutrient Content: A. Soil Analysis: Key To A Successful Nutrient Management PlanDocument1 page2.5. Different Fertilizers and Their Nutrient Content: A. Soil Analysis: Key To A Successful Nutrient Management PlanSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Calcium (Ca) - Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageCalcium (Ca) - Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Carbon - Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio)Document1 pageCarbon - Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio)Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.8. Cropping SystemsDocument1 page1.8. Cropping SystemsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Salient Features: Subsidy PatternDocument1 pageSalient Features: Subsidy PatternSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Recommendation of Seed Treatment For Different Crops Contiued..Document1 pageRecommendation of Seed Treatment For Different Crops Contiued..Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3. Drainage: Eligibility Area of OperationDocument1 page1.6.3. Drainage: Eligibility Area of OperationSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- At Low Rate Over A Long Period of Time. at Frequent Intervals Directly Into The Plant's Root ZoneDocument1 pageAt Low Rate Over A Long Period of Time. at Frequent Intervals Directly Into The Plant's Root ZoneSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.7. Seed: Functions of SeedsDocument1 page1.7. Seed: Functions of SeedsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Layout of Micro Irrigation System: Name of The Crop Critical Stages Oil SeedsDocument1 pageLayout of Micro Irrigation System: Name of The Crop Critical Stages Oil SeedsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Vegetation and Vegetative Management: Zero TillageDocument1 pageVegetation and Vegetative Management: Zero TillageSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation: A Typical Drip Irrigation System Consists of The Following ComponentsDocument1 pageDrip Irrigation: A Typical Drip Irrigation System Consists of The Following ComponentsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Drip Irrigation Over Surface Irrigation Continued...Document1 pageBenefits of Drip Irrigation Over Surface Irrigation Continued...Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 3.methodology of Pressure Settings On Storage Tanks.Document10 pages3.methodology of Pressure Settings On Storage Tanks.heyheyNo ratings yet
- Guide To GRE Awa PDFDocument33 pagesGuide To GRE Awa PDFAbdul KareemNo ratings yet
- ZomatoDocument3 pagesZomato2305112130010No ratings yet
- RefractometryDocument16 pagesRefractometryJoo Yee Chin100% (4)
- ETSE Zeiss True Position Bore Pattern 10-2 UpdateDocument29 pagesETSE Zeiss True Position Bore Pattern 10-2 UpdateJuan Posada GNo ratings yet
- Automan AC and AF Series ASL 62 305 448 Ed.05Document393 pagesAutoman AC and AF Series ASL 62 305 448 Ed.05yhorsNo ratings yet
- ICTDocument3 pagesICTpaul carcedoNo ratings yet
- STP Review Benitez - June 10 2013 Brahms PDFDocument2 pagesSTP Review Benitez - June 10 2013 Brahms PDFcoolth2No ratings yet
- Infosys: Case StudyDocument6 pagesInfosys: Case StudyShivam KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Act Roi WebsitepayDocument2 pagesAct Roi Websitepaynagendra reddy panyamNo ratings yet
- Design Frameworks: Past, Present and FuturesDocument53 pagesDesign Frameworks: Past, Present and FuturesJames Piers Taylor100% (2)
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledLehlohonolo NyakaleNo ratings yet
- Fowler - The New MethodologyDocument18 pagesFowler - The New MethodologypglezNo ratings yet
- FIRST SUMMATIVE TEST IN MEDIA First QuarterDocument2 pagesFIRST SUMMATIVE TEST IN MEDIA First QuarterRhaieyee ElNo ratings yet
- Tea 5170Document9 pagesTea 5170Erasmo Franco SNo ratings yet
- University of KarachiDocument53 pagesUniversity of KarachiWaqasBakaliNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Natural Gas Isentropic ExponentDocument8 pagesCalculation of Natural Gas Isentropic ExponentsekharsamyNo ratings yet
- SCCDocument10 pagesSCCPrakash NanthagopalanNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric Potentiometric Determination of Anionic and Cationic SurfactantsDocument13 pagesTitrimetric Potentiometric Determination of Anionic and Cationic SurfactantsJosué MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Nyepi Packages I RevisedDocument10 pagesNyepi Packages I Revisedreservation.rumahkitatravelNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Module 2Document19 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Module 2eysNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Notes in Hindi-Carbon-&-Its-Compounds PDFDocument21 pagesClass 10 Science Notes in Hindi-Carbon-&-Its-Compounds PDFVinothKumarVinothNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-L1Document14 pagesUnit 4-L1technical analysisNo ratings yet
- August Make Up Class FormDocument7 pagesAugust Make Up Class Formsevblanco34No ratings yet
- Đề HSG 9 Tiếng Anh Phù Ninh 2017Document8 pagesĐề HSG 9 Tiếng Anh Phù Ninh 2017Quỳnh Anh DươngNo ratings yet
- World Health OrganizationDocument13 pagesWorld Health OrganizationVincent Ranara Sabornido100% (1)
- CSE116 Spring 2017 SyllabusDocument7 pagesCSE116 Spring 2017 SyllabusBlakeHurlburtNo ratings yet
Nutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing Fertilizers
Nutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing Fertilizers
Uploaded by
Saroj GautamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing Fertilizers
Nutrient Cost Comparison: Guide For Mixing Fertilizers
Uploaded by
Saroj GautamCopyright:
Available Formats
Soil and Plant Nutrition
The formula for calculating the fertilizer to be Therefore, for soils with sulphur deficiency, am-
applied (kg/ha) = monium sulphate is a better choice and for soils
with normal sulphur levels, urea presents a better
100
N source.
--------------------------------------- X recommended
Nutrient content in the dose (kg/ha) Example - 2
fertilizer material (%)
1. Single Super Phosphate (SSP) with 7 % P
Nutrient cost comparison costs Rs.480 per 100 kg.
Example - 1 2. Di - Ammonium Phosphate (DAP) 20% P
and 18% N costs Rs.1596 per 100 kg.
1. Urea with 46% N costs Rs.562.20 per 100 kg.
2. Ammonium sulphate 20% N costs Rs.1029 per SSP has 7% P i.e. 7 kg P in every 100 kg SSP. There-
100 kg. fore unit value of P in SSP: 480/7= Rs.68.57 per kg P.
Urea has 46% N i.e. 46 kg N in every 100 kg urea. Whereas, DAP has 20% P and 18% N, i.e. 20 kg P
Therefore unit value of N in urea: 562.2/46= Rs.12.22 and 18 kg of N in every 100 kg of DAP.
per kg N. Ammonium sulphate has 20.6% N i.e. 20
Cost of Nitrogen in 100 kg of DAP = (18 X 12.22 ) =
kg N in every 100 kg fertilizer and 24% sulphur.
Rs.219.96. Therefore unit value of P in DAP: (1596
Therefore unit value of N in ammonium sulphate:
– 219.96 = 1376.00); i.e. 1376/20= Rs.68.80 per kg P
1029/20.6= Rs.49.95 per kg N. Thus, the nitrogen is
cheaper in urea. Yet, ammonium sulphate also has Thus, the unit cost of P is the same in both the ferti-
24% sulphur in it. lisers. Yet, DAP also has 18% N in it. Therefore, for
soils with nitrogen requirement, DAP is the better
choice.
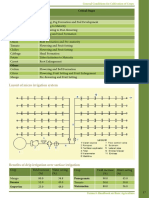
GUIDE FOR MIXING FERTILIZERS
1. Muriate of Potash
2. Sulphate of Potash
3. Sulphate of ammonia
4. Calcium ammonium nitrate
5. Sodium Nitrate
6. Calcium cynanamide
7. Urea
8. Superphosphate single or triple
9. Ammonium phosphate
10. Basic slag
11. Calcium carbonate
1. Muriate of Potash
2. Sulphate of Potash
3. Sulphate of ammonia
4. Calcium ammonium nitrate
5. Sodium Nitrate
6. Calcium cynanamide
7. Urea
8. Superphosphate single or triple
9. Ammonium phosphate
10. Basic slag
11. Calcium carbonate
Fertilizers which can be mixed
Fertilizers which may be mixed shortly before use
Fertilizers which can not be mixed
Note: The crossing point of the required vertical column and horizontal colum indicates the possibility of mixing or otherwise
of the fertilizer
Compatibility of Fertilizers
Farmer’s Handbook on Basic Agriculture 49
You might also like
- Dash 8 QRH PDFDocument142 pagesDash 8 QRH PDFjohn heath50% (4)
- CES Wrong Answer Summary 1e18da38 A505 48c1 b100 8cddd2b264e7Document4 pagesCES Wrong Answer Summary 1e18da38 A505 48c1 b100 8cddd2b264e7Sridharan Narasingan75% (4)
- Calculation of Fertilizers DoseDocument4 pagesCalculation of Fertilizers Dosevigyanashram90% (50)
- Module 1 (Database Management in Construction)Document42 pagesModule 1 (Database Management in Construction)MARTHIE JASELLYN LOPENANo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Computation - CONSUELO - DOMINIC BSA3J2Document6 pagesFertilizer Computation - CONSUELO - DOMINIC BSA3J2Whel DeLima ConsueloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 How To Calculate Rertiliser Rates and CostsDocument16 pagesChapter 14 How To Calculate Rertiliser Rates and CostssuggyNo ratings yet
- Rock PhosphateDocument2 pagesRock PhosphateGrignionNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument40 pagesIlovepdf MergedDhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- Fertiliser CalculationsDocument2 pagesFertiliser CalculationsadithyaNo ratings yet
- Factsheet Product Ammonium Sulphate FINAL 22052018Document4 pagesFactsheet Product Ammonium Sulphate FINAL 22052018Haider AlIraqiNo ratings yet
- Ijas DK 678-680Document3 pagesIjas DK 678-680Dinesh Kumar JajoriaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Effectiveness of TSP and DapDocument3 pagesComparative Study of Effectiveness of TSP and DapEl Mahjoub LAGRININo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY SHEET - Fertilizer ComputationDocument3 pagesACTIVITY SHEET - Fertilizer ComputationAllivasor SiugomaNo ratings yet
- Learner'S Home Task in Technology and Livelihood EducationDocument6 pagesLearner'S Home Task in Technology and Livelihood EducationRonald Matias CristobalNo ratings yet
- NPK Production Technologies Fertilizer FocusDocument6 pagesNPK Production Technologies Fertilizer FocusELIO BARRIOS IBARRANo ratings yet
- Typical Process in The MillDocument4 pagesTypical Process in The MillFauzan MuzakkiNo ratings yet
- Removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R From Aqueous Solution by Pirina Pretreated With Nitric Acid and Commercial Activated CarbonDocument15 pagesRemoval of Remazol Brilliant Blue R From Aqueous Solution by Pirina Pretreated With Nitric Acid and Commercial Activated Carbonceo.didansiNo ratings yet
- MAss Balance of Phosphoric AcidDocument6 pagesMAss Balance of Phosphoric Acidwhãts brøNo ratings yet
- AGRO 234 KC Chart-1 PDFDocument1 pageAGRO 234 KC Chart-1 PDFDhage Shubham0% (2)
- Dept of Agronamy Kharip Crop - Guided by - Prof Inamke.T.D: Botanical NameDocument1 pageDept of Agronamy Kharip Crop - Guided by - Prof Inamke.T.D: Botanical NameSachin BudhwantNo ratings yet
- Palestra EROS - IPNI - SolubilddFosfatosDocument18 pagesPalestra EROS - IPNI - SolubilddFosfatosTania SouzaNo ratings yet
- Energies: Increasing Profits in Food Waste Biorefinery - A Techno-Economic AnalysisDocument14 pagesEnergies: Increasing Profits in Food Waste Biorefinery - A Techno-Economic AnalysisDevson PauloNo ratings yet
- Weights MeasuresDocument2 pagesWeights MeasuresDerek MukokanwaNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer CalculationDocument8 pagesFertilizer CalculationAmir MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2. Fertilizer for RubberDocument11 pages2. Fertilizer for Rubberlab1284uNo ratings yet
- 2017-02-15 Brochure Ammonium Sulfate Plants SCRDocument8 pages2017-02-15 Brochure Ammonium Sulfate Plants SCRSya Fitri MarsellaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 PDFDocument4 pagesExperiment 2 PDFKami TazuNo ratings yet
- Kharip Crop ChartDocument1 pageKharip Crop ChartShaikh SahilNo ratings yet
- Unit2a AcidDocument19 pagesUnit2a AcidKarthik TNo ratings yet
- Fertiliser CalculationsDocument2 pagesFertiliser CalculationsIqbal HussainNo ratings yet
- Fertilization Guide For CoconutsDocument2 pagesFertilization Guide For CoconutsTrade goalNo ratings yet
- Stefanus Johan Biogas Future and Opportunities-R2Document15 pagesStefanus Johan Biogas Future and Opportunities-R2Bimo Nuswantoro SugardoNo ratings yet
- Tarif Analisa EMU Lab (2016) - 1Document1 pageTarif Analisa EMU Lab (2016) - 1Andiko Putro SuryotomoNo ratings yet
- FINAL Phosphate Flow MapDocument2 pagesFINAL Phosphate Flow MapSamuel IliffeNo ratings yet
- NPK FertilizerDocument11 pagesNPK FertilizermajidNo ratings yet
- Technology, Energy Efficiency and Environmental Externalities in The Pulp and Paper Industry - AIT, ThailandDocument140 pagesTechnology, Energy Efficiency and Environmental Externalities in The Pulp and Paper Industry - AIT, ThailandVishal Duggal100% (1)
- Pulses Production (Rabi-2013-14) IN BIHAR: Department of Agriculture Government of BiharDocument13 pagesPulses Production (Rabi-2013-14) IN BIHAR: Department of Agriculture Government of BiharviewpawanNo ratings yet
- Lamberte, Joshua Paul - Exercise 3Document10 pagesLamberte, Joshua Paul - Exercise 3lambertejoshuapaulNo ratings yet
- FERTILIZERSDocument8 pagesFERTILIZERSAdios ANo ratings yet
- Questions Visit Coments SolidaridadDocument10 pagesQuestions Visit Coments SolidaridadcarlosisazaNo ratings yet
- NPK FertilizerDocument11 pagesNPK FertilizerShivaniNo ratings yet
- 03graph01 1055Document5 pages03graph01 1055arulprakashf.sdcNo ratings yet
- TXRF Application Note XRF 460 Rapid Ultra Trace Analysis of Arsenic in Rice by TXRF Spectroscopy EN BRUKERDocument4 pagesTXRF Application Note XRF 460 Rapid Ultra Trace Analysis of Arsenic in Rice by TXRF Spectroscopy EN BRUKERArif SumonNo ratings yet
- 6 ReCiPe111Document1,518 pages6 ReCiPe111Krishan AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Studies On Complete and Partial Acidulation of Eppawela ApatiteDocument17 pagesStudies On Complete and Partial Acidulation of Eppawela ApatiteThusith WijayawardenaNo ratings yet
- Mubarak 2013Document10 pagesMubarak 2013Ahmed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Agronomy: 3.1 Long-Term Fertility Experiment On Cropping Systems Involving Rapeseed-MustardDocument23 pagesAgronomy: 3.1 Long-Term Fertility Experiment On Cropping Systems Involving Rapeseed-MustardManvendra Singh InaniyaNo ratings yet
- Chemcom SIDocument5 pagesChemcom SIRoja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Composite Fish Culture PDFDocument2 pagesComposite Fish Culture PDFHanumant JagtapNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Recycling Agent Dosage in Hot Mix Recycled AsphaltDocument37 pagesOptimization of Recycling Agent Dosage in Hot Mix Recycled AsphaltSAlil GuPtaNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Production Economics: Chapter 17 Two Inputs and Two OutputsDocument39 pagesAgricultural Production Economics: Chapter 17 Two Inputs and Two OutputsHusseinNo ratings yet
- Soil Health Card Number - PB/2017-18/135123536/1 Farmer's Details Sukhwinder SinghDocument2 pagesSoil Health Card Number - PB/2017-18/135123536/1 Farmer's Details Sukhwinder SinghManish BokadiyaNo ratings yet
- Resep Pulvis 1-46Document2 pagesResep Pulvis 1-46Nonori TataNo ratings yet
- ResinDocument14 pagesResinrlharasvityaNo ratings yet
- DR Block C 01, C03, C04 - 20240211 - Cycle 3Document79 pagesDR Block C 01, C03, C04 - 20240211 - Cycle 3ares try putra handrahNo ratings yet
- Mxdfertilizer PPAH PDFDocument4 pagesMxdfertilizer PPAH PDFASDFG21No ratings yet
- Ammonia and Urea Cash Cost - Yara InternationalDocument2 pagesAmmonia and Urea Cash Cost - Yara InternationalPriya VahinipathiNo ratings yet
- DOS Instruction ManualsDocument1 pageDOS Instruction ManualsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Section #1: Getting AcquaintedDocument1 pageSection #1: Getting AcquaintedSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Oilcakes: Nutrient Content of Important Organic ManuresDocument1 pageOilcakes: Nutrient Content of Important Organic ManuresSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- I. Package of Practices - BananaDocument1 pageI. Package of Practices - BananaSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Vermi-Compost:: Organic FertilizersDocument1 pageVermi-Compost:: Organic FertilizersSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrient Microorganism Crops Benefited NitrogenDocument1 pagePlant Nutrient Microorganism Crops Benefited NitrogenSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Boron (B) - Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageBoron (B) - Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Soil Sampling: An IllustrationDocument1 pageSoil Sampling: An IllustrationSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 2.4. Deficiency Symptoms of Nutrients in PlantsDocument1 page2.4. Deficiency Symptoms of Nutrients in PlantsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Zinc (ZN) Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageZinc (ZN) Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Different Fertilizers and Their Nutrient Content: A. Soil Analysis: Key To A Successful Nutrient Management PlanDocument1 page2.5. Different Fertilizers and Their Nutrient Content: A. Soil Analysis: Key To A Successful Nutrient Management PlanSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Calcium (Ca) - Deficiency SymptomsDocument1 pageCalcium (Ca) - Deficiency SymptomsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Yuhbnb 1Document1 pageYuhbnb 1Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Carbon - Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio)Document1 pageCarbon - Nitrogen Ratio (C:N Ratio)Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.8. Cropping SystemsDocument1 page1.8. Cropping SystemsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Salient Features: Subsidy PatternDocument1 pageSalient Features: Subsidy PatternSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Recommendation of Seed Treatment For Different Crops Contiued..Document1 pageRecommendation of Seed Treatment For Different Crops Contiued..Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.6.3. Drainage: Eligibility Area of OperationDocument1 page1.6.3. Drainage: Eligibility Area of OperationSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- At Low Rate Over A Long Period of Time. at Frequent Intervals Directly Into The Plant's Root ZoneDocument1 pageAt Low Rate Over A Long Period of Time. at Frequent Intervals Directly Into The Plant's Root ZoneSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 1.7. Seed: Functions of SeedsDocument1 page1.7. Seed: Functions of SeedsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Layout of Micro Irrigation System: Name of The Crop Critical Stages Oil SeedsDocument1 pageLayout of Micro Irrigation System: Name of The Crop Critical Stages Oil SeedsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Vegetation and Vegetative Management: Zero TillageDocument1 pageVegetation and Vegetative Management: Zero TillageSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Drip Irrigation: A Typical Drip Irrigation System Consists of The Following ComponentsDocument1 pageDrip Irrigation: A Typical Drip Irrigation System Consists of The Following ComponentsSaroj GautamNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Drip Irrigation Over Surface Irrigation Continued...Document1 pageBenefits of Drip Irrigation Over Surface Irrigation Continued...Saroj GautamNo ratings yet
- 3.methodology of Pressure Settings On Storage Tanks.Document10 pages3.methodology of Pressure Settings On Storage Tanks.heyheyNo ratings yet
- Guide To GRE Awa PDFDocument33 pagesGuide To GRE Awa PDFAbdul KareemNo ratings yet
- ZomatoDocument3 pagesZomato2305112130010No ratings yet
- RefractometryDocument16 pagesRefractometryJoo Yee Chin100% (4)
- ETSE Zeiss True Position Bore Pattern 10-2 UpdateDocument29 pagesETSE Zeiss True Position Bore Pattern 10-2 UpdateJuan Posada GNo ratings yet
- Automan AC and AF Series ASL 62 305 448 Ed.05Document393 pagesAutoman AC and AF Series ASL 62 305 448 Ed.05yhorsNo ratings yet
- ICTDocument3 pagesICTpaul carcedoNo ratings yet
- STP Review Benitez - June 10 2013 Brahms PDFDocument2 pagesSTP Review Benitez - June 10 2013 Brahms PDFcoolth2No ratings yet
- Infosys: Case StudyDocument6 pagesInfosys: Case StudyShivam KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Act Roi WebsitepayDocument2 pagesAct Roi Websitepaynagendra reddy panyamNo ratings yet
- Design Frameworks: Past, Present and FuturesDocument53 pagesDesign Frameworks: Past, Present and FuturesJames Piers Taylor100% (2)
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledLehlohonolo NyakaleNo ratings yet
- Fowler - The New MethodologyDocument18 pagesFowler - The New MethodologypglezNo ratings yet
- FIRST SUMMATIVE TEST IN MEDIA First QuarterDocument2 pagesFIRST SUMMATIVE TEST IN MEDIA First QuarterRhaieyee ElNo ratings yet
- Tea 5170Document9 pagesTea 5170Erasmo Franco SNo ratings yet
- University of KarachiDocument53 pagesUniversity of KarachiWaqasBakaliNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Natural Gas Isentropic ExponentDocument8 pagesCalculation of Natural Gas Isentropic ExponentsekharsamyNo ratings yet
- SCCDocument10 pagesSCCPrakash NanthagopalanNo ratings yet
- Titrimetric Potentiometric Determination of Anionic and Cationic SurfactantsDocument13 pagesTitrimetric Potentiometric Determination of Anionic and Cationic SurfactantsJosué MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Nyepi Packages I RevisedDocument10 pagesNyepi Packages I Revisedreservation.rumahkitatravelNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Module 2Document19 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Module 2eysNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Notes in Hindi-Carbon-&-Its-Compounds PDFDocument21 pagesClass 10 Science Notes in Hindi-Carbon-&-Its-Compounds PDFVinothKumarVinothNo ratings yet
- Unit 4-L1Document14 pagesUnit 4-L1technical analysisNo ratings yet
- August Make Up Class FormDocument7 pagesAugust Make Up Class Formsevblanco34No ratings yet
- Đề HSG 9 Tiếng Anh Phù Ninh 2017Document8 pagesĐề HSG 9 Tiếng Anh Phù Ninh 2017Quỳnh Anh DươngNo ratings yet
- World Health OrganizationDocument13 pagesWorld Health OrganizationVincent Ranara Sabornido100% (1)
- CSE116 Spring 2017 SyllabusDocument7 pagesCSE116 Spring 2017 SyllabusBlakeHurlburtNo ratings yet