Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract - Waste Heat Recovery
Abstract - Waste Heat Recovery
Uploaded by
kalaiselvanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Drum Residence Time Agglomerator Paper ALTA 2005Document28 pagesDrum Residence Time Agglomerator Paper ALTA 2005Steve Dennis100% (2)
- Baravis PDFDocument1 pageBaravis PDFAlexander ConquistaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Waste Heat Recovery in IndustriesDocument4 pagesA Review On Waste Heat Recovery in IndustriesBharat ShirsathNo ratings yet
- UUSITALODocument9 pagesUUSITALOMarcosNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Waste Heat Recovery Unit Using The Exhaust Gas Emitted From Internal Combustion EngineDocument6 pagesThermal Analysis of Waste Heat Recovery Unit Using The Exhaust Gas Emitted From Internal Combustion EngineAmal RajNo ratings yet
- IAC Student Webinar May SachinDocument59 pagesIAC Student Webinar May SachinMirnes FejzicNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Waste Heat and PressurDocument4 pagesA New Approach To Waste Heat and Pressurעקיבא אסNo ratings yet
- WHR ResearchDocument22 pagesWHR ResearchSiddharth ModiNo ratings yet
- Final Report of Heat TransferDocument25 pagesFinal Report of Heat Transferimdian0582090No ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery: Training Session On Energy EquipmentDocument32 pagesWaste Heat Recovery: Training Session On Energy EquipmentRomuel PioquintoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, CommerciallyDocument9 pagesSyllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, Commerciallymanvendra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, CommerciallyDocument18 pagesSyllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, Commerciallyalzewam152100% (2)
- Analysis and Perspective On Heat Pump For IndustriDocument27 pagesAnalysis and Perspective On Heat Pump For IndustriJianping TangNo ratings yet
- Air-Source Hybrid Absorption-Compression Heat Pumps With Three-StageDocument16 pagesAir-Source Hybrid Absorption-Compression Heat Pumps With Three-StageDaniel DimaNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery in Cement Plant IJERTV3IS051014 PDFDocument5 pagesWaste Heat Recovery in Cement Plant IJERTV3IS051014 PDFDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of The Flow Streams Behavior in A Self-Regenerative Crucible FurnaceDocument7 pagesNumerical Simulation of The Flow Streams Behavior in A Self-Regenerative Crucible FurnaceperulesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Combustion Systems For Annealing and Pickling LinesDocument5 pagesAdvanced Combustion Systems For Annealing and Pickling LinesAlessandro LazzarettoNo ratings yet
- Ird Cet Paper UscDocument3 pagesIrd Cet Paper UscMohamed Abashar MusmarNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery Vinay ShuklaDocument31 pagesWaste Heat Recovery Vinay ShuklaVnyNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery TechniquesDocument62 pagesWaste Heat Recovery Techniquesdhruv100% (1)
- Heat RecovDocument31 pagesHeat RecovMakatoLeonNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument4 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryMudasar JavedNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, CommerciallyDocument10 pagesSyllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, Commerciallymanvendra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Energy II - EnergyEfficiency and HeatRecoveryDocument27 pagesEnergy II - EnergyEfficiency and HeatRecoverymluisa.boteroNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery in Selected Industries - USEPA '82Document8 pagesWaste Heat Recovery in Selected Industries - USEPA '82Shashank SaneNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2020Document17 pagesZhang 2020WuberestNo ratings yet
- Energy: Opeyemi Bamigbetan, Trygve Magne Eikevik, Petter Nekså, Michael Bantle, Christian SchlemmingerDocument9 pagesEnergy: Opeyemi Bamigbetan, Trygve Magne Eikevik, Petter Nekså, Michael Bantle, Christian SchlemmingerEduardo Jose Tello del pinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Waste Heat RecoveryDocument29 pagesLecture 7 Waste Heat RecoveryUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Co Generation Unit 4Document52 pagesCo Generation Unit 4Johnson Johnson100% (2)
- OT - PAP - A.Deshmukh M.Kavade - 2017 - Study & Review of Heat Recovery Systems For SO2 Gas Generation Process in SugarDocument4 pagesOT - PAP - A.Deshmukh M.Kavade - 2017 - Study & Review of Heat Recovery Systems For SO2 Gas Generation Process in SugarEduardo CandelaNo ratings yet
- Sci Hub - Investigation of The Thermal Performance of A Novel FlatDocument1 pageSci Hub - Investigation of The Thermal Performance of A Novel FlatSamah AhmedNo ratings yet
- CHEN505 Note 1Document6 pagesCHEN505 Note 1OkePreciousEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Waste Management: Fabio Dal Magro, Haoxin Xu, Gioacchino Nardin, Alessandro RomagnoliDocument10 pagesWaste Management: Fabio Dal Magro, Haoxin Xu, Gioacchino Nardin, Alessandro RomagnoliKARAN KHANNANo ratings yet
- Combination of SRC and ORCDocument13 pagesCombination of SRC and ORCBerkay AslanNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument25 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryJoeb DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Furnace Waste ReductionDocument10 pagesFurnace Waste ReductionSanjeev PmNo ratings yet
- QTR2015 6M Waste Heat Recovery PDFDocument40 pagesQTR2015 6M Waste Heat Recovery PDFMuh AmmadNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument19 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryAnjanKumarMahanta100% (2)
- Unit Ii Boilers 2.1BOILER:: 2.2 ComparisonDocument32 pagesUnit Ii Boilers 2.1BOILER:: 2.2 Comparisonmohan velNo ratings yet
- Induction Heating DRMDocument8 pagesInduction Heating DRMHoangNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine-GTU-Sem-1Document78 pagesHeat Engine-GTU-Sem-1Khushank MNo ratings yet
- Handbook: LightingDocument1 pageHandbook: LightingreacharunkNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency Heat-Recirculating Domestic Gas BurnersDocument13 pagesHigh Efficiency Heat-Recirculating Domestic Gas Burnersanton verNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument37 pagesWaste Heat Recoveryommech2020No ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: Javier Peña-Lamas, Juan Martinez-Gomez, Mariano Martín, José María Ponce-OrtegaDocument11 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: Javier Peña-Lamas, Juan Martinez-Gomez, Mariano Martín, José María Ponce-OrtegaJuan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument12 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryJafarNo ratings yet
- Install Waste Heat Process htgts8Document2 pagesInstall Waste Heat Process htgts8api-19908130No ratings yet
- Furnaces and Furnace ReactorsDocument33 pagesFurnaces and Furnace ReactorsSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2451904918304050 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S2451904918304050 MainJonathan TupizaNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat ExtractionDocument9 pagesWaste Heat ExtractionSandeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Optimum Reheat Pressures For Single and Double Reheat Irreversible Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesDetermination of Optimum Reheat Pressures For Single and Double Reheat Irreversible Rankine CycleSiva KulanjiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Presentation - Shared - Updated 19 - 10 - 20Document51 pagesBoiler Presentation - Shared - Updated 19 - 10 - 20Lokesh ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Kalina Cycle: Presented By:-Jyoti Chaudhary ME (3 YR) 1118740020Document16 pagesKalina Cycle: Presented By:-Jyoti Chaudhary ME (3 YR) 1118740020KirtiPurohitNo ratings yet
- Progress and Prospects For Research and Technology Development of Supercritical CO2 Thermal Conversion Systems For Power Energy Storage and Waste HeDocument19 pagesProgress and Prospects For Research and Technology Development of Supercritical CO2 Thermal Conversion Systems For Power Energy Storage and Waste Hegetahun esubalewNo ratings yet
- Rivera Et Al 2018, Experimental Assessment of Double Absorption Heat Transformer Operating With H2O LiBrDocument9 pagesRivera Et Al 2018, Experimental Assessment of Double Absorption Heat Transformer Operating With H2O LiBrRedees RedeesNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Thermal Analysis On Heat Transfer Performance of Heat Pipe-1Document15 pagesFinite Element Thermal Analysis On Heat Transfer Performance of Heat Pipe-1RojithNo ratings yet
- J Applthermaleng 2005 06 001Document11 pagesJ Applthermaleng 2005 06 001buffallo120381No ratings yet
- Meza 2014Document8 pagesMeza 2014Angel LopezNo ratings yet
- Integrating Cogeneration and Intermittent Waste Heat Recovery in Food Processing - Pantaleo Et AlDocument15 pagesIntegrating Cogeneration and Intermittent Waste Heat Recovery in Food Processing - Pantaleo Et AlRobertNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Concentration TermsDocument17 pagesConcentration Termskkbhai1913No ratings yet
- Botox For Plantar FasciitisDocument31 pagesBotox For Plantar FasciitisAngie BongNo ratings yet
- MC Injekt2033 PDFDocument2 pagesMC Injekt2033 PDFhemantrulzNo ratings yet
- Objetivo: Determinar El Nivel de Conocimiento Sobre La Prescripción FarmacológicaDocument17 pagesObjetivo: Determinar El Nivel de Conocimiento Sobre La Prescripción FarmacológicaYefferson Hilario LlantoyNo ratings yet
- European REE ConferenceDocument492 pagesEuropean REE ConferencePablo SebastianNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21 Organic & Inorganic ChemistryDocument5 pagesLesson 21 Organic & Inorganic ChemistryLuke Rogel PazaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium 2Document14 pagesChemical Equilibrium 2Brenda WalkerNo ratings yet
- Lightnin Open Top Fixed Mount MixerDocument16 pagesLightnin Open Top Fixed Mount MixerDave CNo ratings yet
- Product Safety Commission (Afps) : Management: Federal Institute For Occupational Safety and HealthDocument12 pagesProduct Safety Commission (Afps) : Management: Federal Institute For Occupational Safety and HealthFabricio AmorimNo ratings yet
- Validation Part2Document48 pagesValidation Part2gvasNo ratings yet
- Genepax - Water Powered CarDocument2 pagesGenepax - Water Powered CarGaurav Kumar100% (1)
- Pasteurization of MilkDocument16 pagesPasteurization of MilkFaizan TariqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document17 pagesChemistry 2Harshit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- IsotretinoinDocument4 pagesIsotretinoinMagda CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Preparation of Visits by The Competent Inspection AuthoritiesDocument18 pagesChecklist For Preparation of Visits by The Competent Inspection AuthoritiesSrinivas Polikepati100% (1)
- Howweedgrow Ultimate HydroDocument3 pagesHowweedgrow Ultimate HydroPatricio de RegilNo ratings yet
- Upvc Pipes And Fittings: ΩÉ''''eó''''dG ƒ''''µ'''HÉ'''°S ™'''æ'°ü'eDocument38 pagesUpvc Pipes And Fittings: ΩÉ''''eó''''dG ƒ''''µ'''HÉ'''°S ™'''æ'°ü'eRanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Discussion N Conclusion of Unit Separation MembraneDocument3 pagesDiscussion N Conclusion of Unit Separation Membranekarangan08No ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance For AflasDocument10 pagesChemical Resistance For AflasAlex VarNo ratings yet
- Manual Compresor CentrifugoDocument68 pagesManual Compresor CentrifugoJose HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Virtual LeaksDocument0 pagesUnderstanding Virtual LeaksGeorge BadgerNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy FinalDocument142 pagesVital Pulp Therapy FinalParamesh NdcNo ratings yet
- Cyanide Recovery and Detoxification Study On Seabridge Gold's KSM ProjectDocument15 pagesCyanide Recovery and Detoxification Study On Seabridge Gold's KSM ProjectlauramanjarresNo ratings yet
- Table 1: Substrates of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) EnzymesDocument6 pagesTable 1: Substrates of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) EnzymesNurul Kamilah SadliNo ratings yet
- 4089 8019 1 SMDocument12 pages4089 8019 1 SMGusti Ayoe NurjanahNo ratings yet
- Coumarin Analogues From The Citrus Grandis (L.) Osbeck and Their Hepatoprotective ActivityDocument39 pagesCoumarin Analogues From The Citrus Grandis (L.) Osbeck and Their Hepatoprotective ActivityHoàng Sơn Nguyễn LêNo ratings yet
- Super StuccoDocument2 pagesSuper Stuccobalab2311No ratings yet
- Text of Article 1993Document8 pagesText of Article 1993NaufalNo ratings yet
Abstract - Waste Heat Recovery
Abstract - Waste Heat Recovery
Uploaded by
kalaiselvanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract - Waste Heat Recovery
Abstract - Waste Heat Recovery
Uploaded by
kalaiselvanCopyright:
Available Formats
APPLICATION OF HEAT EXCHANGER IN WASTE
HEAT RECOVERY
PRESENTED BY
V. Kalaiselvan,
S. Renald Rich,
Oxford Engineering college,
Pirattiyur,
Trichy.
Kalai.271863@gmail.com
9715982180.
ABSTRACT:
Industrial waste heat refers to energy that is generated in industrial process without
being put in to the practical use. Source of waste heat includes heated combustion gases (which
discharge in to the atmosphere), heated product in the industrial process, heat transfer from
hot body surface … Studies have been estimated that as much as 30 to 50% of industrial energy
consumption is ultimately discharged as waste heat. Waste heat recovery entails capturing and
reusing the waste heat in industrial process for heating or for Mechanical of Electrical work.
Example – Uses of waste heat includes generating electricity, preheating combustion air,
preheating furnace loads and space heating. The result of this investigation serves as a basis for
understanding the state of waste heat recovery technologies. Technology needs are identified
in two broad areas: 1) extending the range of existing technologies to enhance the range of
feasibility and recovery efficiency. 2) Exploring new methods for waste heat recovery, especially
for unconventional waste heat sources.
Objective of this abstract:
Overview of conventional and developing heat recovery technology in abroad.
Evaluate the quantity and quality of industrial waste heat source.
Describe current waste heat recovery practices in different application.
WASTE HEAT RECOVERY:
Waste heat losses arises from both equipment inefficiency and thermodynamic
limitation on the equipment. For example consider any type of furnace in which minimum 40%
of disposion as waste.
Effort has been made to design more energy efficient reverberatory furnace with better
heat transfer and lower exhaust temperatures; however the law of thermodynamics place a
lower limit on the temperature of exhaust gases. Since, heat exchanger involves energy
transformation from a higher temperature source to lower temperature. But, the combustion
temperature always exceed the molten aluminum temperature in order to facilitate the
aluminum.
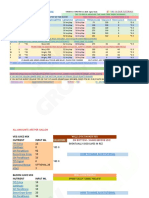
Temperature classification of waste heat sources and recovery techniques:
Temp Example Advantage Disadvantage Recovery methods
Range sources
High Furnaces, iron High quality High Combustion air
>12000F cupola energy, High temperature preheaters, furnace
efficiency creates load pre heaters.
power increased
generation, thermal
High heat stresses on
transfer rate heat exchange
per unit area. materials,
increases
chemical
activities.
Medium Steam boiler More Increased Combustion air
450- exhaust , gas compatible chemical preheat, transfer to
0
1200 F turbine with heat activities/corro low temperature
exhaust, exchanger sion process, organic
reciprocating materials, rankine cycle for
engine practical for power generation
exhaust, drying power
packing oven. generation
Low Gas fired Large For Space heating,
0
<450 F boilers, ovens, quantities of combustion Domestic water
ethylene low- exhausts and heating, Upgrading via
furnace,etc., temperature exchanger a heat pump to
heat corrosion. increase temp for end
contained in use, Organic Rankine
numerous Cycle.
product
streams.
You might also like
- Drum Residence Time Agglomerator Paper ALTA 2005Document28 pagesDrum Residence Time Agglomerator Paper ALTA 2005Steve Dennis100% (2)
- Baravis PDFDocument1 pageBaravis PDFAlexander ConquistaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Waste Heat Recovery in IndustriesDocument4 pagesA Review On Waste Heat Recovery in IndustriesBharat ShirsathNo ratings yet
- UUSITALODocument9 pagesUUSITALOMarcosNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Waste Heat Recovery Unit Using The Exhaust Gas Emitted From Internal Combustion EngineDocument6 pagesThermal Analysis of Waste Heat Recovery Unit Using The Exhaust Gas Emitted From Internal Combustion EngineAmal RajNo ratings yet
- IAC Student Webinar May SachinDocument59 pagesIAC Student Webinar May SachinMirnes FejzicNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Waste Heat and PressurDocument4 pagesA New Approach To Waste Heat and Pressurעקיבא אסNo ratings yet
- WHR ResearchDocument22 pagesWHR ResearchSiddharth ModiNo ratings yet
- Final Report of Heat TransferDocument25 pagesFinal Report of Heat Transferimdian0582090No ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery: Training Session On Energy EquipmentDocument32 pagesWaste Heat Recovery: Training Session On Energy EquipmentRomuel PioquintoNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, CommerciallyDocument9 pagesSyllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, Commerciallymanvendra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, CommerciallyDocument18 pagesSyllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, Commerciallyalzewam152100% (2)
- Analysis and Perspective On Heat Pump For IndustriDocument27 pagesAnalysis and Perspective On Heat Pump For IndustriJianping TangNo ratings yet
- Air-Source Hybrid Absorption-Compression Heat Pumps With Three-StageDocument16 pagesAir-Source Hybrid Absorption-Compression Heat Pumps With Three-StageDaniel DimaNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery in Cement Plant IJERTV3IS051014 PDFDocument5 pagesWaste Heat Recovery in Cement Plant IJERTV3IS051014 PDFDurjoy ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of The Flow Streams Behavior in A Self-Regenerative Crucible FurnaceDocument7 pagesNumerical Simulation of The Flow Streams Behavior in A Self-Regenerative Crucible FurnaceperulesNo ratings yet
- Advanced Combustion Systems For Annealing and Pickling LinesDocument5 pagesAdvanced Combustion Systems For Annealing and Pickling LinesAlessandro LazzarettoNo ratings yet
- Ird Cet Paper UscDocument3 pagesIrd Cet Paper UscMohamed Abashar MusmarNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery Vinay ShuklaDocument31 pagesWaste Heat Recovery Vinay ShuklaVnyNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery TechniquesDocument62 pagesWaste Heat Recovery Techniquesdhruv100% (1)
- Heat RecovDocument31 pagesHeat RecovMakatoLeonNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument4 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryMudasar JavedNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, CommerciallyDocument10 pagesSyllabus Waste Heat Recovery: Classification, Advantages and Applications, Commerciallymanvendra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Energy II - EnergyEfficiency and HeatRecoveryDocument27 pagesEnergy II - EnergyEfficiency and HeatRecoverymluisa.boteroNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery in Selected Industries - USEPA '82Document8 pagesWaste Heat Recovery in Selected Industries - USEPA '82Shashank SaneNo ratings yet
- Zhang 2020Document17 pagesZhang 2020WuberestNo ratings yet
- Energy: Opeyemi Bamigbetan, Trygve Magne Eikevik, Petter Nekså, Michael Bantle, Christian SchlemmingerDocument9 pagesEnergy: Opeyemi Bamigbetan, Trygve Magne Eikevik, Petter Nekså, Michael Bantle, Christian SchlemmingerEduardo Jose Tello del pinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Waste Heat RecoveryDocument29 pagesLecture 7 Waste Heat RecoveryUsman AliNo ratings yet
- Co Generation Unit 4Document52 pagesCo Generation Unit 4Johnson Johnson100% (2)
- OT - PAP - A.Deshmukh M.Kavade - 2017 - Study & Review of Heat Recovery Systems For SO2 Gas Generation Process in SugarDocument4 pagesOT - PAP - A.Deshmukh M.Kavade - 2017 - Study & Review of Heat Recovery Systems For SO2 Gas Generation Process in SugarEduardo CandelaNo ratings yet
- Sci Hub - Investigation of The Thermal Performance of A Novel FlatDocument1 pageSci Hub - Investigation of The Thermal Performance of A Novel FlatSamah AhmedNo ratings yet
- CHEN505 Note 1Document6 pagesCHEN505 Note 1OkePreciousEmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Waste Management: Fabio Dal Magro, Haoxin Xu, Gioacchino Nardin, Alessandro RomagnoliDocument10 pagesWaste Management: Fabio Dal Magro, Haoxin Xu, Gioacchino Nardin, Alessandro RomagnoliKARAN KHANNANo ratings yet
- Combination of SRC and ORCDocument13 pagesCombination of SRC and ORCBerkay AslanNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument25 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryJoeb DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Furnace Waste ReductionDocument10 pagesFurnace Waste ReductionSanjeev PmNo ratings yet
- QTR2015 6M Waste Heat Recovery PDFDocument40 pagesQTR2015 6M Waste Heat Recovery PDFMuh AmmadNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument19 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryAnjanKumarMahanta100% (2)
- Unit Ii Boilers 2.1BOILER:: 2.2 ComparisonDocument32 pagesUnit Ii Boilers 2.1BOILER:: 2.2 Comparisonmohan velNo ratings yet
- Induction Heating DRMDocument8 pagesInduction Heating DRMHoangNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine-GTU-Sem-1Document78 pagesHeat Engine-GTU-Sem-1Khushank MNo ratings yet
- Handbook: LightingDocument1 pageHandbook: LightingreacharunkNo ratings yet
- High Efficiency Heat-Recirculating Domestic Gas BurnersDocument13 pagesHigh Efficiency Heat-Recirculating Domestic Gas Burnersanton verNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument37 pagesWaste Heat Recoveryommech2020No ratings yet
- Energy Conversion and Management: Javier Peña-Lamas, Juan Martinez-Gomez, Mariano Martín, José María Ponce-OrtegaDocument11 pagesEnergy Conversion and Management: Javier Peña-Lamas, Juan Martinez-Gomez, Mariano Martín, José María Ponce-OrtegaJuan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat RecoveryDocument12 pagesWaste Heat RecoveryJafarNo ratings yet
- Install Waste Heat Process htgts8Document2 pagesInstall Waste Heat Process htgts8api-19908130No ratings yet
- Furnaces and Furnace ReactorsDocument33 pagesFurnaces and Furnace ReactorsSamyak JainNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2451904918304050 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S2451904918304050 MainJonathan TupizaNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat ExtractionDocument9 pagesWaste Heat ExtractionSandeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Optimum Reheat Pressures For Single and Double Reheat Irreversible Rankine CycleDocument6 pagesDetermination of Optimum Reheat Pressures For Single and Double Reheat Irreversible Rankine CycleSiva KulanjiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Presentation - Shared - Updated 19 - 10 - 20Document51 pagesBoiler Presentation - Shared - Updated 19 - 10 - 20Lokesh ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- Kalina Cycle: Presented By:-Jyoti Chaudhary ME (3 YR) 1118740020Document16 pagesKalina Cycle: Presented By:-Jyoti Chaudhary ME (3 YR) 1118740020KirtiPurohitNo ratings yet
- Progress and Prospects For Research and Technology Development of Supercritical CO2 Thermal Conversion Systems For Power Energy Storage and Waste HeDocument19 pagesProgress and Prospects For Research and Technology Development of Supercritical CO2 Thermal Conversion Systems For Power Energy Storage and Waste Hegetahun esubalewNo ratings yet
- Rivera Et Al 2018, Experimental Assessment of Double Absorption Heat Transformer Operating With H2O LiBrDocument9 pagesRivera Et Al 2018, Experimental Assessment of Double Absorption Heat Transformer Operating With H2O LiBrRedees RedeesNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Thermal Analysis On Heat Transfer Performance of Heat Pipe-1Document15 pagesFinite Element Thermal Analysis On Heat Transfer Performance of Heat Pipe-1RojithNo ratings yet
- J Applthermaleng 2005 06 001Document11 pagesJ Applthermaleng 2005 06 001buffallo120381No ratings yet
- Meza 2014Document8 pagesMeza 2014Angel LopezNo ratings yet
- Integrating Cogeneration and Intermittent Waste Heat Recovery in Food Processing - Pantaleo Et AlDocument15 pagesIntegrating Cogeneration and Intermittent Waste Heat Recovery in Food Processing - Pantaleo Et AlRobertNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningFrom EverandThermodynamic analysis of geothermal heat pumps for civil air-conditioningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Concentration TermsDocument17 pagesConcentration Termskkbhai1913No ratings yet
- Botox For Plantar FasciitisDocument31 pagesBotox For Plantar FasciitisAngie BongNo ratings yet
- MC Injekt2033 PDFDocument2 pagesMC Injekt2033 PDFhemantrulzNo ratings yet
- Objetivo: Determinar El Nivel de Conocimiento Sobre La Prescripción FarmacológicaDocument17 pagesObjetivo: Determinar El Nivel de Conocimiento Sobre La Prescripción FarmacológicaYefferson Hilario LlantoyNo ratings yet
- European REE ConferenceDocument492 pagesEuropean REE ConferencePablo SebastianNo ratings yet
- Lesson 21 Organic & Inorganic ChemistryDocument5 pagesLesson 21 Organic & Inorganic ChemistryLuke Rogel PazaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium 2Document14 pagesChemical Equilibrium 2Brenda WalkerNo ratings yet
- Lightnin Open Top Fixed Mount MixerDocument16 pagesLightnin Open Top Fixed Mount MixerDave CNo ratings yet
- Product Safety Commission (Afps) : Management: Federal Institute For Occupational Safety and HealthDocument12 pagesProduct Safety Commission (Afps) : Management: Federal Institute For Occupational Safety and HealthFabricio AmorimNo ratings yet
- Validation Part2Document48 pagesValidation Part2gvasNo ratings yet
- Genepax - Water Powered CarDocument2 pagesGenepax - Water Powered CarGaurav Kumar100% (1)
- Pasteurization of MilkDocument16 pagesPasteurization of MilkFaizan TariqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document17 pagesChemistry 2Harshit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- IsotretinoinDocument4 pagesIsotretinoinMagda CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Preparation of Visits by The Competent Inspection AuthoritiesDocument18 pagesChecklist For Preparation of Visits by The Competent Inspection AuthoritiesSrinivas Polikepati100% (1)
- Howweedgrow Ultimate HydroDocument3 pagesHowweedgrow Ultimate HydroPatricio de RegilNo ratings yet
- Upvc Pipes And Fittings: ΩÉ''''eó''''dG ƒ''''µ'''HÉ'''°S ™'''æ'°ü'eDocument38 pagesUpvc Pipes And Fittings: ΩÉ''''eó''''dG ƒ''''µ'''HÉ'''°S ™'''æ'°ü'eRanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Discussion N Conclusion of Unit Separation MembraneDocument3 pagesDiscussion N Conclusion of Unit Separation Membranekarangan08No ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance For AflasDocument10 pagesChemical Resistance For AflasAlex VarNo ratings yet
- Manual Compresor CentrifugoDocument68 pagesManual Compresor CentrifugoJose HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Understanding Virtual LeaksDocument0 pagesUnderstanding Virtual LeaksGeorge BadgerNo ratings yet
- Vital Pulp Therapy FinalDocument142 pagesVital Pulp Therapy FinalParamesh NdcNo ratings yet
- Cyanide Recovery and Detoxification Study On Seabridge Gold's KSM ProjectDocument15 pagesCyanide Recovery and Detoxification Study On Seabridge Gold's KSM ProjectlauramanjarresNo ratings yet
- Table 1: Substrates of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) EnzymesDocument6 pagesTable 1: Substrates of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) EnzymesNurul Kamilah SadliNo ratings yet
- 4089 8019 1 SMDocument12 pages4089 8019 1 SMGusti Ayoe NurjanahNo ratings yet
- Coumarin Analogues From The Citrus Grandis (L.) Osbeck and Their Hepatoprotective ActivityDocument39 pagesCoumarin Analogues From The Citrus Grandis (L.) Osbeck and Their Hepatoprotective ActivityHoàng Sơn Nguyễn LêNo ratings yet
- Super StuccoDocument2 pagesSuper Stuccobalab2311No ratings yet
- Text of Article 1993Document8 pagesText of Article 1993NaufalNo ratings yet