Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chem One Pager
Chem One Pager
Uploaded by
Reid MorganOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chem One Pager
Chem One Pager
Uploaded by
Reid MorganCopyright:
Available Formats
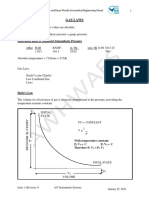
Boyle’s Law P1V1 = P2V2 P1 = Initial At constant At 1.
70, a
Pressure temperature, sample of gas
V1 = Initial pressure takes up
Volume increases and 4.25 L. If the
P2 = New volume pressure is
Pressure decreases increased to 2.40
V2 = New atm, what is the
Volume new volume
(V2)?
(1.70atm)(4.25L)
= (2.40 atm) (v2)
7.225/L = 2.40
atm V2
V2 = 3.01 L
Charles law V1/T1 = V2/T2 V1= Initial At constant A balloon takes
volume Pressure, up 625 L at 0
T1 = Initial volume and Celcius. If it is
temperature temperature heated to 80
V2 = New increases Celcius, what is
Volume the new volume?
T2 = New ( Convert the
Temperature temperature from
celsius to kelvin )
625 L/273 K =
V2/353K
22065 = 273V2
V2 = 808 L
Gay Lussacs P1/T1 = P2/T2 P1 = Initial At constant If the pressure in
Law pressure volume, a car tire is 1.88
T1 = Initial pressure and atm at 25
temperature temperature degrees celsius,
P2 = New increases what will be the
pressure pressure if the
T2 = New temperature
Temperature warms to 37
degrees celsius?
1.88 atm/298 K =
x/310 K
58.28 atm/K =
298x P2 = 1.96
atm
Combined Gas P1V1/T1=P2V2/ V = volume in L All laws A gas at 110 kPa
Law T2 T=Temp in K combined at 30.0 degrees
P = Pressure in celsius fills a
KPa container with an
initial 2.00 L. If
the temperature
is raised 80
degrees celsius,
and pressure is
raised to 440
kPa, what is V2?
(110kPa)(2.00L)(
353)/
(303)(440kPa) =
77660/133320 =
0.58
0.58 L = V2
Ideal Gas Law PV = nRT P = pressure Only use for the What’s the
P = nRT/V V= volume most ideal gases pressure in atm
V= nRT/P N= number of and non of a 0.108 mol
changing
n= VP/RT moles sample of the
variables
R = ideal gas gas at a temp of
constant 20 degrees
T = Temperature celsius, if its
volume is 0.505
L?
P=
(0.108)(0.821)(2
93) / (0.505) =
5.14 atm
You might also like
- Roller Mill Similago II ManualDocument100 pagesRoller Mill Similago II ManualManuel Javier G'100% (1)
- Sluice GateDocument24 pagesSluice GateEldhoThomas100% (1)
- Eurocode 2 Part 1,4 - DDENV 1992-1-4-1994 PDFDocument26 pagesEurocode 2 Part 1,4 - DDENV 1992-1-4-1994 PDFmarineugen0% (1)
- General Chemistry-1Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry-1ampineda4018pamNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas LawDocument19 pagesCombined Gas LawDhea Angela A. Capuyan100% (2)
- GasesDocument65 pagesGasesjNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws ExercisesDocument26 pagesGas Laws ExercisesAnonymousGodiswithyouNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - Chapter 5 The Gaseous StateDocument18 pagesSilo - Tips - Chapter 5 The Gaseous StateJerich Ivan PaalisboNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument6 pagesGas LawskimNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument13 pagesChemical ReactionsAprilyn LaribaNo ratings yet
- Boyles Law and Charles LawDocument23 pagesBoyles Law and Charles LawSharmaine C. TABADANo ratings yet
- Lecture Combined Gas LawDocument3 pagesLecture Combined Gas Lawjacobambuan0805No ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience ReviewerPamee BautistaNo ratings yet
- Combined Gas LawDocument7 pagesCombined Gas LawAllenWORXNo ratings yet
- Ch. 12 - Gases: II. The Gas Laws Boyles Charles Gay-LussacDocument22 pagesCh. 12 - Gases: II. The Gas Laws Boyles Charles Gay-LussacEmmie Denisse ApistarNo ratings yet
- P2 2.5 Atm: T2 20° CelciusDocument3 pagesP2 2.5 Atm: T2 20° Celciusashley jean sapanNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gases: Charles' LawDocument20 pagesIdeal Gases: Charles' LawJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- TF Lecture 07Document6 pagesTF Lecture 07chandumamidi18No ratings yet
- The Gas Laws Boyle's LawDocument4 pagesThe Gas Laws Boyle's LawFrancis Alfred DanaoNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument27 pagesGas LawsChese Ann PepinoNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Compiled Act - Answer KeysDocument5 pagesGas Laws Compiled Act - Answer KeysRamirez JazzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MatterDocument9 pagesChapter 11 - Thermal Properties of MattergnkstarNo ratings yet
- Montessori de San Ildefonso, Inc.: Learning KitDocument6 pagesMontessori de San Ildefonso, Inc.: Learning KitAliah Jashel Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Cheat SheetDocument1 pageGas Laws Cheat SheetWeljun GallardoNo ratings yet
- Eeac 104 Handout 2Document1 pageEeac 104 Handout 2moclarit2212601No ratings yet
- LECTURE 5 Charles LawDocument1 pageLECTURE 5 Charles LawAna May RafalNo ratings yet
- Gas (3 Files Merged)Document76 pagesGas (3 Files Merged)Mashael 7No ratings yet
- Science Quarter 4 ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience Quarter 4 Reviewercali anna75% (4)
- ES III/ADGE 1 - Final - Module 10/week 10Document6 pagesES III/ADGE 1 - Final - Module 10/week 10Oct Toberey MendozaNo ratings yet
- Gas Properties and Laws NotesDocument4 pagesGas Properties and Laws NotesAlAr-JohnTienzoTimeniaNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Gas LawDocument23 pages4.4 Gas LawkhodijahaminNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Model: Review, Ideal Gas Model, Ideal Gas Equation of State, Thermodynamic Properties of Ideal GasesDocument34 pagesIdeal Gas Model: Review, Ideal Gas Model, Ideal Gas Equation of State, Thermodynamic Properties of Ideal GasesJake SyNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws ProblemsDocument46 pagesGas Laws ProblemsIris LeuterioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Temperature and Kinetic Theory Part 2Document45 pagesChapter 1 - Temperature and Kinetic Theory Part 2a194660No ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument63 pagesGas LawsJay-mee Claire V. DioNo ratings yet
- Module 3 (Lesson 1 and 2)Document10 pagesModule 3 (Lesson 1 and 2)rocky.mercado2No ratings yet
- Hello!: I Am Sir DeanDocument30 pagesHello!: I Am Sir DeanDean MalaluanNo ratings yet
- Charles LawDocument2 pagesCharles LawMsAnn000100% (2)
- PHY 103 Equations of StateDocument37 pagesPHY 103 Equations of Statebishal alamNo ratings yet
- Module 12 - Lesson - 1 - The+Gas+LawsDocument23 pagesModule 12 - Lesson - 1 - The+Gas+LawsMihadNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionDocument4 pagesAtmosphere Measurable Properties of Gases: CompositionjenduekieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 GasesDocument30 pagesChapter 13 GasesGwen100% (1)
- General Chemistry: Pressure and Its Common UnitsDocument15 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Pressure and Its Common UnitsDenver John Caloza LamarcaNo ratings yet
- 4-3 Physics WK 3 Combined Gas LawDocument3 pages4-3 Physics WK 3 Combined Gas Lawlaisha chanNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Document47 pagesTopic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Joshua LaBordeNo ratings yet
- Chem0861 GasLawProblemsDocument3 pagesChem0861 GasLawProblemsHavenNo ratings yet
- Physicsweek1and2 220404082331Document70 pagesPhysicsweek1and2 220404082331Alice RiveraNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument18 pagesChemistrywildlife quizNo ratings yet
- Laws of Gases PhysicsDocument11 pagesLaws of Gases PhysicsAngel Jameson SibayanNo ratings yet
- 2001 SAT Practice TestDocument2 pages2001 SAT Practice TestAnonymous 23uIgnINo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Gases 2Document7 pagesLecture Notes - Gases 2goksu dundarNo ratings yet
- Engg ThermodynamicsgfDocument3 pagesEngg Thermodynamicsgfphysics a2No ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument31 pagesGas Lawsapi-546066323No ratings yet
- Gas Laws PPTDocument41 pagesGas Laws PPTIsabelle OdenbachNo ratings yet
- 4 FAD Calculations - Shapoorji-1Document1 page4 FAD Calculations - Shapoorji-1rinabiswasNo ratings yet
- Thermo DynamicsDocument22 pagesThermo DynamicsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Kimia Fisika Pertemuan 1-2Document52 pagesKimia Fisika Pertemuan 1-2BahauddinbalqostolaniNo ratings yet
- The Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThe Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- AC Instruments Systems - Part 1 Jan 22, 2021Document45 pagesAC Instruments Systems - Part 1 Jan 22, 2021Ron McIntyreNo ratings yet
- W-4, Chap.3-Properties of Pure Substances-2Document31 pagesW-4, Chap.3-Properties of Pure Substances-2سيمو بشيريNo ratings yet
- Maryknoll School of Lupon, Inc.: Kambing Baratua ST., Poblacion, Lupon, Davao OrientalDocument13 pagesMaryknoll School of Lupon, Inc.: Kambing Baratua ST., Poblacion, Lupon, Davao OrientalJohn Paull CuaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Limiting The Gas Turbine Load and Operating at Base LoadDocument6 pagesLimiting The Gas Turbine Load and Operating at Base Loadramkrishna100% (2)
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportDulshan uddeepanaNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Boiler Firesides and WatersidesDocument13 pagesCleaning Boiler Firesides and WatersidesAhmed YosifNo ratings yet
- 4IK22RGNDocument7 pages4IK22RGNBlAdE 12No ratings yet
- Kistler CatalogueDocument20 pagesKistler Cataloguetushar girotraNo ratings yet
- Overhaul of Generator EngineDocument51 pagesOverhaul of Generator EngineSayem kaifNo ratings yet
- Cast Steel Production: Properties and Composition: Testing and Inspection at The FoundryDocument15 pagesCast Steel Production: Properties and Composition: Testing and Inspection at The Foundryyared sitotawNo ratings yet
- Series 59 Full Port Ball ValveDocument4 pagesSeries 59 Full Port Ball Valvekyeong cheol leeNo ratings yet
- Catal GPM Sect4 GB 12 2004 RevADocument46 pagesCatal GPM Sect4 GB 12 2004 RevARouchan NaserNo ratings yet
- CR Tools and Spare Parts 20.10Document82 pagesCR Tools and Spare Parts 20.10Oswaldo MongeNo ratings yet
- Drilling Calculation SheetDocument5 pagesDrilling Calculation SheetDewy CoxNo ratings yet
- 1 Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams: F.K.KONG and M.CHEMROUK, University of Newcastle Upon TyneDocument2 pages1 Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams: F.K.KONG and M.CHEMROUK, University of Newcastle Upon TyneCF W FredyNo ratings yet
- Media Search - REHS2210 - Assembly Procedure For The 793D Off-Highway Truck (7000, 7006, 7960)Document383 pagesMedia Search - REHS2210 - Assembly Procedure For The 793D Off-Highway Truck (7000, 7006, 7960)Deyvi0% (1)
- Water FountainDocument6 pagesWater FountainGanesh Bharath KumarNo ratings yet
- DBR MediniNagar JharkhandDocument7 pagesDBR MediniNagar JharkhandinfohydNo ratings yet
- Ignition Model #35496: Installation InstructionsDocument8 pagesIgnition Model #35496: Installation InstructionsAlfonso JaureguiNo ratings yet
- Grove Gate Valve G12Document24 pagesGrove Gate Valve G12Jesus VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions +solutions UT Q1234Document9 pagesExam Questions +solutions UT Q1234LexNo ratings yet
- Photo: GSR750ADocument2 pagesPhoto: GSR750AsilvaNo ratings yet
- Simple Two-Pole DC Motor: BrushedDocument10 pagesSimple Two-Pole DC Motor: BrushedanupthattaNo ratings yet
- MECH3427 Design Project 2017Document8 pagesMECH3427 Design Project 2017Genesis Norbert AlconabaNo ratings yet
- Gesamtübersicht 2018 en Klein PDFDocument100 pagesGesamtübersicht 2018 en Klein PDFCarlos Landeta Garcia100% (1)
- Ufc 3 401 01 Mechanical EngineeringDocument22 pagesUfc 3 401 01 Mechanical EngineeringNoli T. CaronanNo ratings yet
- 2015+Toyota+Tundra+Repair+Manual N11Document289 pages2015+Toyota+Tundra+Repair+Manual N11Biniyam Bekele100% (1)
- Robotics: Jacobians: Velocities and Static Forces II: Sami HaddadinDocument30 pagesRobotics: Jacobians: Velocities and Static Forces II: Sami HaddadinVincent luiNo ratings yet
- A518 04 WDocument10 pagesA518 04 WJustin DiMambroNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco: Industrial Aluminium Piston CompressorsDocument132 pagesAtlas Copco: Industrial Aluminium Piston CompressorsMichael TanNo ratings yet