Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCP
Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCP
Uploaded by
AMIEL SIMON NGOOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCP
Ngo 2bsn1 Ncm109 Prelim NCP
Uploaded by
AMIEL SIMON NGOCopyright:
Available Formats
University of Santo Tomas - Legazpi
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES
Legazpi City
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN NURSING
NCM 109: CARE OF MOTHER AND CHILD AT RISK OR WITH PROBLEMS, ACUTE AND CHRONIC
DEMOGRAPHIC DATA OF YOUR PATIENT
NAME: _____N/A_____ AGE: ______N/A_______ RM./ BED NO.______N/A________ MEDICAL RECORD NO._______N/A____________
DR: _______________N/A______________ DIAGNOSIS: KETONURIA
NURSING PROBLEM: BABY OF A DIABETIC MOM
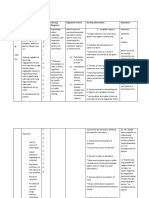
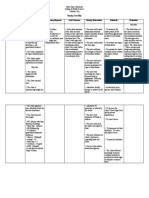
ASSESSMENT BACKGROUND
DATE NURSING DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
OBJECTIVE SUBJECTIVE KNOWLEDGE
-Frequent -Excessive Alteration in Ketonuria is a After 2-3 days -Determine To help in
After 2-3
urination Thirst nutrition needs: Less medical of Nursing client’s evaluating days of
than body requirements condition in Intervention, dietary client’s Nursing
Marc -Vomiting -Nausea
r/t insufficiency of which ketone the following program and level of Intervention
h 9, -Fruity-scente -Dehydratio bodies are usual pattern understandin , the
insulin are to be
2021 d breath n present in the g and/or following
established:
urine. It is compliance to goals were
-Confusion -Heavy -Verbalized
seen in a strict established:
breathing understanding
-High urine conditions in dietary
Page 1 of 7
NGO, AMIEL SIMON S. / 2BSN1
University of Santo Tomas - Legazpi
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES
Legazpi City
ketone levels -Dilated which the body of regiment of regimen. -Achieved
pupils produces condition. normal blood
-Hyperglycemia Possible result of
excess ketones glucose
, -Reports of diagnostic procedures: -Maintain level.
as an
usually >400mg/ Blurry fasting serum
-FINGER-STICK KETONE indication -Monitor Electrolyte
gL vision blood glucose -Normal fluid
BLOOD TEST: that it is fluid and imbalances
levels between and
-Metabolic -Weakness using an electrolyte can lead to
60-100 mg/dl electrolyte
acidosis with and fatigue Under alternative balance to further
Normal balance.
elevated anion 0.6 source of -Increase in prevent complication
urine
gap millimole energy. It is weight at least dehydration s and cardiac -Client will
ketone level
s per liter seen during 24-30 pounds or and arrhythmias. be visiting
-Kussmaul
starvation or as appropriate complication diabetic
breathing
Higher than more commonly s such as clinic for
0.6 to 1.5 -Improved fluid better
normal; test in type 1 decreased
millimole and electrolyte ongoing
again in 2 to diabetes sodium,
s per liter balance diabetes
4 hours mellitus. potassium,
management.
Production of -Patient will calcium, and
1.6 to 3.0 Moderate ketone bodies be free from the magnesium.
-Client will
Page 2 of 7
NGO, AMIEL SIMON S. / 2BSN1
University of Santo Tomas - Legazpi
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES
Legazpi City
is a normal signs and -Monitor Consistently report less
millimole urine
response to a symptoms of blood glucose high blood physical
s per liter ketone
shortage of ketonuria levels and glucose discomfort.
level; call
glucose, meant (fruity-scente administer levels, over
your doctor
to provide an d breath, insulin as 400 mg/dL, are
immediately
alternate excessive appropriate the primary
source of fuel thirst, indicator of
Above Dangerousl
from fatty frequent ketone
3.0 y high level;
acids. urination, production.
millimole go to the ER
Ketonuria is weakness,
s per liter immediately
most common in confusion).
individuals
who have
-URINE STRIP TEST will
diabetes,
show that you have:
particularly
-No ketones type 1 diabetes
-Trace amounts of mellitus. It
ketones can also occur
-Moderate levels of in women who
ketones are pregnant or
-Large amounts of breastfeeding
ketones . If ketone
levels rise too
high for too
Page 3 of 7
NGO, AMIEL SIMON S. / 2BSN1
University of Santo Tomas - Legazpi
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES
Legazpi City
-KETONE BLOOD TEST long, your
RESULT: blood becomes
acidic. This
Below 0.6 mmol/L-
can harm your
Normal range.
health.
0.6 to 1.5 mmol/L-
Presence of ketones in
blood
Above 1.5 mmol/L-
Greater risk for
developing
ketoacidosis.
-Monitor Weight gain
weight daily serves as an
or as indicator for
indicated. determining
caloric
adjustments.
Page 4 of 7
NGO, AMIEL SIMON S. / 2BSN1
University of Santo Tomas - Legazpi
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES
Legazpi City
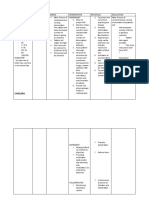
INTERVENTION RATIONALE
-Auscultate bowel sounds, noting the presence of abdominal pain or Abdominal pain is an indication of Ketonuria. Nausea and vomiting may
abdominal bloating, nausea, or vomiting be brought about by a deficiency in carbohydrates, which may result in
the metabolism of fats and development of ketosis.
-Maintain on NPO status as indicated Further carbohydrate and/or fat ingestion have the potential for
undermining efforts to eliminate ketoacids and control blood glucose
levels, and there is an increased risk of vomiting and aspiration
-Monitor laboratory status (Serum glucose, pH, HCO3, acetone) Incidence of fetal and newborn abnormalities is decreased when fasting
blood sugar levels range between 60 and 100 mg/dl, pre-prandial levels
between 60 and 105 mg/dl
- Instruct and teach client to monitor sugar using a finger-stick method. Testing the blood for ketones gives us an earlier warning because ketones
show up in the blood earlier than in urine. This is helpful because
sometimes you cannot give a urine sample due to dehydration.
- Adjust diet or insulin regimen to meet individual needs. Prenatal metabolic needs change throughout the trimesters, and
adjustment is determined by weight gain and laboratory test results.
Insulin needs in the first trimester are 0.7 unit/kg of body weight.
Between 18-24 weeks of gestation, it increases to 0.8 unit/kg; at 34
weeks’ gestation, 0.9 unit/kg, and 1.0 unit/kg by 36- week gestation.
- Teach the importance of regularity of meals and snacks (e.g., three Eating very frequent small meals improves insulin function.
meals or 4 snacks) when taking insulin.
Page 5 of 7
NGO, AMIEL SIMON S. / 2BSN1
University of Santo Tomas - Legazpi
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES
Legazpi City
-Administer glucose solution such as dextrose and half normal saline IV dextrose is added to avoid the development of cerebral edema. In
addition, the rate of insulin infusion may need to be slowed down to
between 0.02 and 0.05 units/kg/hr.
-Provide a diet consisting of 60% carbohydrates, 20% fats, 20% proteins, Diet-specific to the individual is necessary to maintain normoglycemia
in designated number of meals and to obtain desired weight gain. In-depth teaching promotes
understanding of own needs and clarifies misconceptions, especially for
a client with gestational diabetes.
Recommend monitoring urine ketones on awakening and when a planned meal Insufficient caloric intake is reflected by ketonuria, indicating a need
or snack is delayed for an increased intake of carbohydrates or additional snack in the
dietary plan (e.g., recurrent presence of ketonuria on awakening may
be eliminated by 3 am a glass of milk).
Provide information regarding the signs and symptoms and difference of Hyperglycemia in pregnancy is a medical condition resulting from either
hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. pre-existing diabetes or insulin resistance developed during pregnancy.
Transfer of glucose across the placenta stimulates fetal pancreatic
insulin secretion, and insulin acts as an essential growth hormone. If
resistance to maternal insulin action becomes too pronounced, maternal
hyperglycemia occurs and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) may be
present.
A blood sugar reading of less than 60 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL)
is considered hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia during pregnancy happens most
often in women with diabetes. Hypoglycemia can occur in pregnant women
without diabetes, but it’s much more likely to be seen in women taking
Page 6 of 7
NGO, AMIEL SIMON S. / 2BSN1
University of Santo Tomas - Legazpi
COLLEGE OF HEALTH SCIENCES
Legazpi City
insulin.
Prepare for hospitalization if diabetes is not controlled. Infant morbidity is linked to maternal hyperglycemia-induced fetal
hyperinsulinemia.
Page 7 of 7
NGO, AMIEL SIMON S. / 2BSN1
You might also like
- Power Booty 2.0 Education by Lauren SimpsonDocument42 pagesPower Booty 2.0 Education by Lauren SimpsonBernadett Kálucz100% (11)
- Activity - PT - With - Fluid & Lyte ImbalanceDocument3 pagesActivity - PT - With - Fluid & Lyte ImbalanceAngel Joy CatalanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Face Sheet: G3P2, Pregnancy Uterine (PU), 37 Weeks and 5 Days AOG, Previous CS IIDocument14 pagesClinical Face Sheet: G3P2, Pregnancy Uterine (PU), 37 Weeks and 5 Days AOG, Previous CS IICezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- CUB1 ProgressTest02Document4 pagesCUB1 ProgressTest02Aleksandra Jovanovic100% (2)
- Flex USA July-August 2017Document235 pagesFlex USA July-August 2017Quake11100% (2)
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument9 pagesAcute Pyelonephritistaekado-1No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationJP2001100% (1)
- GRP 3 2 Renal Nephrectomy NCPDocument6 pagesGRP 3 2 Renal Nephrectomy NCPPam RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - MCNDocument2 pagesChapter 6 - MCNPrincess Queenie OlarteNo ratings yet
- Structuring Advanced Practice Knowledge An Internet Resource For Education and Practice (Autosaved)Document18 pagesStructuring Advanced Practice Knowledge An Internet Resource For Education and Practice (Autosaved)Dale Ros CollamatNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Document10 pagesEctopic Pregnancy NCP (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2-A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Physical AssessmentDocument5 pagesNursing Physical AssessmentApril Louise PaluganNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process NUTRITIONDocument82 pagesNursing Process NUTRITIONNoci M. FrenkNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan DMDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan DMnikaaraaaNo ratings yet
- B NCP On and Off Fever 2b ImproveddocxDocument6 pagesB NCP On and Off Fever 2b ImproveddocxKylie CatralNo ratings yet
- NCP FinalDocument3 pagesNCP FinalCheska Mae PalicNo ratings yet
- NCP in PediaDocument3 pagesNCP in Pediajoister011750% (2)
- Suppositories: Abenol (CAN)Document2 pagesSuppositories: Abenol (CAN)Mikko McDonie VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document7 pagesExperiment 7kimber_gado100% (2)
- Jose Rizal University & Medical Center: KardexDocument2 pagesJose Rizal University & Medical Center: KardexMichael SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Generic Brand Class Therapeutic Pharmacologic Dosage: PPD's Better Pharmacy Drug Hand Book 9 Edition 2009Document4 pagesGeneric Brand Class Therapeutic Pharmacologic Dosage: PPD's Better Pharmacy Drug Hand Book 9 Edition 2009Crystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsDocument4 pagesPathophysiology: Cholecystitis Non Modifiable Factors Modifiable FactorsLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: During 8 Hours Nursing Management: (5) After 8 HoursRawan KhateebNo ratings yet
- 4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Document11 pages4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Sheda BondNo ratings yet
- NCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsDocument9 pagesNCP GRAND CASE PRE C Nursing ProblemsAngie Mandeoya100% (1)
- NCP Inactivity ToleranceDocument16 pagesNCP Inactivity ToleranceChrisTine M. MoralesNo ratings yet
- Case Study CKD Pinakafinal Na TalagaDocument80 pagesCase Study CKD Pinakafinal Na TalagaLance SilvaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Secondary To Cellulitis DM Type 2Document3 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusion Secondary To Cellulitis DM Type 2MichaelaKatrinaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusionkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Complications in PregnancyDocument36 pagesComplications in PregnancyJADE PATEGANo ratings yet
- X. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesX. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- Copd - NCPDocument6 pagesCopd - NCPMonique Sacherow BacherNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning Incomplete AbortionDocument2 pagesDischarge Planning Incomplete AbortionNaotaka KohinataNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Nursing ManagementDocument5 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Nursing ManagementA.No ratings yet
- Practice Summary Paper For PortfolioDocument9 pagesPractice Summary Paper For Portfolioapi-290938460No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Human Response Pattern AMB/Manifestation Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Outcome Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarielle Chua100% (1)
- NCP ProperDocument9 pagesNCP Properstephanie eduarteNo ratings yet
- Penicillin VDocument3 pagesPenicillin Vapi-3797941No ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: HypomagnesemiaDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: HypomagnesemiaMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Sample Case Presentation - Occult BacteremiaDocument51 pagesSample Case Presentation - Occult BacteremiaPrecious Gutierrez BagazinNo ratings yet
- Levemir Product Insert PDFDocument11 pagesLevemir Product Insert PDFDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Burn - Daily Physical AssessmentDocument8 pagesBurn - Daily Physical AssessmentkrishcelNo ratings yet
- Silliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesDocument8 pagesSilliman University: Nursing Care Plan On Preeclampsia With Severe FeaturesRyan Robert V. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Health Management Related To Mrs. Gama: Provide The Client Enough Knowledge About The ProblemDocument5 pagesIneffective Health Management Related To Mrs. Gama: Provide The Client Enough Knowledge About The ProblemAndrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCPDocument4 pagesCase Study NCPKelly OstolNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Sample Letter Templates (4th Year)Document49 pagesSample Letter Templates (4th Year)Yna LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan On Platelet DisordersDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan On Platelet DisordersbhavanaNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Clausii Is A RodDocument9 pagesBacillus Clausii Is A RodGrax DeeNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Computation 2021Document3 pagesNCM 112 Computation 2021Marie Kelsey Acena Macaraig100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalDocument5 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Inference Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Goal Independent: Short Term GoalJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical PaperDocument18 pagesClinical PaperlhhjklllNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAriaNo ratings yet
- CHFDocument35 pagesCHFNurayunie Abd HalimNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquilloDocument4 pagesDRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyNeri ChavezNo ratings yet
- Examples of Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDocument6 pagesExamples of Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechniquesReya Mae OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Codevita 2020 Zone 1 Q & SDocument14 pagesCodevita 2020 Zone 1 Q & S317126511169 VENKUMAHANTI SAI TARUNNo ratings yet
- Beginner & Advanced Rotator Cuff Exercises For Shoulder Pain - MyodetoxDocument18 pagesBeginner & Advanced Rotator Cuff Exercises For Shoulder Pain - MyodetoxJustin Wigon100% (1)
- Concept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Document6 pagesConcept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Jarod Hembrador100% (1)
- Pex 08 03Document4 pagesPex 08 03Adriana Anaya GaribaldiNo ratings yet
- Basics of Therapeutic Diets PDFDocument12 pagesBasics of Therapeutic Diets PDFFaith MarfilNo ratings yet
- William Boone's 1937 Training ProgramDocument3 pagesWilliam Boone's 1937 Training ProgramMiguelin666No ratings yet
- Lactogrow VS Lactogen 2Document3 pagesLactogrow VS Lactogen 2Mardan Love SunnahNo ratings yet
- Adani Wilmar LTDDocument55 pagesAdani Wilmar LTDAmit ChotaiNo ratings yet
- Ephmra - Atcguidelines2018finalDocument154 pagesEphmra - Atcguidelines2018finalClose UpNo ratings yet
- Notes Enzymes:: What Must Occur For A Reaction To Proceed?Document11 pagesNotes Enzymes:: What Must Occur For A Reaction To Proceed?AlfredoKytouNo ratings yet
- NCP - Diabetes Mellitus Prepregnancy/GestationalDocument13 pagesNCP - Diabetes Mellitus Prepregnancy/GestationalClaudine Christophe100% (1)
- Final Organic VegetablesDocument54 pagesFinal Organic VegetablesMarycon Nacito75% (4)
- Build Your Lagging Chest With The 1 - 4 Rep Pump Out MethodDocument9 pagesBuild Your Lagging Chest With The 1 - 4 Rep Pump Out MethodAliNo ratings yet
- The Mediterranean Diet, by Carlos MirasierrasDocument29 pagesThe Mediterranean Diet, by Carlos MirasierrasCarlos Mirasierras100% (1)
- January Free Chapter - French Women Don't Get Facelifts by Mireille GuilianoDocument28 pagesJanuary Free Chapter - French Women Don't Get Facelifts by Mireille GuilianoRandomHouseAU80% (5)
- Banana Value AdditionDocument10 pagesBanana Value AdditionDr-Shoaib MeoNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Fluid ManagementDocument123 pagesPerioperative Fluid ManagementAnonymous 86gki5No ratings yet
- HLTH640 8WK Syllabus (1) - 1Document4 pagesHLTH640 8WK Syllabus (1) - 1Rockeven DesirNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0924224421005124 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0924224421005124 MainLau CondeNo ratings yet
- 100 Workouts 2015Document209 pages100 Workouts 2015Diana RiosNo ratings yet
- Unauthenticated Download Date - 1/31/17 4:04 AMDocument5 pagesUnauthenticated Download Date - 1/31/17 4:04 AMFahmi RaziNo ratings yet
- Laxatives and PugatiivesDocument4 pagesLaxatives and PugatiivesSultan Abdul Hamid IINo ratings yet
- Recipe CalculationsDocument57 pagesRecipe CalculationsMalak BattahNo ratings yet
- Pregestational ConditionsDocument46 pagesPregestational ConditionsSheryl M. Ablao50% (2)
- RobloxDocument2 pagesRobloxRic PlaysNo ratings yet
- Brain Health For The SelfEmpowered PersonDocument8 pagesBrain Health For The SelfEmpowered PersonMichael McCainNo ratings yet
- ChandanKumar 632972Document11 pagesChandanKumar 632972Chandan JhaNo ratings yet