Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ABUTLN2: Electrical, Electronic, & Mechanical Systems in Buildings
ABUTLN2: Electrical, Electronic, & Mechanical Systems in Buildings
Uploaded by
ken talensCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HandbookDocument604 pagesHandbookcharlesc5746100% (14)
- Introduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesKib-anne Miguel PasikanNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument17 pagesElectrical EnergykuevoradzogloriaNo ratings yet
- Applied Electrical Notes Unit 1Document12 pagesApplied Electrical Notes Unit 1The STUDY koala happyNo ratings yet
- Cfe Bu2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCfe Bu2 ReviewerMaria Katrina Ilumin VersozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - ElectricityDocument29 pagesUnit 2 - ElectricityT. Christabel VijithaNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document9 pagesElectricity 1okguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Wldbe301 Basic of ElectricityDocument116 pagesWldbe301 Basic of ElectricityNshimiyimana pacifiqueNo ratings yet
- Getting Started. Conventional Electricity Supply 2021-22Document19 pagesGetting Started. Conventional Electricity Supply 2021-22Leeroy ZizhouNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Electrical TermsDocument8 pagesGlossary of Electrical TermsRafael jei GabisanNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- Basic EE Module 123Document32 pagesBasic EE Module 123Benmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Unit I Electrical AND Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring Systems 10Document38 pagesUnit I Electrical AND Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring Systems 10NithinNo ratings yet
- PHYS101L LabReport9Document13 pagesPHYS101L LabReport9Leidee Charmellie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of ElectricityDocument8 pagesBasic Concept of Electricityvamps sierNo ratings yet
- Bu RSW 1Document8 pagesBu RSW 1Kate Wencelette AraoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity 1.1Document23 pagesIntroduction To Electricity 1.1August DuqueNo ratings yet
- Amta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical SafetyDocument67 pagesAmta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical Safetydunlut pelemNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10th NotesDocument3 pagesElectricity Class 10th Notesyo yeNo ratings yet
- BEE - Manual ODD 2021Document44 pagesBEE - Manual ODD 2021Deekshith raiNo ratings yet
- Module in EE 211 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument39 pagesModule in EE 211 Basic Electrical EngineeringEbacuado, Regine Mae F.No ratings yet
- ETPaperI PDFDocument133 pagesETPaperI PDFanand kumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalJohn Florenz VasquezNo ratings yet
- Electro 1 Student FileDocument6 pagesElectro 1 Student FileHarveyBidañaNo ratings yet
- G9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityDocument4 pagesG9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityKinmokusei MyoeNo ratings yet
- Electricity and LightingDocument15 pagesElectricity and LightingdarielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE NC II MODULE New Edited MASTER LEODocument26 pagesELECTRICAL INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE NC II MODULE New Edited MASTER LEOOLINSTERG COLLEGENo ratings yet
- CE115 Electrical Part ADocument45 pagesCE115 Electrical Part AMrSamspartNo ratings yet
- Las Q 1 Week 1 Ste9Document6 pagesLas Q 1 Week 1 Ste9KimmmiNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument3 pagesDefinition of TermsMarius VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical SystemDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical SystemTurboiitNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument47 pagesBasic ElectronicsPolyn LopezNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Guia InglishDocument10 pagesTrabajo Guia InglishAlejandroDuranNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits & QuantitiesDocument29 pagesElectrical Circuits & QuantitiesDejaunae Lawson50% (2)
- AIRCRAFT Basic ElectricityDocument327 pagesAIRCRAFT Basic ElectricityndrmnlngNo ratings yet
- Uty Revised ReviewerDocument12 pagesUty Revised ReviewerMark Zed Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Eeuti130 Lec1Document22 pagesEeuti130 Lec1frankorola0207No ratings yet
- Current Electricity 2: For Non-Commercial Purposes Only Enjoy!Document21 pagesCurrent Electricity 2: For Non-Commercial Purposes Only Enjoy!Kanishka SeneviratneNo ratings yet
- Bldutl2 - Building Utilities 2 Electrical, Electronics and Mechanical SystemsDocument6 pagesBldutl2 - Building Utilities 2 Electrical, Electronics and Mechanical Systemsgimel tenorioNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument22 pagesElectricityanu.pavansuresh30No ratings yet
- Experiment # 1Document9 pagesExperiment # 1majorskNo ratings yet
- Electricity Supply, Distribution & InstallationDocument11 pagesElectricity Supply, Distribution & Installationshivani dharamthokNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument4 pagesBasic ElectricityMae PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Circuits: Basic DefinitionsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Circuits: Basic DefinitionsArnulfo LavaresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Voltage and Current: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument31 pagesChapter 2 - Voltage and Current: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadHector VergaraNo ratings yet
- G9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityDocument4 pagesG9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityKinmokusei MyoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Electricity Revision NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 12 - Electricity Revision NotesAyush RajNo ratings yet
- Electrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Document51 pagesElectrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Fiorella Amer CarrNo ratings yet
- Bu 2 Quiz ReviewerDocument5 pagesBu 2 Quiz ReviewerSebastian CincoNo ratings yet
- Direct Current and PowerDocument5 pagesDirect Current and PowerElizabeth AnyegaNo ratings yet
- Utilities Assignment 1 1Document5 pagesUtilities Assignment 1 1Ernest VincentNo ratings yet
- AQA P2 Physics Electricity BookletDocument19 pagesAQA P2 Physics Electricity BookletSteve BishopNo ratings yet
- Physicy Test XDocument12 pagesPhysicy Test XMerimaNo ratings yet
- Electricity One Shot Class10Document49 pagesElectricity One Shot Class10saracastic123No ratings yet
- Basic Principal of Electrical CircuitryDocument19 pagesBasic Principal of Electrical CircuitryAreeba ParvezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Electrical and Electronics ElememntsDocument23 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Electrical and Electronics ElememntsHassan Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Electronics & Comp - SkillDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Electronics & Comp - SkillPAnkaj BhamareNo ratings yet
- Summary of Fundamental in ElectronicsDocument19 pagesSummary of Fundamental in ElectronicsReedvejee Hermoso KiamcoNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument11 pagesBasic ElectricityFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- 18.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2021Document20 pages18.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2021balramsharmaNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument60 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversionkujong agacerNo ratings yet
- 1.electrical Distribution Systems Unit IDocument65 pages1.electrical Distribution Systems Unit ISatishdhora SiddanaNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram of 11kV SubstationDocument46 pagesSingle Line Diagram of 11kV SubstationWelday100% (1)
- Measuring Friction and Wear Properties of Extreme Pressure (EP) Lubricating Oils With The Roller-Disk Geometry Using SRV Test MachineDocument7 pagesMeasuring Friction and Wear Properties of Extreme Pressure (EP) Lubricating Oils With The Roller-Disk Geometry Using SRV Test MachinePyone Ei ZinNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Enetek HightechDocument2 pagesData Sheet For Enetek HightechDenizhan AkınNo ratings yet
- Error CaterpillarDocument47 pagesError CaterpillarMarco Nuñez AcostaNo ratings yet
- Development of A Large Cooling Capacity Single Stage GM CryocoolerDocument5 pagesDevelopment of A Large Cooling Capacity Single Stage GM CryocoolerJaydeep PonkiyaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Centrifuges: Clinical ChemistryDocument27 pagesLaboratory Centrifuges: Clinical ChemistryZeeshan YousufNo ratings yet
- Parallel Driving of Synchronous GeneratorDocument7 pagesParallel Driving of Synchronous GeneratorMKIBETUNo ratings yet
- Ieee Cts and Pts 6-10Document99 pagesIeee Cts and Pts 6-10Thyago De Moura JorgeNo ratings yet
- The New MaterialDocument7 pagesThe New MaterialSteve AbonyiNo ratings yet
- SemiKron SKD-82 - 16Document3 pagesSemiKron SKD-82 - 16Mario Penelo RivaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-10Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-10kingstonNo ratings yet
- Dmet13 Robles L06Document17 pagesDmet13 Robles L06John Marc E. TameraNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: T2000xCF-0C0 and T2000xCC-0C0 Low Voltage Fan Coil ThermostatsDocument4 pagesFigure 1: T2000xCF-0C0 and T2000xCC-0C0 Low Voltage Fan Coil ThermostatsVictor AANo ratings yet
- Motor ControlDocument66 pagesMotor Controlferdie marcos100% (1)
- Varistor Products Overview: Circuit Protection SolutionsDocument50 pagesVaristor Products Overview: Circuit Protection SolutionsChenaker HamzaNo ratings yet
- TNB ICPT (Imbalance Cost Pass Through)Document4 pagesTNB ICPT (Imbalance Cost Pass Through)ttNo ratings yet
- R1Document19 pagesR1sheppy3233No ratings yet
- BELIMO 2 Ways Modulating ValveDocument3 pagesBELIMO 2 Ways Modulating ValvelamNo ratings yet
- Nebol Ungere Aer-Ulei EnglezaDocument30 pagesNebol Ungere Aer-Ulei Englezaangela_draguNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesKerwin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Pages From Combined QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument2 pagesPages From Combined QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelieswaheedNo ratings yet
- A700 Basic ManualDocument188 pagesA700 Basic ManualHong Dong XuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Compressors: Air CompressorDocument8 pagesChapter Six Compressors: Air CompressorMicky AlemuNo ratings yet
- Q874 Analog ElectronicsDocument2 pagesQ874 Analog ElectronicsDivyanshu BoseNo ratings yet
- Suction Cups/grippers: Level Compensator LCDocument2 pagesSuction Cups/grippers: Level Compensator LCBe HappyNo ratings yet
- BS en 26 + A1+a2+a3-2006Document146 pagesBS en 26 + A1+a2+a3-2006Abey VettoorNo ratings yet
ABUTLN2: Electrical, Electronic, & Mechanical Systems in Buildings
ABUTLN2: Electrical, Electronic, & Mechanical Systems in Buildings
Uploaded by
ken talensOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ABUTLN2: Electrical, Electronic, & Mechanical Systems in Buildings
ABUTLN2: Electrical, Electronic, & Mechanical Systems in Buildings
Uploaded by
ken talensCopyright:
Available Formats
National University
COLLEGE OF ARCHITECTURE
ABUTLN2: Electrical, Electronic, & Mechanical Systems in Buildings
Name: DE GUZMAN, JOHANNA MAXINE C. Section: ARC194A. Date: 08-31-21 Score:
Exercise No. 1: Introduction to Electricity
I. Essay (20 pts.)
Write a summary explanation for each of the following topic listed below as discussed under Module 01.
A. Definition of Electricity
The magnetic, chemical, and radiative effects of a certain kind of energy created by friction, induction, or
chemical change.
B. Types & Comparison of Electric Current
Direct Current (DC)
-A current which flows in the same direction at a constant time rate. It is found in any electrical gadget that
uses a battery as its power source.
Alternating Current (AC)
-A current that varies in time and direction on a regular basis. It is used to provide power to houses, offices,
and other buildings.
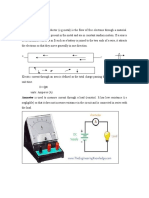
C. Types of Electric Circuits
Closed circuit- is a complete electrical connection in which current flows or circulates
Open circuit- is an electrical circuit without a flow of current.
Series Circuit - a circuit where the same current is circulating through all circuit components.
Parallel Circuit- a circuit in which the components are arranged so that the current divides between them.
It has two or more paths for current to flow through.
Short circuit- is a type of electrical circuit that allows current to flow through an unintended path with no or
very low electrical resistance.
D. Sources of Electricity
Generator- a machine that turns mechanical energy into electricity.
Battery- combination of two or many electric cells that can store and supply electrochemical direct current.
Dynamo Electric Machines - a direct current generator with a switch.
E. Conductors & Insulators
Conductors- a materials or substances which allow the flow of electricity such as; Copper, Brass, Steel,
Gold, and Aluminum
Insulators- a materials or substances that resist the current or do not allows it to flow. Good examples of
insulators are Wood, cloth, glass, mica, quartz, plastic, and rubber.
F. Electrical Energy (Watts)
Electricity is measured in power units called Watts, named for James Watt, the steam engine creator. .A
Watt is an electricity unit equivalent to an ampere under one volt's pressure.
G. Ohm's Law
In the law of Ohm, the current is proportional to the voltage across the two points through a conductor
between two points.
Note: Write your summary answer for each of the topic in a concise manner.
Answers are to be in maximum of three (3) sentences, either in paragraph form or bullet points.
You may include illustrations or drawings to better convey your ideas.
You might also like
- HandbookDocument604 pagesHandbookcharlesc5746100% (14)
- Introduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Electricity & Electrical Systems: Prelim Learning ResourcesKib-anne Miguel PasikanNo ratings yet
- Electrical EnergyDocument17 pagesElectrical EnergykuevoradzogloriaNo ratings yet
- Applied Electrical Notes Unit 1Document12 pagesApplied Electrical Notes Unit 1The STUDY koala happyNo ratings yet
- Cfe Bu2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesCfe Bu2 ReviewerMaria Katrina Ilumin VersozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - ElectricityDocument29 pagesUnit 2 - ElectricityT. Christabel VijithaNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1Document9 pagesElectricity 1okguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Wldbe301 Basic of ElectricityDocument116 pagesWldbe301 Basic of ElectricityNshimiyimana pacifiqueNo ratings yet
- Getting Started. Conventional Electricity Supply 2021-22Document19 pagesGetting Started. Conventional Electricity Supply 2021-22Leeroy ZizhouNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Electrical TermsDocument8 pagesGlossary of Electrical TermsRafael jei GabisanNo ratings yet
- Building Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterDocument28 pagesBuilding Services-Iii (Ar V 2116) 2014-15: B. Arch III SemesterAmandeepKaurNo ratings yet
- Basic EE Module 123Document32 pagesBasic EE Module 123Benmark JabayNo ratings yet
- Unit I Electrical AND Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring Systems 10Document38 pagesUnit I Electrical AND Electronic Systems: Electrical Wiring Systems 10NithinNo ratings yet
- PHYS101L LabReport9Document13 pagesPHYS101L LabReport9Leidee Charmellie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of ElectricityDocument8 pagesBasic Concept of Electricityvamps sierNo ratings yet
- Bu RSW 1Document8 pagesBu RSW 1Kate Wencelette AraoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electricity 1.1Document23 pagesIntroduction To Electricity 1.1August DuqueNo ratings yet
- Amta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical SafetyDocument67 pagesAmta4 1 Introducing Electricity and Electrical Safetydunlut pelemNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10th NotesDocument3 pagesElectricity Class 10th Notesyo yeNo ratings yet
- BEE - Manual ODD 2021Document44 pagesBEE - Manual ODD 2021Deekshith raiNo ratings yet
- Module in EE 211 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument39 pagesModule in EE 211 Basic Electrical EngineeringEbacuado, Regine Mae F.No ratings yet
- ETPaperI PDFDocument133 pagesETPaperI PDFanand kumarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical Terms and Definitions - E-Green ElectricalJohn Florenz VasquezNo ratings yet
- Electro 1 Student FileDocument6 pagesElectro 1 Student FileHarveyBidañaNo ratings yet
- G9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityDocument4 pagesG9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityKinmokusei MyoeNo ratings yet
- Electricity and LightingDocument15 pagesElectricity and LightingdarielleollivierreNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE NC II MODULE New Edited MASTER LEODocument26 pagesELECTRICAL INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE NC II MODULE New Edited MASTER LEOOLINSTERG COLLEGENo ratings yet
- CE115 Electrical Part ADocument45 pagesCE115 Electrical Part AMrSamspartNo ratings yet
- Las Q 1 Week 1 Ste9Document6 pagesLas Q 1 Week 1 Ste9KimmmiNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument3 pagesDefinition of TermsMarius VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical SystemDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical SystemTurboiitNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument47 pagesBasic ElectronicsPolyn LopezNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Guia InglishDocument10 pagesTrabajo Guia InglishAlejandroDuranNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits & QuantitiesDocument29 pagesElectrical Circuits & QuantitiesDejaunae Lawson50% (2)
- AIRCRAFT Basic ElectricityDocument327 pagesAIRCRAFT Basic ElectricityndrmnlngNo ratings yet
- Uty Revised ReviewerDocument12 pagesUty Revised ReviewerMark Zed Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Eeuti130 Lec1Document22 pagesEeuti130 Lec1frankorola0207No ratings yet
- Current Electricity 2: For Non-Commercial Purposes Only Enjoy!Document21 pagesCurrent Electricity 2: For Non-Commercial Purposes Only Enjoy!Kanishka SeneviratneNo ratings yet
- Bldutl2 - Building Utilities 2 Electrical, Electronics and Mechanical SystemsDocument6 pagesBldutl2 - Building Utilities 2 Electrical, Electronics and Mechanical Systemsgimel tenorioNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument22 pagesElectricityanu.pavansuresh30No ratings yet
- Experiment # 1Document9 pagesExperiment # 1majorskNo ratings yet
- Electricity Supply, Distribution & InstallationDocument11 pagesElectricity Supply, Distribution & Installationshivani dharamthokNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument4 pagesBasic ElectricityMae PanlilioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Circuits: Basic DefinitionsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Circuits: Basic DefinitionsArnulfo LavaresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Voltage and Current: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument31 pagesChapter 2 - Voltage and Current: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadHector VergaraNo ratings yet
- G9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityDocument4 pagesG9, 2.6 Mains ElectricityKinmokusei MyoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Electricity Revision NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 12 - Electricity Revision NotesAyush RajNo ratings yet
- Electrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Document51 pagesElectrical Elements of Lift Technology Ed 3Fiorella Amer CarrNo ratings yet
- Bu 2 Quiz ReviewerDocument5 pagesBu 2 Quiz ReviewerSebastian CincoNo ratings yet
- Direct Current and PowerDocument5 pagesDirect Current and PowerElizabeth AnyegaNo ratings yet
- Utilities Assignment 1 1Document5 pagesUtilities Assignment 1 1Ernest VincentNo ratings yet
- AQA P2 Physics Electricity BookletDocument19 pagesAQA P2 Physics Electricity BookletSteve BishopNo ratings yet
- Physicy Test XDocument12 pagesPhysicy Test XMerimaNo ratings yet
- Electricity One Shot Class10Document49 pagesElectricity One Shot Class10saracastic123No ratings yet
- Basic Principal of Electrical CircuitryDocument19 pagesBasic Principal of Electrical CircuitryAreeba ParvezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Electrical and Electronics ElememntsDocument23 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Electrical and Electronics ElememntsHassan Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Electronics & Comp - SkillDocument44 pagesBasic Electrical Electronics & Comp - SkillPAnkaj BhamareNo ratings yet
- Summary of Fundamental in ElectronicsDocument19 pagesSummary of Fundamental in ElectronicsReedvejee Hermoso KiamcoNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument11 pagesBasic ElectricityFrancess Mae AlonzoNo ratings yet
- 18.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2021Document20 pages18.04.24 - Osr - Star Co-Sc - Jee-Adv - 2021balramsharmaNo ratings yet
- Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocument60 pagesElectromechanical Energy Conversionkujong agacerNo ratings yet
- 1.electrical Distribution Systems Unit IDocument65 pages1.electrical Distribution Systems Unit ISatishdhora SiddanaNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram of 11kV SubstationDocument46 pagesSingle Line Diagram of 11kV SubstationWelday100% (1)
- Measuring Friction and Wear Properties of Extreme Pressure (EP) Lubricating Oils With The Roller-Disk Geometry Using SRV Test MachineDocument7 pagesMeasuring Friction and Wear Properties of Extreme Pressure (EP) Lubricating Oils With The Roller-Disk Geometry Using SRV Test MachinePyone Ei ZinNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet For Enetek HightechDocument2 pagesData Sheet For Enetek HightechDenizhan AkınNo ratings yet
- Error CaterpillarDocument47 pagesError CaterpillarMarco Nuñez AcostaNo ratings yet
- Development of A Large Cooling Capacity Single Stage GM CryocoolerDocument5 pagesDevelopment of A Large Cooling Capacity Single Stage GM CryocoolerJaydeep PonkiyaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Centrifuges: Clinical ChemistryDocument27 pagesLaboratory Centrifuges: Clinical ChemistryZeeshan YousufNo ratings yet
- Parallel Driving of Synchronous GeneratorDocument7 pagesParallel Driving of Synchronous GeneratorMKIBETUNo ratings yet
- Ieee Cts and Pts 6-10Document99 pagesIeee Cts and Pts 6-10Thyago De Moura JorgeNo ratings yet
- The New MaterialDocument7 pagesThe New MaterialSteve AbonyiNo ratings yet
- SemiKron SKD-82 - 16Document3 pagesSemiKron SKD-82 - 16Mario Penelo RivaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-10Document7 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-10kingstonNo ratings yet
- Dmet13 Robles L06Document17 pagesDmet13 Robles L06John Marc E. TameraNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: T2000xCF-0C0 and T2000xCC-0C0 Low Voltage Fan Coil ThermostatsDocument4 pagesFigure 1: T2000xCF-0C0 and T2000xCC-0C0 Low Voltage Fan Coil ThermostatsVictor AANo ratings yet
- Motor ControlDocument66 pagesMotor Controlferdie marcos100% (1)
- Varistor Products Overview: Circuit Protection SolutionsDocument50 pagesVaristor Products Overview: Circuit Protection SolutionsChenaker HamzaNo ratings yet
- TNB ICPT (Imbalance Cost Pass Through)Document4 pagesTNB ICPT (Imbalance Cost Pass Through)ttNo ratings yet
- R1Document19 pagesR1sheppy3233No ratings yet
- BELIMO 2 Ways Modulating ValveDocument3 pagesBELIMO 2 Ways Modulating ValvelamNo ratings yet
- Nebol Ungere Aer-Ulei EnglezaDocument30 pagesNebol Ungere Aer-Ulei Englezaangela_draguNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesKerwin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Pages From Combined QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocument2 pagesPages From Combined QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelieswaheedNo ratings yet
- A700 Basic ManualDocument188 pagesA700 Basic ManualHong Dong XuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Compressors: Air CompressorDocument8 pagesChapter Six Compressors: Air CompressorMicky AlemuNo ratings yet
- Q874 Analog ElectronicsDocument2 pagesQ874 Analog ElectronicsDivyanshu BoseNo ratings yet
- Suction Cups/grippers: Level Compensator LCDocument2 pagesSuction Cups/grippers: Level Compensator LCBe HappyNo ratings yet
- BS en 26 + A1+a2+a3-2006Document146 pagesBS en 26 + A1+a2+a3-2006Abey VettoorNo ratings yet