Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grammatical - Morphology and Syntax Discourse - Connection of Sentences of Utterance. Sociolinguistic - Interaction of Language To Society or To
Grammatical - Morphology and Syntax Discourse - Connection of Sentences of Utterance. Sociolinguistic - Interaction of Language To Society or To
Uploaded by
ysa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesThe document discusses various aspects of communication including:
1) It defines purposive communication and lists the elements and barriers of communication.
2) It discusses the 5 C's of communication - courtesy, clarity, concise, concrete, and complete.
3) It covers types of communication including formal/informal, verbal/non-verbal, visual, and written.
4) Principles of communication include knowing your audience, purpose, topic and achieving credibility. Communication should be a process and use multiple techniques.
Original Description:
Original Title
Purposive-Communication
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various aspects of communication including:
1) It defines purposive communication and lists the elements and barriers of communication.
2) It discusses the 5 C's of communication - courtesy, clarity, concise, concrete, and complete.
3) It covers types of communication including formal/informal, verbal/non-verbal, visual, and written.
4) Principles of communication include knowing your audience, purpose, topic and achieving credibility. Communication should be a process and use multiple techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views2 pagesGrammatical - Morphology and Syntax Discourse - Connection of Sentences of Utterance. Sociolinguistic - Interaction of Language To Society or To
Grammatical - Morphology and Syntax Discourse - Connection of Sentences of Utterance. Sociolinguistic - Interaction of Language To Society or To
Uploaded by
ysaThe document discusses various aspects of communication including:
1) It defines purposive communication and lists the elements and barriers of communication.
2) It discusses the 5 C's of communication - courtesy, clarity, concise, concrete, and complete.
3) It covers types of communication including formal/informal, verbal/non-verbal, visual, and written.
4) Principles of communication include knowing your audience, purpose, topic and achieving credibility. Communication should be a process and use multiple techniques.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
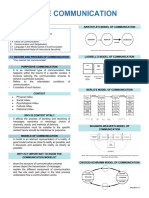
Purposive Communication – process of exchanging
thoughts or communicating in which ideas are
5 C’s in Communication
deliberately thought about to serve its purpose.
Courtesy - politeness
Elements of Communication
Clarity – clear pronunciation, proper grammar
Speaker – source of message or the sender of etc.
message Concise – simple and short
Message – information, ideas, thought Concrete – able to explain directly
conveyed by speaker in words or in actions Complete – 5ws and how , avoid ambiguity
Encoding – process of converting the message
Context on Communication
into words, actions, or other forms
Channel – medium or means of communicating Beliefs
Decoding – process of interpreting the encoded History
message of the speaker by the receiver Tradition
Receiver – recipient of the message, decodes Religion
message
Feedback – reaction, response, or information Specific Context
provided by receiver family
Context – environment where communication
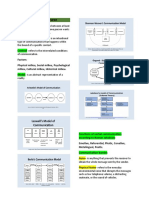
takes place Types of Communication
Barrier – factor that affects the flow of
communication Formal and Informal
Verbal
Barriers of Communication Non verbal – gestures, body language, eye
contact, sign language
Semantic or Language Barriers - science of Visual – visual aids e.g. photograph, diagrams,
meaning. Use words or symbols in different chart
sense. Ex. Jargons Written -sent through writing e.g Email, letter,
Organizational Barrier …
Internal and external
Personal Barrier- judgment, social values,
attitude, bias,pressure of time Ethical Communication –
Psycho-Sociological barrier – depends on the
emotional and psychological status of Guides communication with regards to moral principles
sender/receiver
Principle/ Characteristics of ethical communication
Physical Barrier – physical distraction
Environmental factors like noise, temperature, Honesty
room, voice qualities Courtesy
Defect in medium – telephone, postal system Confidentiality
Respect
Principles of Communication
Credit
Know your audience.
Know your purpose.
Know your topic. Communicative Competence
Anticipate objections.
- Ability to use language system appropriately
Present a rounded picture.
- Communicator’s goal is achieved through
Achieve credibility with your audience.
Follow through on what you say. effective and appropriate interaction
Communicate a little at a time. - Management of messages for the purpose of
Present information in several ways. creating meaning
Develop a practical, useful way to get feedback. -
Use multiple communication techniques.
Grammatical – morphology and syntax
Communication is complex. When listening to
or reading someone else's message, we often Discourse – connection of sentences of utterance.
filter what's Sociolinguistic – interaction of language to society or to
being said through a screen of our own relate language in social context
opinions. One of the major barriers to
- Ability of receiver to accommodate or adjust to
communication is our own ideas and
communication style of the sender
opinions
Strategic Competence – keeping communication
Communication According to Purpose: flowing / sustaining communication
To Inform - Ability to adapt to the use of verbal and non-
To instruct verbal language
To entertain
To persuade Psycholinguistic – how the brain processes the
language spoken or received
- cognitive process e.g thinking,memory, perception,
learning …
Cohesion is the grammatical and lexical relationship of
text.
Coherence is when a message of a text has sense
Linguistic Skill – product of being educated and exposed
to language
Globalization
Interconnectedness of people across the globe
Intercultural communication pertains to the exchange
information of people that belongs to different groups
with unique culture
Drivers of Globalization
Colonization – control of foreigners to the local
in a certain area
Diaspora – immigration / A diaspora is a
scattered population whose origin lies in a
separate geographic locale.
Technology
Multimodal
- Multiple modes of communicating a message
Conveyed through combination of modes
- Gestural
- Spatial
- Audio
- Oral languages
Combination of
- Images
- Motion
- Audio
- Podcast
- Audio-record
- Blog
- Tumblr
- Animation
- Presentation
- Moovly
- Vlog
- Sway
- Website
- Performance
- Oral story telling
- presentation
You might also like
- Oral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Document6 pagesOral Communication Q1 Reviewer For G11Katleya Balitaan78% (9)
- Purposive Communication For Academic PurposesDocument8 pagesPurposive Communication For Academic Purposesrosalyn dumalag100% (7)
- Information Theory and Coding Full BookDocument354 pagesInformation Theory and Coding Full BookŁïkįťh Łęø100% (1)
- Latency Consideration For LDPC FEC Code Wey - 3ca - 1a - 1117Document12 pagesLatency Consideration For LDPC FEC Code Wey - 3ca - 1a - 1117LambertchaoNo ratings yet
- Compression and Coding Algorithms PDFDocument284 pagesCompression and Coding Algorithms PDFananthmtNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication - NotesDocument10 pagesPurposive Communication - Notesleannanicole.bustamanteNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDA SulitNo ratings yet
- Oralcommunication (W1 W16)Document26 pagesOralcommunication (W1 W16)rocky swagNo ratings yet
- 2ND Day ReviewerDocument4 pages2ND Day ReviewerJasmine de LeonNo ratings yet
- Commu RevDocument2 pagesCommu RevuniqlobtchNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication LectureDocument18 pagesPurposive Communication LectureRandolf MartinezNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument10 pagesOral CommunicationCee Jay GerongcoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument9 pagesREVIEWERAtty Joven Allen AsidoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer CommunicationJaimNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerDaennise Louiseanna SebastianNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument8 pagesReviewerApril LalamunanNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument2 pagesPurcom Reviewergimboongaling489No ratings yet
- Oral Communication PrelimDocument2 pagesOral Communication PrelimAngelika ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PURC111Document10 pagesReviewer PURC111priya garciaNo ratings yet
- PURC111Document3 pagesPURC111wooziwaegNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocument3 pagesOral Comm Reviewerdingomez01No ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument3 pagesPurposive CommunicationHazel DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Settings Participants Codes, and Message Content and FormDocument3 pagesSettings Participants Codes, and Message Content and FormJhessa May CanuelNo ratings yet
- J. Paul LeaganDocument15 pagesJ. Paul LeaganAries C. GavinoNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication - ReviewerDocument4 pagesOral Communication - ReviewerSamsamNo ratings yet
- Social Context - The Relationship That ExistsDocument16 pagesSocial Context - The Relationship That ExistsAnonymous x1onhdRNo ratings yet
- Nature of CommunicationDocument4 pagesNature of CommunicationAgtina, Angela Claudine A.No ratings yet
- PC 100 PrelimsDocument12 pagesPC 100 Prelimscali kNo ratings yet
- PURCDocument7 pagesPURCFLEUR MARIE MICHELLE CAHAPAYNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommDocument3 pagesPurposive CommCherith May DelgadoNo ratings yet
- GP COM ReviewerDocument8 pagesGP COM ReviewerKathleen SummerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4Document16 pagesChapter 1-4SJ SuingNo ratings yet
- Module 1&2 (Oral Comm)Document5 pagesModule 1&2 (Oral Comm)Lory TenorioNo ratings yet
- Purc Transes PrelimDocument4 pagesPurc Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Reviewers 1st Midterm 1Document31 pagesReviewers 1st Midterm 1Gizelle FaithNo ratings yet
- Understanding Business CommunicationDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Business Communicationhanikajason0708No ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument13 pagesOral CommunicationAlliah ManilaNo ratings yet
- PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION - Definition and Process of CommunicationDocument10 pagesPURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION - Definition and Process of CommunicationninejapageNo ratings yet
- Purcom MidtermDocument1 pagePurcom MidtermNene OcampoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral ComDocument2 pagesReviewer in Oral ComMarjorie PabloNo ratings yet
- ORAL-COMM Reviewer 1st-QuarterDocument5 pagesORAL-COMM Reviewer 1st-QuarterJohn Marithe Putungan100% (1)
- Week 1 Definition and Process of Communication 1Document23 pagesWeek 1 Definition and Process of Communication 1alexancog456No ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument15 pagesPurcom ReviewerJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocument6 pagesOral Comm ReviewerLeila J OroscoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication PrelimsDocument21 pagesPurposive Communication PrelimsMichiiee Batalla0% (1)
- Reviewer Purposive Chapter 1 5Document12 pagesReviewer Purposive Chapter 1 5than thyNo ratings yet
- 2 Nature Elements Types of CommunicationDocument27 pages2 Nature Elements Types of CommunicationNoemie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Ngec 5Document12 pagesNgec 5Bernard Parong Jr.No ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral CommunicationDocument7 pagesReviewer in Oral Communicationmariel elvambuenaNo ratings yet
- OralCom-Prelim Exam Reviewer-For SendDocument3 pagesOralCom-Prelim Exam Reviewer-For SendAngie EsponillaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication NotesDocument13 pagesOral Communication Notesayaka kamisatoNo ratings yet
- Journal - Ramesh Chandra SinghDocument22 pagesJournal - Ramesh Chandra SinghRameshchandra SinghNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication LECTUREDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication LECTUREJazzel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Gec 5 ReviewerrDocument13 pagesGec 5 ReviewerrAllaika Zyrah FloresNo ratings yet
- DIASS Fourth Quarter ModuleDocument18 pagesDIASS Fourth Quarter ModuleMikex Mike100% (2)
- GE2 Purcom ReviewerDocument6 pagesGE2 Purcom ReviewerEcko DiazNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument19 pagesPurposive CommunicationYza Grace S. PayangdoNo ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument5 pagesOral CommmackyjusainNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument5 pagesPurposive CommunicationRiri KimmyNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument5 pagesOral Communicationshoti lahNo ratings yet
- Module 12 CommunicationDocument12 pagesModule 12 CommunicationMarla Brigitte GalvanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Purposive CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer For Purposive Communicationjohn ivan GarciaNo ratings yet
- Listen, Speak, Lead: Elevate Your Success with Effective CommunicationFrom EverandListen, Speak, Lead: Elevate Your Success with Effective CommunicationNo ratings yet
- Codage TutorialDocument12 pagesCodage TutorialhallNo ratings yet
- CSEP 590 Data Compression: Course Policies Introduction To Data Compression Entropy Variable Length CodesDocument93 pagesCSEP 590 Data Compression: Course Policies Introduction To Data Compression Entropy Variable Length CodesRohan BorgalliNo ratings yet
- How To Build A Working Digital Computer - 1967Document180 pagesHow To Build A Working Digital Computer - 1967HackedChickenNo ratings yet
- Design Integrity NotesDocument4 pagesDesign Integrity Notesdjamila abbadNo ratings yet
- Algorithms For Data Science: CSOR W4246Document58 pagesAlgorithms For Data Science: CSOR W4246EarthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2Document14 pagesChapter - 2Sougata GhoshNo ratings yet
- GE 2 Complete SIM (Modified) 3Document318 pagesGE 2 Complete SIM (Modified) 3Carlo John C. RuelanNo ratings yet
- 2d Full User ManualDocument99 pages2d Full User Manualhanif prayogaNo ratings yet
- Notes On CommunicationDocument8 pagesNotes On CommunicationSWAPNIL MISHRANo ratings yet
- Hamming CodeDocument2 pagesHamming CodeLokesh MeenaNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication Course NotesDocument61 pagesEffective Communication Course Notesdany100% (1)
- Amended IRR of The SRCDocument255 pagesAmended IRR of The SRCEdgar Jino Bartolata0% (1)
- Turbo Codes For PCS Applications: AbstractDocument6 pagesTurbo Codes For PCS Applications: AbstractMudita ChandraNo ratings yet
- Huffman Coding Ms 140400147 Sadia Yunas ButtDocument9 pagesHuffman Coding Ms 140400147 Sadia Yunas ButtendaleNo ratings yet
- 30 CommunicationDocument10 pages30 CommunicationAnnalisa MaielloNo ratings yet
- Fitts & Seeger 1953Document12 pagesFitts & Seeger 1953-下村 優佳-No ratings yet
- Data Compression ExplainedDocument110 pagesData Compression ExplainedARob109No ratings yet
- All Unit MCQ's of Data Compression - TheCodingShefDocument34 pagesAll Unit MCQ's of Data Compression - TheCodingShefValar MorghulisNo ratings yet
- SUF Technical DocumentationDocument237 pagesSUF Technical DocumentationDjordjeNo ratings yet
- TTS Chapter8Document17 pagesTTS Chapter8kadry mohamedNo ratings yet
- A Study of The Emerging Trends in SteganographyDocument12 pagesA Study of The Emerging Trends in SteganographyGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Dynamic Huffman Codes: Jeffrey Scott VitterDocument21 pagesDesign and Analysis of Dynamic Huffman Codes: Jeffrey Scott VitterZlatni PresekNo ratings yet
- New Decoding Methods For LDPC Codes On Error and Error-Erasure ChannelsDocument92 pagesNew Decoding Methods For LDPC Codes On Error and Error-Erasure ChannelsIlke AltinNo ratings yet
- Supplier Interface in Oracle Apps R12Document3 pagesSupplier Interface in Oracle Apps R12Ravi Varma100% (1)
- 3 RD HARDdraftDocument116 pages3 RD HARDdraftluveehazelNo ratings yet
- Python Astm Readthedocs Io en StableDocument44 pagesPython Astm Readthedocs Io en StableMaxime KIENOUNo ratings yet
- AIA CPC XML Documentation PDFDocument38 pagesAIA CPC XML Documentation PDFAnonymous 9I5YIasIpNo ratings yet