Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sildenafil Citrate or Viagra
Sildenafil Citrate or Viagra
Uploaded by
Kat Z0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views3 pagesSildenafil citrate, branded as Viagra, is an antihypertensive and anti-impotence drug. It works by dilating narrow arteries allowing blood to pass fluidly from the heart to the lungs, providing relief by giving the lungs proper oxygen levels. It is prescribed for pulmonary arterial hypertension and to improve exercise ability and delay clinical worsening. Common side effects include headaches, flushing, and stomach pain. Nurses should monitor for cardiovascular and vision issues and drug interactions.
Original Description:
Original Title
Sildenafil Citrate or viagra
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSildenafil citrate, branded as Viagra, is an antihypertensive and anti-impotence drug. It works by dilating narrow arteries allowing blood to pass fluidly from the heart to the lungs, providing relief by giving the lungs proper oxygen levels. It is prescribed for pulmonary arterial hypertension and to improve exercise ability and delay clinical worsening. Common side effects include headaches, flushing, and stomach pain. Nurses should monitor for cardiovascular and vision issues and drug interactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views3 pagesSildenafil Citrate or Viagra
Sildenafil Citrate or Viagra
Uploaded by
Kat ZSildenafil citrate, branded as Viagra, is an antihypertensive and anti-impotence drug. It works by dilating narrow arteries allowing blood to pass fluidly from the heart to the lungs, providing relief by giving the lungs proper oxygen levels. It is prescribed for pulmonary arterial hypertension and to improve exercise ability and delay clinical worsening. Common side effects include headaches, flushing, and stomach pain. Nurses should monitor for cardiovascular and vision issues and drug interactions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
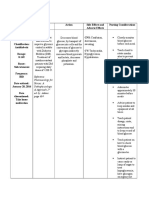
Generic Name: Sildenafil Citrate
Brand Name: Viagra
Classification of Drug:
Chemical Class: Pyrazolopyrimidinone
Derivative
Therapeutic Class: Antihypertensive (pulmonary arterial), Anti-impotence
Mechanism of Action: It provides relief to the patient by dilating the narrow
arteries which will allow blood to pass fluidly from the heart to the lungs. This will
now give the lungs proper amounts of oxygen, making the patient stronger.
Dose and Route:
For treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension
Adults. 20 mg three times a day, P.O.
Adults. 10 mg administered as bolus three times a day, I.V.
For Childhood Primary and Secondary Pulmonary Hypertension
Children and Adolescents weighing more than 20 kg
20 mg three times a day, P.O.
Children weighing 20 kg or less
10 mg three times a day, P.O.
Infants
0.5 to 1 mg/kg/dose PO every 8 hours
Indications: To treat pulmonary arterial hypertension in order to improve
exercise ability and delay clinical worsening of condition in patients classified as
group 1 by the World Health Organization.
Contraindications: Continuous or intermittent nitrate therapy, hypersensitivity to
sildenafil or components
Side Effects: CNS: Headache, flushing, dizziness
GI: Stomach pain, diarrhea
RESP: Difficult or labored breathing, runny nose
MS: Aches or pain in muscles
Skin: Redness, unusually warm skin
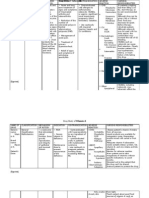
Adverse Reactions: CNS: Headache, dizziness, migraine, tremor, paresthesia,
burning sensation, somnolence, hypoesthesia, cerebrovascular
accident, syncope
CV: Flushing, heart rate increased, palpitations, tachycardia, hypertension,
hypotension, myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, sudden cardiac death,
ventricular arrhythmia, unstable angina
GI: Dyspepsia, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dry mouth, gastritis,
gastroesophageal reflux disease, hemorrhoids, abdominal distension, oral
hypoesthesia
MS: Pain in extremity, back pain, myalgia
OPTIC: Abnormal vision, visual color distortion, retinal hemorrhage, visual
impairment, vision blurred, photophobia, chromatopsia, cyanopsia, eye irritation,
ocular hyperemia
RESP: Pharyngitis, rhinitis, nasal congestion, epistaxis, cough, sinus congestion,
throat tightness, nasal edema, nasal dryness
DERMATOLOGIC: Rash, alopecia, erythema, night sweats
Drug Interactions: Drug: antiarrhythmics, anticonvulsants, digoxin,
levothyroxine, liothyronine, quinolones, tetracyclines, theophylline, warfarin:
Possibly altered absorption of these drugs 1078 sildenafil citrate phosphate salts,
phosphorus salts: Neutralized therapeutic effects of sevelamer ciprofloxacin:
Decreased ciprofloxacin effectiveness
Food: High-fat diet: reduced drug absorption, decreased peak level
Nursing Responsibilities:
1. Determine if the patient is hypersensitive to Sildenafil citrate or to any
components of the product.
2. Monitor cardiovascular status carefully.
3. Monitor serum phosphorus level to determine drug’s effectiveness;
monitor other serum electrolyte levels, especially bicarbonate and
chloride, to detect imbalances.
4. Instruct patient to take drug with meals and to swallow capsules or
tablets whole with water and not to open, break, or chew them.
5. Evaluate patient’s vision and hearing.
6. Instruct patient to notify prescriber immediately if serious cardiac and
vision problems and sudden decrease in or loss of hearing occur.
7. Instruct patient to report severe or prolonged constipation to prescriber
because additional treatment may be needed to prevent serious
complications.
8. Review symptoms of thrombosis, and advise patient to report them
immediately
9. Inform patient that drug can cause serious interactions with many
common drugs. Instruct the patient to tell all prescribers he is taking it.
10. Inform patient that high-fat diet may interfere with drug efficacy.
You might also like
- Drug Study NewDocument4 pagesDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniNo ratings yet
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- SPIKES ProtocolDocument4 pagesSPIKES ProtocolKassem Gharaibeh100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKatrina EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug Studykcbabee0333% (3)
- Drug StudiesDocument16 pagesDrug Studiesvitcloud23100% (2)
- Mefenamic AcidDocument3 pagesMefenamic AcidAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyFelecidario TaerNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesName of Drug Indications Action Contraindication Side Effects Adverse Side Effects Nursing Managementjhappo31No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolDocument26 pagesGeneric Name: Albuterol Brand Name: Salbutamol, Proventil, Ventolin, Accuneb, Airet, Novo-SalbutamolAnna Joy Antone100% (1)
- Emergency DrugsDocument5 pagesEmergency DrugsArra PlacidesNo ratings yet
- Ditropan Drug CardDocument2 pagesDitropan Drug CardBenNo ratings yet
- Name of DrugDocument10 pagesName of DrugBianx PradoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Drug ProfileDocument3 pagesMefenamic Acid Drug ProfileAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventDocument6 pagesAmlodipine, Vit.b Complex, CombiventErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudDocument12 pagesDrug StudKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaDocument10 pagesName of Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Ampicillin Sulbactam GI: Diarrhea, NauseaVictor BiñasNo ratings yet
- CHN Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCHN Drug StudyJoshua Cyryll ComiaNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument1 pageDrug Indication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationSheng Gosep100% (3)
- Drug Study FinalDocument5 pagesDrug Study FinalJackie Ann Marie DapatNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Cortex Where Spread of SeizureDocument11 pagesCortex Where Spread of SeizureDustin JohnNo ratings yet
- OB Med SheetDocument12 pagesOB Med SheetSam DanaNo ratings yet
- CHH Drug Study Week 2Document25 pagesCHH Drug Study Week 2maryxtine24No ratings yet
- Drug StudiesDocument32 pagesDrug StudiesKelly ChanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classificatio N Mechanis MOF Action Indication Contrain Dication Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrug Name Classificatio N Mechanis MOF Action Indication Contrain Dication Side Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesPrincess TinduganNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument7 pagesDrugsEloisa Abarintos RacalNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Document5 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyCris Constantino San JuanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Cards CHF DVTDocument14 pagesPharma Cards CHF DVTRiza Angela BarazanNo ratings yet
- V. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationDocument23 pagesV. Laboratory Result and Diagnostic ExaminationAvigael Gabriel AvilesNo ratings yet
- Brand Names: Generic NameDocument3 pagesBrand Names: Generic NameEzraManzanoNo ratings yet
- Ncp&drugstudDocument12 pagesNcp&drugstudSarah Mae Billano BermudezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismDocument9 pagesDrug Study (Lactulose, Zynapse, Simvastatin) and HTP - CVD Prob CardioembolismRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- MirtazapineDocument4 pagesMirtazapineJEn ValentosNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument11 pagesName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNo ratings yet
- 5th Draft DrugsDocument7 pages5th Draft DrugsShayne Jessemae AlmarioNo ratings yet
- 10 Drug StudyDocument25 pages10 Drug StudyM AnnNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For GDMDocument7 pagesDrug Study For GDMFuture RNNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesDrugs Study For PneumoniaLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Ix. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDocument21 pagesIx. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and DosageDocument6 pagesDrug Name Indication Contraindication Drug Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: Brand Name: Classification: Route and Dosageسبوكاي100% (1)
- ECLAMPSIA Drug StudyDocument10 pagesECLAMPSIA Drug Studyjessica_omegaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ProjectDocument7 pagesDrug Study ProjectMaRic Gabutin Guerra100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyColleen Fretzie Laguardia NavarroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyLynel Joy JamotilloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyIrveen Joy RamirezNo ratings yet
- VIII. Drug StudyDocument11 pagesVIII. Drug StudyCharlayne AnneNo ratings yet
- 5 MG Iv BidDocument17 pages5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Insipidus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandDiabetes Insipidus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- DigoxinDocument4 pagesDigoxinKat ZNo ratings yet
- The North American Vasovagal Pacemaker Study (VPS)Document5 pagesThe North American Vasovagal Pacemaker Study (VPS)Kat ZNo ratings yet
- Dietary Compliance in Celiac Disease: Hugh James FreemanDocument6 pagesDietary Compliance in Celiac Disease: Hugh James FreemanKat ZNo ratings yet
- The Management of Vasovagal Syncope: R.A. Kenny and T. McnicholasDocument8 pagesThe Management of Vasovagal Syncope: R.A. Kenny and T. McnicholasKat ZNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsDocument5 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsKat ZNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Apo-Metoprolol, Betaloc, Lopressor, Novo-Metoprolol, Nu-Drug ClassificationDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Apo-Metoprolol, Betaloc, Lopressor, Novo-Metoprolol, Nu-Drug ClassificationKat ZNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11Document31 pagesLesson 11Kat ZNo ratings yet
- Spain and The Philippines in The 19 Century: Evils in The Colonial Rule During The Spanish ColonizationDocument57 pagesSpain and The Philippines in The 19 Century: Evils in The Colonial Rule During The Spanish ColonizationKat ZNo ratings yet
- Rizal and His Childhood Years in CalambaDocument24 pagesRizal and His Childhood Years in CalambaKat ZNo ratings yet
- KSM Orthopedi New1Document20 pagesKSM Orthopedi New1rspku mayongNo ratings yet
- List of Must Read Books and Journals For DNB AnaesthesiaDocument2 pagesList of Must Read Books and Journals For DNB AnaesthesiaSirisha CkvNo ratings yet
- Key Points To Recognize Quality in HBEL and Associated MonographDocument21 pagesKey Points To Recognize Quality in HBEL and Associated MonographMohab Ameen AldesoukiNo ratings yet
- PG Teacher ApprovalDocument4 pagesPG Teacher ApprovalNandkishor GaikwadNo ratings yet
- The American Journal of Public HealthDocument3 pagesThe American Journal of Public HealthgautamkurtNo ratings yet
- Knoll - Evil in Forensic Psychiatry PDFDocument12 pagesKnoll - Evil in Forensic Psychiatry PDFVictorVeroneseNo ratings yet
- Budiono - Quality Improvement StrategyDocument64 pagesBudiono - Quality Improvement StrategyyaniNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels CH 13Document86 pagesBlood Vessels CH 13Nalla Mirelle CarbonellNo ratings yet
- 1 Acidity CleanseDocument11 pages1 Acidity CleanseSeetha Chimakurthi67% (3)
- The Drug That Cracked Covid by Michael CapuzzoDocument15 pagesThe Drug That Cracked Covid by Michael CapuzzoAll News Pipeline0% (1)
- PheoDocument4 pagesPheoantonijevicuNo ratings yet
- General Care Ear Mould Hearing AidDocument16 pagesGeneral Care Ear Mould Hearing AidJess D'SilvaNo ratings yet
- EVC 2015 ProgrammeDocument24 pagesEVC 2015 ProgrammeguajacolNo ratings yet
- Training Theory and PrinciplesDocument90 pagesTraining Theory and Principlesapi-3695814100% (5)
- The Dynamic Rotation of Langer's Lines On Facial ExpressionDocument7 pagesThe Dynamic Rotation of Langer's Lines On Facial Expressionaulia rachmanNo ratings yet
- Paranoid Schizophrenia Case StudyDocument226 pagesParanoid Schizophrenia Case Studysatra100% (1)
- PMP Clearinghouse SFTP Batch RolloutDocument652 pagesPMP Clearinghouse SFTP Batch RolloutLane BredesonNo ratings yet
- AD - Daftar Produk - 27 Mei 2021Document11 pagesAD - Daftar Produk - 27 Mei 2021adhimaswicaksono1991No ratings yet
- Oneill Health Status Canada Vs UsDocument45 pagesOneill Health Status Canada Vs UsKhalid SukkarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Skills Checklist - RTDocument6 pagesNursing Skills Checklist - RTapi-309674272No ratings yet
- Amentia in Medical DiagnosisDocument10 pagesAmentia in Medical DiagnosisMónica C. GalvánNo ratings yet
- Patient Specific Dental Hygiene Care PlanDocument8 pagesPatient Specific Dental Hygiene Care Planapi-354959885No ratings yet
- Gemstone Healing 3Document3 pagesGemstone Healing 3Fra Lan0% (1)
- FARMAKOLOGIDocument5 pagesFARMAKOLOGIsri wikra wardany yuslimNo ratings yet
- Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov DecDocument3 pagesJan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov DecDyëng RäccâNo ratings yet
- Biobehavioral Resilience To StressDocument372 pagesBiobehavioral Resilience To StressDoina Albescu100% (1)
- English (Respiratory System)Document16 pagesEnglish (Respiratory System)ChitraNo ratings yet
- Quality Improvement ProjectDocument7 pagesQuality Improvement Projectapi-272534722100% (1)
- 2 Skin Irritation enDocument21 pages2 Skin Irritation enMárcia Cristina Pinheiro FonsecaNo ratings yet