Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9 3e
9 3e
Uploaded by
shanmukha anisettiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 2020 TJC JC2 Prelim H2 Math Paper 1 (Solutions)Document23 pages2020 TJC JC2 Prelim H2 Math Paper 1 (Solutions)Ace PTNo ratings yet
- (D) Integration by Substitution: 5: Integration and Its ApplicationsDocument13 pages(D) Integration by Substitution: 5: Integration and Its ApplicationsMark LiNo ratings yet
- TMK2023chap 0.2Document12 pagesTMK2023chap 0.2Miu MakriNo ratings yet
- TJC H2 2021 Math Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument25 pagesTJC H2 2021 Math Prelim P1 SolutionsHormitha SivakumarNo ratings yet
- H2 MYE Revision Package Differentiation SolutionsDocument10 pagesH2 MYE Revision Package Differentiation SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Document13 pages2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2 Integration by Substitution: Thus, LN ( ) +Document6 pages1.1.2 Integration by Substitution: Thus, LN ( ) +Everything What U WantNo ratings yet
- Differential OperatorsDocument11 pagesDifferential OperatorsStanley MwangiNo ratings yet
- Noise and Vibration: Two Degree of Freedom SystemsDocument28 pagesNoise and Vibration: Two Degree of Freedom SystemssoqhNo ratings yet
- Eco501 Assignment4a Solutions Summer2020Document3 pagesEco501 Assignment4a Solutions Summer2020maruf91No ratings yet
- Wk11 Lectrure11 12dec2017 FinalDocument15 pagesWk11 Lectrure11 12dec2017 Finalهاني احمدNo ratings yet
- 2014 jc1 Math Promo-FinalisedDocument139 pages2014 jc1 Math Promo-FinalisedLinda aiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document35 pagesChapter 12ndjwndnnd sjwjhsbdbdbdNo ratings yet
- Math p1c3Document14 pagesMath p1c3kolodoloNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Uz 8Document6 pagesCalc 2 Uz 8Ferhat YoldasNo ratings yet
- Week2 Lecture2 PDFDocument28 pagesWeek2 Lecture2 PDFAbdullah AloglaNo ratings yet
- Siyuan SongDocument16 pagesSiyuan SongTốNhưPhạmNo ratings yet
- Prof OrG Trans45Document21 pagesProf OrG Trans45Saye B.DoloNo ratings yet
- L - 3: First Order & First Degree Differential EquationsDocument15 pagesL - 3: First Order & First Degree Differential EquationsMusayeb HossainNo ratings yet
- Basic CalculusDocument2 pagesBasic CalculusKate CaranguianNo ratings yet
- 19-05-24 Isr - Iit Star Co-Sc (Model-B) Jee Adv 2023 (P-I) Wat-46 Key & SolDocument16 pages19-05-24 Isr - Iit Star Co-Sc (Model-B) Jee Adv 2023 (P-I) Wat-46 Key & SolkantaksathwikNo ratings yet
- KVPY-QE SolutionsDocument9 pagesKVPY-QE SolutionsArsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Practice Test-1 - Paper-1 - SolutionsDocument14 pagesJEE Advanced Practice Test-1 - Paper-1 - SolutionsDev MaanNo ratings yet
- 2019 - April - UG CBCS 2011 Onwards - B.SC., (Mathematics) - MathematicsDocument68 pages2019 - April - UG CBCS 2011 Onwards - B.SC., (Mathematics) - MathematicsBharathi SelvamNo ratings yet
- MAT1581 Assignment 4 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesMAT1581 Assignment 4 - SolutionsLEANATTENo ratings yet
- CJC H2 Promo 2009 SolutionsDocument10 pagesCJC H2 Promo 2009 Solutionstoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Problem 8. 5: (Difficulty: 2)Document10 pagesProblem 8. 5: (Difficulty: 2)Will JohnNo ratings yet
- L3L4 Sem2 2023.24Document32 pagesL3L4 Sem2 2023.24Farahin RdznNo ratings yet
- 2 Control (May 2010)Document2 pages2 Control (May 2010)Primero C ElmejorNo ratings yet
- Solution of Practice Exercise For Lecture 19Document3 pagesSolution of Practice Exercise For Lecture 19Malik Nazim ChannarNo ratings yet
- 2019 YIJC Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsDocument14 pages2019 YIJC Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsGeorge ChooNo ratings yet
- Promo08 Acjc H2 (Soln)Document8 pagesPromo08 Acjc H2 (Soln)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- 5..aod 21.05.21 Ans&solDocument9 pages5..aod 21.05.21 Ans&solKovid AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 2015 BoS Trials Mathematics Extension 2 SolutionsDocument36 pages2015 BoS Trials Mathematics Extension 2 SolutionsIjal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Product and Quotient RuleDocument9 pagesProduct and Quotient RuleDalia EldeabNo ratings yet
- Advanced Circles Ex.2 (B)Document24 pagesAdvanced Circles Ex.2 (B)Ajay SinghNo ratings yet
- Bahan Seminar Kertas 1Document13 pagesBahan Seminar Kertas 1Zulhanif IdrisNo ratings yet
- 4th May Class Notes II4 PDFDocument7 pages4th May Class Notes II4 PDFJayNsteinNo ratings yet
- 2022 JEE Main 4 SolutionDocument13 pages2022 JEE Main 4 SolutionADITYA RAJNo ratings yet
- Ganit Pravinya 2016 Test Paper SolutionDocument6 pagesGanit Pravinya 2016 Test Paper SolutionMihir GargNo ratings yet
- 2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)Document31 pages2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)VincentNo ratings yet
- Further Integration TechniquesDocument39 pagesFurther Integration TechniquesReginNo ratings yet
- Csec Add Maths 2016Document31 pagesCsec Add Maths 2016cartzcj007No ratings yet
- S5 Further Calculus 4 Integration 1-2Document6 pagesS5 Further Calculus 4 Integration 1-2isaiahseruyangeNo ratings yet
- 108220Document77 pages108220Norah CNo ratings yet
- BCS - 12Document18 pagesBCS - 12Shivangi MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Navy Mock Test Answer KeyDocument4 pagesNavy Mock Test Answer KeyPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- March Block Test Timed Trial 2 - SolutionsDocument15 pagesMarch Block Test Timed Trial 2 - SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Completing The SquareDocument19 pagesCompleting The SquarengeekengNo ratings yet
- ProbSet 3 1st-Order DEs SolutionsDocument10 pagesProbSet 3 1st-Order DEs SolutionsMlkhr lgndbNo ratings yet
- Principal Component Analysis: Part ADocument10 pagesPrincipal Component Analysis: Part AbetifiNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4-5 Non Linear Partial Differential EquationDocument7 pagesLecture-4-5 Non Linear Partial Differential EquationAtikul IslamNo ratings yet
- Ial pm1 Ex9cDocument3 pagesIal pm1 Ex9cWandaNo ratings yet
- 4 Linear Differential Equations With ConDocument41 pages4 Linear Differential Equations With ConJuan 2012No ratings yet
- Promo08 MJC H2 (Soln)Document16 pagesPromo08 MJC H2 (Soln)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- WTEC2A1 Class1 SolutionDocument3 pagesWTEC2A1 Class1 Solutionphantom ceilNo ratings yet
- RumusiDocument2 pagesRumusimisterinaNo ratings yet
- Block Test Revision Paper 3 - TJC (Soln)Document9 pagesBlock Test Revision Paper 3 - TJC (Soln)Wen Han LimNo ratings yet
- 7 - Maximum and Minimum Values, Points of InflectionDocument9 pages7 - Maximum and Minimum Values, Points of InflectionhiqmNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- 03 Coordinate Sales PerformanceDocument7 pages03 Coordinate Sales PerformanceSAMUALE ASSEFA MEKURIYANo ratings yet
- CAC Computations Chap 4 1 20Document9 pagesCAC Computations Chap 4 1 20rochelle lagmayNo ratings yet
- VMCSCHDocument8 pagesVMCSCH2402nguyenlinhNo ratings yet
- Stocks Bonds: Bonds and Stocks Are Both Financial Securities With Respective Risks and RewardsDocument2 pagesStocks Bonds: Bonds and Stocks Are Both Financial Securities With Respective Risks and RewardsAndrea TahilNo ratings yet
- IBT 1-2 WeeksDocument7 pagesIBT 1-2 WeeksNicolle Curammeng100% (1)
- Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesRisk ManagementAlejandra CastillaNo ratings yet
- Special Orders: Decision: To Accept or Reject This OfferDocument2 pagesSpecial Orders: Decision: To Accept or Reject This OfferHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Global Reinsurers Maintain EquilibriumDocument89 pagesGlobal Reinsurers Maintain EquilibriumgargramNo ratings yet
- SupplyDocument24 pagesSupplyJay GoraneNo ratings yet
- Tommy AssignmentDocument10 pagesTommy Assignmentخلود البطاحNo ratings yet
- Final Term PaperDocument66 pagesFinal Term PapercshuvodipNo ratings yet
- School of Business and Economics Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument8 pagesSchool of Business and Economics Department of Accounting and FinancetinntinnNo ratings yet
- Pecora FinalReportDocument402 pagesPecora FinalReportAdelino MartinsNo ratings yet
- Solution To Assignment 6Document3 pagesSolution To Assignment 6Khyla DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Aqualisa QuartzDocument5 pagesAqualisa QuartzSrinivasa Raghavachar100% (1)
- Difference Between Money Market and Capital MarketDocument4 pagesDifference Between Money Market and Capital MarketSanjoy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- ZaraDocument14 pagesZaraMax Tan50% (2)
- Index Futures PricingDocument21 pagesIndex Futures PricingVaidyanathan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Credit Risk Associated With Banking Sector Deregulation in West AfricaDocument58 pagesAn Analysis of Credit Risk Associated With Banking Sector Deregulation in West AfricaTheophilus Orraca-TettehNo ratings yet
- Sap Mm-Fi Integration Overview PDFDocument43 pagesSap Mm-Fi Integration Overview PDFSambit Mohanty100% (1)
- Niddf PDFDocument1 pageNiddf PDFMuhammad MudassarNo ratings yet
- B. Com (CA) SyllabusDocument70 pagesB. Com (CA) SyllabusBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Notes ReceivableDocument22 pagesModule 4 - Notes ReceivableJennalyn S. GanalonNo ratings yet
- WTS Dhruva - Five-Years-of-VAT-in-the-UAEDocument53 pagesWTS Dhruva - Five-Years-of-VAT-in-the-UAEZankhana ShahNo ratings yet
- The Effect of The Internet and Social Media On Small-Sized Businesses' Innovation PotentialDocument12 pagesThe Effect of The Internet and Social Media On Small-Sized Businesses' Innovation PotentialAnkita SahaNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Management and Corporate Profitability: Case Study of Selected Manufacturing Companies Listed On The Nigerian Stock ExchangeDocument16 pagesLiquidity Management and Corporate Profitability: Case Study of Selected Manufacturing Companies Listed On The Nigerian Stock ExchangeAta Ullah MukhlisNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Mandatory Meps For Distribution Transformers in AustraliaDocument94 pagesIntroduction of Mandatory Meps For Distribution Transformers in AustraliaPaolo ProspNo ratings yet
- 2ST Lesson 2 Strategic Plan Leads To Marketing TacticsDocument17 pages2ST Lesson 2 Strategic Plan Leads To Marketing TacticsAhmed SheblNo ratings yet
- JUSTIFDocument2 pagesJUSTIFMAY RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
9 3e
9 3e
Uploaded by
shanmukha anisettiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9 3e
9 3e
Uploaded by
shanmukha anisettiCopyright:
Available Formats
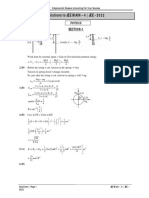
768933-9-3E AID: 261991 | 05/06/2021
Consider the firm’s production function,
1 1
y x1 4 x2 4
and prices of input are w1 1 and w2 2
(a)
The objective is find the factor demands the optional factor quantities are found at
w1
marginal rate of technical substitution (MARTS) that is nothing but price ratio w2
m arg inal product of x1
MRTS = m arg inal productof x2
Mp x1
Mp x2
Now,
dy
Mp x1
= dx1
d
dx1
1 1
x1 4 x2 4
1 3 1
x1 4 x2 4
4
And,
dy
Mp x2
dx2
d
dx2
1
1
x1 4 x2 4
1 1 3
x1 4 x2 4
4
Therefore,
Mp x1
Mp x2
MARTS
1 3 4 14
x1 x2
4
1 1 4 3 4
x1 x2
4
x
2
x1
Hence optimality condition becomes,
x2 w1
x1 w2
1
2
x1 2 x2
Substitute this value in production function them,
1 1
y 2 x2 4
x2 4
1 1
y 2 4 x2 2
x2 y 2 1/2
2
Therefore,
x1 y 2 y 2
y2
x2 y
And 2
Hence proved.
(b)
C y w1 x1 w2 x2
Total cost,
2 2 y2 2 2 y2
1 1
2 2 y2 2 2 y2
1 1
2 2 y2
3
2 2 y2
Hence Proved.
(C)
Supply curve is nothing but a marginal cost curre.
dc y
p
Supply curve dy
d 32 2
p 2 y
= dy
2 2 2y
3
2 2 y p
5
p
y p 5
22
Hence Proved.
You might also like
- 2020 TJC JC2 Prelim H2 Math Paper 1 (Solutions)Document23 pages2020 TJC JC2 Prelim H2 Math Paper 1 (Solutions)Ace PTNo ratings yet
- (D) Integration by Substitution: 5: Integration and Its ApplicationsDocument13 pages(D) Integration by Substitution: 5: Integration and Its ApplicationsMark LiNo ratings yet
- TMK2023chap 0.2Document12 pagesTMK2023chap 0.2Miu MakriNo ratings yet
- TJC H2 2021 Math Prelim P1 SolutionsDocument25 pagesTJC H2 2021 Math Prelim P1 SolutionsHormitha SivakumarNo ratings yet
- H2 MYE Revision Package Differentiation SolutionsDocument10 pagesH2 MYE Revision Package Differentiation SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Document13 pages2020 JC 2 H2 Math Consolidation Test II (Solutions)Timothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- 1.1.2 Integration by Substitution: Thus, LN ( ) +Document6 pages1.1.2 Integration by Substitution: Thus, LN ( ) +Everything What U WantNo ratings yet
- Differential OperatorsDocument11 pagesDifferential OperatorsStanley MwangiNo ratings yet
- Noise and Vibration: Two Degree of Freedom SystemsDocument28 pagesNoise and Vibration: Two Degree of Freedom SystemssoqhNo ratings yet
- Eco501 Assignment4a Solutions Summer2020Document3 pagesEco501 Assignment4a Solutions Summer2020maruf91No ratings yet
- Wk11 Lectrure11 12dec2017 FinalDocument15 pagesWk11 Lectrure11 12dec2017 Finalهاني احمدNo ratings yet
- 2014 jc1 Math Promo-FinalisedDocument139 pages2014 jc1 Math Promo-FinalisedLinda aiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document35 pagesChapter 12ndjwndnnd sjwjhsbdbdbdNo ratings yet
- Math p1c3Document14 pagesMath p1c3kolodoloNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Uz 8Document6 pagesCalc 2 Uz 8Ferhat YoldasNo ratings yet
- Week2 Lecture2 PDFDocument28 pagesWeek2 Lecture2 PDFAbdullah AloglaNo ratings yet
- Siyuan SongDocument16 pagesSiyuan SongTốNhưPhạmNo ratings yet
- Prof OrG Trans45Document21 pagesProf OrG Trans45Saye B.DoloNo ratings yet
- L - 3: First Order & First Degree Differential EquationsDocument15 pagesL - 3: First Order & First Degree Differential EquationsMusayeb HossainNo ratings yet
- Basic CalculusDocument2 pagesBasic CalculusKate CaranguianNo ratings yet
- 19-05-24 Isr - Iit Star Co-Sc (Model-B) Jee Adv 2023 (P-I) Wat-46 Key & SolDocument16 pages19-05-24 Isr - Iit Star Co-Sc (Model-B) Jee Adv 2023 (P-I) Wat-46 Key & SolkantaksathwikNo ratings yet
- KVPY-QE SolutionsDocument9 pagesKVPY-QE SolutionsArsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced Practice Test-1 - Paper-1 - SolutionsDocument14 pagesJEE Advanced Practice Test-1 - Paper-1 - SolutionsDev MaanNo ratings yet
- 2019 - April - UG CBCS 2011 Onwards - B.SC., (Mathematics) - MathematicsDocument68 pages2019 - April - UG CBCS 2011 Onwards - B.SC., (Mathematics) - MathematicsBharathi SelvamNo ratings yet
- MAT1581 Assignment 4 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesMAT1581 Assignment 4 - SolutionsLEANATTENo ratings yet
- CJC H2 Promo 2009 SolutionsDocument10 pagesCJC H2 Promo 2009 Solutionstoh tim lamNo ratings yet
- Problem 8. 5: (Difficulty: 2)Document10 pagesProblem 8. 5: (Difficulty: 2)Will JohnNo ratings yet
- L3L4 Sem2 2023.24Document32 pagesL3L4 Sem2 2023.24Farahin RdznNo ratings yet
- 2 Control (May 2010)Document2 pages2 Control (May 2010)Primero C ElmejorNo ratings yet
- Solution of Practice Exercise For Lecture 19Document3 pagesSolution of Practice Exercise For Lecture 19Malik Nazim ChannarNo ratings yet
- 2019 YIJC Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsDocument14 pages2019 YIJC Paper 1 Suggested SolutionsGeorge ChooNo ratings yet
- Promo08 Acjc H2 (Soln)Document8 pagesPromo08 Acjc H2 (Soln)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- 5..aod 21.05.21 Ans&solDocument9 pages5..aod 21.05.21 Ans&solKovid AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 2015 BoS Trials Mathematics Extension 2 SolutionsDocument36 pages2015 BoS Trials Mathematics Extension 2 SolutionsIjal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Product and Quotient RuleDocument9 pagesProduct and Quotient RuleDalia EldeabNo ratings yet
- Advanced Circles Ex.2 (B)Document24 pagesAdvanced Circles Ex.2 (B)Ajay SinghNo ratings yet
- Bahan Seminar Kertas 1Document13 pagesBahan Seminar Kertas 1Zulhanif IdrisNo ratings yet
- 4th May Class Notes II4 PDFDocument7 pages4th May Class Notes II4 PDFJayNsteinNo ratings yet
- 2022 JEE Main 4 SolutionDocument13 pages2022 JEE Main 4 SolutionADITYA RAJNo ratings yet
- Ganit Pravinya 2016 Test Paper SolutionDocument6 pagesGanit Pravinya 2016 Test Paper SolutionMihir GargNo ratings yet
- 2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)Document31 pages2018 H2 JC1 MSM Differential Equations (Solutions)VincentNo ratings yet
- Further Integration TechniquesDocument39 pagesFurther Integration TechniquesReginNo ratings yet
- Csec Add Maths 2016Document31 pagesCsec Add Maths 2016cartzcj007No ratings yet
- S5 Further Calculus 4 Integration 1-2Document6 pagesS5 Further Calculus 4 Integration 1-2isaiahseruyangeNo ratings yet
- 108220Document77 pages108220Norah CNo ratings yet
- BCS - 12Document18 pagesBCS - 12Shivangi MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Navy Mock Test Answer KeyDocument4 pagesNavy Mock Test Answer KeyPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- March Block Test Timed Trial 2 - SolutionsDocument15 pagesMarch Block Test Timed Trial 2 - SolutionsTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Completing The SquareDocument19 pagesCompleting The SquarengeekengNo ratings yet
- ProbSet 3 1st-Order DEs SolutionsDocument10 pagesProbSet 3 1st-Order DEs SolutionsMlkhr lgndbNo ratings yet
- Principal Component Analysis: Part ADocument10 pagesPrincipal Component Analysis: Part AbetifiNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4-5 Non Linear Partial Differential EquationDocument7 pagesLecture-4-5 Non Linear Partial Differential EquationAtikul IslamNo ratings yet
- Ial pm1 Ex9cDocument3 pagesIal pm1 Ex9cWandaNo ratings yet
- 4 Linear Differential Equations With ConDocument41 pages4 Linear Differential Equations With ConJuan 2012No ratings yet
- Promo08 MJC H2 (Soln)Document16 pagesPromo08 MJC H2 (Soln)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- WTEC2A1 Class1 SolutionDocument3 pagesWTEC2A1 Class1 Solutionphantom ceilNo ratings yet
- RumusiDocument2 pagesRumusimisterinaNo ratings yet
- Block Test Revision Paper 3 - TJC (Soln)Document9 pagesBlock Test Revision Paper 3 - TJC (Soln)Wen Han LimNo ratings yet
- 7 - Maximum and Minimum Values, Points of InflectionDocument9 pages7 - Maximum and Minimum Values, Points of InflectionhiqmNo ratings yet
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)From EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)No ratings yet
- 03 Coordinate Sales PerformanceDocument7 pages03 Coordinate Sales PerformanceSAMUALE ASSEFA MEKURIYANo ratings yet
- CAC Computations Chap 4 1 20Document9 pagesCAC Computations Chap 4 1 20rochelle lagmayNo ratings yet
- VMCSCHDocument8 pagesVMCSCH2402nguyenlinhNo ratings yet
- Stocks Bonds: Bonds and Stocks Are Both Financial Securities With Respective Risks and RewardsDocument2 pagesStocks Bonds: Bonds and Stocks Are Both Financial Securities With Respective Risks and RewardsAndrea TahilNo ratings yet
- IBT 1-2 WeeksDocument7 pagesIBT 1-2 WeeksNicolle Curammeng100% (1)
- Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesRisk ManagementAlejandra CastillaNo ratings yet
- Special Orders: Decision: To Accept or Reject This OfferDocument2 pagesSpecial Orders: Decision: To Accept or Reject This OfferHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Global Reinsurers Maintain EquilibriumDocument89 pagesGlobal Reinsurers Maintain EquilibriumgargramNo ratings yet
- SupplyDocument24 pagesSupplyJay GoraneNo ratings yet
- Tommy AssignmentDocument10 pagesTommy Assignmentخلود البطاحNo ratings yet
- Final Term PaperDocument66 pagesFinal Term PapercshuvodipNo ratings yet
- School of Business and Economics Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument8 pagesSchool of Business and Economics Department of Accounting and FinancetinntinnNo ratings yet
- Pecora FinalReportDocument402 pagesPecora FinalReportAdelino MartinsNo ratings yet
- Solution To Assignment 6Document3 pagesSolution To Assignment 6Khyla DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Aqualisa QuartzDocument5 pagesAqualisa QuartzSrinivasa Raghavachar100% (1)
- Difference Between Money Market and Capital MarketDocument4 pagesDifference Between Money Market and Capital MarketSanjoy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- ZaraDocument14 pagesZaraMax Tan50% (2)
- Index Futures PricingDocument21 pagesIndex Futures PricingVaidyanathan RavichandranNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Credit Risk Associated With Banking Sector Deregulation in West AfricaDocument58 pagesAn Analysis of Credit Risk Associated With Banking Sector Deregulation in West AfricaTheophilus Orraca-TettehNo ratings yet
- Sap Mm-Fi Integration Overview PDFDocument43 pagesSap Mm-Fi Integration Overview PDFSambit Mohanty100% (1)
- Niddf PDFDocument1 pageNiddf PDFMuhammad MudassarNo ratings yet
- B. Com (CA) SyllabusDocument70 pagesB. Com (CA) SyllabusBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Notes ReceivableDocument22 pagesModule 4 - Notes ReceivableJennalyn S. GanalonNo ratings yet
- WTS Dhruva - Five-Years-of-VAT-in-the-UAEDocument53 pagesWTS Dhruva - Five-Years-of-VAT-in-the-UAEZankhana ShahNo ratings yet
- The Effect of The Internet and Social Media On Small-Sized Businesses' Innovation PotentialDocument12 pagesThe Effect of The Internet and Social Media On Small-Sized Businesses' Innovation PotentialAnkita SahaNo ratings yet
- Liquidity Management and Corporate Profitability: Case Study of Selected Manufacturing Companies Listed On The Nigerian Stock ExchangeDocument16 pagesLiquidity Management and Corporate Profitability: Case Study of Selected Manufacturing Companies Listed On The Nigerian Stock ExchangeAta Ullah MukhlisNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Mandatory Meps For Distribution Transformers in AustraliaDocument94 pagesIntroduction of Mandatory Meps For Distribution Transformers in AustraliaPaolo ProspNo ratings yet
- 2ST Lesson 2 Strategic Plan Leads To Marketing TacticsDocument17 pages2ST Lesson 2 Strategic Plan Leads To Marketing TacticsAhmed SheblNo ratings yet
- JUSTIFDocument2 pagesJUSTIFMAY RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet