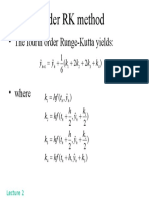Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wind Energy I: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 Slide
Wind Energy I: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 Slide
Uploaded by
Fzico GtmanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Cycles WorksheetanswersDocument2 pagesCycles WorksheetanswersRaheem Don Breedz Phillips0% (1)
- The Russian Sukhovey (Lydolph)Document20 pagesThe Russian Sukhovey (Lydolph)geoffreyjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Anao Clup 2012-2022 Part 1Document56 pagesAnao Clup 2012-2022 Part 1Justine RazonNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - PhotochemistryDocument7 pagesLab Report - PhotochemistryMon RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Wind Field Characterization: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument44 pagesWind Field Characterization: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Wind-Blade Interaction: Consequences For DesignDocument35 pagesWind-Blade Interaction: Consequences For DesignFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- 006 Wind PowerDocument54 pages006 Wind PowerArunNo ratings yet
- W4 Why Wind Is Not Coal - On The Economics ofDocument32 pagesW4 Why Wind Is Not Coal - On The Economics ofrenev.uptksktNo ratings yet
- MIT2 60s20 Lec1Document49 pagesMIT2 60s20 Lec1saad JajjaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy For Commercial UseDocument13 pagesNuclear Energy For Commercial UseZane AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Name:Bernard Billyandi Tampubolon Class:Petroleum Engineering 4 Nim:101316141Document4 pagesName:Bernard Billyandi Tampubolon Class:Petroleum Engineering 4 Nim:101316141Billy TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Session 1.3: Introductory Lectures The Technological Steps of Hydrogen IntroductionDocument35 pagesSession 1.3: Introductory Lectures The Technological Steps of Hydrogen IntroductionHari SimhaNo ratings yet
- 2 Wind Speed Measurements PDFDocument53 pages2 Wind Speed Measurements PDFStuardo López MéndezNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy in Germany: Environment ScienceDocument42 pagesRenewable Energy in Germany: Environment ScienceNgân Kim100% (1)
- Eminar Ourse Emester: Rogram ONS Nergy AW EmesterDocument28 pagesEminar Ourse Emester: Rogram ONS Nergy AW EmesterPalak JoshiNo ratings yet
- France After FukusimaDocument12 pagesFrance After FukusimaKahraman TimurNo ratings yet
- Research On NuclearDocument17 pagesResearch On NuclearIan Kendall Judge-LordNo ratings yet
- Gerlach2011 Paper PV-Wind-Complementarity 6CV.1.32 26thPVSECDocument8 pagesGerlach2011 Paper PV-Wind-Complementarity 6CV.1.32 26thPVSECishantbharadwaj12No ratings yet
- Swedish Commnet On Before The FloodDocument16 pagesSwedish Commnet On Before The FloodIlNo ratings yet
- Hoogwijk 2004Document31 pagesHoogwijk 2004Kamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Géotechnique Lecture 2011: Foundation Design For Offshore Wind TurbinesDocument78 pagesGéotechnique Lecture 2011: Foundation Design For Offshore Wind TurbinesRahul KolateNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Second Law Analysis of Wind Turbine Power PlantsDocument8 pages2011 - Second Law Analysis of Wind Turbine Power PlantsgxydisNo ratings yet
- BE Basic Energy ReloadedDocument19 pagesBE Basic Energy Reloadedarki_37826160No ratings yet
- Simoes ETSAPWaterWorkshop WaterTechs v1Document13 pagesSimoes ETSAPWaterWorkshop WaterTechs v1Meriem PearlNo ratings yet
- It Has A Low Cost of OperationDocument3 pagesIt Has A Low Cost of OperationDuterteNo ratings yet
- GEE L3 Wind OUTDocument43 pagesGEE L3 Wind OUTPol CireraNo ratings yet
- Pubdoc 3 4329 851Document14 pagesPubdoc 3 4329 851MPHATSO CHIRWANo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument23 pages1 IntroductionChengxi FUNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument6 pagesWind EnergyRajat DubeyNo ratings yet
- The Wind Energy RevolutionDocument18 pagesThe Wind Energy RevolutionEliezer BecziNo ratings yet
- Wind Power EnergyDocument14 pagesWind Power EnergyOja ChanelNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Cleaner and Efficient Energy 1Document6 pagesRunning Head: Cleaner and Efficient Energy 1WilsonMachariaMuriukiNo ratings yet
- Hammarström, L. (2012) .Document5 pagesHammarström, L. (2012) .Oli CastilloNo ratings yet
- The Role of Political Uncertainty in The Danish Renewable Energy MarketDocument21 pagesThe Role of Political Uncertainty in The Danish Renewable Energy MarketTyndall Centre for Climate Change ResearchNo ratings yet
- Fridleifssonetal IPCCGeothermalpaper2008Document37 pagesFridleifssonetal IPCCGeothermalpaper2008Ilyas AryaNo ratings yet
- ENV Major EssayDocument6 pagesENV Major EssayLiew Chih HauNo ratings yet
- Chpat 1 Introduction ModifedDocument23 pagesChpat 1 Introduction ModifedManiraj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- MEC559 2021 Chapters1 2Document22 pagesMEC559 2021 Chapters1 2aishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Wind Power: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument12 pagesWind Power: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- SEE6101 01 IntroToEnergy 2015Document47 pagesSEE6101 01 IntroToEnergy 2015kk chanNo ratings yet
- A Quantitative Study of Public Perception On Nuclear Power in NigeriaDocument10 pagesA Quantitative Study of Public Perception On Nuclear Power in NigeriaIJSREDNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy and Sustainable Electricity Generation: Evidence From GermanyDocument14 pagesWind Energy and Sustainable Electricity Generation: Evidence From Germanydimasbrahmana22No ratings yet
- Global Wind DraftDocument11 pagesGlobal Wind DraftjalfonsoaNo ratings yet
- Necessity and Impact of Power To Gas On Energy Transition in GermanyDocument9 pagesNecessity and Impact of Power To Gas On Energy Transition in Germanynintendo907No ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Downtime and Its Importance For Offshore DeploymentDocument11 pagesWind Turbine Downtime and Its Importance For Offshore DeploymentUma TamilNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Technical PaperDocument11 pagesFinal Draft Technical Paperapi-464172251No ratings yet
- 8 IJTPE Issue4 Vol2 No3 Sep2010 pp51 59Document9 pages8 IJTPE Issue4 Vol2 No3 Sep2010 pp51 59mjimenezgNo ratings yet
- Physics 101ah - Lesson 5Document8 pagesPhysics 101ah - Lesson 5Ronald TantiadoNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Condition Monitoring Technical and CoDocument22 pagesWind Turbine Condition Monitoring Technical and Cotuandanhbk10No ratings yet
- Fuel Cells For A Sustainable Future?: Jane Powell, Michael Peters, Alan Ruddell and Jim Halliday March 2004Document36 pagesFuel Cells For A Sustainable Future?: Jane Powell, Michael Peters, Alan Ruddell and Jim Halliday March 2004Tyndall Centre for Climate Change ResearchNo ratings yet
- Applied Energy: Miguel Esteban, David LearyDocument9 pagesApplied Energy: Miguel Esteban, David LearyFareza Andre Pahlevi PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- COURSE INFORMATION - RES FinalDocument16 pagesCOURSE INFORMATION - RES FinalDHARANIKA T C1557No ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy The Pros and Cons - FES Just ClimateDocument15 pagesNuclear Energy The Pros and Cons - FES Just ClimateRana BustamiNo ratings yet
- Textbook Wind Power The Struggle For Control of A New Global Industry 2Nd Edition Ben Backwell Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Wind Power The Struggle For Control of A New Global Industry 2Nd Edition Ben Backwell Ebook All Chapter PDFeric.huether323100% (3)
- Energy: W F D, Joule (J) Newton (N) Meter (M)Document26 pagesEnergy: W F D, Joule (J) Newton (N) Meter (M)Mohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Two Opposite Governmental Positions On EUDocument3 pagesTwo Opposite Governmental Positions On EUpedro jesus montoya laraNo ratings yet
- Japan's Current Nuclear Energy PolicyDocument35 pagesJapan's Current Nuclear Energy PolicyJoe BacchusNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Wind EnergyDocument17 pagesAssignment 1 - Wind EnergySyenHong Nik100% (1)
- 01338529Document7 pages01338529api-3697505No ratings yet
- Fraunhofer ISE AnnualReport 2011Document191 pagesFraunhofer ISE AnnualReport 2011Umut KaramanNo ratings yet
- Adv-Conv All PDFsDocument486 pagesAdv-Conv All PDFsMohammad Abu-SaifNo ratings yet
- Why Offshore Wind EnergyDocument7 pagesWhy Offshore Wind EnergyHerdiana KristiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerDocument4 pagesNuclear PowerStevenNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Crunch: How We're Getting Climate Change Wrong—and How to Fix ItFrom EverandThe Carbon Crunch: How We're Getting Climate Change Wrong—and How to Fix ItRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Wind Turbines - Søren Gundtoft - 3rd Edition - January 2012Document22 pagesWind Turbines - Søren Gundtoft - 3rd Edition - January 2012Fzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- 1 Muka VertikalDocument17 pages1 Muka VertikalFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Design of Naca 4415 Taperless Twistless Wind Turbine Blade Using Twist Optimization For Indonesia Wind CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesDesign of Naca 4415 Taperless Twistless Wind Turbine Blade Using Twist Optimization For Indonesia Wind CharacteristicsFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Channel Height On The Enhanced Heat Transfer Characteristics in A Corrugated Heat Exchanger ChannelDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Channel Height On The Enhanced Heat Transfer Characteristics in A Corrugated Heat Exchanger ChannelFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Investigation Flow On Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine With Betz Chord Distribution, Twist, and WingletDocument7 pagesInvestigation Flow On Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine With Betz Chord Distribution, Twist, and WingletFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Wind-Blade Interaction: Consequences For DesignDocument35 pagesWind-Blade Interaction: Consequences For DesignFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Wind Power: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument12 pagesWind Power: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Wind Field Characterization: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument44 pagesWind Field Characterization: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Power Losses at The Rotor Blade: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument22 pagesPower Losses at The Rotor Blade: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Safety Bracket: Drawn Checked QA MFG ApprovedDocument1 pageSafety Bracket: Drawn Checked QA MFG ApprovedFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Range Kutta MethodDocument1 pageRange Kutta MethodFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Cycles of Matter VocabularyDocument4 pagesCycles of Matter Vocabularyapi-454466657No ratings yet
- Art. 2 (Eduardo) - ProntoDocument10 pagesArt. 2 (Eduardo) - ProntowilliansbarretosNo ratings yet
- DLP - Grade 5 SCIENCEDocument12 pagesDLP - Grade 5 SCIENCEGia CrystalNo ratings yet
- Loona Space Presentation TemplateDocument12 pagesLoona Space Presentation Templateby ScribdNo ratings yet
- Forest Protection and ConservationDocument11 pagesForest Protection and Conservationqwerty asdfgNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science 1st QuarterDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science 1st QuarterKeanu Ribs87% (45)
- Continuous Thermal Overloading Capabilities of Ester Oil Transformers in Oil Directed Cooling ConditionsDocument7 pagesContinuous Thermal Overloading Capabilities of Ester Oil Transformers in Oil Directed Cooling ConditionsDanilo FortesNo ratings yet
- Namibia Electricity Supply Demand Options March 2008 FINALDocument235 pagesNamibia Electricity Supply Demand Options March 2008 FINALVeikko212No ratings yet
- GREENSHIP Homes - Ver 1.0 (1) - DikonversiDocument23 pagesGREENSHIP Homes - Ver 1.0 (1) - Dikonversisagita ayiningtyasNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 1 First Quarter Week 5Document11 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 1 First Quarter Week 5BRYCE JUSTINE AVILLANONo ratings yet
- Climate RegionsDocument5 pagesClimate RegionsNeal RyanNo ratings yet
- Kyocera SolarWaterPumps PDFDocument52 pagesKyocera SolarWaterPumps PDFjuly2nt6No ratings yet
- Rays of Truth Crystals of Light Information and Guidance For The Golden Age by Fred BellDocument868 pagesRays of Truth Crystals of Light Information and Guidance For The Golden Age by Fred BellJesse Lee AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Rammed EarthDocument17 pagesRammed EarthKaran50% (2)
- Science Grade 11 1ST PTDocument5 pagesScience Grade 11 1ST PTJarven SaguinNo ratings yet
- Class IV Evs Assignment Week 24Document7 pagesClass IV Evs Assignment Week 24Abhigyan Mohan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties of MetalsDocument3 pagesOptical Properties of MetalsZahel Salvador50% (2)
- Operational Life Cycle Impact Assessment Weighting Factors Based On Planetary BoundariesDocument8 pagesOperational Life Cycle Impact Assessment Weighting Factors Based On Planetary BoundariesMuhammad Dzaky Alfajr DirantonaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology For Society and Territory Volume 5 2015Document1,304 pagesEngineering Geology For Society and Territory Volume 5 2015Mas'ud KholahNo ratings yet
- AIM: To Determine The Field or In-Situ Density or Unit Weight of Soil by Core Cutter Method ApparatusDocument2 pagesAIM: To Determine The Field or In-Situ Density or Unit Weight of Soil by Core Cutter Method ApparatussunilNo ratings yet
- Principles of Plasma CuttingDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Plasma CuttingTharindu Chathuranga100% (1)
- Plastics The FactsDocument81 pagesPlastics The FactsMr BigNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDocument131 pagesFlashcards - Topic 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelHarriet StrattonNo ratings yet
- NAIMA BI475 Comparing Fiber Glass and Cellulose InsulationDocument6 pagesNAIMA BI475 Comparing Fiber Glass and Cellulose InsulationBehailu FelekeNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument20 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesKrithi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Magmatism PDFDocument14 pagesModule 7 Magmatism PDFRODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
Wind Energy I: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 Slide
Wind Energy I: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 Slide
Uploaded by
Fzico GtmanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wind Energy I: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 Slide
Wind Energy I: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 Slide
Uploaded by
Fzico GtmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Wind Energy I
Wind Energy I
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 1
Wind Energy I Basic information
Michael Hölling (Mike)
Email: michael.hoelling@uni-oldenburg.de
Room: W2-1-126
Phone: 798-3951
Office hours: Fridays 10:00 - 12:00
Prof. Joachim Peinke
Email: peinke@uni-oldenburg.de
Room: W2-1-129
Phone: 798-3536
Hendrik Heißelmann (Tutor for Exercises)
Email: hendrik.heisselmann@uni-oldenburg.de
Room: W2-1-122
Phone: 798-3643
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 2
Wind Energy I Basic information
Slides will be available on Stud.IP webpage and the corresponding link to this lecture shortly
after each class
https://elearning.uni-oldenburg.de
Literature:
E. Hau: Wind Turbines - 2nd edition, Springer, Berlin 2005 (also available in german, title
Windkraftanlagen)
T. Burton et al.: Wind energy Handbook, John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2001
J. Twele und R. Gasch: Windkraftanlagen, Teubner B. G. GmbH, 2005
J. P. Molly. Windenergie, Verlag C.F. Müller, Karlsruhe, 1990
On the internet:
http://www.windinformation.de/
DEWI: http://www.dewi.de/dewi/index.php
DEWI GmbH = Deutsches Windenergie-Institut (German Wind Energy Institute)
BWE: http://www.wind-energie.de (Bundesverband Windenergie e.V.)
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 3
Wind Energy I Class content
5 Wind turbines in
6 Wind - blades
general
2 Wind measurements interaction
7 Π-theorem
8 Wind turbine
characterization
3 Wind field 9 Control strategies
characterization
10 Generator
4 Wind power
11 Electrics / grid
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 4
Wind Energy I Class structure
Thursday 28.10.2010: 1st lesson - motivation for renewable energies
Monday 01.11.2010: Exercise I
Thursday 04.11.2010: 2nd lesson - wind measurements techniques - anemometers
Monday 08.11.2010: Exercise II
Thursday 11.11.2010: 3rd lesson - characterization of wind fields
Monday 15.11.2010: Exercise III
Thursday 18:11.2010: 4th lesson - wind power, Betz limit, power curves of WECs
Monday 22.11.2010: Exercise IV (skip or covered by someone else)
Thursday 25.11.2010: 5th lesson - (covered by Prof. Peinke) history of wind turbines, WEC design
Monday 29.11.2010: Exercise V (skip or covered by someone else)
Thursday 2.12.2010: 6th lesson - interaction of wind field with blade segments
Monday 6.12.2010: Exercise VI
Thursday 9.12.2010: 7th lesson - PI-theorem
Monday 13.12.2010: Exercise VII
Thursday 16.12.2010: 8th lesson - characterization of WECs using dimensionless quantities
Monday 20.12.2010: Exercise VIII Christmas
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 5
Wind Energy I Class structure
Thursday 06.01.2011: 9th lesson - WEC control - different strategies and operation points
Monday 10.01.2011: Exercise IX
Thursday 13.01.2011: 10th lesson - WEC electrics / generator
Monday 17.01.2011: Exercise X
Thursday 20.01.2011: 11th lesson - WEC electrics / generator
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 6
Wind Energy I Energy and Power
What is energy ?
! "
kg · m2
Energy [Joule]: 2
= [J]
s
Different forms of appearances of energy, for example:
mechanical energy (work)
potential energy
kinetic energy
electrical energy
...
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 7
Wind Energy I Energy and Power
Conservation of energy !
Energy can NOT be created or destroyed, it can only be
converted in another form of appearance.
! "
E J
Power: P = = [W ]
t s
therefore
Energy: E = P · t [W · s]
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 8
Wind Energy I Energy and Power
Different units of energy and their conversion factors
from / to Joule Kilowatt hour Electron volt Kilopondmeter Calories
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 9
Wind Energy I Energy and Power
Numbers can become very big and very small
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 10
Wind Energy I Power consumption
Worldwide power demand: 15T W = 1.5 · 10 W , considering
13
6 billion people on earth leads to a power consumption of 2.5kW
per person
GDP = Gross Domestic
Product
German:
Bruttoinlandsprodukt
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 11
Wind Energy I Energy consumption
A power demand of 1.5 · 10 W in one year13
1a = 8760h = 3153600s
corresponds to an energy demand of
E = 1.5 · 10 W · 31536000s = 4.73 · 10 J = 0.473ZJ
13 20
Expressed in tons of coal as a unit for energy
1 ton coal = 29.3GJ = 29.3 · 10 J 9
Expressed in tons of coal as a unit for energy
4.73 · 10 /29.3 · 10 = 1.6 · 10
20 9 10
tons coal
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 12
Wind Energy I Power production
Resources for power production
year
Wind still < 1%
(worldwide)
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 13
Wind Energy I Resource oil
From “Reserves, Resources and Availability of Energy Resources 2005”, BGR annual report
BGR : Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe
Cumulative production : 143 Gt
Reserves : 161 Gt
Resources : 82 Gt
Estimated Ultimate Recovery (EUR) : 386 Gt
Remaining potential : 243 Gt
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 14
Wind Energy I Resource gas
From “Reserves, Resources and Availability of Energy Resources 2005”, BGR annual report
BGR : Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe
Cumulative production : 81 Tm3
Reserves : 179 Tm3
Resources : 207 Tm3
Estimated Ultimate Recovery (EUR) : 467 Tm3
Remaining potential : 386 Tm3
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 15
Wind Energy I Resource lignite (brown coal)
From “Reserves, Resources and Availability of Energy Resources 2005”, BGR annual report
BGR : Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe
Accumulative output : 45 Gt
Reserves : 207 Gt
Resources : 1024 Gt
Estimated Ultimate Recovery (EUR) : 1276 Gt
Remaining potential : 1234 Gt
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 16
Wind Energy I Resource hard coal
From “Reserves, Resources and Availability of Energy Resources 2005”, BGR annual report
BGR : Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe
Accumulative output : 204 Gt
Reserves : 746 Gt
Resources : 4079 Gt
Estimated Ultimate Recovery (EUR) : 5029 Gt
Remaining potential : 4825 Gt
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 17
Wind Energy I Efficiency
How much energy is stored in ALL fossil resources on earth ?
Oil: 386Gt = 16 · 10 J, with 1toe = 42 · 10 J
21 9
Gas: 467T m = 16 · 10 J, with 1000m = 34.6 · 10 J
3 21 3 9
Lignite: 1276Gt = 37 · 10 J, with 1ton coal = 29.3 · 10 J
21 9
Hard coal: 5029Gt = 147 · 10 J, with 1ton coal = 29.3 · 10 J
21 9
This adds up to 216 · 10 J = 216 · 10 W · s
21 21
that is (roughly) stored in all fossil resources.
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 18
Wind Energy I Future of resources
Quo vadis ?
?
?
?
year
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 19
Wind Energy I Energy consumption
10 to 20% is used for electricity
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 20
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Jan. 2007: 383ppm
27% above the max
value of the last
400.000 years
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 21
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
more than 25%
above the max
value of the last
400.000 years
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 22
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 23
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 24
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 25
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 26
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 27
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 28
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 29
Wind Energy I Environmental issues
Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 slide 30
You might also like
- Cycles WorksheetanswersDocument2 pagesCycles WorksheetanswersRaheem Don Breedz Phillips0% (1)
- The Russian Sukhovey (Lydolph)Document20 pagesThe Russian Sukhovey (Lydolph)geoffreyjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Anao Clup 2012-2022 Part 1Document56 pagesAnao Clup 2012-2022 Part 1Justine RazonNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - PhotochemistryDocument7 pagesLab Report - PhotochemistryMon RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Wind Field Characterization: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument44 pagesWind Field Characterization: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Wind-Blade Interaction: Consequences For DesignDocument35 pagesWind-Blade Interaction: Consequences For DesignFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- 006 Wind PowerDocument54 pages006 Wind PowerArunNo ratings yet
- W4 Why Wind Is Not Coal - On The Economics ofDocument32 pagesW4 Why Wind Is Not Coal - On The Economics ofrenev.uptksktNo ratings yet
- MIT2 60s20 Lec1Document49 pagesMIT2 60s20 Lec1saad JajjaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy For Commercial UseDocument13 pagesNuclear Energy For Commercial UseZane AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Name:Bernard Billyandi Tampubolon Class:Petroleum Engineering 4 Nim:101316141Document4 pagesName:Bernard Billyandi Tampubolon Class:Petroleum Engineering 4 Nim:101316141Billy TampubolonNo ratings yet
- Session 1.3: Introductory Lectures The Technological Steps of Hydrogen IntroductionDocument35 pagesSession 1.3: Introductory Lectures The Technological Steps of Hydrogen IntroductionHari SimhaNo ratings yet
- 2 Wind Speed Measurements PDFDocument53 pages2 Wind Speed Measurements PDFStuardo López MéndezNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy in Germany: Environment ScienceDocument42 pagesRenewable Energy in Germany: Environment ScienceNgân Kim100% (1)
- Eminar Ourse Emester: Rogram ONS Nergy AW EmesterDocument28 pagesEminar Ourse Emester: Rogram ONS Nergy AW EmesterPalak JoshiNo ratings yet
- France After FukusimaDocument12 pagesFrance After FukusimaKahraman TimurNo ratings yet
- Research On NuclearDocument17 pagesResearch On NuclearIan Kendall Judge-LordNo ratings yet
- Gerlach2011 Paper PV-Wind-Complementarity 6CV.1.32 26thPVSECDocument8 pagesGerlach2011 Paper PV-Wind-Complementarity 6CV.1.32 26thPVSECishantbharadwaj12No ratings yet
- Swedish Commnet On Before The FloodDocument16 pagesSwedish Commnet On Before The FloodIlNo ratings yet
- Hoogwijk 2004Document31 pagesHoogwijk 2004Kamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Géotechnique Lecture 2011: Foundation Design For Offshore Wind TurbinesDocument78 pagesGéotechnique Lecture 2011: Foundation Design For Offshore Wind TurbinesRahul KolateNo ratings yet
- 2011 - Second Law Analysis of Wind Turbine Power PlantsDocument8 pages2011 - Second Law Analysis of Wind Turbine Power PlantsgxydisNo ratings yet
- BE Basic Energy ReloadedDocument19 pagesBE Basic Energy Reloadedarki_37826160No ratings yet
- Simoes ETSAPWaterWorkshop WaterTechs v1Document13 pagesSimoes ETSAPWaterWorkshop WaterTechs v1Meriem PearlNo ratings yet
- It Has A Low Cost of OperationDocument3 pagesIt Has A Low Cost of OperationDuterteNo ratings yet
- GEE L3 Wind OUTDocument43 pagesGEE L3 Wind OUTPol CireraNo ratings yet
- Pubdoc 3 4329 851Document14 pagesPubdoc 3 4329 851MPHATSO CHIRWANo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument23 pages1 IntroductionChengxi FUNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument6 pagesWind EnergyRajat DubeyNo ratings yet
- The Wind Energy RevolutionDocument18 pagesThe Wind Energy RevolutionEliezer BecziNo ratings yet
- Wind Power EnergyDocument14 pagesWind Power EnergyOja ChanelNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Cleaner and Efficient Energy 1Document6 pagesRunning Head: Cleaner and Efficient Energy 1WilsonMachariaMuriukiNo ratings yet
- Hammarström, L. (2012) .Document5 pagesHammarström, L. (2012) .Oli CastilloNo ratings yet
- The Role of Political Uncertainty in The Danish Renewable Energy MarketDocument21 pagesThe Role of Political Uncertainty in The Danish Renewable Energy MarketTyndall Centre for Climate Change ResearchNo ratings yet
- Fridleifssonetal IPCCGeothermalpaper2008Document37 pagesFridleifssonetal IPCCGeothermalpaper2008Ilyas AryaNo ratings yet
- ENV Major EssayDocument6 pagesENV Major EssayLiew Chih HauNo ratings yet
- Chpat 1 Introduction ModifedDocument23 pagesChpat 1 Introduction ModifedManiraj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- MEC559 2021 Chapters1 2Document22 pagesMEC559 2021 Chapters1 2aishwaryaNo ratings yet
- Wind Power: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument12 pagesWind Power: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- SEE6101 01 IntroToEnergy 2015Document47 pagesSEE6101 01 IntroToEnergy 2015kk chanNo ratings yet
- A Quantitative Study of Public Perception On Nuclear Power in NigeriaDocument10 pagesA Quantitative Study of Public Perception On Nuclear Power in NigeriaIJSREDNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy and Sustainable Electricity Generation: Evidence From GermanyDocument14 pagesWind Energy and Sustainable Electricity Generation: Evidence From Germanydimasbrahmana22No ratings yet
- Global Wind DraftDocument11 pagesGlobal Wind DraftjalfonsoaNo ratings yet
- Necessity and Impact of Power To Gas On Energy Transition in GermanyDocument9 pagesNecessity and Impact of Power To Gas On Energy Transition in Germanynintendo907No ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Downtime and Its Importance For Offshore DeploymentDocument11 pagesWind Turbine Downtime and Its Importance For Offshore DeploymentUma TamilNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Technical PaperDocument11 pagesFinal Draft Technical Paperapi-464172251No ratings yet
- 8 IJTPE Issue4 Vol2 No3 Sep2010 pp51 59Document9 pages8 IJTPE Issue4 Vol2 No3 Sep2010 pp51 59mjimenezgNo ratings yet
- Physics 101ah - Lesson 5Document8 pagesPhysics 101ah - Lesson 5Ronald TantiadoNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Condition Monitoring Technical and CoDocument22 pagesWind Turbine Condition Monitoring Technical and Cotuandanhbk10No ratings yet
- Fuel Cells For A Sustainable Future?: Jane Powell, Michael Peters, Alan Ruddell and Jim Halliday March 2004Document36 pagesFuel Cells For A Sustainable Future?: Jane Powell, Michael Peters, Alan Ruddell and Jim Halliday March 2004Tyndall Centre for Climate Change ResearchNo ratings yet
- Applied Energy: Miguel Esteban, David LearyDocument9 pagesApplied Energy: Miguel Esteban, David LearyFareza Andre Pahlevi PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- COURSE INFORMATION - RES FinalDocument16 pagesCOURSE INFORMATION - RES FinalDHARANIKA T C1557No ratings yet
- Nuclear Energy The Pros and Cons - FES Just ClimateDocument15 pagesNuclear Energy The Pros and Cons - FES Just ClimateRana BustamiNo ratings yet
- Textbook Wind Power The Struggle For Control of A New Global Industry 2Nd Edition Ben Backwell Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Wind Power The Struggle For Control of A New Global Industry 2Nd Edition Ben Backwell Ebook All Chapter PDFeric.huether323100% (3)
- Energy: W F D, Joule (J) Newton (N) Meter (M)Document26 pagesEnergy: W F D, Joule (J) Newton (N) Meter (M)Mohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Two Opposite Governmental Positions On EUDocument3 pagesTwo Opposite Governmental Positions On EUpedro jesus montoya laraNo ratings yet
- Japan's Current Nuclear Energy PolicyDocument35 pagesJapan's Current Nuclear Energy PolicyJoe BacchusNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Wind EnergyDocument17 pagesAssignment 1 - Wind EnergySyenHong Nik100% (1)
- 01338529Document7 pages01338529api-3697505No ratings yet
- Fraunhofer ISE AnnualReport 2011Document191 pagesFraunhofer ISE AnnualReport 2011Umut KaramanNo ratings yet
- Adv-Conv All PDFsDocument486 pagesAdv-Conv All PDFsMohammad Abu-SaifNo ratings yet
- Why Offshore Wind EnergyDocument7 pagesWhy Offshore Wind EnergyHerdiana KristiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PowerDocument4 pagesNuclear PowerStevenNo ratings yet
- The Carbon Crunch: How We're Getting Climate Change Wrong—and How to Fix ItFrom EverandThe Carbon Crunch: How We're Getting Climate Change Wrong—and How to Fix ItRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Wind Turbines - Søren Gundtoft - 3rd Edition - January 2012Document22 pagesWind Turbines - Søren Gundtoft - 3rd Edition - January 2012Fzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- 1 Muka VertikalDocument17 pages1 Muka VertikalFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Design of Naca 4415 Taperless Twistless Wind Turbine Blade Using Twist Optimization For Indonesia Wind CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesDesign of Naca 4415 Taperless Twistless Wind Turbine Blade Using Twist Optimization For Indonesia Wind CharacteristicsFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Channel Height On The Enhanced Heat Transfer Characteristics in A Corrugated Heat Exchanger ChannelDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Channel Height On The Enhanced Heat Transfer Characteristics in A Corrugated Heat Exchanger ChannelFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Investigation Flow On Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine With Betz Chord Distribution, Twist, and WingletDocument7 pagesInvestigation Flow On Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine With Betz Chord Distribution, Twist, and WingletFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Wind-Blade Interaction: Consequences For DesignDocument35 pagesWind-Blade Interaction: Consequences For DesignFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Wind Power: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument12 pagesWind Power: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Wind Field Characterization: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument44 pagesWind Field Characterization: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Power Losses at The Rotor Blade: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideDocument22 pagesPower Losses at The Rotor Blade: Michael Hölling, WS 2010/2011 SlideFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
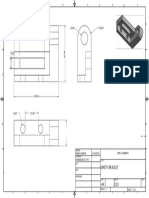
- Safety Bracket: Drawn Checked QA MFG ApprovedDocument1 pageSafety Bracket: Drawn Checked QA MFG ApprovedFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Range Kutta MethodDocument1 pageRange Kutta MethodFzico GtmanNo ratings yet
- Cycles of Matter VocabularyDocument4 pagesCycles of Matter Vocabularyapi-454466657No ratings yet
- Art. 2 (Eduardo) - ProntoDocument10 pagesArt. 2 (Eduardo) - ProntowilliansbarretosNo ratings yet
- DLP - Grade 5 SCIENCEDocument12 pagesDLP - Grade 5 SCIENCEGia CrystalNo ratings yet
- Loona Space Presentation TemplateDocument12 pagesLoona Space Presentation Templateby ScribdNo ratings yet
- Forest Protection and ConservationDocument11 pagesForest Protection and Conservationqwerty asdfgNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science 1st QuarterDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science 1st QuarterKeanu Ribs87% (45)
- Continuous Thermal Overloading Capabilities of Ester Oil Transformers in Oil Directed Cooling ConditionsDocument7 pagesContinuous Thermal Overloading Capabilities of Ester Oil Transformers in Oil Directed Cooling ConditionsDanilo FortesNo ratings yet
- Namibia Electricity Supply Demand Options March 2008 FINALDocument235 pagesNamibia Electricity Supply Demand Options March 2008 FINALVeikko212No ratings yet
- GREENSHIP Homes - Ver 1.0 (1) - DikonversiDocument23 pagesGREENSHIP Homes - Ver 1.0 (1) - Dikonversisagita ayiningtyasNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 1 First Quarter Week 5Document11 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 1 First Quarter Week 5BRYCE JUSTINE AVILLANONo ratings yet
- Climate RegionsDocument5 pagesClimate RegionsNeal RyanNo ratings yet
- Kyocera SolarWaterPumps PDFDocument52 pagesKyocera SolarWaterPumps PDFjuly2nt6No ratings yet
- Rays of Truth Crystals of Light Information and Guidance For The Golden Age by Fred BellDocument868 pagesRays of Truth Crystals of Light Information and Guidance For The Golden Age by Fred BellJesse Lee AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Rammed EarthDocument17 pagesRammed EarthKaran50% (2)
- Science Grade 11 1ST PTDocument5 pagesScience Grade 11 1ST PTJarven SaguinNo ratings yet
- Class IV Evs Assignment Week 24Document7 pagesClass IV Evs Assignment Week 24Abhigyan Mohan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Optical Properties of MetalsDocument3 pagesOptical Properties of MetalsZahel Salvador50% (2)
- Operational Life Cycle Impact Assessment Weighting Factors Based On Planetary BoundariesDocument8 pagesOperational Life Cycle Impact Assessment Weighting Factors Based On Planetary BoundariesMuhammad Dzaky Alfajr DirantonaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology For Society and Territory Volume 5 2015Document1,304 pagesEngineering Geology For Society and Territory Volume 5 2015Mas'ud KholahNo ratings yet
- AIM: To Determine The Field or In-Situ Density or Unit Weight of Soil by Core Cutter Method ApparatusDocument2 pagesAIM: To Determine The Field or In-Situ Density or Unit Weight of Soil by Core Cutter Method ApparatussunilNo ratings yet
- Principles of Plasma CuttingDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Plasma CuttingTharindu Chathuranga100% (1)
- Plastics The FactsDocument81 pagesPlastics The FactsMr BigNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Topic 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelDocument131 pagesFlashcards - Topic 1 Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - Edexcel Chemistry A-LevelHarriet StrattonNo ratings yet
- NAIMA BI475 Comparing Fiber Glass and Cellulose InsulationDocument6 pagesNAIMA BI475 Comparing Fiber Glass and Cellulose InsulationBehailu FelekeNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical CyclesDocument20 pagesBiogeochemical CyclesKrithi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Magmatism PDFDocument14 pagesModule 7 Magmatism PDFRODEL AZARESNo ratings yet