Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rev Earthscience2
Rev Earthscience2
Uploaded by
mcda0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesMinerals are the building blocks of rocks and have distinct crystalline structures and compositions. Rocks consist of aggregates of minerals or organic remains and do not have definite shapes. There are many different types of minerals and rocks that are classified based on their formation processes, compositions, and properties. Key differences between minerals and rocks include minerals having distinct shapes and compositions while rocks have random molecular arrangements and may be mixtures of minerals.
Original Description:
Original Title
REV-EARTHSCIENCE2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMinerals are the building blocks of rocks and have distinct crystalline structures and compositions. Rocks consist of aggregates of minerals or organic remains and do not have definite shapes. There are many different types of minerals and rocks that are classified based on their formation processes, compositions, and properties. Key differences between minerals and rocks include minerals having distinct shapes and compositions while rocks have random molecular arrangements and may be mixtures of minerals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesRev Earthscience2
Rev Earthscience2
Uploaded by
mcdaMinerals are the building blocks of rocks and have distinct crystalline structures and compositions. Rocks consist of aggregates of minerals or organic remains and do not have definite shapes. There are many different types of minerals and rocks that are classified based on their formation processes, compositions, and properties. Key differences between minerals and rocks include minerals having distinct shapes and compositions while rocks have random molecular arrangements and may be mixtures of minerals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
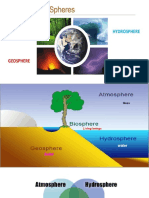
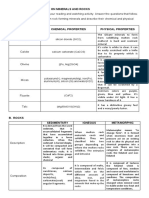
MINERALS ROCKS
Aggregate of one or more minerals. More
Building blocks of rocks
than one mineral e.g IJOLITE (Igneous)
Usually have shape No definite shape
Usually Pretty Not usually pretty
Some are cheap and used to build
More expensive and used in jewelries
infrastructure.
Have no fossils except AMBER. Some have fossils
Molecules are arranged in geometric
Molecules are arranged randomly
shapes/3D
PURE because it is composed of the elements
of periodic table. Pure/Have specific
MIXTURE
compositions (Silicon, Oxygen, Sulfur, Carbon,
Sodium, Chlorine etch)
Formed from crystallization Formed from rock formation
High melting point Low melting point
Some are in form of Crystals. (Transparent,
Minerals with 3D structure)
DIAMOND. Purest Carbon
Minerals are polished to make it look good
AMBER. The only mineral that contains fossils.
Matatagpuan sa dagta ng puno e.g Jurassic
Park
Expensive because it is rare
Gold (Pure) is mineral
Most are formed underneath
2 TYPES OF MINERALS ACCORDING TO
DESCRIPTION
LUSTER
Having the look of polished metals.
METALLIC LUSTER
Gold, Mercury
VITREOUS (Glassy) ADAMANTINE
NON-METALLIC LUSTER (Brilliant/diamond like) PEARLY
Emerald
PROPERTIES OF MINERALS DESCRIPTION
A glow within; intensity of reflected light
LUSTER exhibited by the mineral
Shining of minerals
Measures the resistance of mineral to
abrasion
HARDNESS BLACK DIAMOND. Hardest Mineral
TALC. Softest Mineral
COLOR. Quality such as red, blue, green,
yellow etch.
COLOR AND STREAK STREAK. The color of mineral in powdered
form.
The external shape of a crystal or groups
of crystals
a) PRISMATIC. Prism, Caves, Tube structure
with edges, geometrical shapes having
sides
b) CUBIC. Cube
CRYSTAL FORM/HABIT c) BLADED. Flat-sharp, Flat sword with sharp
edges
d) OCTAHEDRON. Two pyramids base to
base, e.g Diamonds
e) GLOBULAR. Grape-like
f) AMORPHOUS. No definite shape, e.g
Mineraloids, Mercury, Gold
CLEAVAGE. It is the property of mineral to
break along parallel repetitive planes of
CLEAVAGE AND FRACTURE weakness to form smooth flat surfaces.
FRACTURE. Broken surfaces that are
irregular or non-planar
The ratio of the weight of a mineral to the
SPECIFIC GRAVITY weight of an equal volume of water
OTHER PROPERTIES Magnetism, Odor, Taste
“IGNIS” - Latin word, meaning Fire
There are rocks that are derived from the
cooling and solidification of magma or
lava (These two are molten materials of
IGNEOUS ROCKS the Earth)
Must undergo MELTING
Can be both surface and below
Melt down 800-1200 degrees
Formed below the surface of the Earth
These rocks were formed due to changes
in pressure and temperature (HEAT)
conditions
METAMORPHIC ROCKS 100-800 degrees
High pressure, Low temperature
Compact. Kikinis, Change of texture and
color
These rocks formed near the surface of
the Earth
Common sediments features fossils
These rocks are formed by means of
pressure
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Must undergo WEATHERING
Surface only
SEDIMENTARY PROCESS
a) Weathering of rocks
b) Erosion of sediments
c) Deposition
d) Compaction
e) Cementation
2 TYPES OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
Igneous rock formed when magma
INTRUSIVE solidifies inside the volcano
GABBRO, GRANITE, DUNITE, DIORITE
Igneous rock formed when lava solidifies
EXTRUSIVE outside the volcano
BASALT, ANDESITE, RHYOLITE, OBSIDIAN
3 TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
Sedimentary rocks made up of pieces of
other rocks
CLASTIC BRECCIA, SANDSTONE
SHALE, CONGLOMERATE
Formed from organic processes that
involve living organisms producing the
BIOCHEMICAL sediments
LIMESTONE, COAL
Formed when minerals dissolved in water,
begin to precipitate out of the solution
and deposit at the base of the water
CHEMICAL body
EVAPORITE, TRAVERTINE
STALACTITE, STALAGMITE from Caves
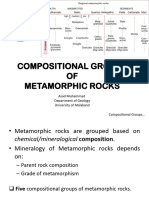
2 TYPES OF METAMORPHIC ROCKS
GNEISS
SLATE
FOLIATED MUSCOVITE
PHYLLITE
MARBLE
NOVACULITE
NON-FOLIATED HORNFELS
QUARTZITE
You might also like
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument38 pagesRocks and MineralsJuliah PeñalosaNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of Minerals 1Document4 pagesPhysical Properties of Minerals 1禮治No ratings yet
- Earth Life Science - HMS12Document24 pagesEarth Life Science - HMS12atienzanorrayneNo ratings yet
- Rock Types and Formation: Modified From A Powerpoint Presentation Prepared by Oluseyi Abegunde CputDocument79 pagesRock Types and Formation: Modified From A Powerpoint Presentation Prepared by Oluseyi Abegunde CputOluseyi AbegundeNo ratings yet
- Earth Science q1-1Document12 pagesEarth Science q1-1Ell LinsyNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument48 pagesRocks and Mineralsianespecial0830No ratings yet
- Earth Sci ReviewerDocument7 pagesEarth Sci ReviewerCarmela EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Petrology PPTDocument27 pagesPetrology PPTbreighamNo ratings yet
- Minerals - RocksDocument52 pagesMinerals - Rocksleann.paguio.03No ratings yet
- Answer To Module 2 (Earth and Life Science)Document9 pagesAnswer To Module 2 (Earth and Life Science)Angel MarieNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Types of Rocks: Activity 1: Classifying Rocks Rock Characteristics Type of Rock Describe How It Is FormedDocument3 pagesEarth Science Types of Rocks: Activity 1: Classifying Rocks Rock Characteristics Type of Rock Describe How It Is FormedRaven CortezaNo ratings yet
- MineralogyDocument70 pagesMineralogyCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- 0004 Glge2a2 RocksDocument51 pages0004 Glge2a2 RocksAndile MavusoNo ratings yet
- The GeosphereDocument23 pagesThe GeosphereGuillermo ChavesNo ratings yet
- Alunan, Jorbelle Dane A.Document3 pagesAlunan, Jorbelle Dane A.JORBELLE DANE ALUNANNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Rocks: Alejandro, Josie May Ambrad, Clouie MaeDocument39 pagesMinerals and Rocks: Alejandro, Josie May Ambrad, Clouie MaeAshley AbrantesNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Minerals and ResourcesDocument6 pagesEarth Science Minerals and ResourcesChristian Neri FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Mineral Characteristic and Types of Rocks: Report by Group# 4Document45 pagesMineral Characteristic and Types of Rocks: Report by Group# 4Chris AltoNo ratings yet
- Igneous Interactive TextbookDocument5 pagesIgneous Interactive Textbookapi-434008934No ratings yet
- Earth Science SHS 4.3 Sedimentary RocksDocument12 pagesEarth Science SHS 4.3 Sedimentary Rockssteven irvine alampayNo ratings yet
- ROCKS AND MINERALS RESOURCES (GROUP 3 - Pasteur)Document8 pagesROCKS AND MINERALS RESOURCES (GROUP 3 - Pasteur)NathalieNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE RocksDocument26 pagesEARTH SCIENCE RocksDAKSINo ratings yet
- Minerals and RocksDocument37 pagesMinerals and RocksNadz mooreNo ratings yet
- Act 2Document4 pagesAct 2Mark Anthony FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument29 pagesTypes of RocksHickory DickoryNo ratings yet
- IgneousDocument43 pagesIgneousAlaNo ratings yet
- Stone U1Document45 pagesStone U1mgsvettyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesEarth Science ReviewerJhon mark QuietaNo ratings yet
- 8G Rocks and WeatheringDocument12 pages8G Rocks and WeatheringRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- E & LS Chapter 3Document130 pagesE & LS Chapter 3jerelyn ermeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Rocks and MineralsDocument58 pagesModule 2 Rocks and MineralsRhianne Ahmithy Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Rocks 1Document29 pagesLesson 6 Rocks 1Akita BanateNo ratings yet
- Rocks: Earth and Life ScienceDocument29 pagesRocks: Earth and Life ScienceRyu HajimeNo ratings yet
- Inbound 5678261831670753443Document85 pagesInbound 5678261831670753443soapyNo ratings yet
- C3l3-C3l4-C3l5-By FN Maravilla MR Mendoza RH Mendoza LP Montecer La Montemayor Da MoralesDocument49 pagesC3l3-C3l4-C3l5-By FN Maravilla MR Mendoza RH Mendoza LP Montecer La Montemayor Da MoralesKarl MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Hwno.3 Bsa1c Saylon Efraine AndreaDocument42 pagesHwno.3 Bsa1c Saylon Efraine Andreaefraineandrea.saylonNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary RocksDocument29 pagesSedimentary Rocksrobjmnz717No ratings yet
- Arevalo Activity 3 Summary Task For Minerals and RocksDocument2 pagesArevalo Activity 3 Summary Task For Minerals and RocksJay-r PosadaNo ratings yet
- Earths Materials and ProcessesDocument32 pagesEarths Materials and ProcessesFrancis PopoyNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Rocks Lenisa P. PerezDocument25 pagesEarth Science Rocks Lenisa P. PerezMichael ScottNo ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument33 pagesClassification of RocksJomelyn W. DawiNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials and ProcessesDocument43 pagesEarth Materials and Processesshyraclarence.doteNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Rocks2Document254 pagesSedimentary Rocks2yovieNo ratings yet
- EC571 Geotechs Lecture 8 - 2018 - 19 - Geoll EnviroDocument9 pagesEC571 Geotechs Lecture 8 - 2018 - 19 - Geoll EnviroPimpa MwiingaNo ratings yet
- Minerals and RocksDocument6 pagesMinerals and RocksVenice MedranoNo ratings yet
- 2-Module Ii-Rocks and Types of MineralDocument12 pages2-Module Ii-Rocks and Types of MineralTrazon Triestian Pedrera CardeñoNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument46 pagesRocks and MineralsMark Angelo Beltran NadayaoNo ratings yet
- Minerals CompressedDocument61 pagesMinerals CompressedHannah Joy Arrianne PascualNo ratings yet
- What Is GeologyDocument26 pagesWhat Is GeologyVicente Antonio Rojas SolísNo ratings yet
- 3 Categories of RocksDocument4 pages3 Categories of RocksSeph LiwanagNo ratings yet
- Activities of Earth SciDocument3 pagesActivities of Earth SciCatalina PerryNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Rocks and MineralsDocument48 pages1.3 Rocks and MineralsrieNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Modules 2 and 3Document25 pagesEarth Science Modules 2 and 3April TapayanNo ratings yet
- Minerals: Rock-Forming Minerals Ore-Forming MineralsDocument3 pagesMinerals: Rock-Forming Minerals Ore-Forming MineralsDarcy EvansNo ratings yet
- MINERALS and ROCKSDocument44 pagesMINERALS and ROCKSKian CalzadoraNo ratings yet
- 2.1 - Minerals and RocksDocument58 pages2.1 - Minerals and RocksTerrence NeptunoNo ratings yet
- Neb 5 V9 FMHDocument11 pagesNeb 5 V9 FMHLudovic Bres EscobarNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Technologies: "Read Only Web"Document5 pagesEmpowerment Technologies: "Read Only Web"mcdaNo ratings yet
- I Nformati Onandcommuni Cati On Technology (I CT) : Web2. 0dynami C PagesDocument15 pagesI Nformati Onandcommuni Cati On Technology (I CT) : Web2. 0dynami C PagesmcdaNo ratings yet
- Gen Math - Functions: Domain 5 0 3 11Document8 pagesGen Math - Functions: Domain 5 0 3 11mcdaNo ratings yet
- 7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E NDocument10 pages7 Characteristics of Living Things: M R S G R E Nmcda100% (1)
- Geology of Middle EarthDocument10 pagesGeology of Middle Earthshawn_gaffneyNo ratings yet
- GDG 7 Batuan MatamorfDocument53 pagesGDG 7 Batuan MatamorfFandy MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Migmatites and Their OriginDocument3 pagesMigmatites and Their OriginDanis Khan100% (1)
- Paschendale The BattlefieldDocument16 pagesPaschendale The BattlefieldbillGREGNo ratings yet
- Lecture Volcanic EruptionDocument2 pagesLecture Volcanic EruptionMarlon EllamilNo ratings yet
- Gardner Et Al 2004Document32 pagesGardner Et Al 2004SedPaleoNo ratings yet
- Antamina SEG PDFDocument30 pagesAntamina SEG PDFEdgar Alexander Yataco Zamudio100% (2)
- Moore 2001 Density of Basalt Core From Hilo Drill Hole, HawaiiDocument10 pagesMoore 2001 Density of Basalt Core From Hilo Drill Hole, HawaiiAbdelmounji AmineNo ratings yet
- 3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYDocument40 pages3-4. SST3005. Rocks and Minerals. KHMYFARAH HIDAYAHNo ratings yet
- Geology of PalawanDocument6 pagesGeology of PalawanDaniel Morabe100% (1)
- Terjemahan Buku StratigrafiDocument6 pagesTerjemahan Buku StratigrafiEmiria SrikandiNo ratings yet
- MudLog NEB-85 Scale 200 (130-5325 FT) - April 25th 2018Document30 pagesMudLog NEB-85 Scale 200 (130-5325 FT) - April 25th 2018parama drillingNo ratings yet
- Volcano Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesVolcano Worksheet PDFJonalvin KE100% (3)
- GG 2008Document20 pagesGG 2008Ratan DasNo ratings yet
- Earth Materials Processes NewDocument47 pagesEarth Materials Processes NewGrace MendozaNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes Quiz g9Document1 pageVolcanoes Quiz g9John Kevin NocheNo ratings yet
- Magnesite DissertationDocument47 pagesMagnesite DissertationMultiTuberNo ratings yet
- Layers of The EarthDocument1 pageLayers of The Eartharigato beybeNo ratings yet
- Facies ConceptsDocument33 pagesFacies Conceptsintan putri100% (1)
- Geology, Porphyry Cu-Au, and Epithermal Cu-Au-Ag Mineralization of The Tombulilato District, North Sulawesi, IndonesiaDocument36 pagesGeology, Porphyry Cu-Au, and Epithermal Cu-Au-Ag Mineralization of The Tombulilato District, North Sulawesi, Indonesiarafles ardianNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Document4 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Framework Upper Kutei Basin - 1989Document24 pagesTectonic Framework Upper Kutei Basin - 1989risalNo ratings yet
- Compositional Groups of Metamorphic Rocks-1Document18 pagesCompositional Groups of Metamorphic Rocks-1Adnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Tanpa Pembahasan PDFDocument79 pagesSkripsi Tanpa Pembahasan PDFAngelina Novretrylove SiallaganNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet Ut 1 Grade 7 - SSTDocument4 pagesRevision Sheet Ut 1 Grade 7 - SSTTamim Rehan. H.No ratings yet
- I 2431 PamphletDocument53 pagesI 2431 PamphletpowerslairNo ratings yet
- Gem Bearing Pegmatites A Review PDFDocument14 pagesGem Bearing Pegmatites A Review PDFJotagrcNo ratings yet
- Petrology Part 1Document26 pagesPetrology Part 1IvoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science11 - Q1 - MOD4 - Classification of Rocks 08082020 PDFDocument18 pagesEarth Science11 - Q1 - MOD4 - Classification of Rocks 08082020 PDFAniahsNelet100% (2)
- Sedimentary Rock IdentificationDocument4 pagesSedimentary Rock IdentificationGilang Putra BahanaNo ratings yet