Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exam 2 Study Guide: Key Terms
Exam 2 Study Guide: Key Terms
Uploaded by
Maciel ZunigaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- American Cinematographer Manual PDFDocument300 pagesAmerican Cinematographer Manual PDFAndrea100% (2)
- Geoengineered Transhumanism: How the Environment Has Been Weaponized by Chemicals, Electromagnetics, & Nanotechnology for Synthetic BiologyFrom EverandGeoengineered Transhumanism: How the Environment Has Been Weaponized by Chemicals, Electromagnetics, & Nanotechnology for Synthetic BiologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Cause Stalking and Terrorist Stalking in America - A Summary of David Lawson S Books by Eleanor WhiteDocument12 pagesCause Stalking and Terrorist Stalking in America - A Summary of David Lawson S Books by Eleanor WhiteBrian Bivins100% (2)
- Eric Coomer: Pawn, Plant or Perp?Document118 pagesEric Coomer: Pawn, Plant or Perp?Chris BentelNo ratings yet
- Reptile The 2009 Manual of The Plaintiffs Revolution Paperback 0977442551 9780977442553 2009923614 - CompressDocument331 pagesReptile The 2009 Manual of The Plaintiffs Revolution Paperback 0977442551 9780977442553 2009923614 - CompressAnil Bhatti88% (8)
- Arthur Bloch - Murphy's Law and Other Reasons Why Things Go Wrong-Price - Stern - Sloan Publishers (1978)Document100 pagesArthur Bloch - Murphy's Law and Other Reasons Why Things Go Wrong-Price - Stern - Sloan Publishers (1978)Kannankn CSPuramNo ratings yet
- Found Footage Horror Films - Fear and The Appearance of Reality by Alexandra Heller-NicholasDocument245 pagesFound Footage Horror Films - Fear and The Appearance of Reality by Alexandra Heller-Nicholaschristiangiambelluca100% (1)
- AAU5614 Technical Specifications (V100R016C10 - 02) (PDF) - ENDocument18 pagesAAU5614 Technical Specifications (V100R016C10 - 02) (PDF) - ENOndra Cizek100% (4)
- Under an Ionized Sky: From Chemtrails to Space Fence LockdownFrom EverandUnder an Ionized Sky: From Chemtrails to Space Fence LockdownRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- ADU4518R1v01: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesADU4518R1v01: Antenna SpecificationsЕгор ПоляковNo ratings yet
- Generations Who Are They Webinar HANDOUT 103117Document1 pageGenerations Who Are They Webinar HANDOUT 103117Von Jezzrel Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- 4th TurningDocument4 pages4th Turninggregzillinger100% (7)
- ConformityDocument27 pagesConformityYogi KatsNo ratings yet
- 2011 - The Master SwitchDocument14 pages2011 - The Master SwitchKarthik RamachandranNo ratings yet
- The Challenges "Facing" Copyright Protection For TattoosDocument34 pagesThe Challenges "Facing" Copyright Protection For TattoosAstrid Sheevette OngNo ratings yet
- Enron AisDocument16 pagesEnron AisJsn Pl Cabg-s0% (1)
- Questions Pour L'examenDocument11 pagesQuestions Pour L'examenPaula Sánchez SuárezNo ratings yet
- The Deep State Shadow Government: The American Republic Must Drain This SwampDocument22 pagesThe Deep State Shadow Government: The American Republic Must Drain This SwampAlice 127.0.0.1No ratings yet
- Important Inventions & DiscoveriesDocument4 pagesImportant Inventions & DiscoveriesRohan SoyNo ratings yet
- Strahlenfolter - International Center Against Abuse of Covert Technologies - Jesse Beltran & Lars Drudgaard Interview On Covert Technologies Affecting Us All - ThetruthdeniedDocument8 pagesStrahlenfolter - International Center Against Abuse of Covert Technologies - Jesse Beltran & Lars Drudgaard Interview On Covert Technologies Affecting Us All - ThetruthdeniedTimo_KaehlkeNo ratings yet
- Evolution (2001 Film) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument11 pagesEvolution (2001 Film) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchadsfsafNo ratings yet
- SSRN-id3213954 Deepfakes, Challenge For Privacy and DemocracyDocument59 pagesSSRN-id3213954 Deepfakes, Challenge For Privacy and DemocracyCamilo Gandolfo EguíaNo ratings yet
- Strahlenfolter - International Center Against Abuse of Covert Technologies - Jesse Beltran & Lars Drudgaard Interview On Covert Technologies Affecting Us All - ThetruthdeniedDocument14 pagesStrahlenfolter - International Center Against Abuse of Covert Technologies - Jesse Beltran & Lars Drudgaard Interview On Covert Technologies Affecting Us All - ThetruthdeniedTimo_KaehlkeNo ratings yet
- Famous Inventions and Their InventorsDocument3 pagesFamous Inventions and Their Inventorsops gahaNo ratings yet
- Project Camelot Interviews - Vol. 1Document438 pagesProject Camelot Interviews - Vol. 1FW040100% (23)
- Eco Defense - Dave Foreman and Bill HaywoodDocument367 pagesEco Defense - Dave Foreman and Bill HaywoodbryansawyerNo ratings yet
- Project Camelot Interviews - Vol. 2Document517 pagesProject Camelot Interviews - Vol. 2FW040100% (17)
- Thomas H. White: Nikola Tesla - The Guy Who DIDN'T "Invent Radio"Document33 pagesThomas H. White: Nikola Tesla - The Guy Who DIDN'T "Invent Radio"viktor369No ratings yet
- Law & Order (Franchise) Law and OrderDocument5 pagesLaw & Order (Franchise) Law and OrderAndreea IacobNo ratings yet
- Quiz ReadTheoryDocument1 pageQuiz ReadTheoryJoel SiñaniNo ratings yet
- 10 11 2010 Taking A Big Bite of Apple Connecticut Law TribuneDocument2 pages10 11 2010 Taking A Big Bite of Apple Connecticut Law TribuneDrewFTBLNo ratings yet
- 00520-20041109 Grokster-ArtistAmicusBrfDocument9 pages00520-20041109 Grokster-ArtistAmicusBrflegalmattersNo ratings yet
- Gazecki Press KitDocument19 pagesGazecki Press KitWilliam GazeckiNo ratings yet
- 4-Memorandum of Law in Response To Motion For Summary JudgementDocument11 pages4-Memorandum of Law in Response To Motion For Summary JudgementBill HustonNo ratings yet
- Eric Coomer vs. Patrick Byrne, Steven Lucescu and The America ProjectDocument68 pagesEric Coomer vs. Patrick Byrne, Steven Lucescu and The America Projectgaryrweiss100% (1)
- Creative Expression and The Human Canvas: An Form D M. C : Avid UmmingsDocument40 pagesCreative Expression and The Human Canvas: An Form D M. C : Avid UmmingsBeata SkowrońskaNo ratings yet
- Final Deliberation Cdi9 Goodluck To AllDocument10 pagesFinal Deliberation Cdi9 Goodluck To AllMa. Belinda NavarraNo ratings yet
- Disclosure - Demi Moore and Michael DouglasDocument10 pagesDisclosure - Demi Moore and Michael DouglasJennybabe PetaNo ratings yet
- "Personality Rights" and Why Mars Argo Has A CaseDocument5 pages"Personality Rights" and Why Mars Argo Has A CaseDangeresque MustachioNo ratings yet
- Whistle BlowingDocument23 pagesWhistle BlowingsonusumankrNo ratings yet
- LESSON NINE Part IIDocument3 pagesLESSON NINE Part IIAndrei BulgaruNo ratings yet
- Voices in The HeadDocument30 pagesVoices in The HeadShamil DinmukhametovNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document7 pagesLecture 1api-282082651No ratings yet
- ViewcontentDocument36 pagesViewcontentPranav BhansaliNo ratings yet
- Alter Ego #5Document30 pagesAlter Ego #5Eduardo PereiraNo ratings yet
- E07 Market Revolution Shark TankDocument12 pagesE07 Market Revolution Shark TankShoushi ShadouyanNo ratings yet
- Clue Sheet 1 (Answers)Document3 pagesClue Sheet 1 (Answers)Mauricio QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Senate Hearing, 106TH Congress - The Third Anniversary of The Telecom Act: A Competition and Antitrust ReviewDocument59 pagesSenate Hearing, 106TH Congress - The Third Anniversary of The Telecom Act: A Competition and Antitrust ReviewScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Breach of ConfidenceDocument1 pageBreach of ConfidenceNahmyNo ratings yet
- Wiseman Direct Cinema 60sDocument22 pagesWiseman Direct Cinema 60sAna LuNo ratings yet
- Technology in Education Technology Presentation in Blue Peach Illustrative Style 2Document25 pagesTechnology in Education Technology Presentation in Blue Peach Illustrative Style 24pvxsnr8vsNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 3rd ConditionalDocument3 pagesUNIT - 3rd ConditionalDafne SackNo ratings yet
- Boomer InventionsDocument21 pagesBoomer InventionsMicah Elyza FuerzasNo ratings yet
- Course3 TelecommunicationDocument8 pagesCourse3 TelecommunicationbelgacemmohamedlyesNo ratings yet
- Winter RC PassageDocument29 pagesWinter RC Passage김동철No ratings yet
- Generations Defined SociologicallyDocument2 pagesGenerations Defined SociologicallyAimen ParachaNo ratings yet
- Milestones in The History of Electronic CommunicationDocument2 pagesMilestones in The History of Electronic CommunicationChillie Bronzal Ullamot100% (2)
- AT&TDocument67 pagesAT&TMelissa FabillarNo ratings yet
- F.O.I.A Proves This Crime Is Real !Document1 pageF.O.I.A Proves This Crime Is Real !Generation GenerationNo ratings yet
- David vs. Goliath: Class Action LawsuitsDocument31 pagesDavid vs. Goliath: Class Action LawsuitsAnish DalmiaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Film and Video: An AnthologyFrom EverandExperimental Film and Video: An AnthologyJackie HatfieldNo ratings yet
- Inmarsat Fleet F77 MesDocument30 pagesInmarsat Fleet F77 MesANDREYNo ratings yet
- User Manual 2570817 RRU ZTEDocument24 pagesUser Manual 2570817 RRU ZTEGun TaNo ratings yet
- KSFO Jeppesen 2018Document6 pagesKSFO Jeppesen 2018corina vargas cocaNo ratings yet
- Radar Technology: ISBN 978-953-307-029-2Document434 pagesRadar Technology: ISBN 978-953-307-029-2RAUL EDUARDO GUTIERREZ COITIÑONo ratings yet
- Sony WH1000XM3 PDFDocument1 pageSony WH1000XM3 PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- Zero.7: Owner'S ManualDocument10 pagesZero.7: Owner'S Manualchristopher ng'ang'a kamauNo ratings yet
- nb868 User Guide v2.2.3Document25 pagesnb868 User Guide v2.2.3BENTABET AKILANo ratings yet
- Black Sea MoU Deficiency Codes (4 February 2021)Document17 pagesBlack Sea MoU Deficiency Codes (4 February 2021)Charalampos ChatzivasileiouNo ratings yet
- Silent Sound Spread SpectrumDocument2 pagesSilent Sound Spread Spectrumjack007xrayNo ratings yet
- Quirk - A University Grammar of EnglishDocument249 pagesQuirk - A University Grammar of EnglishRocio100% (1)
- Drop Call 2g GSM SystemDocument19 pagesDrop Call 2g GSM SystemAhmadArwani88No ratings yet
- ECG Operation Manual V1.1Document41 pagesECG Operation Manual V1.1Abdullah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Channel Simulator DT4630 EnglischDocument4 pagesReal-Time Channel Simulator DT4630 EnglischMICHAEL JOHN TolonghariNo ratings yet
- WIT Notes FadingDocument10 pagesWIT Notes FadingKabo MphanyaneNo ratings yet
- Diag Master 701468 2021-02-20 10-37-50Document197 pagesDiag Master 701468 2021-02-20 10-37-50Andrie IstiyaNo ratings yet
- Olt Nokia MedicionesDocument9 pagesOlt Nokia Medicionesjonathan coria arevaloNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Ons MCQDocument15 pagesChap 5 Ons MCQKHEDEKAR HRUTUJANo ratings yet
- HAARP, The Most Powerful Ionosphere Heater On Earth - Physics TodDocument11 pagesHAARP, The Most Powerful Ionosphere Heater On Earth - Physics TodGlenn KalaverasNo ratings yet
- NR SCG Failure Information.Document3 pagesNR SCG Failure Information.Ali SerunjogiNo ratings yet
- AFT05MP075NDocument21 pagesAFT05MP075NTeyfik koyuncuNo ratings yet
- Seqmsegu PDF 1662235957Document19 pagesSeqmsegu PDF 1662235957Maurits VeenNo ratings yet
- Airplane Flight Manual Supplement, G1000 NXi Textron Aviation G58 Baron Aircraft190-02765-03 - 03Document29 pagesAirplane Flight Manual Supplement, G1000 NXi Textron Aviation G58 Baron Aircraft190-02765-03 - 03Vitor PerrudNo ratings yet
- SGP Notes Part 2Document39 pagesSGP Notes Part 2Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- AV Control Receiver SA-XR57: Operating InstructionsDocument40 pagesAV Control Receiver SA-XR57: Operating InstructionsLuka TrengovskiNo ratings yet
- Analog Power-Line Carrier System Type Opc-2: Communication Solutions For Power UtilitiesDocument35 pagesAnalog Power-Line Carrier System Type Opc-2: Communication Solutions For Power UtilitiesАндрюха ЛуценкоNo ratings yet
- EBCI (Charleroi Airport)Document6 pagesEBCI (Charleroi Airport)Roshan UppalNo ratings yet
- Ericsson 2G OSS CommandDocument2 pagesEricsson 2G OSS CommandSamehTareshNo ratings yet
Exam 2 Study Guide: Key Terms
Exam 2 Study Guide: Key Terms
Uploaded by
Maciel ZunigaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exam 2 Study Guide: Key Terms
Exam 2 Study Guide: Key Terms
Uploaded by
Maciel ZunigaCopyright:
Available Formats
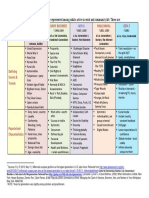
SCOM 2050 • Media, Culture & Society
Exam 2 Study Guide
Description: The second exam will be worth 250 points. Bring Scantron Form 4521 and a pencil.
Key Terms (definitions, significance, and context/dates)
Broadcast Networks
Trustee Principle Prior restraint
Spectrum Scarcity Near v. Minnesota
Telecommunications Act of 1996 The Pentagon Papers
1910 Wireless Ship Act US v. Progressive Magazine
Radio Act of 1927 Obscenity & Prurient
Miller v. California (&3-part Miller Test)
Clutter (aka: hyper-commercialization) The Fairness Doctrine
Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Intellectual property rights
Federal Communication Commission (FCC) Copyright
Permission Marketing Absolute privilege
Public Relations Qualified privilege
Wheeler-Lea Act Gag orders
Parity products Shield laws
Pseudo-event 4th-Estate
Daguerreotype
Persistence of vision Sherman Antitrust Act
Cinematographe Clayton Antitrust Act
The Trust (Edison) International Synergy
Nickelodeons Wage Gap
Movie palaces
Important People (& what they did)
Thomas Edison Joseph Niepce
Emile Berliner William Talbot
Nikola Tesla Eadweard Muybridge
Guglielmo Marconi The Lumiere Brothers
Reginald Fessenden Georges Mieles
Lee DeForest George Eastman
F. Wayland Ayer Vladimir Zworykin
Ivy Lee Philo Farnsworth
Edward Bernays Ted Turner
Amos Kendall Lucille Ball
John Walson
Topics/Questions (pg 1 info rephrased)
Edison’s talking machine
Who patented radio in the US
Who 1st transmitted voice over radio
Year of 1st commercial radio broadcast
All the ways radio was a media innovator
The popularity of radio today
The impact of radio deregulation
What was the Radio Corporation of America (RCA), who created it, and why
The prevalence of commercials/ads
The ancient history of advertising
Advertising in the US before the Civil War
First full service ad agency in the US
The impact of radio on the ad industry
Advertising after WWII
Who regulates advertising?
PR’s PR problem
Definition of PR
How PR differs from advertising
PR before the Civil War
3 historical stages of PR in the US
How PR is flourishing today
The weakness of early still photography technology
How the first picture of motion was captured, who did it, and why that mattered
Early American film industry & The Trust
The movie peak and why attendance declined afterward
How the movie industry works economically
Prior restraint and why it’s bad
The definition of “obscenity”
The fairness doctrine
Who the “Constitution” protects you from
Intellectual property vs. freedom of expression
Slander, libel, and the defenses against them
1st Amendment vs. 6th Amendment
The people who contributed to the invention of television
The first public demonstration of TV and what happened after
Why TV grew so much after WWII
The influence of “I Love Lucy”
The origins of cable
The VCR and its impacts
The economics TV
What has the trend been in terms of regulation of industry in the 20 th and 21st centuries?
What did the Telecommunications Act of 1996 do, and what were its impacts?
The wage gap, its history since 1965, and its modern context
You might also like
- American Cinematographer Manual PDFDocument300 pagesAmerican Cinematographer Manual PDFAndrea100% (2)
- Geoengineered Transhumanism: How the Environment Has Been Weaponized by Chemicals, Electromagnetics, & Nanotechnology for Synthetic BiologyFrom EverandGeoengineered Transhumanism: How the Environment Has Been Weaponized by Chemicals, Electromagnetics, & Nanotechnology for Synthetic BiologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Cause Stalking and Terrorist Stalking in America - A Summary of David Lawson S Books by Eleanor WhiteDocument12 pagesCause Stalking and Terrorist Stalking in America - A Summary of David Lawson S Books by Eleanor WhiteBrian Bivins100% (2)
- Eric Coomer: Pawn, Plant or Perp?Document118 pagesEric Coomer: Pawn, Plant or Perp?Chris BentelNo ratings yet
- Reptile The 2009 Manual of The Plaintiffs Revolution Paperback 0977442551 9780977442553 2009923614 - CompressDocument331 pagesReptile The 2009 Manual of The Plaintiffs Revolution Paperback 0977442551 9780977442553 2009923614 - CompressAnil Bhatti88% (8)
- Arthur Bloch - Murphy's Law and Other Reasons Why Things Go Wrong-Price - Stern - Sloan Publishers (1978)Document100 pagesArthur Bloch - Murphy's Law and Other Reasons Why Things Go Wrong-Price - Stern - Sloan Publishers (1978)Kannankn CSPuramNo ratings yet
- Found Footage Horror Films - Fear and The Appearance of Reality by Alexandra Heller-NicholasDocument245 pagesFound Footage Horror Films - Fear and The Appearance of Reality by Alexandra Heller-Nicholaschristiangiambelluca100% (1)
- AAU5614 Technical Specifications (V100R016C10 - 02) (PDF) - ENDocument18 pagesAAU5614 Technical Specifications (V100R016C10 - 02) (PDF) - ENOndra Cizek100% (4)
- Under an Ionized Sky: From Chemtrails to Space Fence LockdownFrom EverandUnder an Ionized Sky: From Chemtrails to Space Fence LockdownRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (6)
- ADU4518R1v01: Antenna SpecificationsDocument2 pagesADU4518R1v01: Antenna SpecificationsЕгор ПоляковNo ratings yet
- Generations Who Are They Webinar HANDOUT 103117Document1 pageGenerations Who Are They Webinar HANDOUT 103117Von Jezzrel Jumao-asNo ratings yet
- 4th TurningDocument4 pages4th Turninggregzillinger100% (7)
- ConformityDocument27 pagesConformityYogi KatsNo ratings yet
- 2011 - The Master SwitchDocument14 pages2011 - The Master SwitchKarthik RamachandranNo ratings yet
- The Challenges "Facing" Copyright Protection For TattoosDocument34 pagesThe Challenges "Facing" Copyright Protection For TattoosAstrid Sheevette OngNo ratings yet
- Enron AisDocument16 pagesEnron AisJsn Pl Cabg-s0% (1)
- Questions Pour L'examenDocument11 pagesQuestions Pour L'examenPaula Sánchez SuárezNo ratings yet
- The Deep State Shadow Government: The American Republic Must Drain This SwampDocument22 pagesThe Deep State Shadow Government: The American Republic Must Drain This SwampAlice 127.0.0.1No ratings yet
- Important Inventions & DiscoveriesDocument4 pagesImportant Inventions & DiscoveriesRohan SoyNo ratings yet
- Strahlenfolter - International Center Against Abuse of Covert Technologies - Jesse Beltran & Lars Drudgaard Interview On Covert Technologies Affecting Us All - ThetruthdeniedDocument8 pagesStrahlenfolter - International Center Against Abuse of Covert Technologies - Jesse Beltran & Lars Drudgaard Interview On Covert Technologies Affecting Us All - ThetruthdeniedTimo_KaehlkeNo ratings yet
- Evolution (2001 Film) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument11 pagesEvolution (2001 Film) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchadsfsafNo ratings yet
- SSRN-id3213954 Deepfakes, Challenge For Privacy and DemocracyDocument59 pagesSSRN-id3213954 Deepfakes, Challenge For Privacy and DemocracyCamilo Gandolfo EguíaNo ratings yet
- Strahlenfolter - International Center Against Abuse of Covert Technologies - Jesse Beltran & Lars Drudgaard Interview On Covert Technologies Affecting Us All - ThetruthdeniedDocument14 pagesStrahlenfolter - International Center Against Abuse of Covert Technologies - Jesse Beltran & Lars Drudgaard Interview On Covert Technologies Affecting Us All - ThetruthdeniedTimo_KaehlkeNo ratings yet
- Famous Inventions and Their InventorsDocument3 pagesFamous Inventions and Their Inventorsops gahaNo ratings yet
- Project Camelot Interviews - Vol. 1Document438 pagesProject Camelot Interviews - Vol. 1FW040100% (23)
- Eco Defense - Dave Foreman and Bill HaywoodDocument367 pagesEco Defense - Dave Foreman and Bill HaywoodbryansawyerNo ratings yet
- Project Camelot Interviews - Vol. 2Document517 pagesProject Camelot Interviews - Vol. 2FW040100% (17)
- Thomas H. White: Nikola Tesla - The Guy Who DIDN'T "Invent Radio"Document33 pagesThomas H. White: Nikola Tesla - The Guy Who DIDN'T "Invent Radio"viktor369No ratings yet
- Law & Order (Franchise) Law and OrderDocument5 pagesLaw & Order (Franchise) Law and OrderAndreea IacobNo ratings yet
- Quiz ReadTheoryDocument1 pageQuiz ReadTheoryJoel SiñaniNo ratings yet
- 10 11 2010 Taking A Big Bite of Apple Connecticut Law TribuneDocument2 pages10 11 2010 Taking A Big Bite of Apple Connecticut Law TribuneDrewFTBLNo ratings yet
- 00520-20041109 Grokster-ArtistAmicusBrfDocument9 pages00520-20041109 Grokster-ArtistAmicusBrflegalmattersNo ratings yet
- Gazecki Press KitDocument19 pagesGazecki Press KitWilliam GazeckiNo ratings yet
- 4-Memorandum of Law in Response To Motion For Summary JudgementDocument11 pages4-Memorandum of Law in Response To Motion For Summary JudgementBill HustonNo ratings yet
- Eric Coomer vs. Patrick Byrne, Steven Lucescu and The America ProjectDocument68 pagesEric Coomer vs. Patrick Byrne, Steven Lucescu and The America Projectgaryrweiss100% (1)
- Creative Expression and The Human Canvas: An Form D M. C : Avid UmmingsDocument40 pagesCreative Expression and The Human Canvas: An Form D M. C : Avid UmmingsBeata SkowrońskaNo ratings yet
- Final Deliberation Cdi9 Goodluck To AllDocument10 pagesFinal Deliberation Cdi9 Goodluck To AllMa. Belinda NavarraNo ratings yet
- Disclosure - Demi Moore and Michael DouglasDocument10 pagesDisclosure - Demi Moore and Michael DouglasJennybabe PetaNo ratings yet
- "Personality Rights" and Why Mars Argo Has A CaseDocument5 pages"Personality Rights" and Why Mars Argo Has A CaseDangeresque MustachioNo ratings yet
- Whistle BlowingDocument23 pagesWhistle BlowingsonusumankrNo ratings yet
- LESSON NINE Part IIDocument3 pagesLESSON NINE Part IIAndrei BulgaruNo ratings yet
- Voices in The HeadDocument30 pagesVoices in The HeadShamil DinmukhametovNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document7 pagesLecture 1api-282082651No ratings yet
- ViewcontentDocument36 pagesViewcontentPranav BhansaliNo ratings yet
- Alter Ego #5Document30 pagesAlter Ego #5Eduardo PereiraNo ratings yet
- E07 Market Revolution Shark TankDocument12 pagesE07 Market Revolution Shark TankShoushi ShadouyanNo ratings yet
- Clue Sheet 1 (Answers)Document3 pagesClue Sheet 1 (Answers)Mauricio QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Senate Hearing, 106TH Congress - The Third Anniversary of The Telecom Act: A Competition and Antitrust ReviewDocument59 pagesSenate Hearing, 106TH Congress - The Third Anniversary of The Telecom Act: A Competition and Antitrust ReviewScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Breach of ConfidenceDocument1 pageBreach of ConfidenceNahmyNo ratings yet
- Wiseman Direct Cinema 60sDocument22 pagesWiseman Direct Cinema 60sAna LuNo ratings yet
- Technology in Education Technology Presentation in Blue Peach Illustrative Style 2Document25 pagesTechnology in Education Technology Presentation in Blue Peach Illustrative Style 24pvxsnr8vsNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 3rd ConditionalDocument3 pagesUNIT - 3rd ConditionalDafne SackNo ratings yet
- Boomer InventionsDocument21 pagesBoomer InventionsMicah Elyza FuerzasNo ratings yet
- Course3 TelecommunicationDocument8 pagesCourse3 TelecommunicationbelgacemmohamedlyesNo ratings yet
- Winter RC PassageDocument29 pagesWinter RC Passage김동철No ratings yet
- Generations Defined SociologicallyDocument2 pagesGenerations Defined SociologicallyAimen ParachaNo ratings yet
- Milestones in The History of Electronic CommunicationDocument2 pagesMilestones in The History of Electronic CommunicationChillie Bronzal Ullamot100% (2)
- AT&TDocument67 pagesAT&TMelissa FabillarNo ratings yet
- F.O.I.A Proves This Crime Is Real !Document1 pageF.O.I.A Proves This Crime Is Real !Generation GenerationNo ratings yet
- David vs. Goliath: Class Action LawsuitsDocument31 pagesDavid vs. Goliath: Class Action LawsuitsAnish DalmiaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Film and Video: An AnthologyFrom EverandExperimental Film and Video: An AnthologyJackie HatfieldNo ratings yet
- Inmarsat Fleet F77 MesDocument30 pagesInmarsat Fleet F77 MesANDREYNo ratings yet
- User Manual 2570817 RRU ZTEDocument24 pagesUser Manual 2570817 RRU ZTEGun TaNo ratings yet
- KSFO Jeppesen 2018Document6 pagesKSFO Jeppesen 2018corina vargas cocaNo ratings yet
- Radar Technology: ISBN 978-953-307-029-2Document434 pagesRadar Technology: ISBN 978-953-307-029-2RAUL EDUARDO GUTIERREZ COITIÑONo ratings yet
- Sony WH1000XM3 PDFDocument1 pageSony WH1000XM3 PDFjohnNo ratings yet
- Zero.7: Owner'S ManualDocument10 pagesZero.7: Owner'S Manualchristopher ng'ang'a kamauNo ratings yet
- nb868 User Guide v2.2.3Document25 pagesnb868 User Guide v2.2.3BENTABET AKILANo ratings yet
- Black Sea MoU Deficiency Codes (4 February 2021)Document17 pagesBlack Sea MoU Deficiency Codes (4 February 2021)Charalampos ChatzivasileiouNo ratings yet
- Silent Sound Spread SpectrumDocument2 pagesSilent Sound Spread Spectrumjack007xrayNo ratings yet
- Quirk - A University Grammar of EnglishDocument249 pagesQuirk - A University Grammar of EnglishRocio100% (1)
- Drop Call 2g GSM SystemDocument19 pagesDrop Call 2g GSM SystemAhmadArwani88No ratings yet
- ECG Operation Manual V1.1Document41 pagesECG Operation Manual V1.1Abdullah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Channel Simulator DT4630 EnglischDocument4 pagesReal-Time Channel Simulator DT4630 EnglischMICHAEL JOHN TolonghariNo ratings yet
- WIT Notes FadingDocument10 pagesWIT Notes FadingKabo MphanyaneNo ratings yet
- Diag Master 701468 2021-02-20 10-37-50Document197 pagesDiag Master 701468 2021-02-20 10-37-50Andrie IstiyaNo ratings yet
- Olt Nokia MedicionesDocument9 pagesOlt Nokia Medicionesjonathan coria arevaloNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Ons MCQDocument15 pagesChap 5 Ons MCQKHEDEKAR HRUTUJANo ratings yet
- HAARP, The Most Powerful Ionosphere Heater On Earth - Physics TodDocument11 pagesHAARP, The Most Powerful Ionosphere Heater On Earth - Physics TodGlenn KalaverasNo ratings yet
- NR SCG Failure Information.Document3 pagesNR SCG Failure Information.Ali SerunjogiNo ratings yet
- AFT05MP075NDocument21 pagesAFT05MP075NTeyfik koyuncuNo ratings yet
- Seqmsegu PDF 1662235957Document19 pagesSeqmsegu PDF 1662235957Maurits VeenNo ratings yet
- Airplane Flight Manual Supplement, G1000 NXi Textron Aviation G58 Baron Aircraft190-02765-03 - 03Document29 pagesAirplane Flight Manual Supplement, G1000 NXi Textron Aviation G58 Baron Aircraft190-02765-03 - 03Vitor PerrudNo ratings yet
- SGP Notes Part 2Document39 pagesSGP Notes Part 2Krishna SinghNo ratings yet
- AV Control Receiver SA-XR57: Operating InstructionsDocument40 pagesAV Control Receiver SA-XR57: Operating InstructionsLuka TrengovskiNo ratings yet
- Analog Power-Line Carrier System Type Opc-2: Communication Solutions For Power UtilitiesDocument35 pagesAnalog Power-Line Carrier System Type Opc-2: Communication Solutions For Power UtilitiesАндрюха ЛуценкоNo ratings yet
- EBCI (Charleroi Airport)Document6 pagesEBCI (Charleroi Airport)Roshan UppalNo ratings yet
- Ericsson 2G OSS CommandDocument2 pagesEricsson 2G OSS CommandSamehTareshNo ratings yet