Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Notes: Chapter-3 Matrices
Key Notes: Chapter-3 Matrices
Uploaded by
AbraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Key Notes: Chapter-3 MatricesDocument2 pagesKey Notes: Chapter-3 MatricesInvincible FactsNo ratings yet
- Matrices: - An M X N Matrix Is Written AsDocument7 pagesMatrices: - An M X N Matrix Is Written AsnitinNo ratings yet
- Matrices & Determinants PDFDocument60 pagesMatrices & Determinants PDFvenu duggineniNo ratings yet
- Matrices Determinants MathongoDocument12 pagesMatrices Determinants MathongoArya NairNo ratings yet
- 20 FRDocument7 pages20 FRyellaiahNo ratings yet
- 20 Matrices Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages20 Matrices Formula Sheets Quizrrbharasha mahantaNo ratings yet
- 20 Matrices Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument9 pages20 Matrices Formula Sheets Getmarks AppAashrith PemmarajuNo ratings yet
- Matrices WatermarkDocument33 pagesMatrices Watermarksherin joysonNo ratings yet
- Matrices & Determinant: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF FormatDocument7 pagesMatrices & Determinant: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF Formatsiddharthjii22222No ratings yet
- Matrices & Determinant: Most Important Questions & MindmapDocument315 pagesMatrices & Determinant: Most Important Questions & Mindmapsiddharthjii22222No ratings yet
- Bab V Efek PanasDocument40 pagesBab V Efek PanascantikNo ratings yet
- Matrices PYQ 2016 11 YearDocument17 pagesMatrices PYQ 2016 11 Yeararyanraj61090No ratings yet
- Pure Math - Matrix: DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPure Math - Matrix: Definitionsjared liNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MatricesDocument12 pagesChapter 3 MatricesXinhui PongNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of MatricesDocument19 pagesBasic Concept of MatricesSiddharth palNo ratings yet
- 08 MatricesDocument26 pages08 MatricesGeeta MNo ratings yet
- MATRIXCDocument15 pagesMATRIXClatestdaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Matrices)Document23 pagesUnit 3 (Matrices)mukteshwarj4No ratings yet
- Thumbnail SlideDocument188 pagesThumbnail Slidesiddharthjii22222No ratings yet
- Exempler Chapter 3Document23 pagesExempler Chapter 3King of DonsNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgATi AZ84elTr9QFHjj5GeniP9wnXnwroO5 4lp4sULSAabTx1SHLz9u21jnSzuqLqEvHEil PLsaXcqG6FfPuXrQS6SZJ9pkhU81 40PA9Ie I9i5dci4 DbYikCZIyUXnk0yinAF I28DDocument46 pagesACFrOgATi AZ84elTr9QFHjj5GeniP9wnXnwroO5 4lp4sULSAabTx1SHLz9u21jnSzuqLqEvHEil PLsaXcqG6FfPuXrQS6SZJ9pkhU81 40PA9Ie I9i5dci4 DbYikCZIyUXnk0yinAF I28DVoot Kids75No ratings yet
- MatricesDocument6 pagesMatricesPranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 MathematicsDocument8 pagesGrade 12 MathematicsMPS QUESTION PAPER SUBMISSIONNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PT 4 Matrix AlgebraDocument19 pagesUnit 1 PT 4 Matrix Algebrasprinklesdb16No ratings yet
- Matrices: Matrix and Operations On MatricesDocument6 pagesMatrices: Matrix and Operations On Matrices12-A-9- vishalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Maths Formula Notes 1 50Document104 pagesEngineering Maths Formula Notes 1 50PriyaNo ratings yet
- Studyguide360: CHAPTER: 3 and 4 Matrices and Determinants Important Points To RememberDocument20 pagesStudyguide360: CHAPTER: 3 and 4 Matrices and Determinants Important Points To RememberajayNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 3. MatricesDocument17 pagesClass 12 Chapter 3. MatricesShreya SinghNo ratings yet
- MatrixDocument9 pagesMatrixkritikaNo ratings yet
- Day5.Matrices NotesDocument3 pagesDay5.Matrices NoteshaveNo ratings yet
- 19matrices DeterminantsDocument5 pages19matrices DeterminantssatyahbhatNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument12 pagesMatricesPranivoid100% (1)
- Matrices and DeterminantDocument13 pagesMatrices and DeterminantAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- Matrix DetwrminantsDocument9 pagesMatrix DetwrminantsJared GualonNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants: Astrid Xiomara Rodríguez CastelblancoDocument21 pagesMatrices and Determinants: Astrid Xiomara Rodríguez Castelblancoxiomyrodriguez10No ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants: Astrid Xiomara Rodríguez CastelblancoDocument21 pagesMatrices and Determinants: Astrid Xiomara Rodríguez Castelblancoxiomararodriguez10No ratings yet
- 2 (I) MatricesDocument11 pages2 (I) Matriceskps evilNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument7 pagesMatricesPriti DixitNo ratings yet
- Matrices & DeterminantsDocument60 pagesMatrices & DeterminantsPradeep SinglaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Determinants - CETDocument22 pagesModule 7 - Determinants - CETGokul yadavNo ratings yet
- c1 Linear AlgebraDocument33 pagesc1 Linear AlgebraChua ZhenyuNo ratings yet
- matrixAlgebraReview PDFDocument16 pagesmatrixAlgebraReview PDFRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Matrices and DeterminantsDocument15 pagesMatrices and DeterminantsvighneshmanojNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Assignment 1Document8 pagesMatrices - Assignment 1Samarth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Matrices One Shot #BBDocument158 pagesMatrices One Shot #BBPoonam JainNo ratings yet
- 12 Cbse Maths-Matrices02Document40 pages12 Cbse Maths-Matrices02tranquil_452889939No ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Matrices: Properties of Various Types of MatricesDocument7 pagesRevision Notes On Matrices: Properties of Various Types of MatricesVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Elements: Order: No. of ElementsDocument5 pagesElements: Order: No. of Elementsaniketsingh86306No ratings yet
- Mind Map - Matrices - Class 12Document5 pagesMind Map - Matrices - Class 12studyonlyrithuNo ratings yet
- Maths Amrendrasir: Subject Assignment DateDocument7 pagesMaths Amrendrasir: Subject Assignment DateNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Matrices & DeterminantsDocument2 pagesMatrices & DeterminantssayondeepNo ratings yet
- EM Short FormulasDocument24 pagesEM Short FormulasAlia SharmaNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra I-1Document26 pagesLinear Algebra I-1AlessioNo ratings yet
- Algebra of Matrices Level-1Document15 pagesAlgebra of Matrices Level-1BulusuMurtyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics W2: Matrix Algebra BasicsDocument8 pagesAdvanced Statistics W2: Matrix Algebra BasicskinaNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Short NotesDocument3 pagesMatrices - Short NotesAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Matrices1 PDFDocument8 pagesMatrices1 PDFMansoor KhanNo ratings yet
- 3 MATRICES CH 3Document18 pages3 MATRICES CH 3Abhinav Gaming ytNo ratings yet
- Matrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersFrom EverandMatrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument39 pagesClass NotessanthoshNo ratings yet
- National Income Class 12 WsDocument19 pagesNational Income Class 12 WsIsha BhattNo ratings yet
- Matrices Unit IDocument13 pagesMatrices Unit IMadhu spoorthiNo ratings yet
- Sample Mathematicia XIIDocument49 pagesSample Mathematicia XIIMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Usme, Dtu Project On Matrices and Determinants Analysis BY Bharat Saini Tanmay ChhikaraDocument17 pagesUsme, Dtu Project On Matrices and Determinants Analysis BY Bharat Saini Tanmay ChhikaraTanmay ChhikaraNo ratings yet
- Johan G. F. Belinfante, Bernard KolmanDocument175 pagesJohan G. F. Belinfante, Bernard KolmanDany HdzNo ratings yet
- Matrix Methods, Applied Linear Algebra, Third EditionDocument433 pagesMatrix Methods, Applied Linear Algebra, Third Editionk_ij9658100% (3)
- Maths Formula Revision SheetDocument51 pagesMaths Formula Revision SheetShivu GamerNo ratings yet
- Matrix Algebra 1.Document4 pagesMatrix Algebra 1.Snaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument3 pagesMatricesMaths Home Work 123No ratings yet
- Class-Xii Maths - Term-1 - Support Materials & MCQ Questions-FinalDocument75 pagesClass-Xii Maths - Term-1 - Support Materials & MCQ Questions-FinalDevvrat SolankiNo ratings yet
- Edupedia 9th Class Math PaperDocument4 pagesEdupedia 9th Class Math PaperareebaNo ratings yet
- Bihar Board Solutions: Bihar Board 12th Maths Objective Answers Chapter 3 MatricesDocument9 pagesBihar Board Solutions: Bihar Board 12th Maths Objective Answers Chapter 3 MatricesSanjayNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument12 pagesMatricesVenkat GowdaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 3 Matrices Exercise 3.3Document13 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 3 Matrices Exercise 3.3Saksham DixitNo ratings yet
- Georgi Lecture Notes On Weak Interactions Physics Harvard Web Draft 1998Document167 pagesGeorgi Lecture Notes On Weak Interactions Physics Harvard Web Draft 1998manosmagicas7340No ratings yet
- (Darryl D. Hol,) Geometric Mechanics Rotating, TR (B-Ok - CC) PDFDocument304 pages(Darryl D. Hol,) Geometric Mechanics Rotating, TR (B-Ok - CC) PDFOceanNo ratings yet
- BSC Computer Science PDFDocument56 pagesBSC Computer Science PDFB.ArulNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Determinant and MatriXDocument17 pagesChapter - Determinant and MatriXKhushbu KumariNo ratings yet
- Wa0035Document25 pagesWa0035GrishmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics I PDFDocument247 pagesMathematics I PDFCHAMANCHULA ANITHANo ratings yet
- M-1 Question Bank (Imp) : Unit-I MatricesDocument8 pagesM-1 Question Bank (Imp) : Unit-I MatricesSunny VardhanNo ratings yet
- Maths PQ2Document6 pagesMaths PQ2utharun3No ratings yet
- Real Ana SolvedDocument92 pagesReal Ana SolvedRajdip sarkarNo ratings yet
- 2018Document8 pages2018Paras SirasyaNo ratings yet
- Maths QBDocument179 pagesMaths QB8dhruvjainNo ratings yet
- Maths MCQ Collection 2023Document26 pagesMaths MCQ Collection 2023Dk249No ratings yet
- Introduction To EntanglementDocument10 pagesIntroduction To EntanglementmaareaNo ratings yet
- SM 12 Math Eng 201617Document192 pagesSM 12 Math Eng 201617Bhavesh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Maths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-3) - PaperDocument10 pagesMaths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-3) - PaperYash DhokeNo ratings yet
Key Notes: Chapter-3 Matrices
Key Notes: Chapter-3 Matrices
Uploaded by
AbraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Notes: Chapter-3 Matrices
Key Notes: Chapter-3 Matrices
Uploaded by
AbraCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Notes
Chapter-3
Matrices
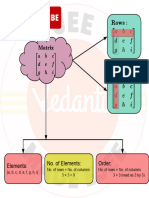
• A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers or functions.
• A matrix having m rows and n columns is called a matrix of order m × n.
• [a ij ]m×1 is a column matrix.
• [a ij ]1×n is a row matrix.
• An m × n matrix is a square matrix if m = n.
• A = A = [aij ]m×n is a diagonal matrix if a ij =0, when i ≠ j
• A = a ji is a scalar matrix if a ij = 0 when i ≠ j, a ij = k (k is some constant), when I=j.
n ×n
A = aij · aij = 1, when i = j, aij = 0, when i ≠ j.
• n×n is an identity matrix, if
• A zero matrix has all its elements as zero.
A = aij = bij = B
• if (i) A and B are of same order, (ii) for all possible values of i and j.
•
kA = k aij
m×n ( )
= k aij
m×n
• – A = (–1)A
• A – B = A + (–1) B
• A+B=B+A
• (A + B) + C = A + (B + C), where A, B and C are of same order.
• k(A + B) = kA + kB, where A and B are of same order, k is constant.
• (k + l ) A = kA + lA, where k and l are constant.
n
• If A = [aij ]m×n and B = [bjk ]n×p , then AB = C = [cik ]m×p , where C tl = ∑ a ijb jk
j=i
(i) A(BC) = (AB)C,
Key Notes
(ii) A(B + C) = AB + AC,
(iii) (A + B)C = AC + BC
If A = aij , then A′ or AT = a ji
• m×n n×m
• (i) (A′)′ = A,
• (ii) (kA)′ = kA′,
• (iii) (A + B)′ = A′ + B′,
• (iv) (AB)′ = B′A′
• A is a symmetric matrix if A′ = A.
• A is a skew symmetric matrix if A′ = –A.
• Any square matrix can be represented as the sum of a symmetric and a skew symmetric
matrix.
• Elementary operations of a matrix are as follows:
(i) R1 ↔ R j or Cl ↔ C j
•
(i) R1 → kR i or Cl ↔ kCl
(i) R1 ↔ R j + kR j or Cl + kC j
• If A and B are two square matrices such that AB = BA = I, then B is the inverse matrix of A and
−1
is denoted by A and A is the inverse of B.
• Inverse of a square matrix, if it exists, is unique.
You might also like
- Key Notes: Chapter-3 MatricesDocument2 pagesKey Notes: Chapter-3 MatricesInvincible FactsNo ratings yet
- Matrices: - An M X N Matrix Is Written AsDocument7 pagesMatrices: - An M X N Matrix Is Written AsnitinNo ratings yet
- Matrices & Determinants PDFDocument60 pagesMatrices & Determinants PDFvenu duggineniNo ratings yet
- Matrices Determinants MathongoDocument12 pagesMatrices Determinants MathongoArya NairNo ratings yet
- 20 FRDocument7 pages20 FRyellaiahNo ratings yet
- 20 Matrices Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages20 Matrices Formula Sheets Quizrrbharasha mahantaNo ratings yet
- 20 Matrices Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument9 pages20 Matrices Formula Sheets Getmarks AppAashrith PemmarajuNo ratings yet
- Matrices WatermarkDocument33 pagesMatrices Watermarksherin joysonNo ratings yet
- Matrices & Determinant: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF FormatDocument7 pagesMatrices & Determinant: All 2023 PYQ in CBT and PDF Formatsiddharthjii22222No ratings yet
- Matrices & Determinant: Most Important Questions & MindmapDocument315 pagesMatrices & Determinant: Most Important Questions & Mindmapsiddharthjii22222No ratings yet
- Bab V Efek PanasDocument40 pagesBab V Efek PanascantikNo ratings yet
- Matrices PYQ 2016 11 YearDocument17 pagesMatrices PYQ 2016 11 Yeararyanraj61090No ratings yet
- Pure Math - Matrix: DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPure Math - Matrix: Definitionsjared liNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MatricesDocument12 pagesChapter 3 MatricesXinhui PongNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of MatricesDocument19 pagesBasic Concept of MatricesSiddharth palNo ratings yet
- 08 MatricesDocument26 pages08 MatricesGeeta MNo ratings yet
- MATRIXCDocument15 pagesMATRIXClatestdaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 (Matrices)Document23 pagesUnit 3 (Matrices)mukteshwarj4No ratings yet
- Thumbnail SlideDocument188 pagesThumbnail Slidesiddharthjii22222No ratings yet
- Exempler Chapter 3Document23 pagesExempler Chapter 3King of DonsNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgATi AZ84elTr9QFHjj5GeniP9wnXnwroO5 4lp4sULSAabTx1SHLz9u21jnSzuqLqEvHEil PLsaXcqG6FfPuXrQS6SZJ9pkhU81 40PA9Ie I9i5dci4 DbYikCZIyUXnk0yinAF I28DDocument46 pagesACFrOgATi AZ84elTr9QFHjj5GeniP9wnXnwroO5 4lp4sULSAabTx1SHLz9u21jnSzuqLqEvHEil PLsaXcqG6FfPuXrQS6SZJ9pkhU81 40PA9Ie I9i5dci4 DbYikCZIyUXnk0yinAF I28DVoot Kids75No ratings yet
- MatricesDocument6 pagesMatricesPranavi MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 MathematicsDocument8 pagesGrade 12 MathematicsMPS QUESTION PAPER SUBMISSIONNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PT 4 Matrix AlgebraDocument19 pagesUnit 1 PT 4 Matrix Algebrasprinklesdb16No ratings yet
- Matrices: Matrix and Operations On MatricesDocument6 pagesMatrices: Matrix and Operations On Matrices12-A-9- vishalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Maths Formula Notes 1 50Document104 pagesEngineering Maths Formula Notes 1 50PriyaNo ratings yet
- Studyguide360: CHAPTER: 3 and 4 Matrices and Determinants Important Points To RememberDocument20 pagesStudyguide360: CHAPTER: 3 and 4 Matrices and Determinants Important Points To RememberajayNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 3. MatricesDocument17 pagesClass 12 Chapter 3. MatricesShreya SinghNo ratings yet
- MatrixDocument9 pagesMatrixkritikaNo ratings yet
- Day5.Matrices NotesDocument3 pagesDay5.Matrices NoteshaveNo ratings yet
- 19matrices DeterminantsDocument5 pages19matrices DeterminantssatyahbhatNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument12 pagesMatricesPranivoid100% (1)
- Matrices and DeterminantDocument13 pagesMatrices and DeterminantAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- Matrix DetwrminantsDocument9 pagesMatrix DetwrminantsJared GualonNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants: Astrid Xiomara Rodríguez CastelblancoDocument21 pagesMatrices and Determinants: Astrid Xiomara Rodríguez Castelblancoxiomyrodriguez10No ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants: Astrid Xiomara Rodríguez CastelblancoDocument21 pagesMatrices and Determinants: Astrid Xiomara Rodríguez Castelblancoxiomararodriguez10No ratings yet
- 2 (I) MatricesDocument11 pages2 (I) Matriceskps evilNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument7 pagesMatricesPriti DixitNo ratings yet
- Matrices & DeterminantsDocument60 pagesMatrices & DeterminantsPradeep SinglaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Determinants - CETDocument22 pagesModule 7 - Determinants - CETGokul yadavNo ratings yet
- c1 Linear AlgebraDocument33 pagesc1 Linear AlgebraChua ZhenyuNo ratings yet
- matrixAlgebraReview PDFDocument16 pagesmatrixAlgebraReview PDFRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Matrices and DeterminantsDocument15 pagesMatrices and DeterminantsvighneshmanojNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Assignment 1Document8 pagesMatrices - Assignment 1Samarth AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Matrices One Shot #BBDocument158 pagesMatrices One Shot #BBPoonam JainNo ratings yet
- 12 Cbse Maths-Matrices02Document40 pages12 Cbse Maths-Matrices02tranquil_452889939No ratings yet
- Revision Notes On Matrices: Properties of Various Types of MatricesDocument7 pagesRevision Notes On Matrices: Properties of Various Types of MatricesVincent VetterNo ratings yet
- Elements: Order: No. of ElementsDocument5 pagesElements: Order: No. of Elementsaniketsingh86306No ratings yet
- Mind Map - Matrices - Class 12Document5 pagesMind Map - Matrices - Class 12studyonlyrithuNo ratings yet
- Maths Amrendrasir: Subject Assignment DateDocument7 pagesMaths Amrendrasir: Subject Assignment DateNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Matrices & DeterminantsDocument2 pagesMatrices & DeterminantssayondeepNo ratings yet
- EM Short FormulasDocument24 pagesEM Short FormulasAlia SharmaNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra I-1Document26 pagesLinear Algebra I-1AlessioNo ratings yet
- Algebra of Matrices Level-1Document15 pagesAlgebra of Matrices Level-1BulusuMurtyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistics W2: Matrix Algebra BasicsDocument8 pagesAdvanced Statistics W2: Matrix Algebra BasicskinaNo ratings yet
- Matrices - Short NotesDocument3 pagesMatrices - Short NotesAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Matrices1 PDFDocument8 pagesMatrices1 PDFMansoor KhanNo ratings yet
- 3 MATRICES CH 3Document18 pages3 MATRICES CH 3Abhinav Gaming ytNo ratings yet
- Matrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersFrom EverandMatrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument39 pagesClass NotessanthoshNo ratings yet
- National Income Class 12 WsDocument19 pagesNational Income Class 12 WsIsha BhattNo ratings yet
- Matrices Unit IDocument13 pagesMatrices Unit IMadhu spoorthiNo ratings yet
- Sample Mathematicia XIIDocument49 pagesSample Mathematicia XIIMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Usme, Dtu Project On Matrices and Determinants Analysis BY Bharat Saini Tanmay ChhikaraDocument17 pagesUsme, Dtu Project On Matrices and Determinants Analysis BY Bharat Saini Tanmay ChhikaraTanmay ChhikaraNo ratings yet
- Johan G. F. Belinfante, Bernard KolmanDocument175 pagesJohan G. F. Belinfante, Bernard KolmanDany HdzNo ratings yet
- Matrix Methods, Applied Linear Algebra, Third EditionDocument433 pagesMatrix Methods, Applied Linear Algebra, Third Editionk_ij9658100% (3)
- Maths Formula Revision SheetDocument51 pagesMaths Formula Revision SheetShivu GamerNo ratings yet
- Matrix Algebra 1.Document4 pagesMatrix Algebra 1.Snaya SharmaNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument3 pagesMatricesMaths Home Work 123No ratings yet
- Class-Xii Maths - Term-1 - Support Materials & MCQ Questions-FinalDocument75 pagesClass-Xii Maths - Term-1 - Support Materials & MCQ Questions-FinalDevvrat SolankiNo ratings yet
- Edupedia 9th Class Math PaperDocument4 pagesEdupedia 9th Class Math PaperareebaNo ratings yet
- Bihar Board Solutions: Bihar Board 12th Maths Objective Answers Chapter 3 MatricesDocument9 pagesBihar Board Solutions: Bihar Board 12th Maths Objective Answers Chapter 3 MatricesSanjayNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument12 pagesMatricesVenkat GowdaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 3 Matrices Exercise 3.3Document13 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Maths Chapter 3 Matrices Exercise 3.3Saksham DixitNo ratings yet
- Georgi Lecture Notes On Weak Interactions Physics Harvard Web Draft 1998Document167 pagesGeorgi Lecture Notes On Weak Interactions Physics Harvard Web Draft 1998manosmagicas7340No ratings yet
- (Darryl D. Hol,) Geometric Mechanics Rotating, TR (B-Ok - CC) PDFDocument304 pages(Darryl D. Hol,) Geometric Mechanics Rotating, TR (B-Ok - CC) PDFOceanNo ratings yet
- BSC Computer Science PDFDocument56 pagesBSC Computer Science PDFB.ArulNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Determinant and MatriXDocument17 pagesChapter - Determinant and MatriXKhushbu KumariNo ratings yet
- Wa0035Document25 pagesWa0035GrishmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics I PDFDocument247 pagesMathematics I PDFCHAMANCHULA ANITHANo ratings yet
- M-1 Question Bank (Imp) : Unit-I MatricesDocument8 pagesM-1 Question Bank (Imp) : Unit-I MatricesSunny VardhanNo ratings yet
- Maths PQ2Document6 pagesMaths PQ2utharun3No ratings yet
- Real Ana SolvedDocument92 pagesReal Ana SolvedRajdip sarkarNo ratings yet
- 2018Document8 pages2018Paras SirasyaNo ratings yet
- Maths QBDocument179 pagesMaths QB8dhruvjainNo ratings yet
- Maths MCQ Collection 2023Document26 pagesMaths MCQ Collection 2023Dk249No ratings yet
- Introduction To EntanglementDocument10 pagesIntroduction To EntanglementmaareaNo ratings yet
- SM 12 Math Eng 201617Document192 pagesSM 12 Math Eng 201617Bhavesh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Maths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-3) - PaperDocument10 pagesMaths Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-3) - PaperYash DhokeNo ratings yet