Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Template For Meds: Respiratory Depression
Template For Meds: Respiratory Depression
Uploaded by
Susan Powell-ProctorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Template For Meds: Respiratory Depression
Template For Meds: Respiratory Depression
Uploaded by
Susan Powell-ProctorCopyright:
Available Formats
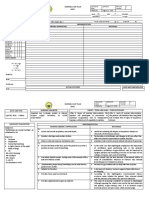
Template for meds
Medication/ Dose Route/Frequency dilaudid 2mg po q6 hour (pt had it on shift)
Generic/Trade hydromorphone
Classification Opioid agonist
Why is Client Receiving? Back pain
Therapeutic Effect- What does it do? Pain relief
Mechanism of Action- How does it do it? Binds to opiate receptors in the CNS.
Alters the perception of and response to painful stimuli while producing generalized
CNS depression.
Suppresses the cough reflex via a direct central action.
Adverse Effects CNS: confusion, sedation, dizziness, dysphoria, euphoria, floating feeling,
hallucinations, headache, unusual dreams
CV: hypotension, bradycardia
Derm: flushing, sweating
EENT: blurred vision, diplopia, miosis
Endo: adrenal insufficiency
GI: constipation, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting
GU: urinary retention
Resp: RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION (INCLUDING CENTRAL SLEEP APNEA AND
SLEEP-RELATED HYPOXEMIA)
Misc: physical dependence, psychological dependence, tolerance
NSG Implications Pain:
Assess type, location, and intensity of pain prior to and 1 hr following IM or PO and 5
min (peak) following IV administration. When titrating opioid doses, increases of 25–
50% should be administered until there is either a 50% reduction in the patient's pain
rating on a numerical or visual analogue scale or the patient reports satisfactory pain
relief. When titrating doses of short-acting hydromorphone, a repeat dose can be
safely administered at the time of the peak if previous dose is ineffective and side
effects are minimal.
o Patients on a continuous infusion should have additional bolus doses
provided every 15–30 min, as needed, for breakthrough pain. The bolus
dose is usually set to the amount of drug infused each hr by continuous
infusion.
o Patients taking extended-release hydromorphone may require additional
short-acting or rapid-onset opioid doses for breakthrough pain. Doses of
Template for meds
short-acting opioids should be equivalent to 10–20% of 24 hr total and
given every 2 hr as needed.
o An equianalgesic chart (see equianalgesic dosing guidelines) should be used
when changing routes or when changing from one opioid to another.
o Prolonged use may lead to physical and psychological dependence and
tolerance. This should not prevent patient from receiving adequate
analgesia. Patients who receive hydromorphone for pain rarely develop
psychological dependence. Progressively higher doses may be required to
relieve pain with long-term therapy.
o Assess risk for opioid addiction, abuse, or misuse prior to administration.
Abuse or misuse of extended-release preparations by crushing, chewing,
snorting, or injecting dissolved product will result in uncontrolled delivery
of hydromorphone and can result in overdose and death.
Cough: Assess cough and lung sounds during antitussive use.
Patient Education Instruct patient on how and when to ask for pain medication. Do not stop
taking without discussing with health care professional; may cause withdrawal symptoms if
discontinued abruptly after prolonged use. Discuss safe use, risks, and proper storage and
disposal of opioid analgesics with patients and caregivers with each Rx. The Patient Counseling
Guide (PCG) is available at www.fda.gov/OpioidAnalgesicREMSPCG.
Advise patient that hydromorphone is a drug with known abuse potential. Protect it
from theft, and never give to anyone other than the individual for whom it was
prescribed. Store out of sight and reach of children, and in a location not accessible by
others.
May cause drowsiness or dizziness. Advise patient to call for assistance when
ambulating or smoking. Caution patient to avoid driving or other activities requiring
alertness until response to medication is known.
Advise patient to notify health care professional if pain control is not adequate or if
side effects occur.
Advise patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
Instruct patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol or other CNS depressants.
Instruct patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC medications,
vitamins, or herbal products being taken and consult health care professional before
taking any new medications.
Encourage patient to turn, cough, and breathe deeply every 2 hr to prevent atelectasis.
Labs to check May ↑ plasma amylase and lipase concentrations.
I would CHECK THESE LABS
You might also like
- Percocet Drug CardDocument1 pagePercocet Drug CardSheri490100% (4)
- Clinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationDocument4 pagesClinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationMohammad OmarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan 1gagandipkS100% (1)
- Slide 2 Principles of Interpersonal ComDocument16 pagesSlide 2 Principles of Interpersonal ComJean GanubNo ratings yet
- GIT Individual Case StudyDocument13 pagesGIT Individual Case StudyKirito Dokkie100% (1)
- Case Study 7 PDFDocument3 pagesCase Study 7 PDFRachael OyebadeNo ratings yet
- DOH ProgramsDocument6 pagesDOH ProgramsrobotkabaNo ratings yet
- Group Work 3 - Nutrition Care ProcessDocument3 pagesGroup Work 3 - Nutrition Care Processcharles estradaNo ratings yet
- C1, C2 InjuriesDocument58 pagesC1, C2 InjuriesVishad NaidooNo ratings yet
- Osteoporosis PDFDocument4 pagesOsteoporosis PDFmawarNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 PTB Plueral EffusionDocument12 pagesCase Study 2 PTB Plueral EffusionKaren Kate AblesNo ratings yet
- Choking: by Jawad AhmedDocument25 pagesChoking: by Jawad Ahmedjawad_ahmedNo ratings yet
- Orthopaedics and Orthopaedic Nursing RNDocument70 pagesOrthopaedics and Orthopaedic Nursing RNFaith LwabilaNo ratings yet
- Final - CholeraDocument12 pagesFinal - CholeraCassey Cureg100% (1)
- NCMB 316Document36 pagesNCMB 316Venansius GanggusNo ratings yet
- Race Cadot RilDocument1 pageRace Cadot RilLindsay Grace MandarioNo ratings yet
- ArcoxiaDocument27 pagesArcoxiaClarissa Mundo OlmilloNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis NCP FINALDocument6 pagesCholelithiasis NCP FINALShreshthi VermaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - BronchopneumoniaDocument108 pagesCase Study - BronchopneumoniaAnthony WallNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document35 pagesPresentation 1Moitri ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument6 pagesIrritable Bowel SyndromemynameNo ratings yet
- DS - CatapresDocument2 pagesDS - CatapresDOni CorleoneNo ratings yet
- Indacaterol GlycopyrroniumDocument1 pageIndacaterol GlycopyrroniumNeulAskiel FloresNo ratings yet
- DS (Ibuprofen)Document6 pagesDS (Ibuprofen)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Therese M. Chapman, Jane K. Mcgavin and Stuart NobleDocument12 pagesTenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Therese M. Chapman, Jane K. Mcgavin and Stuart NobleBagusHibridaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient's Name: L. Fajardo Age: 19 Y.O AddressLeticia ElricNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Gas Exchange (COPD)Document3 pagesNCP - Impaired Gas Exchange (COPD)Karen Joy ItoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Planusama_salaymehNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudyEy'ey OrtizNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: NOC: Swallowing Status Goal: NIC: SwallowingSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Trifluridine and TipiracilDocument3 pagesTrifluridine and TipiracilKristine AcasioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LCPDocument3 pagesDrug Study LCPalleen_viaNo ratings yet
- Penicillin VDocument3 pagesPenicillin Vapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Ethico LegalDocument4 pagesEthico LegalChrisnel Caoile0% (1)
- Pneumonia Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pagesPneumonia Nursing Care PlansBeng AlontoNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersDocument16 pagesAssessment of Patients With Renal Disorders Management of Urinary Tract DisordersJhosita Flora LarocoNo ratings yet
- Monsalud - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMonsalud - Drug StudyJanielle Christine MonsaludNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyJohn Ronald P. RamosNo ratings yet
- Kabiven: (Amino Acids, Electrolytes, Dextrose and Lipid Injectable Emulsion), For Intravenous UseDocument24 pagesKabiven: (Amino Acids, Electrolytes, Dextrose and Lipid Injectable Emulsion), For Intravenous UseDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- Ladybelle P. Gototos Geriatric Nursing Bsn3 Set1 NCPDocument2 pagesLadybelle P. Gototos Geriatric Nursing Bsn3 Set1 NCPLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Mr. Vinay Kumar M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year HCN, SrhuDocument44 pagesPresented By:: Mr. Vinay Kumar M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year HCN, SrhuVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Tramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibDocument4 pagesTramadol, Ketorolac, EterocoxibEric de JulianNo ratings yet
- Oks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!Document10 pagesOks Na To Thank U Aubs!!: Okiii!!! Wuv U All!CiaraNo ratings yet
- CarePlan Psych TemplateDocument14 pagesCarePlan Psych TemplateSasha HayeNo ratings yet
- Acute AppendicitisDocument23 pagesAcute AppendicitisSandie Daniel GabalunosNo ratings yet
- Case Reporrt GerdDocument7 pagesCase Reporrt GerdKarina WidyaNo ratings yet
- FinasterideDocument2 pagesFinasterideSyokoyolanting DondonNo ratings yet
- 07HEAT - WS 03: Solve The Crossword On "Heat" Within 10 MinutesDocument2 pages07HEAT - WS 03: Solve The Crossword On "Heat" Within 10 MinutesSHUBHAM KUMARNo ratings yet
- Pott Disease 1223292121651385 8Document54 pagesPott Disease 1223292121651385 8Ismail SalimNo ratings yet
- Hypertension (HTP)Document4 pagesHypertension (HTP)Charmagne Joci EpantoNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP PaindwightciderNo ratings yet
- NCP Colon CancerDocument8 pagesNCP Colon CancerSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- NephrolithiasisDocument2 pagesNephrolithiasisDeepthiNo ratings yet
- Example Case StudyDocument7 pagesExample Case StudyTerrena Lyn BlackmanNo ratings yet
- Case File GERDDocument9 pagesCase File GERDMutiara Shifa100% (1)
- DilaudidDocument2 pagesDilaudidAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- Respiratory Drugs Midterm ExamDocument10 pagesRespiratory Drugs Midterm ExamKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Generic: Hydromorphone (Im) Brand Name: DilaudidDocument1 pageGeneric: Hydromorphone (Im) Brand Name: DilaudidPreet ChahalNo ratings yet
- Nalbuphine (Nubain)Document2 pagesNalbuphine (Nubain)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Study: Adamson UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Adamson UniversityRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- NURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentDocument1 pageNURS 2516 Clinical Medications Worksheets: Nursing Process-AssessmentAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Operative Assesment of Patients: Moderator: DR - Roshan PradhanDocument36 pagesPre-Operative Assesment of Patients: Moderator: DR - Roshan PradhanNikhil PanjiyarNo ratings yet
- Pain Coach and Toolkit Guide FINAL 7.7.2022Document66 pagesPain Coach and Toolkit Guide FINAL 7.7.2022Meena CtNo ratings yet
- Latest List of Hospitals - 1Document15 pagesLatest List of Hospitals - 1ShashikumarNo ratings yet
- Applied Pharmacology Dental Hygienist 7th Haveles Test BankDocument17 pagesApplied Pharmacology Dental Hygienist 7th Haveles Test Bankfahedq0% (1)
- Burn Injuries and Management - Dr. Ihab AzzamDocument12 pagesBurn Injuries and Management - Dr. Ihab Azzambiii boooNo ratings yet
- Vagus Nerve Neuropathy Related To SARS COV-2 InfectionDocument3 pagesVagus Nerve Neuropathy Related To SARS COV-2 Infectionmpm8471No ratings yet
- Orthodontic Biomechanics KusyDocument3 pagesOrthodontic Biomechanics KusyCaro JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Ebook Pharmacology in Nursing 3Rd Australian New Zealand Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Pharmacology in Nursing 3Rd Australian New Zealand Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFrobert.cardoza447100% (36)
- Emerg Med Clin North Am 2024 Feb 42 (1) 41-52Document12 pagesEmerg Med Clin North Am 2024 Feb 42 (1) 41-52arturo92marinNo ratings yet
- P2 Hes 005Document23 pagesP2 Hes 005Justine RabanesNo ratings yet
- Cardiologist, AMIRI HOSPITAL, MOH, Kuwait.: Dr. Rajesh RajanDocument36 pagesCardiologist, AMIRI HOSPITAL, MOH, Kuwait.: Dr. Rajesh Rajanirfana efendiNo ratings yet
- Avanir Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Et Al. v. Actavis South Atlantic LLC, Et Al., Consol. C.A. No. 11-704-LPS (D. Del. Apr. 30, 2014)Document65 pagesAvanir Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Et Al. v. Actavis South Atlantic LLC, Et Al., Consol. C.A. No. 11-704-LPS (D. Del. Apr. 30, 2014)YCSTBlogNo ratings yet
- Chlamydia Gonorrhea Treatment ChartDocument1 pageChlamydia Gonorrhea Treatment ChartdoodrillNo ratings yet
- Pharma Prelim Assignment 1 - Pharmacodynamics..Document2 pagesPharma Prelim Assignment 1 - Pharmacodynamics..Kimberly Wyne SantosNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1878535221005931 MainDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S1878535221005931 MainFernando NunesNo ratings yet
- Seizure ThresholdDocument5 pagesSeizure ThresholdannNo ratings yet
- CPP & Cqa PDFDocument71 pagesCPP & Cqa PDFanon_695264516100% (1)
- Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate: Injection, UspDocument2 pagesDexamethasone Sodium Phosphate: Injection, UspazedaaNo ratings yet
- Amphetamine Use DisordersDocument22 pagesAmphetamine Use DisordersZaid WaniNo ratings yet
- p450 Table Oct 11 2009Document2 pagesp450 Table Oct 11 2009Naresh BabuNo ratings yet
- Maschio Et Al (2019) Management of Epilelsy in Brain TumorsDocument18 pagesMaschio Et Al (2019) Management of Epilelsy in Brain TumorssitialimahNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Special Procedures: Kenneth M. Luciano, RRTDocument36 pagesRadiographic Special Procedures: Kenneth M. Luciano, RRTKaye A. JardinicoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MontelukastDocument2 pagesDrug Study MontelukastMarjorie Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs and AntidoteDocument114 pagesEmergency Drugs and AntidoteAlexa BelderolNo ratings yet
- Immune Checkpoint Blockade and CAR-T Cell Therapy in Hematologic MalignanciesDocument20 pagesImmune Checkpoint Blockade and CAR-T Cell Therapy in Hematologic MalignanciesAsfahani LatiefahNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Cefixime in Treating Respiratory Tract and Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument9 pagesThe Effect of Cefixime in Treating Respiratory Tract and Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Clinical Spectrum of Atherosclerotic Heart DiseaseDocument50 pagesClinical Spectrum of Atherosclerotic Heart Diseaseadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- UnasynDocument3 pagesUnasynianecunar100% (4)
- 2022-OXFORD-HANDBOOK-OF-ANAESTHESIA-Oxford-Press-5th-Edition ExportDocument4 pages2022-OXFORD-HANDBOOK-OF-ANAESTHESIA-Oxford-Press-5th-Edition ExportHany ElbarougyNo ratings yet