Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs Key
Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs Key
Uploaded by
Sameer HussainOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs Key
Alkyl Halides and Amines Mcqs Key
Uploaded by
Sameer HussainCopyright:
Available Formats
Roll No. Answer Sheet No.
Sig. of Candidate. Sig. of invigilator.
CHEMISTRY CLASS 12
ALKYL HALIDES AND AMINES (Marks 14)
NOTE:Section 'A' is compulsory. All questions carry equal marks. Select the choice which you think is correct with Marker or Pen
ink.Deleting / overwriting is not allowed.Do not use a lead pencil.
Q. 1 The correct order of reactivity of alkyl halides is (1)
A. R– I > R– Br > R– C l B.
> R–
R–FF > R– C l > R– Br C. R–
> R–IC l > R– Br > R– I D. R–
> R–FBr > R– C l > R– F > R–
Q. 2 The product X in the given reaction is
(1)
A. C H3 – C O– C H3 B. C H3 – C H2 – C H O C. C H3 – C H2 – C OOH D. C H3 – C H2 – C H2 – OH
Q. 3 Methylamine is more basic than ammonia, because the (1)
A. methylammonium ion is more stabilised.
B. methylammonium ion is a stronger conjugate base than ammonium ion.
C. sp3 orbital of carbon in methylamine pulls the electron pair towards itself.
D. electron pair in methylamine is strongly attracted by s-orbital of hydrogen atom.
Q. 4 When there is crowding within the substrate molecule, then elimination reaction is favoured over substitution (1)
reaction, because the removal of
A. β -hydrogen atom by base from tertiary planar carbonium ion is easy.
B. α-hydrogen atom by base from tertiary planar carbonium ion is easy.
C. β-hydrogen atom by base from tertiary planar carbonium ion is difficult.
D. α-hydrogen atom by base from tertiary planar carbonium ion is difficult.
Q. 5 All of the following are TRUE about SN 2 reactions EXCEPT they (1)
A. are favoured in non-polar solvent. B. always occur with partial racemisation.
C. involve the formation of transition state. D. always occur with inversion of configuration.
Q. 6 The missing product Z in the given chemical reaction is
(1)
A. A B. B C. C D. D
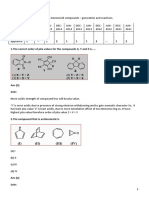
Q. 7 The IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) name of the given amine is
(1)
A. methyl amino butane. B. dimethyl amino propane. C.
-methyl-2-amino
2 D. 2-methyl propyl amino
butane. ethane.
Powered by Knowledge Platform
Q. 8 The MOST stable diazonium salt is (1)
A. C6 H5 − N
+
2
B. C H3 − C H2 − N
+
2
C. C6 H5 − C H2 − N
+
2
D. C H3 − C H2 − C H2 − N
+
2
Powered by Knowledge Platform
Q. 9 Which of the following, on reaction with Grignard’s reagent, result(s) in the formation of a tertiary alcohol?
(1)
I. H C H O II. C H3 C OC H3
III. C H3 C H O IV. C H3 C OOC H3
A. I only B. I and III C. II only D. II and IV
Q. 10 Which action on alkyl cyanides (nitriles) yields primary amines? (1)
A. Alkaline hydrolysis B. Catalytic reduction C. Catalytic hydration D. Acidic hydrolysis
Q. 11 Which statement is CORRECT about the basic character of amines? (1)
A. Aryl amines and alkyl amines are equal in basic strength. B. Alkyl amines and ammonia are equal in basic strength.
C. Aryl amines are stronger bases than ammonia. D. Alkyl amines are stronger bases than ammonia.
Q. 12 A nucleophilic substitution reaction is summarized in the form of its rate equation as follows.
(1)
Rate =
−
k[R − X][OH ]
Which of the following statements is FALSE for the given reaction?
− +
A. The overall reaction is 2nd order. B. OH attacks on R in the final step.
C. The rate determining step is bimolecular.
−
D. OH attacks R– X before R– X bond is broken.
Q. 13 Which of the following statements is TRUE about E1 mechanism? (1)
A. E1 mechanism shows second order kinetics. B. The nucleophile attacks and the leaving group leaves at the
same time.
C. The first step is the slow ionisation of the substrate to give a D. The rate of reaction can be expressed as Rate = k[Alkyl
carbocation. halide][Nucleophile].
Q. 14 LiAlH4 , Ether
(1)
C H 3 C ≡ N + 4[H ] −−−−−−−−→
The above reaction results in the formation of
A. ammonia. B. tertiary amine. C. primary amine. D. secondary amine.
Powered by Knowledge Platform
You might also like
- BR BR BR BRDocument47 pagesBR BR BR BRVesna NikolicNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesMechanism Multiple Choice QuestionsAnonymous pgjIAZoNo ratings yet
- COUPP - 60 Hydraulic Hose Failure AnalysisDocument26 pagesCOUPP - 60 Hydraulic Hose Failure AnalysisRomulus Situ MorankNo ratings yet
- Iit Questions On Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeDocument12 pagesIit Questions On Carbonyl Compounds & Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Chapter No1 Basic Concepts McqsDocument6 pagesMcqs Chapter No1 Basic Concepts McqsHaider JalalNo ratings yet
- LS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024d2f3562799-Bioinorganic (Previous Year)Document9 pagesLS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024d2f3562799-Bioinorganic (Previous Year)Hamit Rana100% (1)
- IsomerismDocument16 pagesIsomerismAnusmita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Mcqs QuestionsDocument9 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Mcqs QuestionsGyanendra Vikram Maurya100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1Document195 pagesOrganic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques-1aditya kumar Agarwal100% (1)
- Alcohol, Ether & Phenol - QuestionDocument3 pagesAlcohol, Ether & Phenol - Questionbest badmintonNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsDocument7 pagesExercise - 1: Basic Objective Questions: Ionic BondsNavita RajgariaNo ratings yet
- 1 Chemistry 1st Year Chapter 6 FullDocument3 pages1 Chemistry 1st Year Chapter 6 Fullmahar zafarNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and PhenolsDocument9 pagesAlcohols and Phenolsdivya divyaNo ratings yet
- 10.true False (D and F Block Elements)Document11 pages10.true False (D and F Block Elements)rajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Physical CHM MCQS For MSCDocument15 pagesPhysical CHM MCQS For MSCPhoton Online Science AcademyNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Electrochemistry: Chemistry by Saad AnwarDocument5 pagesMcqs Electrochemistry: Chemistry by Saad AnwarPhoton Online Science Academy0% (1)
- Chemical Bonding MCQDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding MCQSrinithi MeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Class-XII (Chemistry) Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type QuestionsDocument9 pagesClass-XII (Chemistry) Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type QuestionsPranav DhimanNo ratings yet
- 02 Unit# 2Document8 pages02 Unit# 2Muhammad Bilal ChemIstNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument22 pagesAtomic StructureYash AkhauriNo ratings yet
- CH 14Document28 pagesCH 14ffffffff dfdfdfNo ratings yet
- All MCQs in OneDocument22 pagesAll MCQs in OneNo NameNo ratings yet
- Chem MCQ FinalDocument258 pagesChem MCQ FinalDare DevilNo ratings yet
- MCQ CH 2 ElectrochemistryDocument2 pagesMCQ CH 2 ElectrochemistryGaurav SonarNo ratings yet
- All MCQS First YearDocument85 pagesAll MCQS First YearNazimEhsanMalik25% (4)
- Chemical Equilibrium MCQDocument13 pagesChemical Equilibrium MCQNidhi SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases StudentDocument24 pagesAcids and Bases StudentVictor BritoNo ratings yet
- Aromaticity: Aromaticity: Benzenoid and Non-Benzenoid Compounds - Generation and ReactionsDocument7 pagesAromaticity: Aromaticity: Benzenoid and Non-Benzenoid Compounds - Generation and ReactionsSankar AdhikariNo ratings yet
- MCQDocument4 pagesMCQarpitapanda157No ratings yet
- MCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Document7 pagesMCQ Chemical Kinetics 25 Problems (30 Mins)Sanjeev Chaudhary100% (1)
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument18 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesBhavesh KNo ratings yet
- LS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024b00625d276-Statistical ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesLS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024b00625d276-Statistical ThermodynamicsHamit RanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 11 MCQJay VermaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument19 pagesChemical BondingAman AntilNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sir Yasir Chemistry CH # 18Document2 pagesAssignment Sir Yasir Chemistry CH # 18Yasir QureshiNo ratings yet
- Amines MCQDocument3 pagesAmines MCQaleena'No ratings yet
- LS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024a396c4ea68-Molecular SpectrosDocument8 pagesLS - 0 - 2 - 2d3125 - 024a396c4ea68-Molecular SpectrosHamit RanaNo ratings yet
- DPP - 01 - Reaction MechanismDocument5 pagesDPP - 01 - Reaction Mechanismbaibhav singhNo ratings yet
- MCQs pdf-1 PDFDocument5 pagesMCQs pdf-1 PDFEmman Ann100% (3)
- Coordination MCQDocument11 pagesCoordination MCQSubhasish Sau100% (2)
- Chemistry Mcqs For Ssc-IDocument5 pagesChemistry Mcqs For Ssc-IAbdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- Redox MCQsDocument7 pagesRedox MCQsHarsh Walavalkar100% (1)
- MCQ For Question PaperDocument11 pagesMCQ For Question PaperAjay Sharma Shankyan100% (2)
- Class Test 1: Section A (Multiple-Choice Questions)Document10 pagesClass Test 1: Section A (Multiple-Choice Questions)Kgaugelo TraciaNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases 8.1 and 8.2 MCQDocument4 pagesAcids and Bases 8.1 and 8.2 MCQAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry McqsDocument51 pagesChemistry McqsEngr Muhammad MubeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document5 pagesChapter 01Rana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis MCQDocument11 pagesElectrolysis MCQSavarinathan Maria Rayappan100% (1)
- PRACTICE MCQ HYDROCARBONS - 11ScADocument7 pagesPRACTICE MCQ HYDROCARBONS - 11ScAArda Rahmaini100% (1)
- CSIR UGC NET Model Question Papers Chemical SciencesDocument32 pagesCSIR UGC NET Model Question Papers Chemical SciencesShiksha PortalNo ratings yet
- Set of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inDocument6 pagesSet of 50 Obj in General Organic Chemistry by S.K.sinha HTTP://WWW - Openchemistry.inmyiitchemistry50% (4)
- Mcqs Class 1st Year Chemistry Chapter WiseDocument64 pagesMcqs Class 1st Year Chemistry Chapter Wisezeerak shafiqNo ratings yet
- 0optical Isomerism - QuizDocument3 pages0optical Isomerism - QuizSanjay Mani Tripathi50% (2)
- Alkanes MCQDocument2 pagesAlkanes MCQJeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- CHEM108 GuideDocument18 pagesCHEM108 GuidenadyahginiceNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 1: Career Point Pre-Medical (Topic Wise MCQ)Document20 pagesExercise # 1: Career Point Pre-Medical (Topic Wise MCQ)Sanjay Mani TripathiNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument29 pagesAldehydes and KetonesJiya singhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry QuestionsDocument21 pagesChemistry QuestionsNahwera EvalyneNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes Complete DPPs (Mains + Advance) For ExcelDocument12 pagesHaloalkanes Complete DPPs (Mains + Advance) For ExcelRatneshNo ratings yet
- Chem II - Test 2 Exam Questions - Jan2010Qs-IDocument8 pagesChem II - Test 2 Exam Questions - Jan2010Qs-IutpNo ratings yet
- Alkanes 14-09-2014Document9 pagesAlkanes 14-09-2014Vinod AgrawalNo ratings yet
- NCM 102 Notes 1Document2 pagesNCM 102 Notes 1daclangiaNo ratings yet
- An Assessment of The InternshipDocument1 pageAn Assessment of The InternshipRaj GuruNo ratings yet
- Assignment#2 Submitted To: Dr. Aliya Submitted By: Issma Munir Abbasi MS-SP-19-REL-013Document3 pagesAssignment#2 Submitted To: Dr. Aliya Submitted By: Issma Munir Abbasi MS-SP-19-REL-013issma abbasiNo ratings yet
- Yak 52 Maitenance ManualDocument36 pagesYak 52 Maitenance ManualAvionicsfNo ratings yet
- K68i PC ManualDocument101 pagesK68i PC ManualjjcanoolivaresNo ratings yet
- MFG of Liquid Bromine (In Brief) :-: Raw MaterialsDocument17 pagesMFG of Liquid Bromine (In Brief) :-: Raw MaterialsChakuliNo ratings yet
- WhitePaper WePowerDocument46 pagesWhitePaper WePowerOnur OnukNo ratings yet
- Applications of Eigen Values and VectorsDocument11 pagesApplications of Eigen Values and Vectorsmunim matinNo ratings yet
- CPAR LessonDocument2 pagesCPAR LessonAnabelle MoyamoyNo ratings yet
- FCS195 - Essay 2 GuidelinesDocument2 pagesFCS195 - Essay 2 GuidelinesaaaaanksNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Cable (Solar) : Solar Energy. Ful Lling The Energy Needs of TomorrowDocument4 pagesPhotovoltaic Cable (Solar) : Solar Energy. Ful Lling The Energy Needs of TomorrowNitinNo ratings yet
- KB Shape CodesDocument9 pagesKB Shape CodesPrashanth TNo ratings yet
- Merton On Structural FunctionalismDocument6 pagesMerton On Structural FunctionalismJahnaviSinghNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Dynamics BrochureDocument4 pagesAerospace Dynamics BrochureAdriana Daniela SanduNo ratings yet
- Extended Readings: Chapter 4 Discourse and GenreDocument3 pagesExtended Readings: Chapter 4 Discourse and GenreMPTScribidNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument17 pagesChap 3 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesAlrianne Batonghinog100% (1)
- Food Grade Anti-Corrosion Grease: Special FeaturesDocument2 pagesFood Grade Anti-Corrosion Grease: Special Featureschem KhanNo ratings yet
- Cetirizine Degradation ProductsDocument7 pagesCetirizine Degradation ProductsASHOK KUMAR LENKANo ratings yet
- 2016-03-30 C-412 IOE Report of 326th Session of The ILO Governing Body With CFA Cases in AnnexDocument33 pages2016-03-30 C-412 IOE Report of 326th Session of The ILO Governing Body With CFA Cases in AnnexApriyanti AruanNo ratings yet
- THDC Institute of Hydropower Engineering and TechnologyDocument3 pagesTHDC Institute of Hydropower Engineering and TechnologyAnsh AroraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 AV-314 PIC Memory ArchitectureDocument16 pagesLecture 04 AV-314 PIC Memory ArchitectureMuhammad EhtishamNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Definitions PDFDocument2 pagesCritical Thinking Definitions PDFAlpha Niño S SanguenzaNo ratings yet
- Action Plan LIPAWAN ESDocument3 pagesAction Plan LIPAWAN ESJo RieNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis: Client: ContractorDocument7 pagesJob Safety Analysis: Client: Contractorloveson709No ratings yet
- John Whyte, MD, PHDDocument2 pagesJohn Whyte, MD, PHDFaris Al-sharifNo ratings yet
- SS Ind A21 BVX002 - Approval of Permanent Joining Procedure and PersonnelDocument1 pageSS Ind A21 BVX002 - Approval of Permanent Joining Procedure and PersonnelTuTuy AnNo ratings yet
- A REVIEW OF SOIL ERODIBILITY Case Study of UGBOJU Settlement of OTURKPO Local Government Area of Benue State NigeriaDocument9 pagesA REVIEW OF SOIL ERODIBILITY Case Study of UGBOJU Settlement of OTURKPO Local Government Area of Benue State NigeriaTIZA MICHAEL B.Engr., BBS, MBA, Aff. M. ASCE, ASS.M. UACSE, M. IAENG. M.ITE.No ratings yet
- Ready2Invest Off Plan Property Investor BookDocument51 pagesReady2Invest Off Plan Property Investor BookReady2InvestNo ratings yet
- Analysis of ToothGrowth Data SetDocument4 pagesAnalysis of ToothGrowth Data SetJavo SantibáñezNo ratings yet