Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design of Steel Structures Questions
Design of Steel Structures Questions
Uploaded by
leGion0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
157 views9 pagesThis document contains 34 multiple choice questions related to the design of steel structures. Some key topics covered include: properties and design of riveted and bolted connections, effective length calculations for columns, slenderness ratios of columns, and lacing and battening of built-up steel columns. The questions assess understanding of specifications and formulas used for the design of various steel structural elements.
Original Description:
Design of Steel Structures Questions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 34 multiple choice questions related to the design of steel structures. Some key topics covered include: properties and design of riveted and bolted connections, effective length calculations for columns, slenderness ratios of columns, and lacing and battening of built-up steel columns. The questions assess understanding of specifications and formulas used for the design of various steel structural elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
157 views9 pagesDesign of Steel Structures Questions
Design of Steel Structures Questions
Uploaded by
leGionThis document contains 34 multiple choice questions related to the design of steel structures. Some key topics covered include: properties and design of riveted and bolted connections, effective length calculations for columns, slenderness ratios of columns, and lacing and battening of built-up steel columns. The questions assess understanding of specifications and formulas used for the design of various steel structural elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
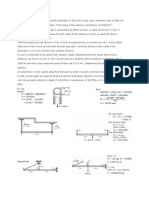
Design of Steel Structures Questions :- a) is at the maximum distance from CG of the
1. The heaviest I-section for same depth is rivet group
a) ISMB b) is at the minimum distance from CG of the
b) ISLB rivet group
c) ISHB c) gives the maximum angle between the two
d) ISWB forces Fa and Fm
Ans: c d) gives the minimum angle between the two
2. Bending compressive and tensile stresses forces Fa and Fm
respectively are calculated based on where, Fa is the load shared by each rivet due to
a) net area and gross area axial load and Fm is the shearing load due to
b) gross area and net area moment in any rivet.
c) net area in both cases Ans: d
d) gross area in both cases 7. Which of the following types of riveted
Ans: b joint is free from bending stresses ?
3. If the thickness of thinnest outside plate is a) lap joint
10 mm, then the maximum pitch of b) butt joint with single cover plate
rivets in tension will be taken as c) butt joint with double cover plates
a) 120 mm d) none of the above
b) 160 mm Ans: c
c) 200 mm 8. The difference between gross diameter and
d) 300 mm nominal diameter for the rivets up to
Ans: b 25 mm diameter is
4. In a gusseted base, when the end of the a) 1.0 mm
column is machined for complete bearing b) 1.5 mm
on the base plate, then the axial load is c) 2.0 mm
assumed to be transferred to base plate d) 2.5 mm
a) fully by direct bearing Ans: b
b) fully through fastenings 9. As compared to field rivets, the shop rivets
c) 50% by direct bearing and 50% through are
fastenings a) stronger
d) 75% by direct bearing and 25% through b) weaker
fastenings c) equally strong
Ans: c d) any of the above
5. When the axis of load lies in the plane of Ans: a
rivet group, then the rivets are subjected 10. If the thickness of plate to be connected by
to a rivet is 16 mm, then suitable size of
a) only shear stresses rivet as per Unwin’s formula will be
b) only tensile stresses a) 16 mm
c) both (a) and (b) b) 20 mm
d) none of the above c) 24 mm
Ans: a d) 27 mm
6. When the axis of load lies in the plane of Ans: c
rivet group, then the most heavily loaded 11. By providing sufficient edge distance, which
rivet will be the one which of the following failures of riveted joint can be
avoided ? a) black bolt
a) tension failure of the plate b) ordinary unfinished bolt
b) shear failure of the rivet c) turned and fitted bolt
c) shear failure of the plate d) high strength bolt
d) crushing failure of the rivet Ans: d
Ans: c 18. In the cross-section of a weld, throat is the
12. Minimum pitch of the rivets shall not be less a) minimum dimension
than b) average dimension
a) 1.5 d c) maximum dimension
b) 2.0 d d) none of the above
c) 2.5 d Ans: a
d) 3.0 d 19. The effective length of a fillet weld should
where d is gross diameter of rivet not be less than
Ans: c a) two times the weld size
13. Efficiency of a riveted joint, having the b) four times the weld size
minimum pitch as per IS : 800, is c) six times the weld size
a) 40% d) weld size
b) 50% Ans: b
c) 60% 20. For a standard 45° fillet, the ratio of size of
d) 70% fillet to throat thickness is
Ans: c a) 1:1
14. Select the correct statement b) 1 : V2
a) Material cost of a rivet is higher than that of a c) V2 : 1
bolt. d) 2: 1
b) Tensile strength of a bolt is lesser than that of Ans: c
a rivet. 21. A butt weld is specified by
c) Bolts are used as a temporary fastenings a) effective throat thickness
whereas rivets are used as permanent fastenings. b) plate thickness
d) Riveting is less noisy than bolting. c) size of weld
Ans: c d) penetration thickness
15. Bolts are most suitable to carry Ans: a
a) shear 22. The actual thickness of butt weld as
b) bending compared to the thickness of plate is usually
c) axial tension a) more
d) shear and bending b) less
Ans: c c) equal
16. Diameter of a bolt hole is usually taken as d) none of the above
a) gross diameter of bolt Ans: a
b) nominal diameter + 1.5 mm 23. According to IS Specifications, the
c) nominal diameter + 2.0 mm maximum pitch of rivets in compression is
d) nominal diameter of bolt a) lesser of 200 mm and 12 t
Ans: b b) lesser of 200 mm and 161
17. When the bolts are subjected to reversal of c) lesser of 300 mm and 32 t
stresses, the most suitable type of bolt is d) lesser of 3 00 mm and 24 t
where t is thickness of thinnest outside plate or d) 350
angle Ans: a
Ans: a 29. The maximum slenderness ratio of a steel
24. A circular column section is generally not column, the design of which is governed by
used in actual practice because wind or
a) it is uneconomical seismic forces is
b) it cannot carry the load safely a) 150
c) it is difficult to connect beams to the round b) 180
sections c) 250
d) all of the above d) 350
Ans: c Ans: c
25. The slenderness ratio of a column supported 30. According to IS:800, in the Merchant
throughout its length by a masonry wall is Rankine formula the value of imperfection index
a) zero (n) is
b) 10 a) 1.0
c) 100 b) 1.4
d) infinity c) 1.8
Ans: a d) 2.0
26. According to IS Specifications, the effective Ans: b
length of a column effectively held in position at 31. The best arrangement to provide unified
both behaviour in built up steel columns is by
ends and restrained in direction at one end is a) lacing
taken as b) battening
a) 0.67 L c) tie plates
b) 0.8 L d) perforated cover plates
c) L Ans: a
d) 1.5 L 32. If the 20 mm rivets are used in lacing bars,
Ans: b then the minimum width of lacing bar should be
27. The effective length of a battened strut a) 40mm
effectively held in position at both ends but not b) 60mm
restrained c) 80mm
in direction is taken as d) 100mm
a) 1.8 L Ans: b
b) L 33. The use of tie plates in laced columns is
c) 1.1 L a) prohibited
d) 1.5 L b) not prohibited
Ans: c c) permitted at start and end of lacing system
28. The maximum slenderness ratio of a only
compression member carrying both dead and d) permitted between two parts of the lacing
superimposed Ans: c
load is 34. Lacing bars in a steel column should be
a) 180 designed to resist
b) 200 a) bending moment due to 2.5% of the column
c) 250 load
b) shear force due to 2.5% of the column load c) 145
c) 2.5% of the column load d) 180
d) both (a) and (b) Ans: c
Ans: b 40. Economical depth of a plate girder
35. Angle of inclination of the lacing bar with corresponds to
the longitudinal axis of the column should a) minimum weight
preferably b) minimum depth
be between c) maximum weight
a) 10° to 30° d) minimum thickness of web
b) 30° to 40° Ans: a
c) 40° to 70° 41. Shear buckling of web in a plate girder is
d) 90° prevented by using
Ans: c a) vertical intermediate stiffener
36. Battening is preferable when the b) horizontal stiffener at neutral axis
i) column carries axial load only c) bearing stiffener
ii) space between the two main components is d) none of the above
not very large Ans: a
iii) column is eccentrically loaded The correct 42. Horizontal stiffener in a plate girder is
answer is provided to safeguard against
a) only (i) a) shear buckling of web plate
b) only (iii) b) compression buckling of web plate
c) (i) and (ii) c) yielding
d) (ii) and (iii) d) all of the above
Ans: c Ans: b
37. The effective length of a battened column is 43. Minimum thickness of web in a plate girder,
increased by when the plate is accessible and also exposed to
a) 5% weather, is
b) 10% a) 5 mm
c) 15% b) 6 mm
d) 20% c) 8 mm
Ans: b d) 10 mm
38. The overlap of batten plates with the main Ans: b
members in welded connections should be more 44. The web crippling due to excessive bearing
than stress can be avoided by
a) 3t a) increasing the web thickness
b) 4t b) providing suitable stiffeners
c) 6t c) increasing the length of the bearing plates
d) 8t d) none of the above
where t = thickness of the batten plate Ans: c
Ans: b 45. As per IS : 800, for compression flange, the
39. The slenderness ratio of lacing bars should outstand of flange plates should not exceed
not exceed a) 121
a) 100 b) 161
b) 120 c) 201
d) 251 The correct answer is
where t = thickness of thinnest flange plate a) only (i)
Ans: b b) both (i) and (ii)
46. Intermediate vertical stiffeners in a plate c) both (i) and (iii)
girder need be provided if the depth of web d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
exceeds Ans: c
a) 501 52. Rivets connecting flange angles to cover
b) 851 plates in a plate girder are subjected to
c) 200 t a) horizontal shear only
d) 2501 b) vertical load only
where t is thickness of web c) both (a) and (b)
Ans: b d) none of the above
47. Bearing stiffener in a plate girder is used to Ans: a
a) transfer the load from the top flange to the 53. The maximum spacing of vertical stiffeners
bottom one is
b) prevent buckling of web a) 1.33 d
c) decrease the effective depth of web b) 1.25 d
d) prevent excessive deflection c) 1.5 d
Ans: b d) 1.75 d
48. The forces acting on the web splice of a plate where d is the distance between flange angles
girder are Ans: c
a) axial forces 54. The range of economical spacing of trusses
b) shear and axial forces varies from
c) shear and bending forces a) L/3 to L/5
d) axial and bending forces b) L/4to2L/5
Ans: c c) L/3 to L/2
49. Gantry girders are designed to resist d) 2L/5 to 3L/5 where L is span
a) lateral loads Ans: a
b) longitudinal loads and vertical loads 55. The maximum permissible span of asbestos
c) lateral, longitudinal and vertical loads cement sheets is
d) lateral and longitudinal loads a) 650 mm
Ans: c b) 810 mm
50. Minimum spacing of vertical stiffeners is c) 1250 mm
limited to d) 1680 mm
a) d/4 Ans: d
b) d/3 56. Normally, the angle of roof truss with
c) d/2 asbestos sheets should not be less than
d) 2d/3 a) 26’/2°
where d is the distance between flange angles b) 30°
Ans: b c) 35°
51. Bearing stiffeners are provided at d) 40°
i) the supports Ans: b
ii) the mid span 57. To minimize the total cost of a roof truss, the
iii) the point of application of concentrated loads ratio of the cost of truss to the cost of purlins
shall c) ± 0.7
be d) 0
a) 1 Ans: c
b) 2 63. The basic wind speed is specified at a height
c) 3 ‘h’ above mean ground level in an open terrain.
d) 4 The
Ans: b value of’h’ is
58. Generally the purlins are placed at the panel a) 10 m
points so as to avoid b) 20 m
a) axial force in rafter c) 25 m
b) shear force in rafter d) 50 m
c) deflection of rafter Ans: a
d) bending moment in rafter 64. The risk coefficient k, depends on
Ans: d a) mean probable design life of structures
59. For the buildings having a low permeability, b) basic wind speed
the internal wind pressure acting normal to the c) both (a) and (b)
wall d) none of the above
and roof surfaces is taken as Ans: c
a) zero 65. The external wind pressure acting on a roof
b) ±0.2p depends on
c) ± 0.5 p a) degree of permeability of roof
d) ±0.7p b) slope of roof
where p is basic wind pressure c) both (a) and (b)
Ans: b d) none of the above
60. The relation between intensity of wind Ans: b
pressure p and velocity of wind V is taken as 66. Area of openings for buildings of large
a) pa V permeability is more than
b) paV2 a) 10% of wall area
c) p a (1/V) b) 20% of wall area
d) paV/2 c) 30% of wall area
Ans: b d) 50% of wall area
Design of Steel Structures Interview Questions Ans: b
61. The live load for a sloping roof with slope 67. As per IS : 875, for the purposes of
15°, where access is not provided to roof, is specifying basic wind velocity, the country has
taken as been divided
a) 0.65 kN/m2 into
b) 0.75 kN/m2 a) 4 zones
c) 1.35 kN/m2 b) 5 zones
d) 1.50 kN/m2 c) 6 zones
Ans: a d) 7 zones
62. The internal pressure coefficient on walls for Ans: c
buildings with large permeability is taken as 68. The number of seismic zones in which the
a) ± 0.2 country has been divided are
b) ±0.5 a) 3
b) 5 b) horizontal, shear due to wind or earthquake +
c) 6 2.5% of column loads
d) 7 c) column loads + 2.5% of horizontal shear due
Ans: b to wind or earthquake
69. Minimum pitch provided in riveted steel d) column loads + full horizontal shear due to
tanks is wind or earthquake
a) 1.5 d Ans: b
b) 2.0 d 75. The minimum thickness of plates in a steel
c) 2.5 d stack should be
d) 3.0 d a) 4 mm
where d is diameter of rivets b) 5 mm
Ans: d c) 6 mm
70. The allowable tensile stress in structural d) 8 mm
mild steel plates for steel tank is assumed as Ans: c
a) 95.0 MPa on net area 76. Maximum pitch of rivets, used in steel
b) 105.5 MPa on net area stacks, is limited to
c) 105.5 MPa on gross area a) 6t
d) 150.0 MPa on gross area b) 101
Ans: b c) 121
71. Steel tanks are mainly designed for d) 161
a) weight of tank where t is thickness of thinner plate being
b) wind pressure connected
c) water pressure Ans: b
d) earthquake forces 77. The diameter of base of conical flare of a
Ans: c steel stack is
72. Which of the following sections should a) less than d
preferably be used at places where torsion b) equal to d
occurs ? c) more than d
a) angle section d) any of the above
b) channel section where d is the diameter of the cylindrical part
c) box type section Ans: c
d) any of the above 78. Hudson’s formula gives the dead weight of a
Ans: c truss bridge as a function of
73. The capacity of the smallest pressed steel a) bottom chord area
tank is b) top chord area
a) 1000 litre c) effective span of bridge
b) 1650 litre d) heaviest axle load of engine
c) 1950 litre Ans: a
d) 2450 litre 79. If the loaded length of span in meters of a
Ans: c railway steel bridge carrying a single track is 6
74. The bracing between two columns of a steel m, then
tank will be designed to resist impact factor is taken as
a) horizontal shear due to wind or earthquake a) 0
only b) 0.5
c) between 0.5 and 1.0 d) 50% of the top panel wind load to bottom
d) 1.0 bracing
Ans: c Ans: d
80. If the floor is supported at or near the bottom 85. Study the following statements.
but top chords of a bridge are not braced, then i) Top lateral bracing prevents the sidesway
the buckling of the chord.
bridge is called ii) Sway bracing keeps the rectangular shape of
a) deck type the bridge cross-section.
b) through type iii) Sway bracing transfers the load from top of
c) half through type end posts to bearings.
d) double deck type The correct answer is
Ans: c a) only (i)
81. The centrifugal force due to curvature of b) both (i) and (ii)
track is assumed to act on the bridge at a height c) both (i) and (iii)
of d) all (i), (ii) and (iii)
a) 1.23 m above the rail level Ans: b
b) 1.50 m above the rail level 86. The bracing provided in the plane of end
c) 1.83 m above the rail level posts is called
d) 2.13 m above the rail level a) sway bracing
Ans: c b) portal bracing
82. The effect of racking forces is considered in c) top lateral bracing
the design of d) bottom lateral bracing
i) lateral braces Ans: b
ii) chord members 87. compression force in two end posts The pin
The correct answer is of a rocker bearing in a bridge is designed for
a) only (i) a) bearing and shear
b) only (ii) b) bending and shear
c) both (i) and (ii) c) bearing and bending
d) none of the above d) bearing, shear and bending
Ans: a Ans: d
83. The portal bracing in a truss bridge is used to 88. The least dimension in case of a circular
a) transfer load from top of end posts to bearings column of diameter D is taken as
b) keep the rectangular shape of the bridge a) 0.5 D
cross-section b) 0.68 D
c) stiffen the structure laterally c) 0.88 D
d) prevent the sidesway buckling of top chord d) D
Ans: a Ans: c
84. The sway bracing is designed to transfer 89. In case of timber structures, the form factor
a) 2Vi % of the top panel wind load to bottom for solid circular cross-section is taken as
bracing a) 1.18
b) 10% of the top panel wind load to bottom b) 1.414
bracing c) 1.67
c) 25% of the top panel wind load to bottom d) 1.81
bracing Ans: a
90. In case of timber structures, the simple c) mechanism and plastic moment conditions
bending formula M = fz may be applied for d) equilibrium condition only
a) rectangular beams up to 300 mm depth Ans: b
b) all rectangular beams 96. The mechanism method of plastic analysis
c) solid circular beams only satisfies
d) all square cross-section beams a) equilibrium and mechanism conditions
Ans: a b) equilibrium and plastic moment conditions
91. The elastic strain for steel is about c) mechanism and plastic moment conditions
a) 1/12 of strain at the initiation of strain d) equilibrium condition only
hardening and about 1/120 of maxi-mum strain Ans: a
b) 1/2 of strain at the initiation of strain 97. Load factor is
hardening and about 1/12 of maxi-mum strain a) always equal to factor of safety
c) 1/12 of strain at the initiation of strain b) always less than factor of safety
hardening and 1/200 of maximum strain c) always greater than factor of safety
d) 1/24 of strain at the initiation of strain d) sometimes greater than factor of safety
hardening and about 1/200 of maximum strain Ans: c
Ans: c 98. The ratio of plastic section modulus to
92. The mechanism method and the statical elastic section modulus
method give a) is equal to 1
a) lower and upper bounds respectively on the b) is always less than 1
strength of structure c) is always greater than 1
b) upper and lower bounds respectively on the d) can be less than 1
strength of structure Ans: c
c) lower bound on the strength of structure 99. Other conditions being same, the load factor
d) upper bound on the strength of structure in indeterminate structures is
Ans: b a) equal to load factor in determinate structures
93. The moment-curvature relation at a plastic b) more than the load factor in determinate
hinge is structures
a) linear c) less than the load factor in determinate
b) parabolic structures
c) constant moment for all curvatures d) unpredictable
d) constant curvature for all moments Ans: b
Ans: c 100. Which of the following conditions is to be
94. Shape factor is a property which depends satisfied both in elastic and plastic analysis ?
a) only on the ultimate stress of the material a) equilibrium condition
b) only on the yield stress of the material b) yield condition
c) only on the geometry of the section c) plastic moment condition
d) both on the yield stress and ultimate stress of d) mechanism condition
material Ans: a
Ans: c
95. The statical method of plastic analysis
satisfies
a) equilibrium and mechanism conditions
b) equilibrium and plastic moment conditions
You might also like
- Steel SSC 10 Yr QuestionDocument47 pagesSteel SSC 10 Yr Questionzahoor balochNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering MCQ'S: Ans. (A)Document4 pagesCivil Engineering MCQ'S: Ans. (A)Nishikanta MondalNo ratings yet
- 180 Top Most Concrete Technology and Design of Concrete Structures Interview Questions Civil Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersDocument29 pages180 Top Most Concrete Technology and Design of Concrete Structures Interview Questions Civil Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersSheezan KhanNo ratings yet
- MCQ's Concrete Technology - Fawad AhmadDocument10 pagesMCQ's Concrete Technology - Fawad AhmadFawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Building Technology and Architectural PlanningDocument39 pagesBuilding Technology and Architectural PlanningKalyani ingoleNo ratings yet
- Objective Civil EngineeringDocument3 pagesObjective Civil EngineeringBiplab Banerjee100% (2)
- 1500-MCQs WITH Answer (Civil Engg.)Document132 pages1500-MCQs WITH Answer (Civil Engg.)karpagavalliNo ratings yet
- PSC Assistant Engg2016Document22 pagesPSC Assistant Engg2016Santanu Mazumdar100% (4)
- MCQ For Acoustics Glass ArchitectureDocument3 pagesMCQ For Acoustics Glass ArchitectureASWIN KUMAR N SNo ratings yet
- Test Paper 1 (Concrete Technology)Document7 pagesTest Paper 1 (Concrete Technology)atulqweNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014 CiviL Answer KeyDocument37 pagesGATE 2014 CiviL Answer KeyJaga NathNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics and FoundationDocument64 pagesSoil Mechanics and Foundationmir imran100% (1)
- Answer Key For Tamil Nadu Town and Country Planning Subordinate Service Exam Held On 22.12.2018Document35 pagesAnswer Key For Tamil Nadu Town and Country Planning Subordinate Service Exam Held On 22.12.2018surabhiNo ratings yet
- MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) Semester - 6 Subject-Advanced Construction TechniquesDocument19 pagesMCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) Semester - 6 Subject-Advanced Construction TechniquesSandip DakleNo ratings yet
- MCQ Module 1 On Thin Cylindrical ShellsDocument13 pagesMCQ Module 1 On Thin Cylindrical ShellsYogendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Software Application - 21CV582Document32 pagesSoftware Application - 21CV582Surendra PNo ratings yet
- BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING MCQsDocument18 pagesBASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING MCQsVimal PalNo ratings yet
- CET308 - Module 5Document26 pagesCET308 - Module 5Sajil KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics 2110013: "GTU Previous Year MCQ"Document5 pagesEngineering Graphics 2110013: "GTU Previous Year MCQ"daivee kmNo ratings yet
- KMC 2018 PDFDocument11 pagesKMC 2018 PDFKailash Chaudhary100% (2)
- Highway Engineering MCQDocument53 pagesHighway Engineering MCQBalram MandalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Civil EngineeringDocument198 pagesIntroduction To Civil EngineeringMohan MohamoudNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering - AEE - CRPQsDocument35 pagesEnvironmental Engineering - AEE - CRPQsSureshKonamNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Ae ExamDocument13 pagesTNPSC Ae ExamnirmalramyaNo ratings yet
- Estimating and Costing.1-10Document10 pagesEstimating and Costing.1-10sukritidan1990No ratings yet
- Ret 2 MCQDocument29 pagesRet 2 MCQRohit Ramesh KaleNo ratings yet
- TRB - 2017 - Final Key - Pyramid IAS Academy-1Document10 pagesTRB - 2017 - Final Key - Pyramid IAS Academy-1Er Jeya PrakashNo ratings yet
- Draughtsman Civil - Semester 4 Module 1 - Roads: Reviewed and Updated On: 01 November 2019 Version 1.1Document24 pagesDraughtsman Civil - Semester 4 Module 1 - Roads: Reviewed and Updated On: 01 November 2019 Version 1.1Abhijith JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Sample MCQDocument23 pagesCivil Engineering Sample MCQHema raghavNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering2Document5 pagesEnvironmental Engineering2ajaydevmalikNo ratings yet
- Civil Engg 2018Document21 pagesCivil Engg 2018Abhishek ShahiNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering MCQ'sDocument8 pagesCivil Engineering MCQ'sNISHIKANTA MONDALNo ratings yet
- HIGHWAY Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesHIGHWAY Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsleGion100% (1)
- RCC MCQ 2Document4 pagesRCC MCQ 2Prashanth SunagarNo ratings yet
- Environmental Engineering - 2Document60 pagesEnvironmental Engineering - 2Ubai DullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Road Cross Section ElementsDocument46 pagesChapter 1 Road Cross Section ElementsGopiKrishna100% (1)
- Design of Steel Structures Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For Freshers and Experienced PDF Free Download - Preparation For EngineeringDocument17 pagesDesign of Steel Structures Multiple Choice Questions and Answers For Freshers and Experienced PDF Free Download - Preparation For EngineeringSaran Raj KurubaNo ratings yet
- Airport Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument1 pageAirport Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsengineeringmcqsNo ratings yet
- Building ServicesDocument2 pagesBuilding ServicesSaddaqatNo ratings yet
- Multiple QuestionsDocument53 pagesMultiple Questionsdonald.dadzieNo ratings yet
- Ar6015 - Spa-Mcq BankDocument17 pagesAr6015 - Spa-Mcq BankSrilakshmi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structures Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument1 pageDesign of Steel Structures Multiple Choice Questionsengineeringmcqs100% (1)
- MCQDocument8 pagesMCQShubham100% (1)
- MCQ ConcreteDocument4 pagesMCQ ConcreteNeha ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Old Q-FinalDocument48 pagesOld Q-Finalkapil NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Stair Case MCQDocument7 pagesStair Case MCQJayesh JagtapNo ratings yet
- Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit 1Document60 pagesBasic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Unit 1namdeo_anantNo ratings yet
- Arches MCQDocument9 pagesArches MCQjampanivenkat8No ratings yet
- Concrete Technology MCQ Civil EngineeringDocument11 pagesConcrete Technology MCQ Civil EngineeringAjay PawarNo ratings yet
- 2 PSC Guide For Civil Engineers, DeojiDocument708 pages2 PSC Guide For Civil Engineers, DeojiLbs Dolidar100% (2)
- Civil Mini Project DivyaKamathDocument63 pagesCivil Mini Project DivyaKamathJanaki Vamaraju100% (1)
- Engineering DrawingDocument16 pagesEngineering DrawingSabeeh HasnainNo ratings yet
- Ce 405: Environmental Engineering-I: Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesCe 405: Environmental Engineering-I: Important QuestionsVahid AbdNo ratings yet
- Surveying 2 Jan 2014Document2 pagesSurveying 2 Jan 2014Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- SDD Steel+Document16 pagesSDD Steel+jugalpawar7No ratings yet
- 120 TOP DESIGN of STEEL STRUCTURES Multiple ChoiceDocument35 pages120 TOP DESIGN of STEEL STRUCTURES Multiple ChoiceQaria shehzadi100% (1)
- MCQ On Design of Steel StructuresDocument2 pagesMCQ On Design of Steel StructuresNikhil WananjeNo ratings yet
- LacingDocument5 pagesLacinganon_57992799No ratings yet
- Bits RCCDocument5 pagesBits RCCalekhya gollapudiNo ratings yet
- CE Exit Exam OTDocument21 pagesCE Exit Exam OTOmen JettNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesSoil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsleGionNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument8 pagesFLUID MECHANICS Multiple Choice QuestionsleGion0% (1)
- HIGHWAY Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesHIGHWAY Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsleGion100% (1)
- Building Materials and Construction Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument14 pagesBuilding Materials and Construction Multiple Choice QuestionsleGionNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL Engineering Objective Type QuestionsDocument14 pagesENVIRONMENTAL Engineering Objective Type QuestionsleGion100% (2)
- Peculiarity of Physical and Axial Compressive Strength of Hand and Machine Made First Class Bricks Found in Different Parts of ManipurDocument7 pagesPeculiarity of Physical and Axial Compressive Strength of Hand and Machine Made First Class Bricks Found in Different Parts of ManipurleGionNo ratings yet
- Characteristic Strength of Machine Made First Class Bricks Found in Different Parts of ManipurDocument7 pagesCharacteristic Strength of Machine Made First Class Bricks Found in Different Parts of ManipurleGionNo ratings yet
- 6991 1725 01a - MO Wireline Drill Rod Leaflet Low Res - tcm836-1766102 PDFDocument12 pages6991 1725 01a - MO Wireline Drill Rod Leaflet Low Res - tcm836-1766102 PDFvangoetheNo ratings yet
- Study On Concrete With Human Hair Fibre Reinforced ConcreteDocument1 pageStudy On Concrete With Human Hair Fibre Reinforced ConcreteantonytechnoNo ratings yet
- PSA Valves CriticalDesignFeatures MARKEDDocument41 pagesPSA Valves CriticalDesignFeatures MARKEDdj22500No ratings yet
- Htls ConductorDocument65 pagesHtls ConductorSaurav Gautam0% (1)
- HD5050EADocument2 pagesHD5050EARobert KočevarNo ratings yet
- Dangote CementDocument23 pagesDangote CementRobel FirewNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURE REPORT OF BIRATNAGAR (28th-DEC-2020)Document50 pagesSTRUCTURE REPORT OF BIRATNAGAR (28th-DEC-2020)Kshitiz Lamichhane100% (1)
- BBM 10103 Material TechnologyDocument34 pagesBBM 10103 Material TechnologyYury KunNo ratings yet
- Bohler PipelineDocument28 pagesBohler PipelinepreyeshNo ratings yet
- Ar010Document340 pagesAr010Maritza EnriquezNo ratings yet
- EN WalerDocument8 pagesEN WalervsnsfbNo ratings yet
- Bolt DesignDocument6 pagesBolt DesignKamlesh DalavadiNo ratings yet
- Technical Notes ENGDocument37 pagesTechnical Notes ENGDario Mamani VillrgasNo ratings yet
- Damage Assessment of Topping Furnaces Radiant Tubes and Creep Behaviour of ASTM A335 P5 SteelDocument9 pagesDamage Assessment of Topping Furnaces Radiant Tubes and Creep Behaviour of ASTM A335 P5 Steelkararangge outdoorNo ratings yet
- Standards Comparison Steels For Offshore StructuresDocument9 pagesStandards Comparison Steels For Offshore Structureshvdb72No ratings yet
- Design of RBS Connections For SpecialDocument51 pagesDesign of RBS Connections For SpecialSaeedNo ratings yet
- Materials: Bending Experiment and Mechanical Properties Analysis of Composite Sandwich Laminated Box BeamsDocument22 pagesMaterials: Bending Experiment and Mechanical Properties Analysis of Composite Sandwich Laminated Box BeamsJulendra AriatedjaNo ratings yet
- MFE004Document34 pagesMFE004Logic ManjuNo ratings yet
- A Theory For Fatigue Failure Under Multiaxial Stress-Strain ConditionsDocument27 pagesA Theory For Fatigue Failure Under Multiaxial Stress-Strain ConditionsFabián Stark CatongaNo ratings yet
- Normal StressDocument4 pagesNormal StressGilbertNo ratings yet
- Linear Analysis of Concrete Frames Considering Joint FlexibilityDocument16 pagesLinear Analysis of Concrete Frames Considering Joint FlexibilityluffiM13No ratings yet
- Mathcad - PART II Ceiling (ICU) 20200602 (Update) - 2Document418 pagesMathcad - PART II Ceiling (ICU) 20200602 (Update) - 2BQ HeNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For PVelite Basic LevelDocument41 pagesTraining Manual For PVelite Basic LevelRajaram100% (1)
- WTanksDocument26 pagesWTanksestebanosorionovaNo ratings yet
- Indraratna Et Al. 2006Document13 pagesIndraratna Et Al. 2006giridharrajeshNo ratings yet
- OPGWDocument18 pagesOPGWGuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Rigid Pavement AASHTO 1993Document9 pagesRigid Pavement AASHTO 1993wiryaNo ratings yet
- Design of Aluminum Structure 1Document3 pagesDesign of Aluminum Structure 1Ray Coello100% (2)
- DTE Unit 1 MCQs (Keys Shafts and Couplings)Document6 pagesDTE Unit 1 MCQs (Keys Shafts and Couplings)Mannam Sarath Sarath100% (2)