Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Item Specification: Emission Control System
Item Specification: Emission Control System
Uploaded by
ZM OhnCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Juju Sundin, Sarah Murdoch-Juju Sundin's Birth Skills - Proven Pain-Management Techniques For Your Labour and Birth PDFDocument287 pagesJuju Sundin, Sarah Murdoch-Juju Sundin's Birth Skills - Proven Pain-Management Techniques For Your Labour and Birth PDFCamila BastosNo ratings yet
- HACCP Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesHACCP Multiple Choice Questionsaloke ganguly92% (12)
- Santa Fe-Service ManualDocument353 pagesSanta Fe-Service ManualAdam Pegiel89% (9)
- Toyota Cressida/Supra 7m Service ManualDocument98 pagesToyota Cressida/Supra 7m Service Manualmidgo100% (2)
- Manual Taller Kymco Xciting 400s INGLES PDFDocument426 pagesManual Taller Kymco Xciting 400s INGLES PDFRuben DiazNo ratings yet
- Engine K21 and K25 Engine FuelDocument19 pagesEngine K21 and K25 Engine FuelPablo Rojas Valenzuela100% (1)
- 7.1. Emission Control SystemDocument18 pages7.1. Emission Control SystemChristian Icaza SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- CVVTDocument50 pagesCVVTMoaed Kanbar94% (18)
- 2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual FLDocument10 pages2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual FLAndy DellingerNo ratings yet
- Herbs That Kill Cancer and HIVDocument6 pagesHerbs That Kill Cancer and HIVsilentweaponsquietwars100% (1)
- Item Specification: Emission Control SystemDocument20 pagesItem Specification: Emission Control SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Tucson Emission Control System 2.0Document19 pagesTucson Emission Control System 2.0wilder0l0pezNo ratings yet
- Ec Kia Soul 2014Document175 pagesEc Kia Soul 2014erick alexander hernandezNo ratings yet
- SM - 04 Tucson TL 2015+ 1.6L - Emission Control SystemDocument19 pagesSM - 04 Tucson TL 2015+ 1.6L - Emission Control Systemzozo0424No ratings yet
- Genesis 3.8L Section 8Document18 pagesGenesis 3.8L Section 8Nacho MowjiNo ratings yet
- Elantra 2.0 EC (137) G 2.0 MPIDocument23 pagesElantra 2.0 EC (137) G 2.0 MPIjoan velaNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument26 pagesEmission Control SystemnahomNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument21 pagesEmission Control Systemvesa hintikkaNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument21 pagesEmission Control SystemdanyNo ratings yet
- Elantra 91 Emission Control SystemDocument49 pagesElantra 91 Emission Control Systemahmad adelNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument17 pagesEmission Control SystemCesar GiraccaNo ratings yet
- Emissions Control SystemsDocument15 pagesEmissions Control SystemsTharsikan singamNo ratings yet
- 04-Emission Control SystemDocument28 pages04-Emission Control SystemangelNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument28 pagesEmission Control Systemsled novaNo ratings yet
- Continuously Variable Valve TimingDocument12 pagesContinuously Variable Valve TiminggamerpipeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Part D: Emission Control SystemsDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Part D: Emission Control SystemsJhon HancockNo ratings yet
- Emissions Control SystemDocument17 pagesEmissions Control SystemBrayan CatalanNo ratings yet
- 2GR-FE Emission ControlDocument23 pages2GR-FE Emission ControlLuks FernandezNo ratings yet
- p2 5S-FE+ENGINE+REPAIR+MANUALDocument19 pagesp2 5S-FE+ENGINE+REPAIR+MANUALMuhammad SafdarNo ratings yet
- 06 Sistema de Control de EmisionesDocument29 pages06 Sistema de Control de EmisionesmongongoNo ratings yet
- Santa Fe Service ManualDocument384 pagesSanta Fe Service ManualMihaita PrepelitaNo ratings yet
- 2AZ-FE Emission ControlDocument25 pages2AZ-FE Emission ControlLuks FernandezNo ratings yet
- Emision Control Sistem Kia PicantoDocument25 pagesEmision Control Sistem Kia PicantorohmanNo ratings yet
- EvapEmission PDFDocument8 pagesEvapEmission PDFpivillamilNo ratings yet
- 9Document80 pages9Namsa LABORATORIO100% (1)
- Emission Control SystemsDocument13 pagesEmission Control SystemsСергейУ-УNo ratings yet
- Fuel System Excel 87Document72 pagesFuel System Excel 87vpol25No ratings yet
- Ec (2jz-Gte) PDFDocument12 pagesEc (2jz-Gte) PDFAshokNo ratings yet
- 05 Emission ControlsDocument16 pages05 Emission ControlsvixentdNo ratings yet
- PCVDocument20 pagesPCVyared abebeNo ratings yet
- Partbook GA 5 - GA 15 Atlas CopcoDocument77 pagesPartbook GA 5 - GA 15 Atlas CopcoService PTNK33% (3)
- Emission ControlDocument26 pagesEmission ControllogammicNo ratings yet
- JourneyDocument194 pagesJourneyjuan carlos garciaNo ratings yet
- AIM:-Service Positive Crankcase Ventilation System: Practical - 3Document6 pagesAIM:-Service Positive Crankcase Ventilation System: Practical - 3saiyed amanNo ratings yet
- Intake Air SystemsDocument8 pagesIntake Air SystemsJosé AntonioNo ratings yet
- Sistema de Inyeccion Mono-JetronicDocument6 pagesSistema de Inyeccion Mono-JetronicDiego De La FuenteNo ratings yet
- Crdi BoshDocument61 pagesCrdi BoshIsmahan Ochi Noro100% (1)
- Fuel Evaporation SystemDocument9 pagesFuel Evaporation SystemToua YajNo ratings yet
- Basic Testing Pajero 1991Document12 pagesBasic Testing Pajero 1991nadaNo ratings yet
- 310-00C Fuel System - General Information - 5.0L 32V Ti-VCT/5.0L Ti-VCT V8 (308kW/418PS) 2016 MustangDocument30 pages310-00C Fuel System - General Information - 5.0L 32V Ti-VCT/5.0L Ti-VCT V8 (308kW/418PS) 2016 MustangJaciel LMNo ratings yet
- STC Oil Control Valve (Mechanical) - 5Document2 pagesSTC Oil Control Valve (Mechanical) - 5Parveen KashyapNo ratings yet
- QSK60 Familiarization - Compatibility ModeDocument68 pagesQSK60 Familiarization - Compatibility Modethainarime100% (1)
- Emisie Suzuki VL800Document6 pagesEmisie Suzuki VL800Crisan SorinNo ratings yet
- Section 2 EngineDocument14 pagesSection 2 EngineMarco OlivettoNo ratings yet
- DD15 CompressorDocument11 pagesDD15 CompressorarieNo ratings yet
- 4P GQ en 07Document0 pages4P GQ en 07aiigee100% (1)
- Fuel Control ValveDocument12 pagesFuel Control ValveALVARO OLACHICANo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Operator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingFrom EverandOperator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Coding and ProgrammingDocument59 pagesCoding and ProgrammingZM Ohn100% (1)
- Engine Management OverviewDocument73 pagesEngine Management OverviewZM Ohn100% (3)
- Fitting Instructions - Defender td5 SnorkelDocument7 pagesFitting Instructions - Defender td5 SnorkelZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Land Rover Bosch GS8.87 Transmission Management (D2 & RR P38)Document13 pagesLand Rover Bosch GS8.87 Transmission Management (D2 & RR P38)ZM OhnNo ratings yet
- D4 Maintenance Check Sheet - Discovery 4 (LA) All Models - UK EU - 10-11MY - KMDocument2 pagesD4 Maintenance Check Sheet - Discovery 4 (LA) All Models - UK EU - 10-11MY - KMZM Ohn100% (1)
- Replacement Replacement Replacement: Semcon JLR Owner Guide Ver 1.00 LANGUAGE: English-En MARQUE: Landrover ModelDocument7 pagesReplacement Replacement Replacement: Semcon JLR Owner Guide Ver 1.00 LANGUAGE: English-En MARQUE: Landrover ModelZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Restraint: Item Resistance ( )Document49 pagesRestraint: Item Resistance ( )ZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Nanocom Evolution TD5 Map Facility and GuideDocument2 pagesNanocom Evolution TD5 Map Facility and GuideZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Engine+Electrical+System+2 4LDocument53 pagesEngine+Electrical+System+2 4LZM Ohn100% (1)
- Tightening Torques Items N.M KGF.M LB-FT: 4 Wheel Drive (4WD) SystemDocument35 pagesTightening Torques Items N.M KGF.M LB-FT: 4 Wheel Drive (4WD) SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Item Specification: Emission Control SystemDocument20 pagesItem Specification: Emission Control SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Engine Electrical SystemDocument48 pagesEngine Electrical SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Heating, Ventilation and Air ConditioningDocument88 pagesHeating, Ventilation and Air ConditioningZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Item Specification: Steering SystemDocument29 pagesItem Specification: Steering SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Discovery II Valeo BCU ECU GuideDocument20 pagesDiscovery II Valeo BCU ECU GuideZM OhnNo ratings yet
- General InformationDocument21 pagesGeneral InformationZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Puma Defender Alm-EcuDocument11 pagesPuma Defender Alm-EcuZM Ohn100% (1)
- Suspension SystemDocument70 pagesSuspension SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Emotional WellnessDocument3 pagesEmotional Wellnesspaula_evangelista_3100% (1)
- Affective AssessmentDocument34 pagesAffective AssessmentEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures Covid 19: CIDESCO Sections, CIDESCO Schools CIDESCO MembersDocument14 pagesStandard Operating Procedures Covid 19: CIDESCO Sections, CIDESCO Schools CIDESCO MembersShaji VkNo ratings yet
- FA1 - Mole CalculationsDocument3 pagesFA1 - Mole CalculationsDenjiNo ratings yet
- TEST 2 06530622 Q eDocument16 pagesTEST 2 06530622 Q eIG LibraryNo ratings yet
- RTL Critical Thinking Skills e LearningDocument50 pagesRTL Critical Thinking Skills e LearningElías Tamez100% (1)
- Principles of NMR Protein Spectroscopy Frequencies and SpectraDocument14 pagesPrinciples of NMR Protein Spectroscopy Frequencies and SpectrakisanthombareNo ratings yet
- Performance Chemicals For Enhanced Oil RecoveryDocument6 pagesPerformance Chemicals For Enhanced Oil RecoveryMiguel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Field Guide Alien Species in European Forests PDFDocument132 pagesField Guide Alien Species in European Forests PDFIonut MarianNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Kelas 9 MtsDocument5 pagesSoal Uts Kelas 9 Mtsindah sNo ratings yet
- A-GIS-based-methodology-for-safe-site-selection-of Building in A Hilly RegionDocument13 pagesA-GIS-based-methodology-for-safe-site-selection-of Building in A Hilly RegionArch K3NNo ratings yet
- Lumax LED-Presentation PDFDocument31 pagesLumax LED-Presentation PDFSalman HashmiNo ratings yet
- Solvent Evaporation: Fast, Reliable and AffordableDocument24 pagesSolvent Evaporation: Fast, Reliable and Affordablepandiya rajanNo ratings yet
- Iccec CCCDocument22 pagesIccec CCCpdanishNo ratings yet
- 2018-09-10 in Touch WeeklyDocument76 pages2018-09-10 in Touch WeeklyAnonymous QfXnHbTRzNo ratings yet
- P&G Value Pricing PapaerDocument1 pageP&G Value Pricing PapaerkkktaxNo ratings yet
- Locking Plates - Advantages & Indications 1-11Document27 pagesLocking Plates - Advantages & Indications 1-11nishantsinghbmeNo ratings yet
- Nestle: Nestlé's Mission Statement (R1)Document11 pagesNestle: Nestlé's Mission Statement (R1)Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Dinner MenuDocument3 pagesDinner MenueatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- 03 PS200 Quick OpnDocument2 pages03 PS200 Quick OpnPopa VasileNo ratings yet
- SmartLogger3000 User Manual PDFDocument192 pagesSmartLogger3000 User Manual PDFJ Armando Gastelo RoqueNo ratings yet
- Notice: Ocean Transportation Intermediary Licenses: InterCaribbean Cargo, Inc., Et Al.Document2 pagesNotice: Ocean Transportation Intermediary Licenses: InterCaribbean Cargo, Inc., Et Al.Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Senate Bill 897v8 NC FY 2010-11 Budget As RatifiedDocument189 pagesSenate Bill 897v8 NC FY 2010-11 Budget As RatifiedBobby CogginsNo ratings yet
- Societal MarketingDocument7 pagesSocietal Marketingraje.jk86% (14)
- Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA)Document5 pagesLatent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA)Fina Ahmad FitrianaNo ratings yet
- 11th Mock Test Municipal & Town OfficerDocument5 pages11th Mock Test Municipal & Town OfficerAnam BalochNo ratings yet
- Artikel 8 - (CURRICULUM EVALUATION)Document12 pagesArtikel 8 - (CURRICULUM EVALUATION)Kikit8No ratings yet
Item Specification: Emission Control System
Item Specification: Emission Control System
Uploaded by
ZM OhnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Item Specification: Emission Control System
Item Specification: Emission Control System
Uploaded by
ZM OhnCopyright:
Available Formats
Emission Control System
Description
Emissions Control System consists of three major systems.
• Crankcase Emission Control System prevents blow-by gas from releasing into the atmosphere. This system
recycles gas back into the intake manifold (Closed Crankcase Ventilation Type).
• Evaporative Emission Control System prevents evaporative gas from releasing into the atmosphere. This system
burns gas at appropriate engine operating condition after gathering it in the canister.
• Exhaust Emission Control System converts the three pollutants [hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO),
and oxides of nitrogen (NOx)] into harmless substances by using the 3-way catalytic converter.
Emission Control System
Specifications
Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV)
Specification
Item Specification
Coil Resistance (Ω) 22.0 ~ 26.0 [20°C(68°F)]
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS)
Type: Piezo-Resistive Pressure Sensor
cardiagn.com
Specification
Pressure (kPa) Output Voltage (V)
-3.75 (-0.038, -
4.5
15.05)
0 1.5
+1.25 (0.013, 5.02) 0.5
Canister Close Valve (CCV)
Specification
Item Specification
19.8 ~ 21.8
Coil Resistance (Ω)
[20°C(68°F)]
Tightening Torques
Item kgf.m N.m lb-ft
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Valve installation 0.8 ~ 1.2 7.8 ~ 11.8 5.8 ~ 8.7
Emission Control System
Troubleshooting
Symptom Suspect area
Engine will not start or stuggle to start Vapor hose damaged or disconnected
Engine stuggle to start Malfunction of the Purge Control Solenoid Valve
Vapor hose damaged or disconnected
Rough idle or engine stalls
Malfunction of the PCV valve
Rough idle Malfunction of the Evaporative Emission Control System
Excessive oil consumption Positive crankcase ventilation line clogged
Emission Control System
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
Schematic Diagram
cardiagn.com
Emission Control System
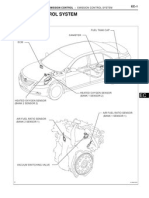
Components Location
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
cardiagn.com
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
1. PCV Valve 6. Fuel Level Sender (FLS)
2. Canister 7. Fuel Tank Air Filter
3. Purge Control Solenoid Valve 8. Catalytic Converter [WCC, Bank 1]
(PCSV) 9. Catalytic Converter [WCC, Bank 2]
4. Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS) 10. Catalytic Converter [UCC]
5. Canister Close Valve (CCV)
1. PCV Valve 2. Canister
4. Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS)
3. Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV)
6. Fuel Level Seder (FLS)
cardiagn.com
5. Canister Close Valve (CCV) 8. Catalytic Converter [WCC, Bank 1]
7. Fuel Tank Air Filter
9. Catalytic Converter [WCC, Bank 2] 10. Catalytic Converter [UCC]
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
Emission Control System
Schematic Diagram
cardiagn.com
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
Emission Control System
Inspection
1. After disconnecting the vapor hose from the PCV valve, remove the PCV valve.
2. Reconnect the PCV valve to the vapor hose.
3. Inspect the PCV vlave operation.
(1) Run the engine at idle.
(2) Put a finger on the open end of the PCV valve.
(3) Make sure that intake manifold vaccum can be felt.
The plunger inside the PCV valve will move back and forth at
vacuum.
cardiagn.com
4. If the vacuum is not felt, clean or replace the vapor hose.
Emission Control System
Operation Principle
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
Emission Control System
Removal
1. Disconnect the vapor hose (A).
2. Remove the PCV valve (B).
Inspection
1. Insert a thin stick (A) into the PCV valve (B) from the threaded side to check that the plunger moves.
cardiagn.com
If the plunger does not move (PCV valve is clogged), clean or replace the valve.
Installation
1. Installation is reverse of removal.
PCV Valve installation :
7.8 ~ 11.8 N.m (0.8 ~ 1.2 kgf.m, 5.8 ~ 8.7 lb-ft)
Emission Control System
Description
Evaporative Emission Control System prevents fuel vapor stored in fuel tank from vaporizing into the atmosphere.
When the fuel evaporates in the fuel tank, the vapor passes through vent hoses or tubes to canister filled with
charcoal. The canister temporarily holds the vapor in the charcoal. If ECM determines to draw the gathered vapor
into the combustion chambers during certain operating conditions, it will vacuum into intake manifold.
Evaporative System Monitoring
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
cardiagn.com
Evaporative And ORVR Emission Control System
This system consists of below items;
- Fill vent valve
- Fuel shut-off valve
- Fuel cut valve (for roll over)
- Two way valve (pressure/vacuum relief)
- Fuel liquid/vapor separator which is installed beside the filler pipe
- Charcoal canister which is mounted under the rear floor LH side member and protector
- Tubes and miscellaneous connections
While refueling, ambient air is drawn into the filler pipe so as not to emit fuel vapors in the air. The fuel vapor in the
tank is then forced to flow into the canister via the fill vent valve. The fuel liquid/vapor separator isolates liquid fuel
and passes the pure vapor to the charcoal canister.
While the engine is operating, the trapped vapor in the canister is drawn into the intake manifold and then into the
engine combustion chamber. According to this purge process, the charcoal canister is purged and recovers its
absorbing capability.
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
1. Fuel Filler Cap 8. Evaporative Hose
cardiagn.com
2. Fuel Filler Pipe 9. Canister
3. Fuel Shut-OFF Valve 10. Canister Close Valve (CCV)
4. Fuel Tank 11. Fuel Feed Line
5. ORVR Valve 12. Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor
6. 2-Way & Cut Valve (FTPS)
7. Evaporative Hose 13. Purge Control Solenoid
Valve (PCSV)
Emission Control System
Schematic Diagram
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
cardiagn.com
Canister
Canister is filled with charcoal and absorbs evaporated vapor in fuel tank. The gathered fuel vapor in canister is
drawn into the intake manifold by the ECM/PCM when appropriate conditions are set.
Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV)
Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV) is installed in the passage connecting canister and intake manifold. It is a duty
type solenoid valve and is operated by ECM/PCM signal.
To draw the absorbed vapor into the intake manifold, the ECM/PCM will open the PCSV, otherwise the passage
remains closed.
Fuel Filler Cap
A ratchet tightening device on the threaded fuel filler cap reduces the chances of incorrect installation, seals the fuel
filler. After the gasket on the fuel filler cap and the fill neck flange make contact, the ratchet produces a loud clicking
noise indicating the seal has been set.
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS)
The Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS) is an integral part of the monitoring system. The FTPS checks Purge Control
Solenoid Valve (PCSV) operation and leaks in the Evaporative Emission Control System by monitoring pressure and
vacuum level in the fuel tank during PCSV operating cycles.
Canister Close Valve (CCV)
The Canister Close Valve (CCV) is located between the canister and the fuel tank air filter. It closes off the air inlet
to the canister for the Evaporative Emissions System and also prevents fuel vapors from escaping from the Canister
when the vehicle is not operating.
Evaporative System Monitoring
Evaporative Emission Control Monitoring System consists of fuel vapor generation, evacuation, and leakage check
step. At first, the OBD-II system checks if vapor generation due to fuel temperature is small enough to start
monitoring. Then it evacuates the evaporative system by means of PCSV with ramp in order to maintain a certain
vacuum level. The final step is to check if there is vacuum loss by any leakage of the system.
Vapor Generation Checking
During stabilization period, the PCSV and the CCV are closed. The system pressure is measured as starting pressure
(DP_A). After a certain defined period (T1), the system pressure (DP_B) is measured again and the difference from
the starting pressure is calculated. If this difference (DP_B - DP_A) is bigger than a threshold, there should be
excessive vapor and the monitor is aborted for next checking. On the contrary, if the difference is lower than another
negative threshold, PCSV is regarded as malfunction such as clogged at open position.
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
Evacuation
PCSV is opened with a certain ramp for the pressure to reach down to a certain level. If pressure can’t be lowered
below a threshold, the system is regarded as fuel cap-opened or having a large leakage.
Leaking Checking
PCSV is closed and the system waits for a period to get stabilized pressure. During checking period (T2), the system
measures the beginning and the end of the system pressure (DP_C, DP_D). The diagnosis value is the pressure
difference corrected by natural vapor generation (DP_B - DP_A) rate from the vapor generation checking step.
Components Location
cardiagn.com
1. Purge Control Solenoid Valve 4. Canister Close Valve (CCV)
(PCSV) 5. Canister
2. Vapor line 6. Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS)
3. Fuel tank air filter
Emission Control System
Removal
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF and disconnect the battery negative (-) cable.
2. Lift the vehicle.
3. Disconnect the canister close valve connector (A).
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
4. Disconnect the ventilation tube quick-connector (B) from the fuel tank air filter and canister close valve.
5. Disconnect the vapor tube quick-connector (A).
6. Remove the canister assembly bracket (D) after removing the mounting bolts (B) and nut (C).
cardiagn.com
7. Remove the canister braket (B) installation bolt (A).
8. Remove the fuel tank air filter & canister close valve assembly (A) after rotating it in the direction of the arrow in
the figure.
Inspection
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
1. Check for the following items visually.
A. Cracks or leakage of the canister
B. Loose connection, distortion, or damage of the vapor hose/tube
A: Canister ↔ Atmosphere
B: Canister ↔ Fuel Tank
C: Canister ↔ Intake Manifold
Installation
1. Install in the reverse order of removal.
Emission Control System
cardiagn.com
Description
A ratchet tightening device on the threaded fuel filler cap reduces the chances of incorrect installation, which would
seal the fuel filler. After the gasket on the fuel filler cap and the filler neck flange contact each other, the ratchet
produces a loud clicking noise indicating the seal has been set.
1. Cover 5. Spring
2. Torsion spring 6. Plate seal
3. Retainer 7. Vacuum valve
4. Gasket seal 8. Spring
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
Emission Control System
Removal
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF and disconnect the battery negative (-) cable.
2. Lift the vehicle.
3. Disconnect the canister close valve connector (A).
4. Disconnect the ventilation tube quick-connector (B) from the fuel tank air filter and canister close valve.
5. Disconnect the vapor tube quick-connector (A).
cardiagn.com
6. Remove the canister assembly bracket (D) after removing the mounting bolts (B) and nut (C).
7. Remove the canister braket (B) installation bolt (A).
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
8. Remove the fuel tank air filter & canister close valve assembly (A) after rotating it in the direction of the arrow in
the figure.
9. Release the lever (A), and then separate the canister close valve (B) from the fuel tank air filter (C) after rotating
it in the direction of the arrow in the figure.
Installation
• Install the component with the specified torques.
cardiagn.com
• Note that internal damage may occur when the component is dropped. In this case, use it after inspecting.
1. Install in the reverse order of removal.
Emission Control System
Description
Exhaust emissions (CO, HC, NOx) are controlled by a combination of engine modifications and the addition of
special control components.
Modifications to the combustion chamber, intake manifold, camshaft and ignition system form the basic control
system.
These items have been integrated into a highly effective system which controls exhaust emissions while maintaining
good drivability and fuel economy.
Air/Fuel Mixture Control System [Multiport Fuel Injection (MFI) System]
The MFI system uses signals from the heated oxygen sensor to activate and control the injector installed in the
manifold for each cylinder, thus precisely regulating the air/fuel mixture ratio and reducing emissions.
This in turn allows the engine to produce exhaust gas of the proper composition to permit the use of a three way
catalyst. The three way catalyst is designed to convert the three pollutants [hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide
(CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx)] into harmless substances. There are two operating modes in the MFI system.
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
1. Open Loop air/fuel ratio is controlled by information programmed into the ECM.
2. Closed Loop air/fuel ratio is adjusted by the ECM based on information supplied by the oxygen sensor.
Emission Control System
Description
The catalytic converter of the gasoline engine is a three way catalyst. It oxidizes carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons
(HC), and separates oxygen from the oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
cardiagn.com
Emission Control System
Removal
[Catalytic Converter (WCC)]
1. Remove the exhaust manifold.
(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Exhaust Manifold")
[Catalytic Converter (UCC)]
1. Remove the Center Muffler.
(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Center Muffler")
Installation
1. Install in the reverse order of removal.
Emission Control System
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
Description
Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT) system advances or retards the valve timing of the intake and exhaust
valve in accordance with the ECM control signal which is calculated by the engine speed and load.
By controlling CVVT, the valve over-lap or under-lap occurs, which makes better fuel economy and reduces exhaust
gases (NOx, HC). CVVT improves engine performance through reduction of pump loss, internal EGR effect,
improvement of combustion stability, improvement of volumetric efficiency, and increase of expansion work.
This system consist of
- the CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) which supplies the engine oil to the cam phaser or runs out the engine oil
from the cam phaser in accordance with the ECM PWM (Pulse With Modulation) control signal,
- the CVVT Oil Temperature Sensor (OTS) which measures the engine oil temperature,
- and the Cam Phaser which varies the cam phase by using the hydraulic force of the engine oil.
The engine oil getting out of the CVVT oil control valve varies the cam phase in the direction (Intake
Advance/Exhaust Retard) or opposite direction (Intake Retard/Exhaust Advance) of the engine rotation by rotating
the rotor connected with the camshaft inside the cam phaser.
cardiagn.com
Operation Principle
The CVVT has the mechanism rotating the rotor vane with hydraulic force generated by the engine oil supplied to the
advance or retard chamber in accordance with the CVVT oil control valve control.
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
cardiagn.com
[CVVT System Mode]
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
(1) Low Speed / Low Load (2) Part Load
(3) Low Speed / High Load (4) High Speed / High Load
cardiagn.com
Exhaust Valve Intake Valve
Driving
Condition Valve Valve
Effect Effect
Timing Timing
(1) Low * Valve Under-lap
Completely Completely * Valve Under-lap
Speed * Improvement of
Advance Retard * Improvement of combustion stability
/Low Load combustion stability
* Increase of expansion
work
(2) Part
Retard * Reduction of pumping Retard * Reduction of pumping loss
Load
loss
* Reduction of HC
(3) Low
* Increase of expansion * Prevention of intake back flow (Improvement
Speed Retard Advance
work of volumetric efficiency)
/High Load
(4) High
* Reduction of pumping
Speed Advance Retard * Improvement of volumetric efficiency
loss
/High Load
C:\Users\ej20\Desktop\KI 15\Sorento 2015\Emission Control System.mht 2014-06-10
You might also like
- Juju Sundin, Sarah Murdoch-Juju Sundin's Birth Skills - Proven Pain-Management Techniques For Your Labour and Birth PDFDocument287 pagesJuju Sundin, Sarah Murdoch-Juju Sundin's Birth Skills - Proven Pain-Management Techniques For Your Labour and Birth PDFCamila BastosNo ratings yet
- HACCP Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesHACCP Multiple Choice Questionsaloke ganguly92% (12)
- Santa Fe-Service ManualDocument353 pagesSanta Fe-Service ManualAdam Pegiel89% (9)
- Toyota Cressida/Supra 7m Service ManualDocument98 pagesToyota Cressida/Supra 7m Service Manualmidgo100% (2)
- Manual Taller Kymco Xciting 400s INGLES PDFDocument426 pagesManual Taller Kymco Xciting 400s INGLES PDFRuben DiazNo ratings yet
- Engine K21 and K25 Engine FuelDocument19 pagesEngine K21 and K25 Engine FuelPablo Rojas Valenzuela100% (1)
- 7.1. Emission Control SystemDocument18 pages7.1. Emission Control SystemChristian Icaza SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- CVVTDocument50 pagesCVVTMoaed Kanbar94% (18)
- 2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual FLDocument10 pages2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual FLAndy DellingerNo ratings yet
- Herbs That Kill Cancer and HIVDocument6 pagesHerbs That Kill Cancer and HIVsilentweaponsquietwars100% (1)
- Item Specification: Emission Control SystemDocument20 pagesItem Specification: Emission Control SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Tucson Emission Control System 2.0Document19 pagesTucson Emission Control System 2.0wilder0l0pezNo ratings yet
- Ec Kia Soul 2014Document175 pagesEc Kia Soul 2014erick alexander hernandezNo ratings yet
- SM - 04 Tucson TL 2015+ 1.6L - Emission Control SystemDocument19 pagesSM - 04 Tucson TL 2015+ 1.6L - Emission Control Systemzozo0424No ratings yet
- Genesis 3.8L Section 8Document18 pagesGenesis 3.8L Section 8Nacho MowjiNo ratings yet
- Elantra 2.0 EC (137) G 2.0 MPIDocument23 pagesElantra 2.0 EC (137) G 2.0 MPIjoan velaNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument26 pagesEmission Control SystemnahomNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument21 pagesEmission Control Systemvesa hintikkaNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument21 pagesEmission Control SystemdanyNo ratings yet
- Elantra 91 Emission Control SystemDocument49 pagesElantra 91 Emission Control Systemahmad adelNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument17 pagesEmission Control SystemCesar GiraccaNo ratings yet
- Emissions Control SystemsDocument15 pagesEmissions Control SystemsTharsikan singamNo ratings yet
- 04-Emission Control SystemDocument28 pages04-Emission Control SystemangelNo ratings yet
- Emission Control SystemDocument28 pagesEmission Control Systemsled novaNo ratings yet
- Continuously Variable Valve TimingDocument12 pagesContinuously Variable Valve TiminggamerpipeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Part D: Emission Control SystemsDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Part D: Emission Control SystemsJhon HancockNo ratings yet
- Emissions Control SystemDocument17 pagesEmissions Control SystemBrayan CatalanNo ratings yet
- 2GR-FE Emission ControlDocument23 pages2GR-FE Emission ControlLuks FernandezNo ratings yet
- p2 5S-FE+ENGINE+REPAIR+MANUALDocument19 pagesp2 5S-FE+ENGINE+REPAIR+MANUALMuhammad SafdarNo ratings yet
- 06 Sistema de Control de EmisionesDocument29 pages06 Sistema de Control de EmisionesmongongoNo ratings yet
- Santa Fe Service ManualDocument384 pagesSanta Fe Service ManualMihaita PrepelitaNo ratings yet
- 2AZ-FE Emission ControlDocument25 pages2AZ-FE Emission ControlLuks FernandezNo ratings yet
- Emision Control Sistem Kia PicantoDocument25 pagesEmision Control Sistem Kia PicantorohmanNo ratings yet
- EvapEmission PDFDocument8 pagesEvapEmission PDFpivillamilNo ratings yet
- 9Document80 pages9Namsa LABORATORIO100% (1)
- Emission Control SystemsDocument13 pagesEmission Control SystemsСергейУ-УNo ratings yet
- Fuel System Excel 87Document72 pagesFuel System Excel 87vpol25No ratings yet
- Ec (2jz-Gte) PDFDocument12 pagesEc (2jz-Gte) PDFAshokNo ratings yet
- 05 Emission ControlsDocument16 pages05 Emission ControlsvixentdNo ratings yet
- PCVDocument20 pagesPCVyared abebeNo ratings yet
- Partbook GA 5 - GA 15 Atlas CopcoDocument77 pagesPartbook GA 5 - GA 15 Atlas CopcoService PTNK33% (3)
- Emission ControlDocument26 pagesEmission ControllogammicNo ratings yet
- JourneyDocument194 pagesJourneyjuan carlos garciaNo ratings yet
- AIM:-Service Positive Crankcase Ventilation System: Practical - 3Document6 pagesAIM:-Service Positive Crankcase Ventilation System: Practical - 3saiyed amanNo ratings yet
- Intake Air SystemsDocument8 pagesIntake Air SystemsJosé AntonioNo ratings yet
- Sistema de Inyeccion Mono-JetronicDocument6 pagesSistema de Inyeccion Mono-JetronicDiego De La FuenteNo ratings yet
- Crdi BoshDocument61 pagesCrdi BoshIsmahan Ochi Noro100% (1)
- Fuel Evaporation SystemDocument9 pagesFuel Evaporation SystemToua YajNo ratings yet
- Basic Testing Pajero 1991Document12 pagesBasic Testing Pajero 1991nadaNo ratings yet
- 310-00C Fuel System - General Information - 5.0L 32V Ti-VCT/5.0L Ti-VCT V8 (308kW/418PS) 2016 MustangDocument30 pages310-00C Fuel System - General Information - 5.0L 32V Ti-VCT/5.0L Ti-VCT V8 (308kW/418PS) 2016 MustangJaciel LMNo ratings yet
- STC Oil Control Valve (Mechanical) - 5Document2 pagesSTC Oil Control Valve (Mechanical) - 5Parveen KashyapNo ratings yet
- QSK60 Familiarization - Compatibility ModeDocument68 pagesQSK60 Familiarization - Compatibility Modethainarime100% (1)
- Emisie Suzuki VL800Document6 pagesEmisie Suzuki VL800Crisan SorinNo ratings yet
- Section 2 EngineDocument14 pagesSection 2 EngineMarco OlivettoNo ratings yet
- DD15 CompressorDocument11 pagesDD15 CompressorarieNo ratings yet
- 4P GQ en 07Document0 pages4P GQ en 07aiigee100% (1)
- Fuel Control ValveDocument12 pagesFuel Control ValveALVARO OLACHICANo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Operator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingFrom EverandOperator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- Coding and ProgrammingDocument59 pagesCoding and ProgrammingZM Ohn100% (1)
- Engine Management OverviewDocument73 pagesEngine Management OverviewZM Ohn100% (3)
- Fitting Instructions - Defender td5 SnorkelDocument7 pagesFitting Instructions - Defender td5 SnorkelZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Land Rover Bosch GS8.87 Transmission Management (D2 & RR P38)Document13 pagesLand Rover Bosch GS8.87 Transmission Management (D2 & RR P38)ZM OhnNo ratings yet
- D4 Maintenance Check Sheet - Discovery 4 (LA) All Models - UK EU - 10-11MY - KMDocument2 pagesD4 Maintenance Check Sheet - Discovery 4 (LA) All Models - UK EU - 10-11MY - KMZM Ohn100% (1)
- Replacement Replacement Replacement: Semcon JLR Owner Guide Ver 1.00 LANGUAGE: English-En MARQUE: Landrover ModelDocument7 pagesReplacement Replacement Replacement: Semcon JLR Owner Guide Ver 1.00 LANGUAGE: English-En MARQUE: Landrover ModelZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Restraint: Item Resistance ( )Document49 pagesRestraint: Item Resistance ( )ZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Nanocom Evolution TD5 Map Facility and GuideDocument2 pagesNanocom Evolution TD5 Map Facility and GuideZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Engine+Electrical+System+2 4LDocument53 pagesEngine+Electrical+System+2 4LZM Ohn100% (1)
- Tightening Torques Items N.M KGF.M LB-FT: 4 Wheel Drive (4WD) SystemDocument35 pagesTightening Torques Items N.M KGF.M LB-FT: 4 Wheel Drive (4WD) SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Item Specification: Emission Control SystemDocument20 pagesItem Specification: Emission Control SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Engine Electrical SystemDocument48 pagesEngine Electrical SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Heating, Ventilation and Air ConditioningDocument88 pagesHeating, Ventilation and Air ConditioningZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Item Specification: Steering SystemDocument29 pagesItem Specification: Steering SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Discovery II Valeo BCU ECU GuideDocument20 pagesDiscovery II Valeo BCU ECU GuideZM OhnNo ratings yet
- General InformationDocument21 pagesGeneral InformationZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Puma Defender Alm-EcuDocument11 pagesPuma Defender Alm-EcuZM Ohn100% (1)
- Suspension SystemDocument70 pagesSuspension SystemZM OhnNo ratings yet
- Emotional WellnessDocument3 pagesEmotional Wellnesspaula_evangelista_3100% (1)
- Affective AssessmentDocument34 pagesAffective AssessmentEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures Covid 19: CIDESCO Sections, CIDESCO Schools CIDESCO MembersDocument14 pagesStandard Operating Procedures Covid 19: CIDESCO Sections, CIDESCO Schools CIDESCO MembersShaji VkNo ratings yet
- FA1 - Mole CalculationsDocument3 pagesFA1 - Mole CalculationsDenjiNo ratings yet
- TEST 2 06530622 Q eDocument16 pagesTEST 2 06530622 Q eIG LibraryNo ratings yet
- RTL Critical Thinking Skills e LearningDocument50 pagesRTL Critical Thinking Skills e LearningElías Tamez100% (1)
- Principles of NMR Protein Spectroscopy Frequencies and SpectraDocument14 pagesPrinciples of NMR Protein Spectroscopy Frequencies and SpectrakisanthombareNo ratings yet
- Performance Chemicals For Enhanced Oil RecoveryDocument6 pagesPerformance Chemicals For Enhanced Oil RecoveryMiguel MartinezNo ratings yet
- Field Guide Alien Species in European Forests PDFDocument132 pagesField Guide Alien Species in European Forests PDFIonut MarianNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Kelas 9 MtsDocument5 pagesSoal Uts Kelas 9 Mtsindah sNo ratings yet
- A-GIS-based-methodology-for-safe-site-selection-of Building in A Hilly RegionDocument13 pagesA-GIS-based-methodology-for-safe-site-selection-of Building in A Hilly RegionArch K3NNo ratings yet
- Lumax LED-Presentation PDFDocument31 pagesLumax LED-Presentation PDFSalman HashmiNo ratings yet
- Solvent Evaporation: Fast, Reliable and AffordableDocument24 pagesSolvent Evaporation: Fast, Reliable and Affordablepandiya rajanNo ratings yet
- Iccec CCCDocument22 pagesIccec CCCpdanishNo ratings yet
- 2018-09-10 in Touch WeeklyDocument76 pages2018-09-10 in Touch WeeklyAnonymous QfXnHbTRzNo ratings yet
- P&G Value Pricing PapaerDocument1 pageP&G Value Pricing PapaerkkktaxNo ratings yet
- Locking Plates - Advantages & Indications 1-11Document27 pagesLocking Plates - Advantages & Indications 1-11nishantsinghbmeNo ratings yet
- Nestle: Nestlé's Mission Statement (R1)Document11 pagesNestle: Nestlé's Mission Statement (R1)Abdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Dinner MenuDocument3 pagesDinner MenueatlocalmenusNo ratings yet
- 03 PS200 Quick OpnDocument2 pages03 PS200 Quick OpnPopa VasileNo ratings yet
- SmartLogger3000 User Manual PDFDocument192 pagesSmartLogger3000 User Manual PDFJ Armando Gastelo RoqueNo ratings yet
- Notice: Ocean Transportation Intermediary Licenses: InterCaribbean Cargo, Inc., Et Al.Document2 pagesNotice: Ocean Transportation Intermediary Licenses: InterCaribbean Cargo, Inc., Et Al.Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Senate Bill 897v8 NC FY 2010-11 Budget As RatifiedDocument189 pagesSenate Bill 897v8 NC FY 2010-11 Budget As RatifiedBobby CogginsNo ratings yet
- Societal MarketingDocument7 pagesSocietal Marketingraje.jk86% (14)
- Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA)Document5 pagesLatent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA)Fina Ahmad FitrianaNo ratings yet
- 11th Mock Test Municipal & Town OfficerDocument5 pages11th Mock Test Municipal & Town OfficerAnam BalochNo ratings yet
- Artikel 8 - (CURRICULUM EVALUATION)Document12 pagesArtikel 8 - (CURRICULUM EVALUATION)Kikit8No ratings yet