Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsScience 7: Chapter 1: Central Science Investigation Lesson 1: The Scientic Method
Science 7: Chapter 1: Central Science Investigation Lesson 1: The Scientic Method
Uploaded by
Mary Rose D. OrenseThis document discusses the scientific method and experimental variables. It explains the steps of the scientific method as making observations, stating the problem, formulating a hypothesis, performing experiments, and stating a conclusion. It describes the three types of variables in an experiment as the independent variable manipulated by the researcher, the dependent variable or observed result, and controlled variables held constant. The document also defines pure substances and their types as either elements that cannot be broken down further or compounds consisting of two or more bonded elements. It provides information about common elements in the Earth's atmosphere and crust.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Índice Guild of American Lutherie BooksDocument283 pagesÍndice Guild of American Lutherie BooksDaniel AndradeNo ratings yet
- Adventurers' Guild - SwordtagDocument12 pagesAdventurers' Guild - Swordtagtruly epicNo ratings yet
- Stock Statement Format For Bank LoanDocument1 pageStock Statement Format For Bank Loanpsycho Neha40% (5)
- Chemistry PDF DocumentDocument14 pagesChemistry PDF DocumentJ. TsilmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry NotesAngelo Kyle AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To ChemistryGobes Owen BlancoNo ratings yet
- 1.1+the Nature of Science - 1Document33 pages1.1+the Nature of Science - 1Rolled SibuyiNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience RevieweranalizapedrajamercadoNo ratings yet
- Branches of BiologyDocument3 pagesBranches of BiologyDith JarillaNo ratings yet
- Biology E-Note SS 1Document4 pagesBiology E-Note SS 1beanyachiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Jr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Strenght and StabilityDocument11 pagesStrenght and StabilityAyu SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- 2 Scientific MethodDocument25 pages2 Scientific MethodENbie Starz SlluNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document20 pagesUnit 1S APNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - MechanicsDocument4 pagesWeek 2 - MechanicsRafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- Science 20 Process SkillsDocument11 pagesScience 20 Process SkillsticoninxNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document39 pagesModule 2Cindy BononoNo ratings yet
- General Bio NotesDocument11 pagesGeneral Bio NotesDylan W.No ratings yet
- All VocabDocument34 pagesAll Vocabapi-294055859No ratings yet
- Lesson1 Units and Measurements TBPDocument37 pagesLesson1 Units and Measurements TBPSapphire RedNo ratings yet
- Chem Reviewer (Terms)Document12 pagesChem Reviewer (Terms)Jake GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Biology 001 Weekly Test 1Document5 pagesBiology 001 Weekly Test 1tituschiamaka895No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Gases Lesson1 - 12Document97 pagesChapter 3 Gases Lesson1 - 12Julius Salas100% (1)
- Quarter 1 Science 7 ReviewerDocument9 pagesQuarter 1 Science 7 ReviewerRussel LaugoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Vocabulary List: Name - Date - PeriodDocument1 pageUnit 1 Vocabulary List: Name - Date - PeriodFlorie Fe Rosario OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Chemistry Week 1 2 HandoutDocument2 pagesEnhanced Chemistry Week 1 2 HandoutMelissa Jean BayobayNo ratings yet
- Lab01 Scientific InvestigationDocument9 pagesLab01 Scientific InvestigationdanaNo ratings yet
- M1 Units Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument19 pagesM1 Units Physical Quantities and MeasurementLawrence AguilosNo ratings yet
- Summer Class Lesson 1Document32 pagesSummer Class Lesson 1Xyrelle Correo STE 8-EUROPANo ratings yet
- 01 Properties Composition and Changes of MatterDocument11 pages01 Properties Composition and Changes of MatterChrissa GuicoNo ratings yet
- Gen Sci Rev PDFDocument2 pagesGen Sci Rev PDFMaddieNo ratings yet
- The Scientific MethodDocument25 pagesThe Scientific MethodCzesarinePreciousJadeManibog100% (1)
- BIO122 Chapter 2-1Document55 pagesBIO122 Chapter 2-1Mohd AsrulNo ratings yet
- Gen Came DescriptionsDocument7 pagesGen Came DescriptionsbriguelajustineNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic ResearchDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Basic ResearchG19 Domino, MarionNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: 2. Science, Matter, Energy and SystemsDocument29 pagesEnvironmental Science: 2. Science, Matter, Energy and SystemsNguyễn Quỳnh HươngNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Characteristics of ResearchDocument20 pagesMeaning and Characteristics of ResearchHANSEL HOPE A PEREZNo ratings yet
- By: Jelord B. RosalitaDocument16 pagesBy: Jelord B. Rosalitajusten camingawanNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument52 pagesMicros28vgcyygf2No ratings yet
- Introduction To Earth ScienceDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Earth ScienceGorJessSpazzersNo ratings yet
- Biology FinalsDocument21 pagesBiology FinalsShaina NovicioNo ratings yet
- Environmentalsciencechapter 2 NotesDocument8 pagesEnvironmentalsciencechapter 2 Notesapi-357037845No ratings yet
- Self Learnin G: in Science Grade 10Document16 pagesSelf Learnin G: in Science Grade 10Rizalie Pablico MacahiligNo ratings yet
- Lim - Assignment #1Document3 pagesLim - Assignment #1Mhich GeyrozagaNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method Teacher EdDocument16 pagesScientific Method Teacher Edalan arcaNo ratings yet
- Physics Book-1Document31 pagesPhysics Book-1Abel Wisimaji MsiskaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Physics PDFDocument26 pagesNature of Physics PDFKnowledge HubNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument45 pagesGeneral Chemistryrieann leonNo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesLiving in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manualjerrybriggs7d5t0v100% (27)
- Dwnload Full Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFdanagarzad90y100% (17)
- Scientific MethodsDocument40 pagesScientific MethodskyisinlinlettNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument50 pagesScience ReviewerDon KeyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Doing Scientific InvestigationDocument4 pagesModule 1 Doing Scientific InvestigationLJ Valdez91% (11)
- 2eso-U1 ScientificActivityNETDocument14 pages2eso-U1 ScientificActivityNETrocioruizvaldiviaNo ratings yet
- Biology Remedial Module PDFDocument185 pagesBiology Remedial Module PDFBetseha Merawi67% (3)
- Unit 1 Class Study ToolDocument43 pagesUnit 1 Class Study Tool염진호No ratings yet
- Chapter 01 and 02 Book AnswersDocument76 pagesChapter 01 and 02 Book Answersfilip78fNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Year Note - 2023Document119 pagesGrade 10 Year Note - 2023maqhawentsakoNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument11 pagesBio Reviewerlarra100% (1)
- ZoologyDocument5 pagesZoologyrjdc972No ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument8 pagesChemistry ReviewerJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- Standing on the Shoulder of Richard Feynman to Teach Physics BetterFrom EverandStanding on the Shoulder of Richard Feynman to Teach Physics BetterNo ratings yet
- Riello G750 ManuelDocument21 pagesRiello G750 Manuelmelvin hoferNo ratings yet
- Cutting Program: W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07Document2 pagesCutting Program: W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07frodrez_931726No ratings yet
- Waupaca Elevator BrochureDocument16 pagesWaupaca Elevator BrochureMade Agus BudiarthaNo ratings yet
- TMO Journal Pantacle - 2001-1Document29 pagesTMO Journal Pantacle - 2001-1Frater T.A.S.100% (6)
- 4 Exploration of Coal - IV Coal Resource EstimationDocument30 pages4 Exploration of Coal - IV Coal Resource EstimationRasmiranjan Jena RajaNo ratings yet
- OTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingDocument16 pagesOTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingFrds123No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics SA1 RevisionDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Mathematics SA1 Revisionaryan bhanssaliNo ratings yet
- Maxwell Intro 17.0 SP WS5.2 Workshop Instructions Magneto Transient 3D PDFDocument22 pagesMaxwell Intro 17.0 SP WS5.2 Workshop Instructions Magneto Transient 3D PDFzhang881907No ratings yet
- Citric Acid SDS PestellDocument5 pagesCitric Acid SDS PestellTrisNo ratings yet
- Global Ethical Issues Unit 3Document15 pagesGlobal Ethical Issues Unit 3aditi anandNo ratings yet
- HVAC Commissioning Checklist ENERGY STAR Certified Homes, Version 3 - 3.1 (RevDocument2 pagesHVAC Commissioning Checklist ENERGY STAR Certified Homes, Version 3 - 3.1 (Revorganicspolybond100% (2)
- Psychopathology Class Resource List William F. Doverspike, PHD BibliographyDocument115 pagesPsychopathology Class Resource List William F. Doverspike, PHD BibliographyJosé Luis SHNo ratings yet
- List of Miniatures: BeastmenDocument2 pagesList of Miniatures: BeastmenItsaconnetNo ratings yet
- CTEO Chapter II B Chemistry and 10 Clinker FactsDocument43 pagesCTEO Chapter II B Chemistry and 10 Clinker FactsFranciscoCorreaJara100% (2)
- Changes From Rev AK To Rev AL Skyview Installation GuideDocument608 pagesChanges From Rev AK To Rev AL Skyview Installation GuideF BakımNo ratings yet
- Low-Level Equilibrium Trap - Wikipedia PDFDocument12 pagesLow-Level Equilibrium Trap - Wikipedia PDFMiss MishraNo ratings yet
- Q1 2024 Cox Automotive Industry Insights and Forecast Call PresentationDocument40 pagesQ1 2024 Cox Automotive Industry Insights and Forecast Call PresentationelgonzawebNo ratings yet
- Medibuddy-EnrolPolicyConditions 22Document23 pagesMedibuddy-EnrolPolicyConditions 22Vadivelan BaskarNo ratings yet
- AKVA Group Cage Farming Aquaculture 2014 2015Document78 pagesAKVA Group Cage Farming Aquaculture 2014 2015norisnorisNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument44 pagesPolynomialsSumit ManeNo ratings yet
- 16660I - HSB - 0017 Software and Setting Update - FinalDocument10 pages16660I - HSB - 0017 Software and Setting Update - Finalrizal_aspanNo ratings yet
- Conduction Power Loss in MOSFET Synchronous Rectifier With Parallel-Connected Schottky Barrier DiodeDocument7 pagesConduction Power Loss in MOSFET Synchronous Rectifier With Parallel-Connected Schottky Barrier DiodeMuhammad Saqib AliNo ratings yet
- International Coatings MaintenanceDocument19 pagesInternational Coatings Maintenanceluckystrike9008100% (2)
- Atomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsDocument50 pagesAtomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsACSVNo ratings yet
- P.5 English Revision Set 2 Namagunga Primary Boarding SchoolDocument14 pagesP.5 English Revision Set 2 Namagunga Primary Boarding SchoolnkugwafavourNo ratings yet
- Vibrant Picture. Smooth Motion. Magical Light: 4K UHD HDR Android TVDocument3 pagesVibrant Picture. Smooth Motion. Magical Light: 4K UHD HDR Android TVPascal LandsheereNo ratings yet
- Preventing Misuse of Medicines DR - Marwa Salih Al-NaimiDocument12 pagesPreventing Misuse of Medicines DR - Marwa Salih Al-NaimiMustafa MuayedNo ratings yet
Science 7: Chapter 1: Central Science Investigation Lesson 1: The Scientic Method
Science 7: Chapter 1: Central Science Investigation Lesson 1: The Scientic Method
Uploaded by
Mary Rose D. Orense0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesThis document discusses the scientific method and experimental variables. It explains the steps of the scientific method as making observations, stating the problem, formulating a hypothesis, performing experiments, and stating a conclusion. It describes the three types of variables in an experiment as the independent variable manipulated by the researcher, the dependent variable or observed result, and controlled variables held constant. The document also defines pure substances and their types as either elements that cannot be broken down further or compounds consisting of two or more bonded elements. It provides information about common elements in the Earth's atmosphere and crust.
Original Description:
Original Title
SCIENCE-7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the scientific method and experimental variables. It explains the steps of the scientific method as making observations, stating the problem, formulating a hypothesis, performing experiments, and stating a conclusion. It describes the three types of variables in an experiment as the independent variable manipulated by the researcher, the dependent variable or observed result, and controlled variables held constant. The document also defines pure substances and their types as either elements that cannot be broken down further or compounds consisting of two or more bonded elements. It provides information about common elements in the Earth's atmosphere and crust.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views2 pagesScience 7: Chapter 1: Central Science Investigation Lesson 1: The Scientic Method
Science 7: Chapter 1: Central Science Investigation Lesson 1: The Scientic Method
Uploaded by
Mary Rose D. OrenseThis document discusses the scientific method and experimental variables. It explains the steps of the scientific method as making observations, stating the problem, formulating a hypothesis, performing experiments, and stating a conclusion. It describes the three types of variables in an experiment as the independent variable manipulated by the researcher, the dependent variable or observed result, and controlled variables held constant. The document also defines pure substances and their types as either elements that cannot be broken down further or compounds consisting of two or more bonded elements. It provides information about common elements in the Earth's atmosphere and crust.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
SCIENCE 7
CHAPTER 1: CENTRAL SCIENCE INVESTIGATION
LESSON 1: THE SCIENTIC METHOD
SCIENTIFIC METHOD- There is a series of process
STEPS IN SCIENTIFIC METHOD
1. MAKE AN OBSERVATION- You makes an observation with the use of your five senses.
2. STATE THE PROBLEM- You identifies a problem after you make observations.
3. FORMULATE A HYPOTHESIS- It is a possible solution to your problem or a possible
explanation for the observation you make.
4. PERFORM EXPERIMENTS- To prove whether a hypothesis is valid, experiments are
performed. These are done by creating one or more setups that will match the hypothesis
and prove its validity.
5. STATE A CONCLUSION – After conducting a series of experiments, a conclusion is made
regarding the validity of the hypothesis. There should be no doubt that the results of the
experiments support the hypothesis.
MODEL- Once many hypothesis agree with the observations and experiments, you may then
assemble these into a theory.
THEORY- Is a set of tested hypothesis that attempts to explain some part of nature.
NATURAL LAW- This generally observed behaviour may be formulated into statement.
LAW- is a summary of observed and measurable behaviour while a theory is an explanation of such a
behavior.
LESSON 2: EXPERIMENTAL VARIABLES AND THE FAIR TEST
VARIABLES- The things that are changing.
THREE KINDS OF VARIABLES
1. INDEPENDENT VARIABLE- Is the one you change or manipulate.
2. DEPENDENT VARIABLE- Is the result or consequence after you make changes to the
independent variable.
3. CONTROL VARIABLE- Are elements that are held constant or remain unchanged all
throughout the experiments.
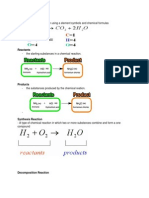
CHAPTER 2: PURE SUBSTANCES: A TEST OF PURITY
LESSON 3: THE PURE SUBSTANCES
MIXTURE- is a substance with a variable composition formed when two or more substances mix
together.
PURE SUBSTANCE- Will always has the same composition.
TWO TYPES OF PURE SUBSTANCE
1. ELEMENTS-a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler format
2. COMPOUNDS- a mixture of two or more elements, and is created when two hydrogen atoms
bond to an oxygen atom.
LESSON 4: THE ELEMENTS AND COMPOUNDS
Kuya Cul remembered that the idea of the element was first presented by the Irish scientist ROBERT
BOYLE (1627-1691). His greatest contribution to science is his insistence that science should be
strictly based on experiments.
The periodic table of elements containing the symbols of the elements and some other information
about them.
THE ELEMENTS ON THE EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE:
NITROGEN-78%
OXYGEN- 21%
ARGON- 0.9%
CARBON DIOXIDE- 0.03%
THE ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION OF EARTH’S CRUST BY WEIGHT IS:
OXYGEN- 46.60%
SILICON- 27.12%
ALUMINUM- 8.13%
IRON- 5.00%
CALCIUM-3.63%
SODIUM- 2.83%
POTASSIUM-2.70%
MAGNESIUM- 2.09%
OTHER ELEMENTS- 1.30%
You might also like
- Índice Guild of American Lutherie BooksDocument283 pagesÍndice Guild of American Lutherie BooksDaniel AndradeNo ratings yet
- Adventurers' Guild - SwordtagDocument12 pagesAdventurers' Guild - Swordtagtruly epicNo ratings yet
- Stock Statement Format For Bank LoanDocument1 pageStock Statement Format For Bank Loanpsycho Neha40% (5)
- Chemistry PDF DocumentDocument14 pagesChemistry PDF DocumentJ. TsilmanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry NotesAngelo Kyle AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To ChemistryGobes Owen BlancoNo ratings yet
- 1.1+the Nature of Science - 1Document33 pages1.1+the Nature of Science - 1Rolled SibuyiNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument8 pagesScience RevieweranalizapedrajamercadoNo ratings yet
- Branches of BiologyDocument3 pagesBranches of BiologyDith JarillaNo ratings yet
- Biology E-Note SS 1Document4 pagesBiology E-Note SS 1beanyachiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Jr CarpelaNo ratings yet
- Strenght and StabilityDocument11 pagesStrenght and StabilityAyu SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- 2 Scientific MethodDocument25 pages2 Scientific MethodENbie Starz SlluNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document20 pagesUnit 1S APNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - MechanicsDocument4 pagesWeek 2 - MechanicsRafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- Science 20 Process SkillsDocument11 pagesScience 20 Process SkillsticoninxNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document39 pagesModule 2Cindy BononoNo ratings yet
- General Bio NotesDocument11 pagesGeneral Bio NotesDylan W.No ratings yet
- All VocabDocument34 pagesAll Vocabapi-294055859No ratings yet
- Lesson1 Units and Measurements TBPDocument37 pagesLesson1 Units and Measurements TBPSapphire RedNo ratings yet
- Chem Reviewer (Terms)Document12 pagesChem Reviewer (Terms)Jake GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Biology 001 Weekly Test 1Document5 pagesBiology 001 Weekly Test 1tituschiamaka895No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Gases Lesson1 - 12Document97 pagesChapter 3 Gases Lesson1 - 12Julius Salas100% (1)
- Quarter 1 Science 7 ReviewerDocument9 pagesQuarter 1 Science 7 ReviewerRussel LaugoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Vocabulary List: Name - Date - PeriodDocument1 pageUnit 1 Vocabulary List: Name - Date - PeriodFlorie Fe Rosario OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Chemistry Week 1 2 HandoutDocument2 pagesEnhanced Chemistry Week 1 2 HandoutMelissa Jean BayobayNo ratings yet
- Lab01 Scientific InvestigationDocument9 pagesLab01 Scientific InvestigationdanaNo ratings yet
- M1 Units Physical Quantities and MeasurementDocument19 pagesM1 Units Physical Quantities and MeasurementLawrence AguilosNo ratings yet
- Summer Class Lesson 1Document32 pagesSummer Class Lesson 1Xyrelle Correo STE 8-EUROPANo ratings yet
- 01 Properties Composition and Changes of MatterDocument11 pages01 Properties Composition and Changes of MatterChrissa GuicoNo ratings yet
- Gen Sci Rev PDFDocument2 pagesGen Sci Rev PDFMaddieNo ratings yet
- The Scientific MethodDocument25 pagesThe Scientific MethodCzesarinePreciousJadeManibog100% (1)
- BIO122 Chapter 2-1Document55 pagesBIO122 Chapter 2-1Mohd AsrulNo ratings yet
- Gen Came DescriptionsDocument7 pagesGen Came DescriptionsbriguelajustineNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Basic ResearchDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Basic ResearchG19 Domino, MarionNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: 2. Science, Matter, Energy and SystemsDocument29 pagesEnvironmental Science: 2. Science, Matter, Energy and SystemsNguyễn Quỳnh HươngNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Characteristics of ResearchDocument20 pagesMeaning and Characteristics of ResearchHANSEL HOPE A PEREZNo ratings yet
- By: Jelord B. RosalitaDocument16 pagesBy: Jelord B. Rosalitajusten camingawanNo ratings yet
- MicrosDocument52 pagesMicros28vgcyygf2No ratings yet
- Introduction To Earth ScienceDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Earth ScienceGorJessSpazzersNo ratings yet
- Biology FinalsDocument21 pagesBiology FinalsShaina NovicioNo ratings yet
- Environmentalsciencechapter 2 NotesDocument8 pagesEnvironmentalsciencechapter 2 Notesapi-357037845No ratings yet
- Self Learnin G: in Science Grade 10Document16 pagesSelf Learnin G: in Science Grade 10Rizalie Pablico MacahiligNo ratings yet
- Lim - Assignment #1Document3 pagesLim - Assignment #1Mhich GeyrozagaNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method Teacher EdDocument16 pagesScientific Method Teacher Edalan arcaNo ratings yet
- Physics Book-1Document31 pagesPhysics Book-1Abel Wisimaji MsiskaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Physics PDFDocument26 pagesNature of Physics PDFKnowledge HubNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument45 pagesGeneral Chemistryrieann leonNo ratings yet
- Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesLiving in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manualjerrybriggs7d5t0v100% (27)
- Dwnload Full Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Living in The Environment 17th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFdanagarzad90y100% (17)
- Scientific MethodsDocument40 pagesScientific MethodskyisinlinlettNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument50 pagesScience ReviewerDon KeyNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Doing Scientific InvestigationDocument4 pagesModule 1 Doing Scientific InvestigationLJ Valdez91% (11)
- 2eso-U1 ScientificActivityNETDocument14 pages2eso-U1 ScientificActivityNETrocioruizvaldiviaNo ratings yet
- Biology Remedial Module PDFDocument185 pagesBiology Remedial Module PDFBetseha Merawi67% (3)
- Unit 1 Class Study ToolDocument43 pagesUnit 1 Class Study Tool염진호No ratings yet
- Chapter 01 and 02 Book AnswersDocument76 pagesChapter 01 and 02 Book Answersfilip78fNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Year Note - 2023Document119 pagesGrade 10 Year Note - 2023maqhawentsakoNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument11 pagesBio Reviewerlarra100% (1)
- ZoologyDocument5 pagesZoologyrjdc972No ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewerDocument8 pagesChemistry ReviewerJerico NaveraNo ratings yet
- Standing on the Shoulder of Richard Feynman to Teach Physics BetterFrom EverandStanding on the Shoulder of Richard Feynman to Teach Physics BetterNo ratings yet
- Riello G750 ManuelDocument21 pagesRiello G750 Manuelmelvin hoferNo ratings yet
- Cutting Program: W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07Document2 pagesCutting Program: W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07 W04FR144-07frodrez_931726No ratings yet
- Waupaca Elevator BrochureDocument16 pagesWaupaca Elevator BrochureMade Agus BudiarthaNo ratings yet
- TMO Journal Pantacle - 2001-1Document29 pagesTMO Journal Pantacle - 2001-1Frater T.A.S.100% (6)
- 4 Exploration of Coal - IV Coal Resource EstimationDocument30 pages4 Exploration of Coal - IV Coal Resource EstimationRasmiranjan Jena RajaNo ratings yet
- OTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingDocument16 pagesOTC-24958 MEIDP Owen Fracture Zone CrossingFrds123No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics SA1 RevisionDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 10 Mathematics SA1 Revisionaryan bhanssaliNo ratings yet
- Maxwell Intro 17.0 SP WS5.2 Workshop Instructions Magneto Transient 3D PDFDocument22 pagesMaxwell Intro 17.0 SP WS5.2 Workshop Instructions Magneto Transient 3D PDFzhang881907No ratings yet
- Citric Acid SDS PestellDocument5 pagesCitric Acid SDS PestellTrisNo ratings yet
- Global Ethical Issues Unit 3Document15 pagesGlobal Ethical Issues Unit 3aditi anandNo ratings yet
- HVAC Commissioning Checklist ENERGY STAR Certified Homes, Version 3 - 3.1 (RevDocument2 pagesHVAC Commissioning Checklist ENERGY STAR Certified Homes, Version 3 - 3.1 (Revorganicspolybond100% (2)
- Psychopathology Class Resource List William F. Doverspike, PHD BibliographyDocument115 pagesPsychopathology Class Resource List William F. Doverspike, PHD BibliographyJosé Luis SHNo ratings yet
- List of Miniatures: BeastmenDocument2 pagesList of Miniatures: BeastmenItsaconnetNo ratings yet
- CTEO Chapter II B Chemistry and 10 Clinker FactsDocument43 pagesCTEO Chapter II B Chemistry and 10 Clinker FactsFranciscoCorreaJara100% (2)
- Changes From Rev AK To Rev AL Skyview Installation GuideDocument608 pagesChanges From Rev AK To Rev AL Skyview Installation GuideF BakımNo ratings yet
- Low-Level Equilibrium Trap - Wikipedia PDFDocument12 pagesLow-Level Equilibrium Trap - Wikipedia PDFMiss MishraNo ratings yet
- Q1 2024 Cox Automotive Industry Insights and Forecast Call PresentationDocument40 pagesQ1 2024 Cox Automotive Industry Insights and Forecast Call PresentationelgonzawebNo ratings yet
- Medibuddy-EnrolPolicyConditions 22Document23 pagesMedibuddy-EnrolPolicyConditions 22Vadivelan BaskarNo ratings yet
- AKVA Group Cage Farming Aquaculture 2014 2015Document78 pagesAKVA Group Cage Farming Aquaculture 2014 2015norisnorisNo ratings yet
- PolynomialsDocument44 pagesPolynomialsSumit ManeNo ratings yet
- 16660I - HSB - 0017 Software and Setting Update - FinalDocument10 pages16660I - HSB - 0017 Software and Setting Update - Finalrizal_aspanNo ratings yet
- Conduction Power Loss in MOSFET Synchronous Rectifier With Parallel-Connected Schottky Barrier DiodeDocument7 pagesConduction Power Loss in MOSFET Synchronous Rectifier With Parallel-Connected Schottky Barrier DiodeMuhammad Saqib AliNo ratings yet
- International Coatings MaintenanceDocument19 pagesInternational Coatings Maintenanceluckystrike9008100% (2)
- Atomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsDocument50 pagesAtomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsACSVNo ratings yet
- P.5 English Revision Set 2 Namagunga Primary Boarding SchoolDocument14 pagesP.5 English Revision Set 2 Namagunga Primary Boarding SchoolnkugwafavourNo ratings yet
- Vibrant Picture. Smooth Motion. Magical Light: 4K UHD HDR Android TVDocument3 pagesVibrant Picture. Smooth Motion. Magical Light: 4K UHD HDR Android TVPascal LandsheereNo ratings yet
- Preventing Misuse of Medicines DR - Marwa Salih Al-NaimiDocument12 pagesPreventing Misuse of Medicines DR - Marwa Salih Al-NaimiMustafa MuayedNo ratings yet