Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1.4 Proteins
1.4 Proteins
Uploaded by
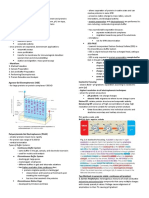
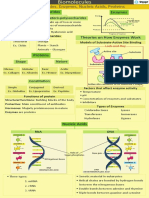
BlitzSZNThis document discusses several key factors that influence enzyme-substrate interactions and enzyme reaction rates. It notes that the three-dimensional shape of the enzyme's active site is complementary to that of the substrate. It also lists several factors that can affect the rate of enzyme reactions, including temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentrations, and the presence of inhibitors. Finally, it provides context on protein structure and folding, noting how the primary structure of amino acids determines the overall three-dimensional structure of the protein.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Review:: Label The Following Regions On This Generalised tRNA Molecule, Outlining The Function of EachDocument4 pagesReview:: Label The Following Regions On This Generalised tRNA Molecule, Outlining The Function of EachIndrani GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 005 Ch03 Proteins v2020 PDFDocument4 pages005 Ch03 Proteins v2020 PDFshahidabubaker19No ratings yet
- Bio - Chap 4Document3 pagesBio - Chap 4iamNashix22No ratings yet
- Biomolecules (Coloured)Document10 pagesBiomolecules (Coloured)r62080950No ratings yet
- Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry: RSC - Li/obcDocument8 pagesOrganic & Biomolecular Chemistry: RSC - Li/obcKent Harry CumpioNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Apr 10, 2024Document17 pagesAdobe Scan Apr 10, 2024chimtukingNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture Notes (Protein Structure 1)Document6 pagesBiochemistry Lecture Notes (Protein Structure 1)MarcChang75% (4)
- Protein Structure PDFDocument2 pagesProtein Structure PDFIoannis PanagopoulosNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Proteins Part 2 of 3Document7 pagesModule 3 - Proteins Part 2 of 3Rolie Jan LabradorNo ratings yet
- 1.4 ProteinDocument4 pages1.4 ProteinRachell RequellNo ratings yet
- Peptide BondDocument2 pagesPeptide BondA PutoyNo ratings yet
- Fu Et Al 2016 One Pot Synthesis of Block Copolymers by Orthogonal Ring Opening Polymerization and Pet RaftDocument6 pagesFu Et Al 2016 One Pot Synthesis of Block Copolymers by Orthogonal Ring Opening Polymerization and Pet Raftyuika620No ratings yet
- Biochem 002Document24 pagesBiochem 002Hend maarofNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM 3 Three Dimensional Structure of ProteinsDocument4 pagesBIOCHEM 3 Three Dimensional Structure of ProteinsRudolph MendozaNo ratings yet
- BMM LEC 5 SN Structure & Function of Amino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsDocument2 pagesBMM LEC 5 SN Structure & Function of Amino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Proteins ReviewerDocument5 pagesAmino Acids and Proteins ReviewerDaine MarconNo ratings yet
- Terms I Should Remember BiochemDocument1 pageTerms I Should Remember BiochemAmyNo ratings yet
- Primary Structure: Beta SheetDocument1 pagePrimary Structure: Beta Sheetthat/niggaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Protein OrganizationDocument61 pagesLevels of Protein OrganizationMariam AbdouNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument1 pageAmino Acids and ProteinsQuang OngNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3Liu IvyNo ratings yet
- Proteins: AP BiologyDocument11 pagesProteins: AP BiologyJESSANETTE SAN PABLONo ratings yet
- Zhang-Et-Al. Chemical-Modification-Of-Hydroxyl-Terminated-Polybutadiene-And-Its-Application-In-Composite-Propellants (HTPB) (Propellant) (Recipe)Document11 pagesZhang-Et-Al. Chemical-Modification-Of-Hydroxyl-Terminated-Polybutadiene-And-Its-Application-In-Composite-Propellants (HTPB) (Propellant) (Recipe)darin koblickNo ratings yet
- MiuDocumento 923461 Carbs.9aed.2018.JeffHardin, GregoryBertoni-Becker SWorldoftheCell-Pearson (2018)Document5 pagesMiuDocumento 923461 Carbs.9aed.2018.JeffHardin, GregoryBertoni-Becker SWorldoftheCell-Pearson (2018)ashleyvasquezp16No ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Macromolecules Part II-1Document37 pagesChapter 5-Macromolecules Part II-1janardhan aghavNo ratings yet
- DNA Biology Science Education Presentation in Blue Orange Illustrated StyleDocument13 pagesDNA Biology Science Education Presentation in Blue Orange Illustrated Stylemangleshkanik123No ratings yet
- Biología 3Document4 pagesBiología 3María PNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Protein Structure and FunctionDocument62 pagesCh03 Protein Structure and FunctionMonica VallejoNo ratings yet
- Backup of MBB 130 Lab Reviewer LE 1Document3 pagesBackup of MBB 130 Lab Reviewer LE 1Richelle Mae PadillaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry IntroductionDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry IntroductionPrecious PerniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Proteins & Proteins Purification TechniquesDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Proteins & Proteins Purification Techniquesdaniel AfiqNo ratings yet
- There Are Many Steps Between DNA and Protein: Figure 7-39Document70 pagesThere Are Many Steps Between DNA and Protein: Figure 7-39Viết TùngNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Chemistry and Packing of Amino AcidsDocument6 pagesLecture 2-Chemistry and Packing of Amino AcidsSparsh NegiNo ratings yet
- Asynchro 1013Document2 pagesAsynchro 1013Jan Vincent BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Protein: by El Wathan Organic Chemistry For Third GradeDocument66 pagesProtein: by El Wathan Organic Chemistry For Third GradenadaNo ratings yet
- Acs - Chemrev.0c00067 DDDocument36 pagesAcs - Chemrev.0c00067 DDFikret MamedovNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - C5 Proteins Higher Orders of StructureDocument5 pagesBiochemistry - C5 Proteins Higher Orders of StructureKim LlamasNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Peptidyl-tRNA Mimics For Structural Biology ApplicationsDocument13 pagesSynthesis of Peptidyl-tRNA Mimics For Structural Biology Applicationsarusha faheemNo ratings yet
- I. 1° Structure Determination of A Polypeptide General StepsDocument6 pagesI. 1° Structure Determination of A Polypeptide General StepsAllyson CarlosNo ratings yet
- Protein and Nucleic AcidDocument17 pagesProtein and Nucleic AcidlinhNo ratings yet
- SL Option B BiochemistryDocument13 pagesSL Option B Biochemistrypymkmg7c4dNo ratings yet
- Biokimia Lanjut - 2 (PROTEIN) S2 Kimia - Unud 2020Document51 pagesBiokimia Lanjut - 2 (PROTEIN) S2 Kimia - Unud 2020AriSuandiNo ratings yet
- Tema 18 EngDocument24 pagesTema 18 EngChristian Artero AndreuNo ratings yet
- J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 14844 - HEA ReviewDocument19 pagesJ. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 14844 - HEA ReviewGracy TombocNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Chemistry SOLDocument3 pagesYear 12 Chemistry SOLHansika SamudralaNo ratings yet
- WK11 Cc-LecDocument14 pagesWK11 Cc-LecAira UsiNo ratings yet
- Complex Formation Chitosan ProteinsDocument10 pagesComplex Formation Chitosan ProteinsaleezaNo ratings yet
- 2020 jacs.9b12013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 589−597 Asymmetric Synthesis of α‑Aminoboronates via Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective C (sp3) −H BorylationDocument9 pages2020 jacs.9b12013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 589−597 Asymmetric Synthesis of α‑Aminoboronates via Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective C (sp3) −H BorylationHamza AnsarNo ratings yet
- Polysaccharides Enzymes Nucleic Acids ProteinsDocument1 pagePolysaccharides Enzymes Nucleic Acids Proteinsjagadish dasariNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Concept Map ANSWER KEY: Protein ThymineDocument1 pageBiochemistry Concept Map ANSWER KEY: Protein ThymineTLE Group 2 LHS 9 Halle, Florence, GrantNo ratings yet
- Domains PDFDocument4 pagesDomains PDFSoumava PalitNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Mikua 2 PPDocument9 pagesJurnal Mikua 2 PPmpmkmfapertaNo ratings yet
- Biotek 3 ProteinDocument25 pagesBiotek 3 ProteinArfan NurdinNo ratings yet
- rojas et al 2007 single component α iminocarboxamide nickel ethylene polymerization and copolymerization initiatorsDocument7 pagesrojas et al 2007 single component α iminocarboxamide nickel ethylene polymerization and copolymerization initiatorsflacorun1710No ratings yet
- (BCHM) A S01 T04 CoenzymesDocument9 pages(BCHM) A S01 T04 CoenzymeshellokrisjaejoongNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Biochemistry 2022Document14 pagesAmino Acids Biochemistry 2022MercyNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument12 pagesProteinsSaloni PatelNo ratings yet
- DPN-Biochem I - Lecture 7 - Methods For Protein Purifcation and CharacterizationDocument35 pagesDPN-Biochem I - Lecture 7 - Methods For Protein Purifcation and Characterizationchienyu2002No ratings yet
- Acid Amino NotesDocument4 pagesAcid Amino NotesCikgu RameshNo ratings yet
- Bioelectrochemistry: Fundamentals, Experimental Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandBioelectrochemistry: Fundamentals, Experimental Techniques and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Blackmagic 3G-SDI Arduino Shield ManualDocument244 pagesBlackmagic 3G-SDI Arduino Shield ManualbopufouriaNo ratings yet
- Question Papers of Two Year M. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations April - 2012Document29 pagesQuestion Papers of Two Year M. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations April - 2012mdphilipNo ratings yet
- Important Maths QuestionsDocument15 pagesImportant Maths QuestionsArun KumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Game TheoryDocument85 pagesGame TheoryMuthuKumar RajendranNo ratings yet
- Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDocument2 pagesParallel Lines Cut by A TransversalAnita MeghaniNo ratings yet
- PT - Mathematics 4 - Q4Document6 pagesPT - Mathematics 4 - Q4Ric Arellano, JrNo ratings yet
- Total StationDocument12 pagesTotal StationLic Torres JimenezNo ratings yet
- Mixing (Industrial Pharmacy)Document8 pagesMixing (Industrial Pharmacy)Haroon Rahim71% (7)
- Dynapac CC950 Dynapac CC950: Double Drum Vibratory Rollers Double Drum Vibratory RollersDocument2 pagesDynapac CC950 Dynapac CC950: Double Drum Vibratory Rollers Double Drum Vibratory RollersNadir MohamedNo ratings yet
- EMC Documentum Configuration GUide For SAP PDFDocument37 pagesEMC Documentum Configuration GUide For SAP PDFClarissa Fracassi100% (1)
- Contador 542-072a-ManualDocument8 pagesContador 542-072a-ManualRONALD ALFONSO PACHECO TORRESNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy LabDocument7 pagesWork and Energy LabnonononoNo ratings yet
- Design and Stress Analysis of A General Aviation ADocument8 pagesDesign and Stress Analysis of A General Aviation AGhassan MousaNo ratings yet
- Repair Manual Hydrostatic Pump Motor PDFDocument112 pagesRepair Manual Hydrostatic Pump Motor PDFВячеслав Шапочка100% (3)
- Dynamics Lab: Department of Production EngineeringDocument13 pagesDynamics Lab: Department of Production EngineeringAditi RayNo ratings yet
- Questions About Reverse OsmosisDocument6 pagesQuestions About Reverse OsmosisManjunath HrmNo ratings yet
- v25 Algebra 1 5.02.odtDocument6 pagesv25 Algebra 1 5.02.odtSam's vrNo ratings yet
- Bab 14-Distribusi Tegangan Tanah VertikalDocument41 pagesBab 14-Distribusi Tegangan Tanah VertikalNovia FlorensiaNo ratings yet
- WEG CFW500 Programming Manual v3 1x 10006739425 enDocument218 pagesWEG CFW500 Programming Manual v3 1x 10006739425 enwilsonwdarNo ratings yet
- New Application /change Request Format: Schematic FlowDocument4 pagesNew Application /change Request Format: Schematic FlowUDAYNo ratings yet
- Richard FeynmanDocument4 pagesRichard FeynmanyashNo ratings yet
- Resume: Michael AaronsonDocument16 pagesResume: Michael AaronsonMichaelAaronsonNo ratings yet
- Compact Machining Center: M140X1 ItemDocument6 pagesCompact Machining Center: M140X1 ItemXi FengNo ratings yet
- Financial ModellingDocument13 pagesFinancial ModellingPRACHI DASNo ratings yet
- Makridakis (2020)Document21 pagesMakridakis (2020)100111No ratings yet
- Read Me HALO CEDocument9 pagesRead Me HALO CERafie BonoanNo ratings yet
- t156 1 Forklift Merlo P35.9ev Oem Service ManualDocument100 pagest156 1 Forklift Merlo P35.9ev Oem Service ManualChomi100% (1)
- tp6998 PDFDocument206 pagestp6998 PDFAlexandre PatrocinioNo ratings yet
- Physics: International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument2 pagesPhysics: International General Certificate of Secondary EducationAr Ar ViNo ratings yet
1.4 Proteins
1.4 Proteins
Uploaded by
BlitzSZN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageThis document discusses several key factors that influence enzyme-substrate interactions and enzyme reaction rates. It notes that the three-dimensional shape of the enzyme's active site is complementary to that of the substrate. It also lists several factors that can affect the rate of enzyme reactions, including temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentrations, and the presence of inhibitors. Finally, it provides context on protein structure and folding, noting how the primary structure of amino acids determines the overall three-dimensional structure of the protein.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses several key factors that influence enzyme-substrate interactions and enzyme reaction rates. It notes that the three-dimensional shape of the enzyme's active site is complementary to that of the substrate. It also lists several factors that can affect the rate of enzyme reactions, including temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentrations, and the presence of inhibitors. Finally, it provides context on protein structure and folding, noting how the primary structure of amino acids determines the overall three-dimensional structure of the protein.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 page1.4 Proteins
1.4 Proteins
Uploaded by
BlitzSZNThis document discusses several key factors that influence enzyme-substrate interactions and enzyme reaction rates. It notes that the three-dimensional shape of the enzyme's active site is complementary to that of the substrate. It also lists several factors that can affect the rate of enzyme reactions, including temperature, pH, substrate and enzyme concentrations, and the presence of inhibitors. Finally, it provides context on protein structure and folding, noting how the primary structure of amino acids determines the overall three-dimensional structure of the protein.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
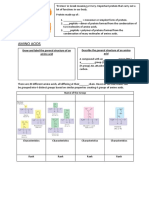
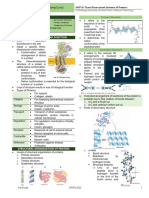
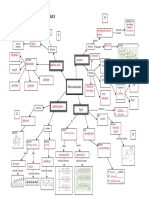
Enzyme and Substrate shape is Contains peptide
substrate complementary to Active site bonds
Temperature active site
concentrations
Factors Induced-
fit model Specific Sequence of AAs in
Competitive and
affecting Enzyme- structure of primary structure
non-competitive enzyme substrate active site Polypeptide determines where
inhibitors reactions complexes chain bonds form, and
Structure hence 3D structure
Lower activation of protein
determines Primary
pH energy of the Enzymes
reaction function structure
Biological
Purple = positive catalysts Folding ɑ-helix or β-
result sheet
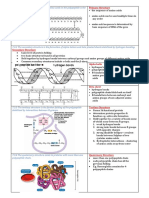
Biuret 1.4 PROTEINS Structure
Secondary
structure
Blue = negative
reagent Test Hydrogen bonds
result and folding between NH
and CO groups
NH2 group, COOH group, R Quaternary
side chain and H bond all Amino acid (AA) structure Tertiary
attached to central Monomers structure Specific 3D
carbon atom shape of protein
Dipeptide - 2 AAs Protein can Contains ionic bonds,
20 AAs occur in living contain multiple disulfide bridges and
organisms, differ only Polypeptide - many AAs polypeptides
Multiple polypeptide hydrogen bonds
in the R side chain
chains linked together
Condensation reaction
Peptide bonds AQA
https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
https://bit.ly/pmt-edu https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
You might also like
- Review:: Label The Following Regions On This Generalised tRNA Molecule, Outlining The Function of EachDocument4 pagesReview:: Label The Following Regions On This Generalised tRNA Molecule, Outlining The Function of EachIndrani GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 005 Ch03 Proteins v2020 PDFDocument4 pages005 Ch03 Proteins v2020 PDFshahidabubaker19No ratings yet
- Bio - Chap 4Document3 pagesBio - Chap 4iamNashix22No ratings yet
- Biomolecules (Coloured)Document10 pagesBiomolecules (Coloured)r62080950No ratings yet
- Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry: RSC - Li/obcDocument8 pagesOrganic & Biomolecular Chemistry: RSC - Li/obcKent Harry CumpioNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Apr 10, 2024Document17 pagesAdobe Scan Apr 10, 2024chimtukingNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture Notes (Protein Structure 1)Document6 pagesBiochemistry Lecture Notes (Protein Structure 1)MarcChang75% (4)
- Protein Structure PDFDocument2 pagesProtein Structure PDFIoannis PanagopoulosNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Proteins Part 2 of 3Document7 pagesModule 3 - Proteins Part 2 of 3Rolie Jan LabradorNo ratings yet
- 1.4 ProteinDocument4 pages1.4 ProteinRachell RequellNo ratings yet
- Peptide BondDocument2 pagesPeptide BondA PutoyNo ratings yet
- Fu Et Al 2016 One Pot Synthesis of Block Copolymers by Orthogonal Ring Opening Polymerization and Pet RaftDocument6 pagesFu Et Al 2016 One Pot Synthesis of Block Copolymers by Orthogonal Ring Opening Polymerization and Pet Raftyuika620No ratings yet
- Biochem 002Document24 pagesBiochem 002Hend maarofNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM 3 Three Dimensional Structure of ProteinsDocument4 pagesBIOCHEM 3 Three Dimensional Structure of ProteinsRudolph MendozaNo ratings yet
- BMM LEC 5 SN Structure & Function of Amino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsDocument2 pagesBMM LEC 5 SN Structure & Function of Amino Acids, Peptides & ProteinsSARAH SAFIAH TAJUL ARIFFINNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Proteins ReviewerDocument5 pagesAmino Acids and Proteins ReviewerDaine MarconNo ratings yet
- Terms I Should Remember BiochemDocument1 pageTerms I Should Remember BiochemAmyNo ratings yet
- Primary Structure: Beta SheetDocument1 pagePrimary Structure: Beta Sheetthat/niggaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Protein OrganizationDocument61 pagesLevels of Protein OrganizationMariam AbdouNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument1 pageAmino Acids and ProteinsQuang OngNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document16 pagesLecture 3Liu IvyNo ratings yet
- Proteins: AP BiologyDocument11 pagesProteins: AP BiologyJESSANETTE SAN PABLONo ratings yet
- Zhang-Et-Al. Chemical-Modification-Of-Hydroxyl-Terminated-Polybutadiene-And-Its-Application-In-Composite-Propellants (HTPB) (Propellant) (Recipe)Document11 pagesZhang-Et-Al. Chemical-Modification-Of-Hydroxyl-Terminated-Polybutadiene-And-Its-Application-In-Composite-Propellants (HTPB) (Propellant) (Recipe)darin koblickNo ratings yet
- MiuDocumento 923461 Carbs.9aed.2018.JeffHardin, GregoryBertoni-Becker SWorldoftheCell-Pearson (2018)Document5 pagesMiuDocumento 923461 Carbs.9aed.2018.JeffHardin, GregoryBertoni-Becker SWorldoftheCell-Pearson (2018)ashleyvasquezp16No ratings yet
- Chapter 5-Macromolecules Part II-1Document37 pagesChapter 5-Macromolecules Part II-1janardhan aghavNo ratings yet
- DNA Biology Science Education Presentation in Blue Orange Illustrated StyleDocument13 pagesDNA Biology Science Education Presentation in Blue Orange Illustrated Stylemangleshkanik123No ratings yet
- Biología 3Document4 pagesBiología 3María PNo ratings yet
- Ch03 Protein Structure and FunctionDocument62 pagesCh03 Protein Structure and FunctionMonica VallejoNo ratings yet
- Backup of MBB 130 Lab Reviewer LE 1Document3 pagesBackup of MBB 130 Lab Reviewer LE 1Richelle Mae PadillaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry IntroductionDocument4 pagesClinical Chemistry IntroductionPrecious PerniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Proteins & Proteins Purification TechniquesDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Proteins & Proteins Purification Techniquesdaniel AfiqNo ratings yet
- There Are Many Steps Between DNA and Protein: Figure 7-39Document70 pagesThere Are Many Steps Between DNA and Protein: Figure 7-39Viết TùngNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Chemistry and Packing of Amino AcidsDocument6 pagesLecture 2-Chemistry and Packing of Amino AcidsSparsh NegiNo ratings yet
- Asynchro 1013Document2 pagesAsynchro 1013Jan Vincent BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Protein: by El Wathan Organic Chemistry For Third GradeDocument66 pagesProtein: by El Wathan Organic Chemistry For Third GradenadaNo ratings yet
- Acs - Chemrev.0c00067 DDDocument36 pagesAcs - Chemrev.0c00067 DDFikret MamedovNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - C5 Proteins Higher Orders of StructureDocument5 pagesBiochemistry - C5 Proteins Higher Orders of StructureKim LlamasNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Peptidyl-tRNA Mimics For Structural Biology ApplicationsDocument13 pagesSynthesis of Peptidyl-tRNA Mimics For Structural Biology Applicationsarusha faheemNo ratings yet
- I. 1° Structure Determination of A Polypeptide General StepsDocument6 pagesI. 1° Structure Determination of A Polypeptide General StepsAllyson CarlosNo ratings yet
- Protein and Nucleic AcidDocument17 pagesProtein and Nucleic AcidlinhNo ratings yet
- SL Option B BiochemistryDocument13 pagesSL Option B Biochemistrypymkmg7c4dNo ratings yet
- Biokimia Lanjut - 2 (PROTEIN) S2 Kimia - Unud 2020Document51 pagesBiokimia Lanjut - 2 (PROTEIN) S2 Kimia - Unud 2020AriSuandiNo ratings yet
- Tema 18 EngDocument24 pagesTema 18 EngChristian Artero AndreuNo ratings yet
- J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 14844 - HEA ReviewDocument19 pagesJ. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8, 14844 - HEA ReviewGracy TombocNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Chemistry SOLDocument3 pagesYear 12 Chemistry SOLHansika SamudralaNo ratings yet
- WK11 Cc-LecDocument14 pagesWK11 Cc-LecAira UsiNo ratings yet
- Complex Formation Chitosan ProteinsDocument10 pagesComplex Formation Chitosan ProteinsaleezaNo ratings yet
- 2020 jacs.9b12013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 589−597 Asymmetric Synthesis of α‑Aminoboronates via Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective C (sp3) −H BorylationDocument9 pages2020 jacs.9b12013 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 589−597 Asymmetric Synthesis of α‑Aminoboronates via Rhodium-Catalyzed Enantioselective C (sp3) −H BorylationHamza AnsarNo ratings yet
- Polysaccharides Enzymes Nucleic Acids ProteinsDocument1 pagePolysaccharides Enzymes Nucleic Acids Proteinsjagadish dasariNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Concept Map ANSWER KEY: Protein ThymineDocument1 pageBiochemistry Concept Map ANSWER KEY: Protein ThymineTLE Group 2 LHS 9 Halle, Florence, GrantNo ratings yet
- Domains PDFDocument4 pagesDomains PDFSoumava PalitNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Mikua 2 PPDocument9 pagesJurnal Mikua 2 PPmpmkmfapertaNo ratings yet
- Biotek 3 ProteinDocument25 pagesBiotek 3 ProteinArfan NurdinNo ratings yet
- rojas et al 2007 single component α iminocarboxamide nickel ethylene polymerization and copolymerization initiatorsDocument7 pagesrojas et al 2007 single component α iminocarboxamide nickel ethylene polymerization and copolymerization initiatorsflacorun1710No ratings yet
- (BCHM) A S01 T04 CoenzymesDocument9 pages(BCHM) A S01 T04 CoenzymeshellokrisjaejoongNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids Biochemistry 2022Document14 pagesAmino Acids Biochemistry 2022MercyNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument12 pagesProteinsSaloni PatelNo ratings yet
- DPN-Biochem I - Lecture 7 - Methods For Protein Purifcation and CharacterizationDocument35 pagesDPN-Biochem I - Lecture 7 - Methods For Protein Purifcation and Characterizationchienyu2002No ratings yet
- Acid Amino NotesDocument4 pagesAcid Amino NotesCikgu RameshNo ratings yet
- Bioelectrochemistry: Fundamentals, Experimental Techniques and ApplicationsFrom EverandBioelectrochemistry: Fundamentals, Experimental Techniques and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Blackmagic 3G-SDI Arduino Shield ManualDocument244 pagesBlackmagic 3G-SDI Arduino Shield ManualbopufouriaNo ratings yet
- Question Papers of Two Year M. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations April - 2012Document29 pagesQuestion Papers of Two Year M. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations April - 2012mdphilipNo ratings yet
- Important Maths QuestionsDocument15 pagesImportant Maths QuestionsArun KumarvermaNo ratings yet
- Game TheoryDocument85 pagesGame TheoryMuthuKumar RajendranNo ratings yet
- Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDocument2 pagesParallel Lines Cut by A TransversalAnita MeghaniNo ratings yet
- PT - Mathematics 4 - Q4Document6 pagesPT - Mathematics 4 - Q4Ric Arellano, JrNo ratings yet
- Total StationDocument12 pagesTotal StationLic Torres JimenezNo ratings yet
- Mixing (Industrial Pharmacy)Document8 pagesMixing (Industrial Pharmacy)Haroon Rahim71% (7)
- Dynapac CC950 Dynapac CC950: Double Drum Vibratory Rollers Double Drum Vibratory RollersDocument2 pagesDynapac CC950 Dynapac CC950: Double Drum Vibratory Rollers Double Drum Vibratory RollersNadir MohamedNo ratings yet
- EMC Documentum Configuration GUide For SAP PDFDocument37 pagesEMC Documentum Configuration GUide For SAP PDFClarissa Fracassi100% (1)
- Contador 542-072a-ManualDocument8 pagesContador 542-072a-ManualRONALD ALFONSO PACHECO TORRESNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy LabDocument7 pagesWork and Energy LabnonononoNo ratings yet
- Design and Stress Analysis of A General Aviation ADocument8 pagesDesign and Stress Analysis of A General Aviation AGhassan MousaNo ratings yet
- Repair Manual Hydrostatic Pump Motor PDFDocument112 pagesRepair Manual Hydrostatic Pump Motor PDFВячеслав Шапочка100% (3)
- Dynamics Lab: Department of Production EngineeringDocument13 pagesDynamics Lab: Department of Production EngineeringAditi RayNo ratings yet
- Questions About Reverse OsmosisDocument6 pagesQuestions About Reverse OsmosisManjunath HrmNo ratings yet
- v25 Algebra 1 5.02.odtDocument6 pagesv25 Algebra 1 5.02.odtSam's vrNo ratings yet
- Bab 14-Distribusi Tegangan Tanah VertikalDocument41 pagesBab 14-Distribusi Tegangan Tanah VertikalNovia FlorensiaNo ratings yet
- WEG CFW500 Programming Manual v3 1x 10006739425 enDocument218 pagesWEG CFW500 Programming Manual v3 1x 10006739425 enwilsonwdarNo ratings yet
- New Application /change Request Format: Schematic FlowDocument4 pagesNew Application /change Request Format: Schematic FlowUDAYNo ratings yet
- Richard FeynmanDocument4 pagesRichard FeynmanyashNo ratings yet
- Resume: Michael AaronsonDocument16 pagesResume: Michael AaronsonMichaelAaronsonNo ratings yet
- Compact Machining Center: M140X1 ItemDocument6 pagesCompact Machining Center: M140X1 ItemXi FengNo ratings yet
- Financial ModellingDocument13 pagesFinancial ModellingPRACHI DASNo ratings yet
- Makridakis (2020)Document21 pagesMakridakis (2020)100111No ratings yet
- Read Me HALO CEDocument9 pagesRead Me HALO CERafie BonoanNo ratings yet
- t156 1 Forklift Merlo P35.9ev Oem Service ManualDocument100 pagest156 1 Forklift Merlo P35.9ev Oem Service ManualChomi100% (1)
- tp6998 PDFDocument206 pagestp6998 PDFAlexandre PatrocinioNo ratings yet
- Physics: International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument2 pagesPhysics: International General Certificate of Secondary EducationAr Ar ViNo ratings yet