Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acute Bronchitis Lance Angelo Bernandino BSN II
Acute Bronchitis Lance Angelo Bernandino BSN II
Uploaded by
Lance Angelo BernandinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acute Bronchitis Lance Angelo Bernandino BSN II
Acute Bronchitis Lance Angelo Bernandino BSN II
Uploaded by
Lance Angelo BernandinoCopyright:
Available Formats
About Acute Bronchitis
Key facts about Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis comes on suddenly.
It causes the tubes that carry air to your lungs to swell.
It usually gets better on its own without the need for medication.
The infection usually lasts for 3 to 10 days, but the cough can continue
for several weeks.
It is different from chronic bronchitis, a long-term disease. There is no
cure for chronic bronchitis.
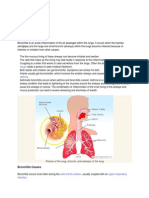
Acute bronchitis is a sudden swelling in the major airways into your lungs,
called bronchi. It is usually caused by a virus, but it can also be caused by
breathing in things that irritate your lungs, such as tobacco smoke, fumes,
dust, and air pollution. Bacteria sometimes cause acute bronchitis.
How Acute Bronchitis affects your body
When you have acute bronchitis, the cells that line your airways,
called bronchi, become inflamed. The infection usually starts in the nose or
throat and travels to the lungs. When the body tries to fight the infection, it
causes the tubes leading to your lungs to swell. This causes you to cough.
Sometimes it is a dry cough, but often you will cough up mucus.
Because your airways are swollen, less air can move through the tubes to
your lungs. This can cause wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of
breath.
Eventually, your body fights the infection and heals. Acute bronchitis usually
lasts for 3 to 10 days. However, you may cough and produce mucus for
several weeks after the infection heals.
Treating Acute Bronchitis
If you are diagnosed with acute bronchitis, you may miss school or work for a
few days because of your symptoms. You also may have a cough that lasts
up to 3 weeks but slowly improves.
This infection usually lasts no longer than 1 to 2 weeks. Your provider may
recommend rest, fluids, a cough suppressant, and a pain reliever. A humidifier
or steamer may also help. You may need inhaled medicine to open your
airways if you are wheezing.
Antibiotics have not been proven to heal acute bronchitis or reduce
symptoms. Because viruses cause most cases of acute bronchitis, antibiotics
are not used. Antibiotics are only effective against bacteria.
In addition, using antibiotics when they aren’t recommended can cause side
effects. Using antibiotics too often also may mean that your body won’t
respond to antibiotics when it needs to. If your provider thinks that bacteria
caused your acute bronchitis, he or she might then prescribe antibiotics.
Managing Acute Bronchitis
Usually, the symptoms of acute bronchitis last only a couple of weeks.
However, if you have a cough that won’t go away, it may be the sign of a more
serious disease. Contact your health care provider to describe these long-
term symptoms.
Preventing Acute Bronchitis
Avoiding things that irritate your lungs is important for preventing acute
bronchitis as well as treating it. If you smoke, quit. To help protect your
lungs, wear a mask over your mouth and nose when using lung irritants such
as paint, paint remover, or varnish.
Other ways to help prevent acute bronchitis include:
Washing your hands often to reduce your exposure to viruses and
bacteria
Getting a flu shot every year
Ask your provider if you should get a pneumonia shot, especially if you’re 60
years of age or older.
LANCE ANGELO BERNANDINO
BSN-II
You might also like
- Dark Demon - Christine FeehanDocument4 pagesDark Demon - Christine Feehantheresa1970No ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitisjosanne938No ratings yet
- What Is Acute BronchitisDocument11 pagesWhat Is Acute BronchitisKerri-DojhnHallNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument9 pagesBronchitisMS AntikaNo ratings yet
- BRONCHITIS Know Your Symptoms and When to Seek Professional Help As It Can Be DeadlyFrom EverandBRONCHITIS Know Your Symptoms and When to Seek Professional Help As It Can Be DeadlyNo ratings yet
- Chronic BronchitisDocument5 pagesChronic BronchitisJemalyn M. Saludar100% (2)
- How to Deal with Bronchitis: Coping with Bronchitis and Its Health EffectsFrom EverandHow to Deal with Bronchitis: Coping with Bronchitis and Its Health EffectsNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument6 pagesBronchitisNader Smadi100% (1)
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitiscorsaruNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis: Week 5 1Document5 pagesBronchitis: Week 5 1jessNo ratings yet
- By DPS StudentsDocument10 pagesBy DPS StudentszarakonhaiNo ratings yet
- What Is BronchitisDocument1 pageWhat Is BronchitisMelvin Lopez SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Asthma Vs BronchitisDocument4 pagesAsthma Vs BronchitisEmma CebanNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Treatment Guide: How to Treat Bronchitis, Emphysema and COPDFrom EverandBronchitis Treatment Guide: How to Treat Bronchitis, Emphysema and COPDNo ratings yet
- Key Facts About Chronic BronchitisDocument3 pagesKey Facts About Chronic BronchitiskvishwanathNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocument16 pagesDiseases of The Respiratory SystemScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- BHS Ingg BronkitisDocument12 pagesBHS Ingg BronkitisdeyrikaNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis (Biochem Presentation)Document42 pagesBronchitis (Biochem Presentation)SiewLiZhenNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument15 pagesBronchitisAakanksha vaishnav100% (1)
- MAKALAH Mom OliveDocument9 pagesMAKALAH Mom Olivemaragantigaming04officialNo ratings yet
- Essential Oils For BronchitisDocument26 pagesEssential Oils For BronchitissanjaigNo ratings yet
- Acute BronchitisDocument2 pagesAcute BronchitisChristabella Natalia WijayaNo ratings yet
- What Is Bronchitis: Understanding The Bronchitis Symptoms And Curing ItFrom EverandWhat Is Bronchitis: Understanding The Bronchitis Symptoms And Curing ItNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument4 pagesBronchitisGokul SmartNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Naturist TreatmentDocument2 pagesBronchitis Naturist TreatmentTimar2100% (1)
- Obcl-2-Cu - Week 3 BronchitisDocument9 pagesObcl-2-Cu - Week 3 BronchitisMichelle Gliselle Guinto MallareNo ratings yet
- Defenition of BronchitisDocument3 pagesDefenition of BronchitisulfhasNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Chronic BronchitisDocument6 pagesCase Study For Chronic BronchitisGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Acute Bronchitis HandoutDocument5 pagesAcute Bronchitis HandoutDianne LegionNo ratings yet
- LUNG Bronchitis 5Document2 pagesLUNG Bronchitis 5aniketr9870No ratings yet
- Pneumonia Is A Condition That Causes The Lungs To Become Inflamed As A Result of A BacterialDocument3 pagesPneumonia Is A Condition That Causes The Lungs To Become Inflamed As A Result of A BacterialDhonnalyn Amene CaballeroNo ratings yet
- LungsDocument18 pagesLungsMaritess JacintoNo ratings yet
- Lungs InfectionsDocument7 pagesLungs InfectionsMac PhersonNo ratings yet
- Signs & SymptomsDocument2 pagesSigns & SymptomsWahyuni ErwinNo ratings yet
- Bronchopneumonia - MedscapeDocument7 pagesBronchopneumonia - MedscapecleoaerNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To CoughsDocument5 pagesComplete Guide To CoughsbramsNo ratings yet
- What Is Bronchitis?Document4 pagesWhat Is Bronchitis?Benny TheodoreNo ratings yet
- Walking Pneumonia HealthDocument4 pagesWalking Pneumonia HealthneljohnaciboNo ratings yet
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument9 pagesBroncho Pneumoniamunie munieNo ratings yet
- Whatis BronchiectasisDocument2 pagesWhatis Bronchiectasisハルァン ファ烏山No ratings yet
- Symptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniaDocument10 pagesSymptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniajessyNo ratings yet
- Makalah B.inggris EsiDocument11 pagesMakalah B.inggris EsiUMINo ratings yet
- Coughs & ColdsDocument20 pagesCoughs & Coldsangelstar24087381No ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter - Most Common Communicable Diseases and Its Prevention and ControlDocument7 pages3RD Quarter - Most Common Communicable Diseases and Its Prevention and ControlJocel May TaboradaNo ratings yet
- TB and Copd!Document9 pagesTB and Copd!RachnaNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis in ChildrenDocument3 pagesBronchitis in ChildrenVibhaSingh1No ratings yet
- What Is Bronchitis?Document3 pagesWhat Is Bronchitis?normina dagendelNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts On CoughsDocument12 pagesFast Facts On CoughsLany T. CataminNo ratings yet
- Symptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniaDocument10 pagesSymptoms of Bronchopneumonia in Adults and Children: PneumoniajessyNo ratings yet
- Disease Monograph: CausesDocument4 pagesDisease Monograph: CausesRawan AlmutairiNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis - Biology 11SDocument15 pagesBronchitis - Biology 11SChantoya SmallNo ratings yet
- "Bronchitis": Respiratory DisorderDocument40 pages"Bronchitis": Respiratory Disorderaswin379No ratings yet
- Sinusitis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocument5 pagesSinusitis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDyane VatriciaNo ratings yet
- Cough Task 1Document4 pagesCough Task 1Sheharyar SandhuNo ratings yet
- What and Where Are The Sinuses?Document10 pagesWhat and Where Are The Sinuses?jercx_trigaNo ratings yet
- Alex Pidd - Stav & Runes Notebook - A Beginners GuideDocument47 pagesAlex Pidd - Stav & Runes Notebook - A Beginners Guidemichael ellis0% (1)
- SSDCDocument1 pageSSDCManoj Digi LoansNo ratings yet
- PRENTAC Typical Job Descriptions Process Safety EngineersDocument5 pagesPRENTAC Typical Job Descriptions Process Safety EngineerspstindiaNo ratings yet
- Sterling Scholar EssaysDocument5 pagesSterling Scholar Essaysapi-255099497No ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner Cover LetterDocument4 pagesNurse Practitioner Cover Letterafjwfoffvlnzyy100% (2)
- COBECON - Math ProblemsDocument16 pagesCOBECON - Math ProblemsdocumentsNo ratings yet
- Profit Maximization in Various Market Structure: de Jesus, Lerrie Quejada, Abegail Vilog, LheamDocument32 pagesProfit Maximization in Various Market Structure: de Jesus, Lerrie Quejada, Abegail Vilog, LheamJohn Stephen EusebioNo ratings yet
- Bennet - Coleman - and - Co - Vs - Union - of - India - and - Ors - 13m770054COM695345 PDFDocument21 pagesBennet - Coleman - and - Co - Vs - Union - of - India - and - Ors - 13m770054COM695345 PDFSandeep SavarkarNo ratings yet
- BibliographyDocument2 pagesBibliography__________________________No ratings yet
- Admin Law Project FinalDocument26 pagesAdmin Law Project FinalAnurag PrasharNo ratings yet
- ACMS 40390: Fall 2010: Zxu2@nd - EduDocument2 pagesACMS 40390: Fall 2010: Zxu2@nd - EduChiOfGreeNo ratings yet
- Reparando Boot ServerDocument6 pagesReparando Boot ServerErlon TroianoNo ratings yet
- 4th SemDocument14 pages4th SemManoj kumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Business Statistics (SUBMITION DATE 10/12/2013)Document2 pagesAssignment On Business Statistics (SUBMITION DATE 10/12/2013)Negero ArarsoNo ratings yet
- Non-Caries Dental DiseaseDocument61 pagesNon-Caries Dental Diseaseapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Social Motivation For Code Switching in Sujatha Novels in TamilDocument4 pagesSocial Motivation For Code Switching in Sujatha Novels in TamilEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Ec8392 Digital Electronics SyllabusDocument2 pagesEc8392 Digital Electronics SyllabusNandha KumarNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Exam Paper May 2012Document23 pagesManagement Accounting Exam Paper May 2012MahmozNo ratings yet
- Chapter One (1) 1. Risk and Related TopicsDocument12 pagesChapter One (1) 1. Risk and Related TopicssolomonaauNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Radiology - New Cover2021Document154 pagesDiagnostic Radiology - New Cover2021fouzi bentayebNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 "How Well Am I Doing?" - Financial Statement AnalysisDocument134 pagesChapter 16 "How Well Am I Doing?" - Financial Statement AnalysisTyra Joyce RevadaviaNo ratings yet
- Not So Popular Party Girl Dork DiariesDocument30 pagesNot So Popular Party Girl Dork DiariesLISNY VALLECILLONo ratings yet
- P.1 Reading Revised Lesson Notes Term I 2020Document44 pagesP.1 Reading Revised Lesson Notes Term I 2020kaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- MP Clerks ChrisDocument33 pagesMP Clerks ChrisChrisstael KaranjaNo ratings yet
- Right Left: Abdominal Aorta and BranchesDocument1 pageRight Left: Abdominal Aorta and Branchesjesus Porras ColonNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesLesson Planapi-189222578No ratings yet
- GE 5 Lesson 1Document2 pagesGE 5 Lesson 1Angelica AbogandaNo ratings yet
- Capacitive TransducerDocument21 pagesCapacitive Transducersourabhyadav14No ratings yet
- MATH 121 Assignment DDocument4 pagesMATH 121 Assignment DVladlightNo ratings yet