Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 157 - 157)
Teaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 157 - 157)
Uploaded by
Victoria TranCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Language Teacher ToolkitDocument435 pagesThe Language Teacher Toolkitalsd100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 31 Formulas p.300-341Document42 pages31 Formulas p.300-341Victoria TranNo ratings yet
- Handout-Virtual SEA IELTS Teachers Training 2021Document234 pagesHandout-Virtual SEA IELTS Teachers Training 2021Victoria TranNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 200 - 202)Document3 pagesTeaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 200 - 202)Victoria TranNo ratings yet
- Ieltsliz-Model AnswersDocument4 pagesIeltsliz-Model AnswersVictoria Tran100% (1)
- Approaches To Language in The Classroom ContextDocument89 pagesApproaches To Language in The Classroom ContextEduardo SchillerNo ratings yet
- پنج زبانشناسی شناختی و تاثیر ان بر اموزش زبانDocument5 pagesپنج زبانشناسی شناختی و تاثیر ان بر اموزش زبانMohammadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge University Press: Format. All SSLA Submissions Must Conform To The Requirements of The LatestDocument11 pagesCambridge University Press: Format. All SSLA Submissions Must Conform To The Requirements of The Latestfernanda salazarNo ratings yet
- The Role of Using Computer ...Document51 pagesThe Role of Using Computer ...sabriNo ratings yet
- INGLÉS Oposiciones Secundaria 1 PDFDocument5 pagesINGLÉS Oposiciones Secundaria 1 PDFJUDITH GALLEGO SEGURA100% (1)
- TEFL PPT 1 Overview Approach Method Tech PDFDocument124 pagesTEFL PPT 1 Overview Approach Method Tech PDFVictoria FrancouNo ratings yet
- Interactional FeedbackDocument28 pagesInteractional FeedbackSilvia Amutio PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Critical Period HypothesisDocument10 pagesCritical Period HypothesisBenedict ShabongNo ratings yet
- MIL - Module 1Document5 pagesMIL - Module 1Imie Omamalin GuisehanNo ratings yet
- Principles For Teaching Speaking SkillsDocument2 pagesPrinciples For Teaching Speaking SkillsSymr MhzzbNo ratings yet
- Teaching English To Young Learners: More Teacher Education and More Children's Literature!Document26 pagesTeaching English To Young Learners: More Teacher Education and More Children's Literature!rahi anjumNo ratings yet
- Second Language Learning in The ClassroomDocument2 pagesSecond Language Learning in The Classroomingilizce1No ratings yet
- Second Language AcquisitionDocument3 pagesSecond Language AcquisitionHazel Abila50% (2)
- Errors in Language LearningDocument5 pagesErrors in Language LearningSebastian Hawker100% (1)
- Gec 105 NotesDocument9 pagesGec 105 NotesVictoria TomolinNo ratings yet
- Pack 1 Yesdi̇lDocument22 pagesPack 1 Yesdi̇lZeynep Laledağı AkınNo ratings yet
- Statements of Purpose Guidelines and Sample EssaysDocument51 pagesStatements of Purpose Guidelines and Sample Essaysyawnbot botNo ratings yet
- Methods & Approaches To Teaching English As A Foreign LanguageDocument4 pagesMethods & Approaches To Teaching English As A Foreign LanguagePamelaNo ratings yet
- Conversation Techniques in The English ClassDocument8 pagesConversation Techniques in The English ClassSofica TomescuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 3 Combined PowerpointsDocument177 pagesLesson 2 3 Combined PowerpointsGodwin Jerome ReyesNo ratings yet
- Oral PPT Evaluation FormDocument2 pagesOral PPT Evaluation FormIeva ViļumaNo ratings yet
- Bilingual Language Development What Do Early Years Practitioners Need To KnowDocument12 pagesBilingual Language Development What Do Early Years Practitioners Need To Knowxiaohui maNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Researching Listening (2nd Ed.)Document3 pagesTeaching and Researching Listening (2nd Ed.)Kang AleNo ratings yet
- Typology of Bilingual EducationDocument7 pagesTypology of Bilingual EducationKristel Mariz TorricerNo ratings yet
- LIU23002 - Language and The Mind Module Handout 2020-21Document4 pagesLIU23002 - Language and The Mind Module Handout 2020-21Ayako GNo ratings yet
- Linguistics NotesDocument5 pagesLinguistics NotesNoelyn AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Tesol Workshiop s00135139Document14 pagesTesol Workshiop s00135139api-286535131No ratings yet
- Project For AP PsychologyDocument2 pagesProject For AP PsychologyMatthewNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Using Technology in English Language TeachingDocument4 pagesThe Benefits of Using Technology in English Language TeachingStelli OanaNo ratings yet
Teaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 157 - 157)
Teaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 157 - 157)
Uploaded by
Victoria TranOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Teaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 157 - 157)
Teaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 157 - 157)
Uploaded by
Victoria TranCopyright:
Available Formats
Copyright © 2011. Taylor & Francis Group. All rights reserved.
142
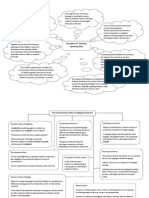
Concept 5.1 Positive and negative factors in self-report and other-report
Potential Type of report
factors
Self-report Other-report
Positive • Self-report is one of the very few ways that we can gain • Many kinds of other-report exist, largely via
Created from vu on 2021-09-07 02:41:16.
access to the learner’s thoughts, feelings, attitudes, and observation (live observation in the classroom,
strategies. computer tracking, neurological observation).
• Self-report may be needed as a check on the findings of • Other-report can be a check on the findings of
other-report. self-report.
• Social desirability response bias (tendency to report what the • Social desirability response bias is not present in
participant thinks the researcher wants) is not an issue in L2 other-report.
learning strategy studies (a) if it is made clear that there are • Other-report in the classroom and via computer
no right or wrong answers and that what participants say tracking is not generally intrusive.
will not influence evaluations of the individual by others, and • Other-report is not clouded by participant
(b) if, in formal studies, anonymity and confidentiality are memory loss, irrelevant comments, inarticulateness,
established. or inability to generalize across tasks.
Central, http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/vu/detail.action?docID=1569680.
Negative • Interpretations of retrospective self-report might be clouded • Other-report might miss the internal aspects of
by memory loss; automaticity of the behaviour, making it L2 learning that could be reported by the
unconscious; or complexity (Anderson and Vandergrift, learner, so self-report is needed.
1996). • Even if good observations are possible by the
• Interpretations might be marred by a participant’s irrelevant teacher or researcher, the correct interpretation
comments about “epiphenomena,” inarticulateness, or of what the observations mean might be difficult
inability to generalize over a number of recent task or elusive.
performances (see White et al., 2007). • Other-report can be hampered by the
• Interpretations can be hampered by the researcher’s lack of researcher’s lack of understanding or cultural
TEACHING AND RESEARCHING LANGUAGE LEARNING STRATEGIES
understanding or cultural assumptions too distant from or assumptions.
too similar to those of the participant.
Oxford, Rebecca L.. Teaching and Researching: Language Learning Strategies, Taylor & Francis Group, 2011. ProQuest Ebook
• If a self-report occurs during an L2 task, this can be
experienced as intrusive (Cohen and Scott, 1996) or
burdensome (Branch, 2000).
• Self-report can have social desirability response bias under
some circumstances.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (350)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (824)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Language Teacher ToolkitDocument435 pagesThe Language Teacher Toolkitalsd100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 31 Formulas p.300-341Document42 pages31 Formulas p.300-341Victoria TranNo ratings yet
- Handout-Virtual SEA IELTS Teachers Training 2021Document234 pagesHandout-Virtual SEA IELTS Teachers Training 2021Victoria TranNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 200 - 202)Document3 pagesTeaching and Researching Language Learning Strateg... - (PG 200 - 202)Victoria TranNo ratings yet
- Ieltsliz-Model AnswersDocument4 pagesIeltsliz-Model AnswersVictoria Tran100% (1)
- Approaches To Language in The Classroom ContextDocument89 pagesApproaches To Language in The Classroom ContextEduardo SchillerNo ratings yet
- پنج زبانشناسی شناختی و تاثیر ان بر اموزش زبانDocument5 pagesپنج زبانشناسی شناختی و تاثیر ان بر اموزش زبانMohammadNo ratings yet
- Cambridge University Press: Format. All SSLA Submissions Must Conform To The Requirements of The LatestDocument11 pagesCambridge University Press: Format. All SSLA Submissions Must Conform To The Requirements of The Latestfernanda salazarNo ratings yet
- The Role of Using Computer ...Document51 pagesThe Role of Using Computer ...sabriNo ratings yet
- INGLÉS Oposiciones Secundaria 1 PDFDocument5 pagesINGLÉS Oposiciones Secundaria 1 PDFJUDITH GALLEGO SEGURA100% (1)
- TEFL PPT 1 Overview Approach Method Tech PDFDocument124 pagesTEFL PPT 1 Overview Approach Method Tech PDFVictoria FrancouNo ratings yet
- Interactional FeedbackDocument28 pagesInteractional FeedbackSilvia Amutio PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Critical Period HypothesisDocument10 pagesCritical Period HypothesisBenedict ShabongNo ratings yet
- MIL - Module 1Document5 pagesMIL - Module 1Imie Omamalin GuisehanNo ratings yet
- Principles For Teaching Speaking SkillsDocument2 pagesPrinciples For Teaching Speaking SkillsSymr MhzzbNo ratings yet
- Teaching English To Young Learners: More Teacher Education and More Children's Literature!Document26 pagesTeaching English To Young Learners: More Teacher Education and More Children's Literature!rahi anjumNo ratings yet
- Second Language Learning in The ClassroomDocument2 pagesSecond Language Learning in The Classroomingilizce1No ratings yet
- Second Language AcquisitionDocument3 pagesSecond Language AcquisitionHazel Abila50% (2)
- Errors in Language LearningDocument5 pagesErrors in Language LearningSebastian Hawker100% (1)
- Gec 105 NotesDocument9 pagesGec 105 NotesVictoria TomolinNo ratings yet
- Pack 1 Yesdi̇lDocument22 pagesPack 1 Yesdi̇lZeynep Laledağı AkınNo ratings yet
- Statements of Purpose Guidelines and Sample EssaysDocument51 pagesStatements of Purpose Guidelines and Sample Essaysyawnbot botNo ratings yet
- Methods & Approaches To Teaching English As A Foreign LanguageDocument4 pagesMethods & Approaches To Teaching English As A Foreign LanguagePamelaNo ratings yet
- Conversation Techniques in The English ClassDocument8 pagesConversation Techniques in The English ClassSofica TomescuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 3 Combined PowerpointsDocument177 pagesLesson 2 3 Combined PowerpointsGodwin Jerome ReyesNo ratings yet
- Oral PPT Evaluation FormDocument2 pagesOral PPT Evaluation FormIeva ViļumaNo ratings yet
- Bilingual Language Development What Do Early Years Practitioners Need To KnowDocument12 pagesBilingual Language Development What Do Early Years Practitioners Need To Knowxiaohui maNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Researching Listening (2nd Ed.)Document3 pagesTeaching and Researching Listening (2nd Ed.)Kang AleNo ratings yet
- Typology of Bilingual EducationDocument7 pagesTypology of Bilingual EducationKristel Mariz TorricerNo ratings yet
- LIU23002 - Language and The Mind Module Handout 2020-21Document4 pagesLIU23002 - Language and The Mind Module Handout 2020-21Ayako GNo ratings yet
- Linguistics NotesDocument5 pagesLinguistics NotesNoelyn AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Tesol Workshiop s00135139Document14 pagesTesol Workshiop s00135139api-286535131No ratings yet
- Project For AP PsychologyDocument2 pagesProject For AP PsychologyMatthewNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Using Technology in English Language TeachingDocument4 pagesThe Benefits of Using Technology in English Language TeachingStelli OanaNo ratings yet