Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transport Mechanisms
Transport Mechanisms
Uploaded by
Jayrelle D. SafranOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transport Mechanisms
Transport Mechanisms
Uploaded by
Jayrelle D. SafranCopyright:
Available Formats
TRANSPORT MECHANISMS
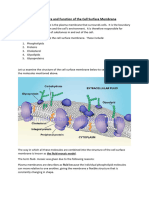
Structure, function and importance of the plasma membrane
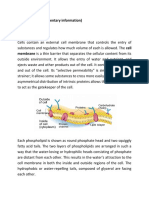
Plasma membranes
Are made up of a phospholipid bilayer in an aqueous environment.
Phospholipids are the foundation of all known biological membranes.
The lipid bilayer forms as a result of the interaction between the non-polar (hydrophobic or water-fearing)
phospholipid tails, the polar (hydrophilic or water-loving) phospholipid heads, and the surrounding water.
STRUCTURES: (RECALL)
1. Transmembrane proteins – serves as channels and function as identification tags
2. membrane proteins – functions as enzymes; as paste or glue forming junctions
3. cholesterol – makes the bilayer stronger.
TRANSPORT MECHANISMS
1. PASSIVE TRANSPORT - heat energy of the cellular environment provides all of the energy, hence, this is not
energy-costly to the cell.
A. Diffusion - is a type of passive transport described as the natural tendency for molecules to move
constantly occurs when the materials on one side of the membrane have a different concentration than
the materials on the other side.
a.Osmosis – a type of diffusion associated with the movement of water molecules through a
membrane.
B. Facilitated Diffusion - utilizes protein transmembrane channels that are specific to certain molecules.
- driven by the concentration of molecules on the inside and the outside of the
membrane
2. ACTIVE TRANSPORT - requires the cell to do work, requiring the cell to expend its energy reserves.
Types of Solutions
1. HYPERTONIC SOLUTION - solution with a higher concentration of solute.
o Water moves out of the cell.
2. HYPOTONIC SOLUTION - solution with a lower concentration of solutes.
o Water moves into the cell.
3. ISOTONIC SOLUTION - Solutions of equal solution concentration.
o Cell gains water at the same rate that it loses it.
HOW DO CELLS BEHAVE IN DIFFERENT SOLUTIONS?
ISOTONIC
o Animal cell’s volume remains constant in this solution
o Plant cell is flaccid and wilts in this condition.
HYPOTONIC
o Red blood cell gains water, swells, and may eventually burst due to excessive water intake.
o Plant cell is turgid and healthy in a hypotonic solution.
HYPERTONIC
o Animal cell shrinks and can die due to water loss.
o Plant cell loses water, shrivels, and its plasma membrane detaches from the cell wall; causes death.
ENDOCYTOSIS
- Generalized non-selective process wherein large molecules enter the cell.
- In this process, the plasma membrane engulfs the particle or fluid droplet and pinches off a membranous sac or
vesicle with a particular fluid inside into the cytoplasm.
1. Phagocytosis - endocytosis of a particulate material
2. Pinocytosis - Endocytosis of liquid material.
3. Receptor-mediated endocytosis - involves the transport of materials through coated vesicles.
EXOCYTOSIS
- The reverse process where a membrane-bound vesicle filled with bulky materials moves to the plasma
membrane and fuses with it. In this process, the vehicle’s contents are released out of the cell.
You might also like
- Family Nursing Care Plan 2 Education of Their Child As Foreseeable CrisisDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan 2 Education of Their Child As Foreseeable CrisisJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Dorothy Johnson - Behavioral System ModelDocument3 pagesDorothy Johnson - Behavioral System ModelJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Bio FinalDocument8 pagesBio FinalChris SmithNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3 Cell Structures and Their FunctionsVince Martin ManaigNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Reviewer 1Document5 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Reviewer 1Shane Patricia CalmaNo ratings yet
- 7 Transport-Mechanism2Document62 pages7 Transport-Mechanism2aldrin braganzaNo ratings yet
- General Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)Document4 pagesGeneral Biology (Grade 11 STEM - 1st Semester)alfonsogwenmnqNo ratings yet
- Cell Boundaries Module 2Document17 pagesCell Boundaries Module 2Vedha SinghNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell MembraneQaran PrintingNo ratings yet
- 1 Cellular Transport VidDocument57 pages1 Cellular Transport Vidchizy bananaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneDocument15 pagesCell Membrane Membrane: How Substances Get Across The MembraneMariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Movement of Subtances Across Plasma MembraneDocument414 pagesMovement of Subtances Across Plasma MembranezazaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Document7 pagesBIOLOGY NOTES iAL Biology Unit 1Student Alejandro Zhou WeiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Mechanism: General Biology 1Document12 pagesCellular Transport Mechanism: General Biology 1Kenn KennNo ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument30 pagesTransport MechanismsApril VeraNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport NotesDocument24 pagesCell Membrane Transport NotesJason RobinsonNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasismadhutkNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument24 pagesUntitled PresentationFreyacresaNo ratings yet
- AkdogDocument10 pagesAkdognorhain4.aNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisMal FujitakaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Membrane Structure and FunctionIrish Jem BantolinoNo ratings yet
- The Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisDocument13 pagesThe Plasma Membrane and HomeostasisMaxellLanceClementNo ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument5 pagesCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariNo ratings yet
- Transport Mind MapDocument49 pagesTransport Mind MapMiryaNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane & HomeostasisDocument50 pagesCell Membrane & Homeostasisapi-233187566No ratings yet
- B. Topic 2. Movement Through The CellDocument23 pagesB. Topic 2. Movement Through The CellRica T. DagosNo ratings yet
- Transport MembranDocument34 pagesTransport MembranTia Herdiana WardaniNo ratings yet
- The Plasma MembraneDocument5 pagesThe Plasma MembraneFarhana AktharNo ratings yet
- Cell ConstituentsDocument8 pagesCell ConstituentsSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Topic-2ADocument9 pagesBiology Notes: Topic-2Alaiba amirNo ratings yet
- X Membrane and TransportDocument35 pagesX Membrane and TransportHitesh MoreNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3Document8 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 3MSKNo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument4 pagesChapter 3-Movement of Subtances Across The Plasma MembraneMuhammad AddinNo ratings yet
- Act2 Bio SciDocument4 pagesAct2 Bio SciPamaran, Kristel DenishNo ratings yet
- Transport Mec Hanisms in Biological MembranesDocument51 pagesTransport Mec Hanisms in Biological Membranesjm earlytepNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument46 pagesMembrane Structure and FunctionHurmat AmnaNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 Membrane TransportDocument29 pagesLect 2 Membrane Transportramadan100% (1)
- KANESS (016-4573342) 10, JLN TPT 10, Taman Puchong Tekali, 47150, Puchong, Selangor Chapter 2: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument6 pagesKANESS (016-4573342) 10, JLN TPT 10, Taman Puchong Tekali, 47150, Puchong, Selangor Chapter 2: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneKaness MathzNo ratings yet
- C3Movement Across The Plasma MembraneDocument14 pagesC3Movement Across The Plasma Membranemagdelena100% (1)
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocument10 pagesBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17No ratings yet
- GRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)Document3 pagesGRADE 11 (Supplementary Information)EleinaNo ratings yet
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument11 pagesMembrane Structure and FunctionShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane NotesDocument6 pagesCell Membrane NotesBianca RamirezNo ratings yet
- BIO Ch.7VocabDocument2 pagesBIO Ch.7VocababNo ratings yet
- 3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsDocument67 pages3 - Plasma Membrane and Transport MechanismsThom PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- By: Tiffany M. AustriaDocument10 pagesBy: Tiffany M. Austrianyzgirl17No ratings yet
- Bio OL Chapter 3 & 4Document9 pagesBio OL Chapter 3 & 4zuhra123coolNo ratings yet
- 2.1.5 Biology Ocr ADocument5 pages2.1.5 Biology Ocr AFatima AfifiNo ratings yet
- Senior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized SubjectDocument53 pagesSenior High School: Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (Stem) Specialized Subjectpotato macchiatoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureDocument4 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Reviewer: CHAPTER 3: Cell Structure and Their Functions 3.1 Cell StructureChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 BioDocument12 pagesChapter 5 BioGeorges SarkisNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport PowerpointDocument50 pagesCellular Transport PowerpointPortia EgkenNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Pre-ReadingDocument7 pagesCh. 5 Pre-ReadingDJ ISAACS50% (2)
- Biology - Module 4Document6 pagesBiology - Module 4ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Significance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport MechanismDocument10 pagesSignificance of Liquid in Biological Membranes and Transport Mechanismroshan khanNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Chapter 5Document23 pagesCell Bio Chapter 5busachala517No ratings yet
- Cell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima SharmaDocument4 pagesCell Classix Notes Session2 Made by Purnima Sharmajeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Mader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesMader/Biology, 11/e - Chapter Outline: 5.1 Plasma Membrane Structure and Functionapi-455371000No ratings yet
- Q2.1 Transport Mechanism 2Document45 pagesQ2.1 Transport Mechanism 2kasandra cristy galonNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Theory 2Document18 pagesAnimal Physiology Theory 2ao868598No ratings yet
- Rle Form LC Con TemplatesDocument34 pagesRle Form LC Con TemplatesJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Safran, Jayrelle Aldrin Shayne D. - Act # 4finals (8th Rotation)Document5 pagesSafran, Jayrelle Aldrin Shayne D. - Act # 4finals (8th Rotation)Jayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Safran, Jayrelle Aldrin Shayne D. - Act # 1.5 Finals (7th Rotation)Document1 pageSafran, Jayrelle Aldrin Shayne D. - Act # 1.5 Finals (7th Rotation)Jayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Med Admin PPT Part 1Document80 pagesMed Admin PPT Part 1Jayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- 2ND Rot - Nightingale TurzarDocument2 pages2ND Rot - Nightingale TurzarJayrelle D. Safran100% (1)
- NCP Altered Thermoregulation HypothermiaDocument2 pagesNCP Altered Thermoregulation HypothermiaJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: City of San Fernando, La UnionDocument3 pagesCollege of Nursing: City of San Fernando, La UnionJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Newborn ReflexesDocument10 pagesNewborn ReflexesJayrelle D. Safran100% (1)
- Apgar and Ballard ScoringDocument36 pagesApgar and Ballard ScoringJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Essential Intrapartum Newborn Care: Prepared byDocument41 pagesEssential Intrapartum Newborn Care: Prepared byJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Medication: Prepared By: Level II InstructorsDocument105 pagesParenteral Medication: Prepared By: Level II InstructorsJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Universal PrecautionDocument46 pagesUniversal PrecautionJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Essential Intrapartum Newborn Care: Prepared byDocument41 pagesEssential Intrapartum Newborn Care: Prepared byJayrelle D. Safran100% (1)
- Kami Export ID IM SC NewDocument104 pagesKami Export ID IM SC NewJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Topic # 1 Leopold's ManueverDocument39 pagesTopic # 1 Leopold's ManueverJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Assisting Delivery: Mrs. Helen Segundo LubianoDocument34 pagesAssisting Delivery: Mrs. Helen Segundo LubianoJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: Homoios - "The Same" Stasis - "Standing" Homeostasis - "Standing or Staying The Same"Document6 pagesHomeostasis: Homoios - "The Same" Stasis - "Standing" Homeostasis - "Standing or Staying The Same"Jayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3.A Bag TechniqueDocument38 pagesTOPIC 3.A Bag TechniqueJayrelle D. Safran100% (1)
- Topic # 2 PartographDocument42 pagesTopic # 2 PartographJayrelle D. Safran100% (1)
- Multiple Organ Dysfunction SyndromeDocument5 pagesMultiple Organ Dysfunction SyndromeDrOjas RuDra ParasharNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulators: By: Payal Suthar Department of PharmacognosyDocument26 pagesImmunomodulators: By: Payal Suthar Department of PharmacognosyHely Patel100% (1)
- Extra Cells A and MSDocument29 pagesExtra Cells A and MSKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SummaryDocument42 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SummaryBrythym Mojeca De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- SPM Biology Essays CollectionDocument31 pagesSPM Biology Essays CollectionYvonne Choo Shuen Lann100% (49)
- Self-Learning Home Task (SLHT)Document11 pagesSelf-Learning Home Task (SLHT)GraceEstoleCalo100% (1)
- Ambroxol PDFDocument45 pagesAmbroxol PDFFatah Jati PNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 and UNIT 5 ISDocument9 pagesUNIT 4 and UNIT 5 ISMarinelle TumanguilNo ratings yet
- Bio Reaction PaperDocument2 pagesBio Reaction PaperGlydele Mae Eragol Fuene0% (2)
- Lesson 6 - Cell Membrane Phospholipid BilayerDocument3 pagesLesson 6 - Cell Membrane Phospholipid BilayerEarl Caesar Quiba PagunsanNo ratings yet
- CH 12-Brooker Biology-Gene Expression at The Molecular LevelDocument4 pagesCH 12-Brooker Biology-Gene Expression at The Molecular Leveltiffycutie1No ratings yet
- Osmosis Virtual LabDocument2 pagesOsmosis Virtual Labapi-33857887483% (6)
- Shinjita Das M.D., Rachel Reynolds M.D. (Auth.), Joshua Zeichner (Eds.) - Acneiform Eruptions in Dermatology - A Differential Diagnosis-Springer-Verlag New York (2014) PDFDocument405 pagesShinjita Das M.D., Rachel Reynolds M.D. (Auth.), Joshua Zeichner (Eds.) - Acneiform Eruptions in Dermatology - A Differential Diagnosis-Springer-Verlag New York (2014) PDFMaryNo ratings yet
- Zincassignment 2Document4 pagesZincassignment 2Namrata GangavelliNo ratings yet
- Non Coding RNADocument22 pagesNon Coding RNANaomiKerryaThompsonNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 2 Meiosis+and+Sexual+ReproductionDocument38 pagesCA Lesson 2 Meiosis+and+Sexual+ReproductionNKANo ratings yet
- Science II Mission 35Document61 pagesScience II Mission 35sauravkhare466No ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument45 pagesTranscription and TranslationDev AshwaniNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument3 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationMeek Adan RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Lec 2 Dr. Asaad Taha Dr. Maryam AbdDocument17 pagesMicrobiology: Lec 2 Dr. Asaad Taha Dr. Maryam AbdAhmed MazinNo ratings yet
- UprgenyDocument9 pagesUprgenyJose Rafael Villafan BernalNo ratings yet
- Dr. Tahir Mehmood: Bioenergetics and Metabolism (Cr.04) CHEM - 423 and 623Document43 pagesDr. Tahir Mehmood: Bioenergetics and Metabolism (Cr.04) CHEM - 423 and 623ASAD MALIKNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Division QDocument6 pages3 Cell Division QsyukriNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure-WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesCell Structure-WPS OfficeyennaNo ratings yet
- Article BiochDocument10 pagesArticle BiochSophie BaranskiNo ratings yet
- Krebs Cycle Ppt. H1Document13 pagesKrebs Cycle Ppt. H1Princy100% (2)
- Ws1-Membrane Transport WorksheetDocument3 pagesWs1-Membrane Transport WorksheetTy BakrNo ratings yet