Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Basis of Life
Chemical Basis of Life
Uploaded by
tjCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Full Download PDF of The Cell: A Molecular Approach 7th Edition (Ebook PDF) All ChapterDocument41 pagesFull Download PDF of The Cell: A Molecular Approach 7th Edition (Ebook PDF) All Chapterkutsisanouh100% (14)
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 2 - Chemical Basis of Life)Document16 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 2 - Chemical Basis of Life)ANDREA GRAZILLE NAVAIRANo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil Test ReportDocument2 pagesTransformer Oil Test Reportibubu2380% (5)
- IB Biology Revision Notes FULLDocument3 pagesIB Biology Revision Notes FULLAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- (w3) Basic Chemistry and Chemical CompositionDocument4 pages(w3) Basic Chemistry and Chemical Compositioncsiman2431No ratings yet
- 2 Chemical Basis of LifeDocument2 pages2 Chemical Basis of Lifeelaq drNo ratings yet
- Gen Biology 2ND MonthlyDocument3 pagesGen Biology 2ND Monthlypearl japsonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument2 pagesChemical Basis of LifeEllaine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of Life: Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemical Basis of Life: Basic ChemistryMauanay, Marjelyn P.No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document3 pagesUnit 2Kyla Marie PacubasNo ratings yet
- Organic and Biological ChemistryDocument18 pagesOrganic and Biological ChemistryjenniferwookairuNo ratings yet
- Biochem Introduction PDFDocument5 pagesBiochem Introduction PDFJustin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 1: Biochemistry Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageAP Biology Unit 1: Biochemistry Cheat Sheet: by Viamelia sabaNo ratings yet
- Matter Exist In: (Examples) : Molecules and CompoundsDocument2 pagesMatter Exist In: (Examples) : Molecules and CompoundsprincessmagpatocNo ratings yet
- PhyScience 1Document3 pagesPhyScience 1Joshua Jireh SevillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- PH-PHR 216 Physical Pharmacy: @mei - Sria !1Document3 pagesPH-PHR 216 Physical Pharmacy: @mei - Sria !1Seania BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 6 EnzymesDocument3 pages6 EnzymesIYA LABAONo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 1 Biochemistry Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAP Biology Unit 1 Biochemistry Cheat Sheetf2vn65zbh9No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYkhayceemeade2No ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Physical PropertiesDocument3 pagesChemistry 1: Physical Propertieskeith herreraNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Energy PathwaysDocument17 pagesCarbohydrates Energy Pathwaysronaldbasihan03No ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesDocument2 pagesLesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Inorganic and Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesInorganic and Organic ChemistryValerie BorrioNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Microbial GrowthDocument8 pagesMicrobiology Microbial GrowthSamantha TachtenbergNo ratings yet
- A-P Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of LifeDocument16 pagesA-P Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of LifeMONIQUE VELASCONo ratings yet
- PHARMACEUTICAL and CHEMISTRY OF INORGANIC MEDICINALSDocument36 pagesPHARMACEUTICAL and CHEMISTRY OF INORGANIC MEDICINALSanon_937994778No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Levels of Organization of The Human BodyDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Levels of Organization of The Human BodyFrancine Danielle TiponesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: University of St. La Salle College of Engineering Engineering Sciences ReviewDocument5 pagesChemistry: University of St. La Salle College of Engineering Engineering Sciences ReviewJonas ParreñoNo ratings yet
- CHEM (No Formula)Document4 pagesCHEM (No Formula)palacioaya28No ratings yet
- Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words and Definition For Revision 4Document2 pagesWorksheet IGCSE Match Key Words and Definition For Revision 4oscarbec0% (1)
- Adv Chem Reviewer 1st QTRDocument6 pagesAdv Chem Reviewer 1st QTRValery Ken CañegaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem II Lec 1 2Document111 pagesOrganic Chem II Lec 1 2Bình NguyễnNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerARRON FLOYD DINGALNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer (Enzymes)Document6 pagesBiochem Reviewer (Enzymes)VicentaAngeloudeLeonNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Systems of The Cell PDFDocument6 pagesBiochemical Systems of The Cell PDFCzerinne AlarillaNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument6 pagesPhysical ScienceCAYABAN, RISHA MARIE DV.No ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument7 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryClarence MallariNo ratings yet
- Anaphy NotesDocument3 pagesAnaphy NotesTreshia SusonNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEMISTRY 1 1stDocument4 pagesGEN CHEMISTRY 1 1strenmarseyerNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5Ann Margaret Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Biochem MidtermsDocument6 pagesBiochem MidtermskizzaymenteraNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4695793937270644090Document6 pagesInbound 4695793937270644090joshuatimothylaoNo ratings yet
- Biological ElementsDocument16 pagesBiological Elementsmarwaaishah01No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Carbon: PhosphateDocument7 pagesCharacteristics of Carbon: Phosphate둡챙브로No ratings yet
- Physical Science: Ternary Compounds: Physical Change vs. Chemical ChangeDocument7 pagesPhysical Science: Ternary Compounds: Physical Change vs. Chemical ChangeJoshua Jireh SevillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Bio Chem NotesDocument5 pagesBio Chem NotesRose ImeeNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYPrincess Diane AgripaNo ratings yet
- Combustion of FuelsDocument6 pagesCombustion of FuelsRobby Royce Casida100% (1)
- BIOENERGETICS Notes 3Document3 pagesBIOENERGETICS Notes 3Hya LaniogNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesMicrobial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsAGENT M.DNo ratings yet
- Gen Chemistry 1: Same AsnDocument3 pagesGen Chemistry 1: Same Asnjames BernalNo ratings yet
- Energy EnzymesDocument16 pagesEnergy EnzymesZeldeign ManuelNo ratings yet
- High Chemical Energy: Sugar Oxygen Organic Compounds (From Light) LightDocument3 pagesHigh Chemical Energy: Sugar Oxygen Organic Compounds (From Light) LightKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic: Classifying MatterDocument11 pagesAtoms and The Periodic: Classifying MattercharlieNo ratings yet
- Chem Reviewer (Lec & Lab)Document9 pagesChem Reviewer (Lec & Lab)adelaine perasNo ratings yet
- WP Contentuploads202210AQA Topic 1 Key Terms PDFDocument3 pagesWP Contentuploads202210AQA Topic 1 Key Terms PDFLilyayayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Sas 1 Sas 5Document25 pagesLecture Notes Sas 1 Sas 5Louise Nicole CastroNo ratings yet
- Elements Oflife, Chemical ReactionDocument3 pagesElements Oflife, Chemical ReactionLey ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument10 pagesChemical Basis of LifeCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- CHEM Reviewer Grade 12Document3 pagesCHEM Reviewer Grade 12RaphaelNo ratings yet
- International Glass Art Retail DirectoryDocument82 pagesInternational Glass Art Retail DirectorytoxicwindNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Quarter 2 Week 1 3Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistry Quarter 2 Week 1 3Istian VlogsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Settlement of Claims For Compensation - 0Document6 pagesGuidelines For Settlement of Claims For Compensation - 0irshadNo ratings yet
- Chemray420 Service Manual V1.0eDocument77 pagesChemray420 Service Manual V1.0eJose PersiaNo ratings yet
- S.No. Paper Code Title of The Paper Author AffiliationDocument7 pagesS.No. Paper Code Title of The Paper Author AffiliationDanie RoyNo ratings yet
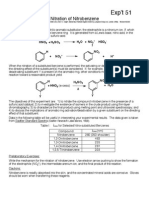
- Exp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzeneDocument4 pagesExp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzenelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 7.1-1 Regulations On Safety, Health and Hygiene - MergedDocument159 pagesInformation Sheet 7.1-1 Regulations On Safety, Health and Hygiene - MergedMæbēTh CuarterosNo ratings yet
- Reflective Writing 2Document4 pagesReflective Writing 2Noriel GirayNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term S1 ChemistryDocument27 pages1ST Term S1 ChemistryPeter Omovigho Dugbo100% (2)
- Neet BiologyDocument9 pagesNeet Biologyjaseelanu2No ratings yet
- Geotechnical Applications of Waste Materials PDFDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Applications of Waste Materials PDFG. SASIDHARA KURUPNo ratings yet
- Control of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFDocument36 pagesControl of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFPrakashNo ratings yet
- Thermetco-Thermocouple Welder TW9Document10 pagesThermetco-Thermocouple Welder TW9ghostinshellNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution PPT Civil NITHINDocument18 pagesWater Pollution PPT Civil NITHINmudavath jagapathibabuNo ratings yet
- CHIR EndsemDocument516 pagesCHIR EndsemSoikat DasNo ratings yet
- Jordan Hartley Health Snack Recipe E-BookDocument25 pagesJordan Hartley Health Snack Recipe E-BookMandi Lee100% (1)
- Das Consultants: Design of 1000KL Capacity OHTDocument19 pagesDas Consultants: Design of 1000KL Capacity OHTPrashant GargNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Reading and Writing: QuestionsDocument20 pagesTest 1 Reading and Writing: QuestionsMacarena Diaz CasadoNo ratings yet
- Phase Transfer CatalysisDocument15 pagesPhase Transfer CatalysisUnnati SinariNo ratings yet
- CESD-10 Website PDFDocument3 pagesCESD-10 Website PDFDoc HadiNo ratings yet
- Beginning Trumpet PP - Lesson 1Document12 pagesBeginning Trumpet PP - Lesson 1api-233367985No ratings yet
- Comparison of Simple Potential Functions For Simulating Liquid WaterDocument11 pagesComparison of Simple Potential Functions For Simulating Liquid WaterAdarsh PNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Blacks Under CompressionDocument7 pagesElectrical Conductivity of Carbon Blacks Under CompressionМирослав Кузишин100% (1)
- Podar International School Practice Sheet STD: X Topic: 12.2: Electricity Subject: PhysicsDocument6 pagesPodar International School Practice Sheet STD: X Topic: 12.2: Electricity Subject: PhysicsHemant PadalkarNo ratings yet
- Booking Report 6-23-2021Document2 pagesBooking Report 6-23-2021WCTV Digital Team0% (1)
- Cep Sop KSKDocument11 pagesCep Sop KSKSonrat100% (1)
- User Manual: Easylogic™ Dm6000H / Dm6200H SeriesDocument50 pagesUser Manual: Easylogic™ Dm6000H / Dm6200H SeriesLucio SalesNo ratings yet
Chemical Basis of Life
Chemical Basis of Life
Uploaded by
tjOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Basis of Life
Chemical Basis of Life
Uploaded by
tjCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
Monday, August 9, 2021 4:18 PM
Basic Chemistry Chemical reactions Lipids
Chemistry – concerned with atomic composition and structure of - Substances interact either to form or to break chemical - Contains C,H, O
substances and the reactions they undergo bonds - Major group of organic molecules that are defined as being
- Reactants – substances that enter into a chemical relatively insoluble in water
reaction
Matter, Mass, and Weight - Products – substances that result from the chemical rxn Saturated fatty acids
Matter - A+B(reactants) -> C+D(products) - Each carbon is ful with hydrogen
- anything that occupies space and has mass - Single covalent bonds between carbon atoms
Classification of Chemical Rxns ○ Beef pork, cheese
Mass 1. Synthesis Unsaturated
- amount of matter in an object - combination of reactants - One ore more double covalent bonds between carbons
- Internationak unit is Kilogram / Kg - Build a new molecule ○ Fish oils
- Energy requiring
Weight - ADP+P -> ATP Phospholipids
- gravitational force acting on an object 2. Decomposition - Composed of. Polar region containing phosphate and non
- breakdown of larger reactants polar region consisting two fatty acid chains
- Energy-releasing - The phosphate head - hydrophilic / water soluble
Elements and Atoms - ATP -> ADP + P - The nonpolar end - hydrophobic / repelled by water / lipid-
Element 3. Exchange soluble
- simplest type of matter having unique chemical properties (would - Combination of decomposition and synthesis
depend on its atom) - AB+CD -> AC + BD Protein
- Composed of atoms of only one kind -> element carbon is composed - HCI +NaOH -> NaCi +H2O - All proteins are organic macromolecules that contain
of carbon atoms 4. Reversible carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen, bound together by
- Calcium helps form bones, sodium ions are essential for neuronal - Reactants can form products, products can form covalent bonds
activity reactants - Most proteins contain sulfur and some contain small
○ Compound - made up of two or more elements amount of phosphorus
Atom Anabolism – synthesis rxns that occur in the body - Building blocks of proteins: amino acids
- smallest particle of an element that has the chemical characteristics Catabolism – decomposition rxns that occur in the body
of that element Metabolism – anabolic + catabolic rxns in the body
- Composed of subatomic particles, some of which have an electrical
charge (ptotons, electrons, and neutrons) Energy and Chemical Rxns
- Retains physical and chemical properties Energy
- capacity to do work
Potential Energy
- stored energy
Kinetic Energy
- energy caused by movement
Chemical Energy
- form of potential energy stored in chemical bonds
- May require or release energy
- Functions of proteins
○ Used to make skin , hair, nails and muscles
○ Part of the hemoglobin molecule
○ Act as enzymes
Electrical Charge ○ Immune system functions
- Tendency of particles to be attracted to each other or repulsed each ○ Muscle contractions
other ○ Providing structure and energy
- One of the fundamental properties of matter - Denaturation : if the hydrgen bonds that maintain the shape
of the protein are broken, the protein becomes
2 Types of Electrical Charge nonfunctional
1. Positive
- Particles with the same charge repulsed from each other Enzymes
2. Negative - Increase the rate of chemical reactions withoutthe enzyme
- Particles with the opposite charge attracts each other Rate of Chemical Reactions (RCTC)
1. Reactants being permanently changed
Atomic Structure 2. Concentration
3. Temperature Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA
- The higher the temperature the faster the rate ?? Puta - The basic unit of nucleic acids is the nucelotide, which is
3 major subatomic particles monosaccharide with an attached phosphate and nitrogen
ano bato
4. Catalysts base
1. Neutrons 2 types
- no electrical charge / uncharged particles - increases the rate of chem rxn without itself being
permanently changed or depleted 1. DNA
- Found in the center of the atom which is called the nucleus a. Contain the monosaccharide deoxyribise and the
○ Nucleus – formed by protons and neutrons - Enzyme is a protein catalyst that increase that increases
the rate at which chemical reaction proceeds organic bases adenine, thymine, guanine and
cytosine
2. Protons b. Genetic material of cells
- positive charges c. Contains genes which determine the structure of
- Found in the center of the atom which is called the nucleus proteins
○ Nucleus – formed by protons and neutrons d. Basic building blocks are nucleotides
e. Double strand
3. Electrons 2. RNA
- negative charges a. Single strand
- Are found in an electron cloud and are constantly orbiting the nucleus b. The thymin is replaced with uracil
○ Electron cloud – where electrons are most likely to be found
- Since each atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, the
positive and negative charges cancel each other. Therefore, each
atom is electrically neutral
- Atomic number – no of protons in each atom / total mass of an atom
- Mass number – no. of protons + no. of neutrons in each atom
- Protons and neutrons - have similar mass / 1 dalton
- The lower curve requires low activation of energy to gain
the product
- The higher curve requires high activation of energy to
gain the product
Acids and Bases
Acid
- proton H+ donor
- Ph below 7
Base
- proton H+ acceptor
- Ph higher than 7
Electrons and Chemical Bonding
Chemical Bonding
- electrons are transferred or shared between atoms
- Occur when outermost electrons are transferred or shred between
Adenosine Triphosphate
atoms - Stores energy, which can be used in cell processes
Types of Chemical Bonds
1. Ions and Ionic Bond
- electrons are transferred
- Ions
○ a charged atom formed because of a donatin or gain of an
electron(s)
○ Example: NA+, CI
§ Holds them together because there’s an attraction
between the two opposite charges
§ Held together by electrical attractions
The pH Scale
- Indicates the H+ concentration of a solution
Ø Neutral – equal no. of H+ and OH-; pH of 7.0 Ø
Ø Acidic – H+ > OH-; pH less than 7.0
Ø Basic – H+ > OH-; pH greater than 7.0
7.35 – 7.45 – normal pH range of blood
Acidosis – blood pH drops beow 7.35
Alkalosis – blood pH rises above 7.45
2. Covalent Bond
- Two atoms shares one or more pairs of electrons Inorganic Chemistry vs. Organic Chemistry
- Example: hydrogen molecule (H2) • Inorganic
- Polar covalent bond ○ Deals with those substances that do not contain
○ unequal, asymmetrical sharing of electrons carbon
○ Can cause slight negative/positive charge • Organic
- Polar molecules ○ Study of carbon-containing substances
○ molecules with asymmetrical electrical charge
○ Example: H2O - Some carbon containing compounds are not organic in
- Nonpolar covalent bond that they do not also contain hydrogen -> carbon dioxide
○ equal sharing of electrons bet. Atoms
- Nonpolar molecules Salts
○ molecules with symmetrical electrical charge - Forms when an acid reacts with a base
○ Similar electronegativity = Equally shared atoms
Buffer
- Chemicals that resist changes in pH
Inorganic Molecules
- Do not contain Carbon
Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Oxygen
- involved with the extraction of energy from food
molecules
- Extracted from food molecules
Carbon Dioxide
- Consist of one carbon atom bound to two oxygen atom
- by-product of the breakdown of food molecules
Water
- Has many unique properties due to its polar nature
- Essential t life because it performs the following
functions:
1. Stabilizing body temperature.
2. Protection; lubricant/cushion.
3. Facilitating chemical reactions.
4. Transporting substances
Intermolecular Forces
Organic Molecules
Hydrogen Bonds - Carbon containing
- Weak attraction bet the oppositely charged regions of polar - Carbon’s ability to form covalent bonds with other atoms
molecules makes possible the formatin of the large, diverse,
- Formed when a positive charge / end is attracted to a negative complicated molecules
charge end of another molecule
4 Major Groups of Organic Molecues
Dissociation 1. Carbohydrates
- Separation of ions in an ionic compound by polar water molecules - CHO
- Dissociated ions are sometimes calles electrolytes - Broken down to provide energy
- H:O is a 2:1 ratio
- Oxygen is one of the by products
2. Monosaccharides
- Building blocks of carbohydrates
- smallest carbohydrates; simple sugars
- Glucose – blood sugar
- Fructose – fruit sugar
3. Disaccharides
- 2 monosaccharides / sugar
- Glucose + sugar = Sucrose – table sugar
4. Polysaccharides
- many monosaccharides / sugar
- Glycogen – main storage form of glucse in humans and
animal starch
- Plant starch - found in plants
- Cellulose - found in plants
Molecules and Compounds
Molecule – two or more atoms that are chemically combined
Compound – two or more diff. types of atoms that are chemically
combined
You might also like
- Full Download PDF of The Cell: A Molecular Approach 7th Edition (Ebook PDF) All ChapterDocument41 pagesFull Download PDF of The Cell: A Molecular Approach 7th Edition (Ebook PDF) All Chapterkutsisanouh100% (14)
- Anatomy & Physiology (Chapter 2 - Chemical Basis of Life)Document16 pagesAnatomy & Physiology (Chapter 2 - Chemical Basis of Life)ANDREA GRAZILLE NAVAIRANo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil Test ReportDocument2 pagesTransformer Oil Test Reportibubu2380% (5)
- IB Biology Revision Notes FULLDocument3 pagesIB Biology Revision Notes FULLAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- (w3) Basic Chemistry and Chemical CompositionDocument4 pages(w3) Basic Chemistry and Chemical Compositioncsiman2431No ratings yet
- 2 Chemical Basis of LifeDocument2 pages2 Chemical Basis of Lifeelaq drNo ratings yet
- Gen Biology 2ND MonthlyDocument3 pagesGen Biology 2ND Monthlypearl japsonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument2 pagesChemical Basis of LifeEllaine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of Life: Basic ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemical Basis of Life: Basic ChemistryMauanay, Marjelyn P.No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document3 pagesUnit 2Kyla Marie PacubasNo ratings yet
- Organic and Biological ChemistryDocument18 pagesOrganic and Biological ChemistryjenniferwookairuNo ratings yet
- Biochem Introduction PDFDocument5 pagesBiochem Introduction PDFJustin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 1: Biochemistry Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageAP Biology Unit 1: Biochemistry Cheat Sheet: by Viamelia sabaNo ratings yet
- Matter Exist In: (Examples) : Molecules and CompoundsDocument2 pagesMatter Exist In: (Examples) : Molecules and CompoundsprincessmagpatocNo ratings yet
- PhyScience 1Document3 pagesPhyScience 1Joshua Jireh SevillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Physical and Chemical Properties of MatterAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- PH-PHR 216 Physical Pharmacy: @mei - Sria !1Document3 pagesPH-PHR 216 Physical Pharmacy: @mei - Sria !1Seania BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 6 EnzymesDocument3 pages6 EnzymesIYA LABAONo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 1 Biochemistry Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAP Biology Unit 1 Biochemistry Cheat Sheetf2vn65zbh9No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYkhayceemeade2No ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Physical PropertiesDocument3 pagesChemistry 1: Physical Propertieskeith herreraNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Energy PathwaysDocument17 pagesCarbohydrates Energy Pathwaysronaldbasihan03No ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesDocument2 pagesLesson 1.3 Pure Substances and MixturesAndrea MurielNo ratings yet
- Inorganic and Organic ChemistryDocument8 pagesInorganic and Organic ChemistryValerie BorrioNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Microbial GrowthDocument8 pagesMicrobiology Microbial GrowthSamantha TachtenbergNo ratings yet
- A-P Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of LifeDocument16 pagesA-P Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of LifeMONIQUE VELASCONo ratings yet
- PHARMACEUTICAL and CHEMISTRY OF INORGANIC MEDICINALSDocument36 pagesPHARMACEUTICAL and CHEMISTRY OF INORGANIC MEDICINALSanon_937994778No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Levels of Organization of The Human BodyDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Levels of Organization of The Human BodyFrancine Danielle TiponesNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: University of St. La Salle College of Engineering Engineering Sciences ReviewDocument5 pagesChemistry: University of St. La Salle College of Engineering Engineering Sciences ReviewJonas ParreñoNo ratings yet
- CHEM (No Formula)Document4 pagesCHEM (No Formula)palacioaya28No ratings yet
- Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words and Definition For Revision 4Document2 pagesWorksheet IGCSE Match Key Words and Definition For Revision 4oscarbec0% (1)
- Adv Chem Reviewer 1st QTRDocument6 pagesAdv Chem Reviewer 1st QTRValery Ken CañegaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem II Lec 1 2Document111 pagesOrganic Chem II Lec 1 2Bình NguyễnNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument12 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerARRON FLOYD DINGALNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer (Enzymes)Document6 pagesBiochem Reviewer (Enzymes)VicentaAngeloudeLeonNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Systems of The Cell PDFDocument6 pagesBiochemical Systems of The Cell PDFCzerinne AlarillaNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument6 pagesPhysical ScienceCAYABAN, RISHA MARIE DV.No ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument7 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistryClarence MallariNo ratings yet
- Anaphy NotesDocument3 pagesAnaphy NotesTreshia SusonNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEMISTRY 1 1stDocument4 pagesGEN CHEMISTRY 1 1strenmarseyerNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document3 pagesWeek 5Ann Margaret Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Biochem MidtermsDocument6 pagesBiochem MidtermskizzaymenteraNo ratings yet
- Inbound 4695793937270644090Document6 pagesInbound 4695793937270644090joshuatimothylaoNo ratings yet
- Biological ElementsDocument16 pagesBiological Elementsmarwaaishah01No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Carbon: PhosphateDocument7 pagesCharacteristics of Carbon: Phosphate둡챙브로No ratings yet
- Physical Science: Ternary Compounds: Physical Change vs. Chemical ChangeDocument7 pagesPhysical Science: Ternary Compounds: Physical Change vs. Chemical ChangeJoshua Jireh SevillaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryDelosreyes ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Bio Chem NotesDocument5 pagesBio Chem NotesRose ImeeNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRYPrincess Diane AgripaNo ratings yet
- Combustion of FuelsDocument6 pagesCombustion of FuelsRobby Royce Casida100% (1)
- BIOENERGETICS Notes 3Document3 pagesBIOENERGETICS Notes 3Hya LaniogNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesMicrobial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsAGENT M.DNo ratings yet
- Gen Chemistry 1: Same AsnDocument3 pagesGen Chemistry 1: Same Asnjames BernalNo ratings yet
- Energy EnzymesDocument16 pagesEnergy EnzymesZeldeign ManuelNo ratings yet
- High Chemical Energy: Sugar Oxygen Organic Compounds (From Light) LightDocument3 pagesHigh Chemical Energy: Sugar Oxygen Organic Compounds (From Light) LightKenneth Rodriguez HerminadoNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic: Classifying MatterDocument11 pagesAtoms and The Periodic: Classifying MattercharlieNo ratings yet
- Chem Reviewer (Lec & Lab)Document9 pagesChem Reviewer (Lec & Lab)adelaine perasNo ratings yet
- WP Contentuploads202210AQA Topic 1 Key Terms PDFDocument3 pagesWP Contentuploads202210AQA Topic 1 Key Terms PDFLilyayayNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Sas 1 Sas 5Document25 pagesLecture Notes Sas 1 Sas 5Louise Nicole CastroNo ratings yet
- Elements Oflife, Chemical ReactionDocument3 pagesElements Oflife, Chemical ReactionLey ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument10 pagesChemical Basis of LifeCrystal MaidenNo ratings yet
- CHEM Reviewer Grade 12Document3 pagesCHEM Reviewer Grade 12RaphaelNo ratings yet
- International Glass Art Retail DirectoryDocument82 pagesInternational Glass Art Retail DirectorytoxicwindNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Quarter 2 Week 1 3Document7 pagesGeneral Chemistry Quarter 2 Week 1 3Istian VlogsNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Settlement of Claims For Compensation - 0Document6 pagesGuidelines For Settlement of Claims For Compensation - 0irshadNo ratings yet
- Chemray420 Service Manual V1.0eDocument77 pagesChemray420 Service Manual V1.0eJose PersiaNo ratings yet
- S.No. Paper Code Title of The Paper Author AffiliationDocument7 pagesS.No. Paper Code Title of The Paper Author AffiliationDanie RoyNo ratings yet
- Exp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzeneDocument4 pagesExp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzenelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 7.1-1 Regulations On Safety, Health and Hygiene - MergedDocument159 pagesInformation Sheet 7.1-1 Regulations On Safety, Health and Hygiene - MergedMæbēTh CuarterosNo ratings yet
- Reflective Writing 2Document4 pagesReflective Writing 2Noriel GirayNo ratings yet
- 1ST Term S1 ChemistryDocument27 pages1ST Term S1 ChemistryPeter Omovigho Dugbo100% (2)
- Neet BiologyDocument9 pagesNeet Biologyjaseelanu2No ratings yet
- Geotechnical Applications of Waste Materials PDFDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Applications of Waste Materials PDFG. SASIDHARA KURUPNo ratings yet
- Control of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFDocument36 pagesControl of Hospital Acquired Infection PDFPrakashNo ratings yet
- Thermetco-Thermocouple Welder TW9Document10 pagesThermetco-Thermocouple Welder TW9ghostinshellNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution PPT Civil NITHINDocument18 pagesWater Pollution PPT Civil NITHINmudavath jagapathibabuNo ratings yet
- CHIR EndsemDocument516 pagesCHIR EndsemSoikat DasNo ratings yet
- Jordan Hartley Health Snack Recipe E-BookDocument25 pagesJordan Hartley Health Snack Recipe E-BookMandi Lee100% (1)
- Das Consultants: Design of 1000KL Capacity OHTDocument19 pagesDas Consultants: Design of 1000KL Capacity OHTPrashant GargNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Reading and Writing: QuestionsDocument20 pagesTest 1 Reading and Writing: QuestionsMacarena Diaz CasadoNo ratings yet
- Phase Transfer CatalysisDocument15 pagesPhase Transfer CatalysisUnnati SinariNo ratings yet
- CESD-10 Website PDFDocument3 pagesCESD-10 Website PDFDoc HadiNo ratings yet
- Beginning Trumpet PP - Lesson 1Document12 pagesBeginning Trumpet PP - Lesson 1api-233367985No ratings yet
- Comparison of Simple Potential Functions For Simulating Liquid WaterDocument11 pagesComparison of Simple Potential Functions For Simulating Liquid WaterAdarsh PNo ratings yet
- Electrical Conductivity of Carbon Blacks Under CompressionDocument7 pagesElectrical Conductivity of Carbon Blacks Under CompressionМирослав Кузишин100% (1)
- Podar International School Practice Sheet STD: X Topic: 12.2: Electricity Subject: PhysicsDocument6 pagesPodar International School Practice Sheet STD: X Topic: 12.2: Electricity Subject: PhysicsHemant PadalkarNo ratings yet
- Booking Report 6-23-2021Document2 pagesBooking Report 6-23-2021WCTV Digital Team0% (1)
- Cep Sop KSKDocument11 pagesCep Sop KSKSonrat100% (1)
- User Manual: Easylogic™ Dm6000H / Dm6200H SeriesDocument50 pagesUser Manual: Easylogic™ Dm6000H / Dm6200H SeriesLucio SalesNo ratings yet