Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Periodicity Part 1
Periodicity Part 1
Uploaded by
Green SlimeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Periodicity Part 1
Periodicity Part 1
Uploaded by
Green SlimeCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3: Periodicity
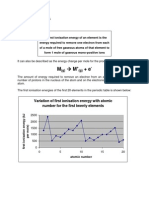
9.1 Physical Properties of Elements of Period 2 and Period 3 - Boron atom has first ionisation which is lower than expected.
Variation in Physical Properties Be: 1s22s2 B: 1s22s22px1
1) Atomic radius : - covalent radius More energy is needed to remove electron from a fully filled s orbital
- metallic radius than from a singly occupied p orbital.
- van der Waals radius - Oxygen atom has 1st IE lower than nitrogen atom bcs nitrogen has
2) Factors Affecting Atomic radii : stable half-filled p orbitals. By removing one electron from oxygen
a) Screening effect: atom, O+ ion can form a stable electronic configuration.
- is caused by the mutual repulsion between electrons in the N : 1s22s22p3 O : 1s22s22p4 O+ : 1s22s22p3
inner shell with those in the outer shell The p4 configurations of the oxygen atoms, the two electron in the same
- the screening effect of the inner shell electrons causes the orbital result in greater electrostatic repulsion. This makes it easier to
atomic size to increase . remove an electron from p4 configuration than p3 configuration. Thus,
- the greater the number of filled inner shells, the greater the more energy is required to remove an electron from half-filled p orbitals
screening effect and the larger the atomic size. - Variation of 1st ionisation energy for the third period elements has
b) Nuclear charge: the shape of the graph as the elements of second period. The 1st
- the nuclear charge pulls all the electrons closer to the nucleus ionisation energy of third period elements is always lower than the
& causes the atomic size to decrease. corresponding elements of second period.
- effective nuclear charge , Zeff - lower the ionisation energy, the elements are most likely to be a metal.
𝑍𝑒𝑓𝑓 = 𝑍 − 𝜎 ; 𝑍 = 𝑛𝑢𝑐𝑙𝑒𝑎𝑟 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒 &
𝜎 = 𝑛𝑢𝑚 𝑜𝑓 𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑖𝑛𝑛𝑒𝑟 𝑠ℎ𝑒𝑙𝑙 Successive ionisation energies
- higher the effective nuclear charge, the smaller the atomic size -There is an increase in effective nuclear charge when successive
electrons being removed, therefore the successive ionisation
Atomic Radii across Period 2 & 3 energies for an atom are always increasing.
- atomic radius decreases across the period bcs : - when first electron from the inner shell is being removed, there is
→ nuclear charge increases & the number of electrons also increases great difference in ionisation energy compared to previous
→ screening effect remains almost unchanged within same period ionisation energy.
bcs the electrons are added to the same shell - the determination of the position of the elements in the periodic
→ Thus, effective nuclear charge increases, the valence electrons are table by successive ionisation method only applicable to s and p
pulled closer to the nucleus & the atomic radius decrease. block elements.
Atomic Radii down a group Electronegativity
- atomic radius increase going down the group bcs : - is the ability of the atom in a covalent bond to attract shared
→ the nuclear charge increase and increase in the number of shells electrons to itself
filled with electrons between the valence electrons and the nucleus. - the greater an atom’s electronegativity, the greater its ability to
→ Increase in screening effect of outer electrons by inner electrons attract electrons to itself.
→ Increase in screening effect > increase in nuclear charge - the electronegativity increases across a period from left to right
→ the effective nuclear charge decreases and the outermost shell → atomic radius decreases while nuclear charge increases. The
electrons are held less tightly by the nucleus causing the atomic attractions for electrons increases and electronegativity increases.
radius to increase. - the electronegativity decreases down a group
→ the nuclear charge increases but the screening effect also
Ionic Radii increases as the atomic size increase. The attractions for electrons
- isoelectronic : ions that have same number of electrons decreases and hence electronegativity decreases.
- Cationic radius is smaller than its atomic radius.
→ Na, Mg & Al with bigger atomic radii tends to lose electron to form Al2O3 is suitable used as inside coating at high temperature bcs :
+ve ions. Therefore, they are reducing agents - it is ionic compound - high charged density of Al3+
→ cation are reducing agents : 𝑁𝑎 > 𝑀𝑔 > 𝐴𝑙 with –ve 𝐸 ° - high melting & boiling point - enthalpy of formation is exothermic
- Anionic radius is bigger than its atomic radius. Ion with high charge density :
→ anion are oxidising agents : 𝐶𝑙2 > 𝑆 > 𝑃 with +ve 𝐸 ° - high charge & small size - high polarising power
- The cations from same element, cation with higher ionic charge is - has covalent characteristic - ionic oxide is amphoteric
smaller. - has high hydration energy - will form complex ion
The cations Li+ to B3+ are The anions N3- to F- are Metallic bond : - no. of valence electrons ↑ , bond ↑ .
isoelectronic isoelectronic - atomic radius ↑ , bond ↓
Ionic radii decrease bcs the number of electrons remains constant but Van der Waals force : RMM ↑ , bond ↑
the number of protons increases. Screening effect remains constant & Covalent bond : radius ↑ , bond ↑
effective nuclear charge increase. Ionic bond : charge ↑ , size ↓ , bond ↑
Ionisation energy SUMMARY
-magnitude of IE depends on:
a) electronic configuration of the atom :
→ an atom with a stable electronic configuration has higher IE
b) atomic radius :
→ for a bigger atom, outermost electrons are further from nucleus
and are more shielded by the inner electrons, they are less
attracted to the nucleus & are easier to remove.
c) the effective nuclear charge :
→ higher effective nuclear charge, stronger attractive force of
electrons towards the nucleus, more difficult for the electron to
be removed.
- Across the period, atomic size becomes smaller (due to the higher ** Oxides of P, S and Cl exists as simple covalent molecules. Atoms in the
effective nuclear charge), the ionisation energy becomes higher. molecules are bonded covalently but the intermolecular forces are
- Ionisation energy of the lithium is the lowest in the period bcs the weak van der Waals force.
atomic size is the biggest. ** Sulphur have stronger van der Waals forces compare to phosphorus.
- Ionisation energy of neon atom is the highest in the period bcs the
smallest atomic size & its stable octet structure
YongJie
You might also like
- Air Conditioning Lab Report 1920Document19 pagesAir Conditioning Lab Report 1920Luyao ZHANGNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme For Term 2 Trial Exam, STPM 2019 (Gbs Melaka) Section A (45 Marks)Document7 pagesMarking Scheme For Term 2 Trial Exam, STPM 2019 (Gbs Melaka) Section A (45 Marks)Michelles JimNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Physical Chemistry of FoodDocument192 pagesAn Introduction To The Physical Chemistry of FoodBishoyYousif100% (3)
- A - Level Inorganic ChemistryDocument543 pagesA - Level Inorganic Chemistrystephenshada9No ratings yet
- A039level Chemistry Inorganic NotesDocument108 pagesA039level Chemistry Inorganic NotesNasser SsennogaNo ratings yet
- A - Level Inorganic Chemistry 2-1Document171 pagesA - Level Inorganic Chemistry 2-1kitderoger_391648570No ratings yet
- AS Level Summary-Unit 1Document11 pagesAS Level Summary-Unit 1Filiz Kocayazgan ShanablehNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table: Iind PartDocument31 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic Table: Iind PartKeshan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocument105 pagesInorganic Chemistry NotesOdongo TonnyNo ratings yet
- Ionization EnergyDocument8 pagesIonization EnergyHafiza Sikder AnishaNo ratings yet
- Document From Michi?Document55 pagesDocument From Michi?audrey abaasaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocument11 pagesPeriodic Table and Periodicityakeemoluwadamilare623No ratings yet
- Chem Topic 2 and 3Document4 pagesChem Topic 2 and 3aliyaahsnahNo ratings yet
- Chem Inorganic A'levelDocument95 pagesChem Inorganic A'levelAlvin HavinzNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chem 1 2 PDFDocument73 pagesInorganic Chem 1 2 PDFYT ChongNo ratings yet
- 2 chapter 2 原子半径以及电离能Document33 pages2 chapter 2 原子半径以及电离能Pingping chenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Periodic Table (SUEC) AnswerDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Periodic Table (SUEC) AnswerLee AustinNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry NotesDocument10 pagesA-Level Chemistry NotesHannah Bryson-JonesNo ratings yet
- Enc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdDocument49 pagesEnc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdSri VanyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Document9 pagesEngineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Nivetha ENo ratings yet
- F5T22 Nurfadhayeen Nasrulhaq - ChemistryDocument22 pagesF5T22 Nurfadhayeen Nasrulhaq - ChemistryNur NasrulhaqNo ratings yet
- Periodicity in Elements NotesDocument7 pagesPeriodicity in Elements NotesjqgjwgnnwkNo ratings yet
- A Level Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocument95 pagesA Level Inorganic Chemistry NotesnaluwairoericjohnNo ratings yet
- Chem 111 Week Three Notes BDocument7 pagesChem 111 Week Three Notes BnyachiosirNo ratings yet
- Ion EnergiesDocument4 pagesIon EnergiesNamratha NairNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties: Chemistry For (I.I.T. J.E.E.)Document11 pagesPeriodic Properties: Chemistry For (I.I.T. J.E.E.)Gagan Raj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Chemical StructureDocument6 pagesChemical StructureThea GermanNo ratings yet
- Periodicity: The Periodic Table and Physical PropertiesDocument25 pagesPeriodicity: The Periodic Table and Physical PropertiesJi Min LimNo ratings yet
- 4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument68 pages4.2: Variation of Physical and Chemical PropertiesAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Lesson 9Document17 pagesGeneral Chemistry Lesson 9dreih MadrigNo ratings yet
- Atomic Radii: R Is A Radius of AtomDocument7 pagesAtomic Radii: R Is A Radius of AtomGHS Chak JhumraNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties and Their Graduation in Group andDocument14 pagesPeriodic Properties and Their Graduation in Group andbhogalsahib1408No ratings yet
- Ib PPT 4 SL PDFDocument103 pagesIb PPT 4 SL PDFzarna nirmal rawalNo ratings yet
- CBI 1 - Fundamentals of ChemistryDocument10 pagesCBI 1 - Fundamentals of ChemistryRianna NNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: ElectronegativityDocument2 pagesPeriodic Trends: ElectronegativityZaara RyeenNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties of The ElementsDocument57 pagesPeriodic Properties of The ElementstalktotiffanychengNo ratings yet
- downloadChemistryA levelNotesEdexcel IALUnit 1Detailed3.20Bonding20and20StructureDocument14 pagesdownloadChemistryA levelNotesEdexcel IALUnit 1Detailed3.20Bonding20and20Structurelaksandy360No ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument6 pagesSemiconductordksingh369No ratings yet
- Intro To SemiconductorsDocument27 pagesIntro To SemiconductorsRolando CelesteNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics 10ELN15-25 NotesDocument146 pagesBasic Electronics 10ELN15-25 Noteskmpshastry88% (8)
- Mojza-AS-Chemistry-Notes CompressedDocument64 pagesMojza-AS-Chemistry-Notes CompressedNoor MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Engineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Document70 pagesEngineering Material Presentation: Presented To: Engr. Nadeem Hassan Presented By: Abdul Rauf 2k17-Che-17Abdul Rauf ChNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure PDFDocument14 pagesBonding and Structure PDFWandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Electrons in AtomsDocument32 pagesChapter 2 - Electrons in AtomsFandyNo ratings yet
- Lect2 PhysicsRadiography ch4 JMDocument56 pagesLect2 PhysicsRadiography ch4 JMKnow-7No ratings yet
- PeriodicTable and Trends DPDocument109 pagesPeriodicTable and Trends DPSurya NairNo ratings yet
- Periodicitiy PDFDocument14 pagesPeriodicitiy PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- As 1 PerDocument4 pagesAs 1 PerzoeakatNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms.Document62 pagesElectrons in Atoms.Md.Tanjim reza TurjoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument27 pagesUntitledFatimah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 3 NotesNickNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document2 pagesCH 7Heather SiuNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Bonding 4.1to 4.5 14.1to 14.2Document156 pagesTopic 4 Bonding 4.1to 4.5 14.1to 14.2SujithNo ratings yet
- Chap 1.1Document48 pagesChap 1.1Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Group 2Document32 pages1.1 Group 2SN1-0622 Khairul Bariah Binti IzaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding theories-SectionH-S Chatterjee PDFDocument110 pagesChemical Bonding theories-SectionH-S Chatterjee PDFAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Atomic Radii: Atomic Structure: Periodic TrendsDocument5 pagesAtomic Radii: Atomic Structure: Periodic TrendsRajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By:: Mrs. Rashmi Dhiman Laksh Arora 10 /A Roll No: 27Document52 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By:: Mrs. Rashmi Dhiman Laksh Arora 10 /A Roll No: 27Noorpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Semi ConductorDocument38 pagesLec1 Semi ConductorArifah HamidunNo ratings yet
- Periodic PropertiesDocument30 pagesPeriodic Propertiescleofe omas-asNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Magnetism (Part2)Document26 pagesElectricity and Magnetism (Part2)ShinjiNo ratings yet
- 11c Classification, Periodicity (Class Notes)Document20 pages11c Classification, Periodicity (Class Notes)RAJEEV KARAKOTINo ratings yet
- 2019 SEM 2 KTE KULIM, KEDAH (Q) (3) 27 AugDocument2 pages2019 SEM 2 KTE KULIM, KEDAH (Q) (3) 27 AugGreen SlimeNo ratings yet
- 2019 SEM 2 SMJK JIT SIN, PENAG (Q & A) (4) 30 AugDocument14 pages2019 SEM 2 SMJK JIT SIN, PENAG (Q & A) (4) 30 AugGreen SlimeNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sem 2 Kte Kulim, Kedah (A)Document4 pages2019 Sem 2 Kte Kulim, Kedah (A)Green SlimeNo ratings yet
- 2019 SEM 2 Kelantan (Q & A) (2) 26 AugDocument12 pages2019 SEM 2 Kelantan (Q & A) (2) 26 AugGreen SlimeNo ratings yet
- 2019 Sem 2 Gbs Melaka (Q)Document3 pages2019 Sem 2 Gbs Melaka (Q)Green SlimeNo ratings yet
- SMJK Chung Ling: ButterworthDocument4 pagesSMJK Chung Ling: ButterworthGreen SlimeNo ratings yet
- Answer All Questions in This Section.: 2015-2-NS-ST PAUL Section A (45 Marks)Document2 pagesAnswer All Questions in This Section.: 2015-2-NS-ST PAUL Section A (45 Marks)Green SlimeNo ratings yet
- Upgrade Sport FacilitiesDocument2 pagesUpgrade Sport FacilitiesGreen SlimeNo ratings yet
- Sturdy-Physically Strong and Solid or Thick, and Therefore Unlikely To Break or Be Hurt PatentDocument2 pagesSturdy-Physically Strong and Solid or Thick, and Therefore Unlikely To Break or Be Hurt PatentGreen SlimeNo ratings yet
- A Preliminary Study On The Physicochemical Propertis of Pigments Sty-nBA-MMA Emulsion FilmsDocument11 pagesA Preliminary Study On The Physicochemical Propertis of Pigments Sty-nBA-MMA Emulsion Filmsvarvara viNo ratings yet
- Chm520 Report 1Document11 pagesChm520 Report 1Kayrul Rafie0% (1)
- UUSITALODocument9 pagesUUSITALOMarcosNo ratings yet
- TS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFDocument5 pagesTS SR Chemistry Imp Questions PDFUnknown Khan100% (3)
- Plate Fin and Compact Heat ExchangerDocument49 pagesPlate Fin and Compact Heat Exchangerafit666100% (3)
- Two Year All India Aakash Test Series AIATS For NEET 2025 - Class XI - 0Document4 pagesTwo Year All India Aakash Test Series AIATS For NEET 2025 - Class XI - 0let's trendNo ratings yet
- Spelling Bee WordsDocument3 pagesSpelling Bee WordsDana GomezNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Module 36Document10 pagesScience 10 - Module 36Karlyn Kaye SalungaNo ratings yet
- SNC2D Chemistry Practice TestDocument8 pagesSNC2D Chemistry Practice TestSteve M Hall0% (1)
- Drying TheoryDocument12 pagesDrying TheorySepehr BagheriNo ratings yet
- Some Liquid Holdup Experimental Data in Trickle-BedDocument6 pagesSome Liquid Holdup Experimental Data in Trickle-BedKrittini IntoramasNo ratings yet
- CHE2162 Week 9 Tutorial PDFDocument4 pagesCHE2162 Week 9 Tutorial PDFHua KhienNo ratings yet
- 3 4 Heat TransferDocument2 pages3 4 Heat Transferapi-222503660No ratings yet
- 0 044422 Revisionsheetwithak10satDocument11 pages0 044422 Revisionsheetwithak10sathajalisalem4No ratings yet
- MSDS Abyssinian OilDocument4 pagesMSDS Abyssinian OilswerNo ratings yet
- Saybolt Furol Viscosity Test PrepDocument1 pageSaybolt Furol Viscosity Test PrepMirabella Di BastidaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 Free and Forced Convection Heat Transfer From Heated Surfaces 1Document4 pagesExperiment No. 5 Free and Forced Convection Heat Transfer From Heated Surfaces 1Walid AdnanNo ratings yet
- Study Rankers: Notes of CH 2 Acids, Bases and Salts - Class 10th ScienceDocument15 pagesStudy Rankers: Notes of CH 2 Acids, Bases and Salts - Class 10th Sciencejaya kumariNo ratings yet
- Determination of Garment PHDocument19 pagesDetermination of Garment PHSami KocahanNo ratings yet
- Effect of H2-Injection On The Thermodynamic and Transportation Schouten2004Document8 pagesEffect of H2-Injection On The Thermodynamic and Transportation Schouten2004YvesfNo ratings yet
- Wool ShrinkageDocument17 pagesWool Shrinkagepatanjaliict100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - PsychrometryDocument12 pagesChapter 8 - PsychrometryamdevaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry BasicsDocument22 pagesBiochemistry Basicsjazlamba09No ratings yet
- CHEM PH ACTIVITYDocument2 pagesCHEM PH ACTIVITYAllyssa AbanNo ratings yet
- Emerging Solar Cell PDFDocument23 pagesEmerging Solar Cell PDFJaffar LoneNo ratings yet
- Fluorescence MicroscopeDocument1 pageFluorescence MicroscopePatrick ManriqueNo ratings yet
- Dehydration of 2 3-Butanediol To Mek.2Document9 pagesDehydration of 2 3-Butanediol To Mek.2hidayahNo ratings yet
- PFRDocument19 pagesPFRKangae IlhamNo ratings yet