Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 viewsWrite Down 10 Different Learnings or Takeaways That You Were Able To Glean From The Content
Write Down 10 Different Learnings or Takeaways That You Were Able To Glean From The Content
Uploaded by
Armel Bacdayan LacanariaThe document provides a summary of 10 key learnings around cybersecurity topics:
1) Current state of cybersecurity and important security terms
2) Threat actors and how they can be individuals or groups
3) Malware types like viruses, ransomware, and spyware
4) Common network attacks like reconnaissance, access, and DoS attacks
5) IP vulnerabilities and threats exploited by spoofing source IP addresses
6) TCP and UDP vulnerabilities exploited in protocols and lack of encryption
7) IP services vulnerabilities in ARP, DNS, DHCP exploited by spoofing
8) Network security best practices of confidentiality, availability, and integrity
9) Cryptography techniques for secure communication using encryption
10) Ethical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Mol Learn Login - Google SearchDocument2 pagesMol Learn Login - Google SearchHAMMAD SHAHNo ratings yet
- The Certified Ethical Hacker Exam - version 8 (The concise study guide)From EverandThe Certified Ethical Hacker Exam - version 8 (The concise study guide)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (9)
- Wishpond Landing Page AssignmentDocument3 pagesWishpond Landing Page AssignmentTerrence CroweNo ratings yet
- 13 17 AnswerDocument31 pages13 17 Answers2187022No ratings yet
- Network Security Part 1Document85 pagesNetwork Security Part 1amolmhNo ratings yet
- Principle of SecurityDocument73 pagesPrinciple of SecurityBab KebedeNo ratings yet
- INT 242 Network Attacks-1Document32 pagesINT 242 Network Attacks-1tech_415983648No ratings yet
- Preguntas Tres Primeros Capitulos Netacad Prueba 1 CCNP3 en InglesDocument27 pagesPreguntas Tres Primeros Capitulos Netacad Prueba 1 CCNP3 en InglesPatricioNo ratings yet
- Advanced Networks and Security Part 2 - Partial Exam 11 January 2017Document3 pagesAdvanced Networks and Security Part 2 - Partial Exam 11 January 2017diegoantivirusNo ratings yet
- TCP IP VulnerabilitiesDocument17 pagesTCP IP VulnerabilitiesHemant Sudhir WavhalNo ratings yet
- SNIFFING Gif3Document5 pagesSNIFFING Gif3khanssaoudjaffar0219No ratings yet
- Network Security Lec 1Document43 pagesNetwork Security Lec 1Snehal PoptaniNo ratings yet
- 2 Cybersecurity Fundamentals Network SecurityDocument57 pages2 Cybersecurity Fundamentals Network Securityrafaelricardo2705No ratings yet
- Cyber Sec and Digital Forensics-Lec4Document34 pagesCyber Sec and Digital Forensics-Lec4persie parkerNo ratings yet
- Đề Cương TACNN LtDocument8 pagesĐề Cương TACNN LtAnh Nguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Palo DNS SecurityDocument6 pagesPalo DNS SecurityDeepak VargheseNo ratings yet
- IP SPOOFING DocumentationDocument18 pagesIP SPOOFING DocumentationAncy AnasNo ratings yet
- Reconnaissance Scanning Gaining Access Maintaining Access Clearing TrackDocument11 pagesReconnaissance Scanning Gaining Access Maintaining Access Clearing TrackAlejo LomNo ratings yet
- Answers To Ethical Hacker Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnswers To Ethical Hacker Interview Questionstsultim bhutiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Network Security.: A. Vimal BabuDocument79 pagesIntroduction To Network Security.: A. Vimal Babukktamang09No ratings yet
- Network SniffingDocument9 pagesNetwork SniffingDr. Suman RaniNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security - Sample Short Questions1 - For StudentsDocument11 pagesCyber Security - Sample Short Questions1 - For Studentsसौभाग्य त्रिवेदीNo ratings yet
- #Session Task 15-SniffingDocument7 pages#Session Task 15-Sniffingsemperor81No ratings yet
- Cyber Security Sem6Document38 pagesCyber Security Sem6thirstyeulerNo ratings yet
- 21BCE5693Document5 pages21BCE5693VIKASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: IS Network and Telecommunications RisksDocument34 pagesChapter Six: IS Network and Telecommunications RisksJay ManNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document34 pagesCH 4አርቲስቶቹ Artistochu animation sitcom by habeshan memeNo ratings yet
- Co6i-Eti-Unit 6 NotesDocument13 pagesCo6i-Eti-Unit 6 NotesMSBTE ObserverNo ratings yet
- 13-1 CH02.Cisco Network Security-FW, IPS, IPsec VPNsDocument92 pages13-1 CH02.Cisco Network Security-FW, IPS, IPsec VPNsSai PNo ratings yet
- Network Security: MSC Course byDocument9 pagesNetwork Security: MSC Course bymheba11No ratings yet
- Different Types of Network Attacks and Security Threats and Counter MeasuresDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of Network Attacks and Security Threats and Counter MeasuresSimar Chauhan100% (1)
- Netsec WS 20131109 BDDocument353 pagesNetsec WS 20131109 BDmmi1982100% (1)
- DFS40083 - Chapter 5Document60 pagesDFS40083 - Chapter 5F2066 MUHAMMAD JOSHWAN BIN MUHD IRWAN JOHNSONNo ratings yet
- TCP UDP AttacksDocument1 pageTCP UDP Attackstouk toukNo ratings yet
- The National Law Institute University, Bhopal: "Operational Working of Ettercap Tool"Document11 pagesThe National Law Institute University, Bhopal: "Operational Working of Ettercap Tool"Atul AroraNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument8 pagesOSI ModelMr. RakeshNo ratings yet
- Domain-5 Notes PDFDocument20 pagesDomain-5 Notes PDFRayhanNo ratings yet
- 2095 ALI SHAFQAT SHAFQAT SAGHIR - Final 9890 982598084Document12 pages2095 ALI SHAFQAT SHAFQAT SAGHIR - Final 9890 982598084Ali ShafqatNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking TrainingDocument31 pagesEthical Hacking TrainingKhoi DangNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Chapter 16-Network SecurityDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Chapter 16-Network SecurityErickson Alex Vargas RoqueNo ratings yet
- CehexamDocument8 pagesCehexamEkaNo ratings yet
- 19cse304-Cybersecurity Answer KeyDocument19 pages19cse304-Cybersecurity Answer KeyabhiNo ratings yet
- 4 SecurityDocument34 pages4 SecurityHiwot TadesseNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 1 Ccna Security PDFDocument6 pagesCapitulo 1 Ccna Security PDFRafael RojasNo ratings yet
- General Presentation Topic: Man in The Middle AttackDocument7 pagesGeneral Presentation Topic: Man in The Middle AttackVivek JamwalNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 1 Exam AnswersDocument5 pagesCCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 1 Exam AnswersRussell FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ccna S 2.0Document116 pagesCcna S 2.0loffy hackerNo ratings yet
- 18 DataCenter Security OverviewDocument22 pages18 DataCenter Security Overviewrnaveed01No ratings yet
- CCNA Security Module 1 100%Document4 pagesCCNA Security Module 1 100%Akbal Larios100% (1)
- Network Layer SecurityDocument30 pagesNetwork Layer Securityderara jemalNo ratings yet
- Cns 1 - 5 UnitsDocument111 pagesCns 1 - 5 UnitsbhanutejakagithaNo ratings yet
- Network Infrastructure and Risk ElementsDocument13 pagesNetwork Infrastructure and Risk Elementsabdulsamad4691No ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesFrom EverandWireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Network Security Traceback Attack and React in the United States Department of Defense NetworkFrom EverandNetwork Security Traceback Attack and React in the United States Department of Defense NetworkNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- Designing and Implementing Linux Firewalls and QoS using netfilter, iproute2, NAT and l7-filterFrom EverandDesigning and Implementing Linux Firewalls and QoS using netfilter, iproute2, NAT and l7-filterNo ratings yet
- Configuring IPCop Firewalls: Closing Borders with Open SourceFrom EverandConfiguring IPCop Firewalls: Closing Borders with Open SourceNo ratings yet
- Subject Offering 1T2223 August20V.6 1Document15 pagesSubject Offering 1T2223 August20V.6 1Armel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs (1) My AnswersDocument6 pages6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs (1) My AnswersArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Truth Table 1Document3 pagesQuiz-Truth Table 1Armel Bacdayan Lacanaria50% (2)
- R Q R Q R Q R (Q Q (Q QV (Q R Q: Mabeninsig@uc-Bcf - Edu.phDocument1 pageR Q R Q R Q R (Q Q (Q QV (Q R Q: Mabeninsig@uc-Bcf - Edu.phArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras: College of Information Technology / Computer ScienceDocument7 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras: College of Information Technology / Computer ScienceArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- University of The Cordilleras College of Information Technology and Computer ScienceDocument1 pageUniversity of The Cordilleras College of Information Technology and Computer ScienceArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Documentation: Armel B. LacanariaDocument2 pagesDocumentation: Armel B. LacanariaArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- CC8 Determining MLBB Causes Video Game Addiction To The CITCS-1DDocument7 pagesCC8 Determining MLBB Causes Video Game Addiction To The CITCS-1DArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise in Data Structures 1Document2 pagesLaboratory Exercise in Data Structures 1Armel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Javelin BoardDocument2 pagesJavelin BoardArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Globalization On Communication and EducationDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Globalization On Communication and EducationArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- 12mcei12 - Network Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment With Report GenerationDocument91 pages12mcei12 - Network Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment With Report GenerationproftechitspecialistNo ratings yet
- CP R77.20.20 1470 1490 ApplianceLocal AdminGuideDocument172 pagesCP R77.20.20 1470 1490 ApplianceLocal AdminGuidepaulohrodriguesNo ratings yet
- Theory Test 1 MemoDocument3 pagesTheory Test 1 MemoHenry TshafaNo ratings yet
- An Ode To Social Media - Sample PagesDocument7 pagesAn Ode To Social Media - Sample PagesAileenNo ratings yet
- Z LibraryDocument5 pagesZ LibraryKaranNo ratings yet
- Gmail - Your Plastiq Payment ID #Pny9emp Has Been Approved (Ref - 00D61alVC. - 5004N1LhgXK - Ref)Document3 pagesGmail - Your Plastiq Payment ID #Pny9emp Has Been Approved (Ref - 00D61alVC. - 5004N1LhgXK - Ref)Zearl ClarkNo ratings yet
- WEB Programming Laboratory Manual BSC 6 Sem: Web Design Lab HTMLDocument54 pagesWEB Programming Laboratory Manual BSC 6 Sem: Web Design Lab HTMLgayathrinaik12No ratings yet
- Review Test Questions: View: ID CorrectDocument2 pagesReview Test Questions: View: ID CorrectgustavoNo ratings yet
- Att Bridged Mode Vs Ip Passthrough Nov2012 v3Document5 pagesAtt Bridged Mode Vs Ip Passthrough Nov2012 v3mpkp28No ratings yet
- Project Proposal DraftDocument1 pageProject Proposal DraftCarl Axel M. FajardoNo ratings yet
- MIS607 - CybersecurityDocument9 pagesMIS607 - CybersecurityAshraful RibatNo ratings yet
- System Design and Analysis - Information Security and Cyber CrimeDocument29 pagesSystem Design and Analysis - Information Security and Cyber CrimeMilon MahatoNo ratings yet
- Harvard NotesDocument4 pagesHarvard Notesmiskinmusic123No ratings yet
- Fortigate Cli 50Document1,129 pagesFortigate Cli 50nexrothNo ratings yet
- I. Ra 10931 Beneficiary Profile Summary: (Last Name, First Name, Middle Name)Document2 pagesI. Ra 10931 Beneficiary Profile Summary: (Last Name, First Name, Middle Name)Cherelyn De LunaNo ratings yet
- Information Security Privacy SyllabusDocument1 pageInformation Security Privacy SyllabusANUPMA PRITYNo ratings yet
- Long Term Project Based EngagementsDocument4 pagesLong Term Project Based EngagementsIko JaroNo ratings yet
- Juniper CommandsDocument6 pagesJuniper CommandsYibrail Veliz PluaNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide To NMAPDocument2 pagesQuick Reference Guide To NMAPMarcelo Alexandre de FreitasNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity 2024Document3 pagesCybersecurity 2024korodemichael81No ratings yet
- SAP MV45AFZZ Cancel Document Saving ProcessDocument4 pagesSAP MV45AFZZ Cancel Document Saving ProcessFSignettiNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument41 pagesCyber SecuritySuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper About "Hacking The Online Scammers Who Tricked Us!"Document1 pageReaction Paper About "Hacking The Online Scammers Who Tricked Us!"Larrah Josefa BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesInterview QuestionssalimkottayilNo ratings yet
- Paket 5000 Up 531 08.25.22 25 08 2022Document7 pagesPaket 5000 Up 531 08.25.22 25 08 2022pathul azizNo ratings yet
- Web Technology Solved Mcqs Set 1Document6 pagesWeb Technology Solved Mcqs Set 1DESI DOSENo ratings yet
- How To Configure Linux Dns Server Step by Step Guide Example and ImplementationDocument85 pagesHow To Configure Linux Dns Server Step by Step Guide Example and ImplementationSujeet SinghNo ratings yet
- WebCruiser Web Vulnerability Scanner Test ReportDocument14 pagesWebCruiser Web Vulnerability Scanner Test ReportjhonassaNo ratings yet
Write Down 10 Different Learnings or Takeaways That You Were Able To Glean From The Content
Write Down 10 Different Learnings or Takeaways That You Were Able To Glean From The Content
Uploaded by
Armel Bacdayan Lacanaria0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesThe document provides a summary of 10 key learnings around cybersecurity topics:
1) Current state of cybersecurity and important security terms
2) Threat actors and how they can be individuals or groups
3) Malware types like viruses, ransomware, and spyware
4) Common network attacks like reconnaissance, access, and DoS attacks
5) IP vulnerabilities and threats exploited by spoofing source IP addresses
6) TCP and UDP vulnerabilities exploited in protocols and lack of encryption
7) IP services vulnerabilities in ARP, DNS, DHCP exploited by spoofing
8) Network security best practices of confidentiality, availability, and integrity
9) Cryptography techniques for secure communication using encryption
10) Ethical
Original Description:
Original Title
Write down 10 different learnings or takeaways that you were able to glean from the content
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides a summary of 10 key learnings around cybersecurity topics:
1) Current state of cybersecurity and important security terms
2) Threat actors and how they can be individuals or groups
3) Malware types like viruses, ransomware, and spyware
4) Common network attacks like reconnaissance, access, and DoS attacks
5) IP vulnerabilities and threats exploited by spoofing source IP addresses
6) TCP and UDP vulnerabilities exploited in protocols and lack of encryption
7) IP services vulnerabilities in ARP, DNS, DHCP exploited by spoofing
8) Network security best practices of confidentiality, availability, and integrity
9) Cryptography techniques for secure communication using encryption
10) Ethical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesWrite Down 10 Different Learnings or Takeaways That You Were Able To Glean From The Content
Write Down 10 Different Learnings or Takeaways That You Were Able To Glean From The Content
Uploaded by
Armel Bacdayan LacanariaThe document provides a summary of 10 key learnings around cybersecurity topics:
1) Current state of cybersecurity and important security terms
2) Threat actors and how they can be individuals or groups
3) Malware types like viruses, ransomware, and spyware
4) Common network attacks like reconnaissance, access, and DoS attacks
5) IP vulnerabilities and threats exploited by spoofing source IP addresses
6) TCP and UDP vulnerabilities exploited in protocols and lack of encryption
7) IP services vulnerabilities in ARP, DNS, DHCP exploited by spoofing
8) Network security best practices of confidentiality, availability, and integrity
9) Cryptography techniques for secure communication using encryption
10) Ethical
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Write down 10 different learnings or takeaways that you were able to glean from the content.
My 10 different learning or takeaways that I was able to glean from the content are:
1. The current state of cybersecurity
- Cybercriminals have the ability to take small to large infrastructures using
different hacking tools.
- Maintaining a secure network ensures the safety of network users and protects
commercial interests. There are six security terms (assets, vulnerability, threat,
exploit, mitigation, and risk) which user should be aware.
2. Threat actors
- A threat actor is anyone who is either is a key driver of, or participates in, a
malicious action that targets an organization’s IT security. A threat actor can be a
single person carrying out a security incident, as well as a group, an organization,
or even a country involved in carrying out a cyberattack.
3. Malwares
- A malware is a name for a number of malicious software variants, this includes
viruses, ransomwares, and spywares. A malware is a shorthand for malicious
software.
4. Common network attacks
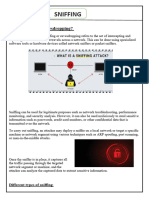
- Networks are susceptible to different malwares like reconnaissance attack, access
attack, and DoS attack.
5. IP vulnerabilities and threats
- IP do not validate whether the source IP address contained in a packet, threat
actors take advantage of this and send packets using a spoofed source IP address.
Some of the common IP related attacks are: ICMP attacks, amplification and
reflection attacks, address spoofing attacks, man-in-the-middle attack, and session
hijacking.
6. TCP and UDP vulnerabilities
- A TCP segment information appears immediately after the IP header
- There are six control bits of the TCP segment:
o URG – Urgent pointer field significant
o ACK – Acknowledgement field significant
o PSH – Push function
o RST – Reset the connection
o SYN – Synchronize sequence numbers
o FIN – No more data from sender
- TCP provides different services:
o Reliable delivery
o Flow control
o Stateful communication
- UDP is commonly used by DNS, TFTP, NFS, and SNMP. UDP is a
connectionless transport layer protocol. UDP is not encrypted though you can add
encryption to UDP. The lack of encryption means that anyone can see the traffic,
change it, and send it on to its destination.
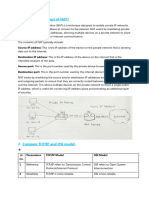
7. IP services
- ARP Vulnerabilities
o The ARP protocol vulnerability is one of the most common vulnerabilities
in the TCP / IP four-layer architecture. The network protocol
vulnerabilities can lead to the intrusion and attack of the information
system, and disable or disable the normal defense function of the system
- ARP Cache Poisoning
o a technique by which an attacker sends (spoofed) Address Resolution
Protocol (ARP) messages onto a local area network. a technique by which
an attacker sends (spoofed) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages
onto a local area network.
- DNS attacks
o an exploit in which an attacker takes advantage of vulnerabilities in the
domain name system (DNS).
- DNS Tunneling
o a method of cyber-attack that encodes the data of other programs or
protocols in DNS queries and responses.
- DHCP
o DHCP servers dynamically provide IP configuration information to
clients.
- DHCP Attacks
o A DHCP spoofing attack occurs when a rogue DHCP server is connected
to the network and provides false IP configuration parameters to legitimate
clients. A rogue server can provide a variety of misleading information:
Wrong default gateway, wrong DNS server, wrong IP address.
8. Network security best practices
- Confidentiality, Availability, and Integrity
o Confidentiality - Only authorized individuals, entities, or processes can
access sensitive information. It may require using cryptographic
encryption algorithms such as AES to encrypt and decrypt data.
o Integrity - Refers to protecting data from unauthorized alteration. It
requires the use of cryptographic hashing algorithms such as SHA.
o Availability - Authorized users must have uninterrupted access to
important resources and data. It requires implementing redundant services,
gateways, and links
- To ensure secure communications across both public and private networks, you
must secure devices including routers, switches, servers, and hosts. VPN, ASA
Firewall, IPS, ESA/WSA, AAA Server are several security devices and services.
9. Cryptography
- Cryptography is the study of secure communications techniques that allow only
the sender and intended recipient of a message to view its contents. Cryptography
provides for secure communication in the presence of malicious third-parties
known as adversaries. Encryption uses an algorithm and a key to transform an
input (i.e., plaintext) into an encrypted output (i.e., ciphertext).
10. Ethical hacking
- Ethical hacking is a process of detecting vulnerabilities in an application, system,
or organization's infrastructure that an attacker can use to exploit an individual or
organization. They use this process to prevent cyberattacks and security breaches
by lawfully hacking into the systems and looking for weak points.
You might also like
- Mol Learn Login - Google SearchDocument2 pagesMol Learn Login - Google SearchHAMMAD SHAHNo ratings yet
- The Certified Ethical Hacker Exam - version 8 (The concise study guide)From EverandThe Certified Ethical Hacker Exam - version 8 (The concise study guide)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (9)
- Wishpond Landing Page AssignmentDocument3 pagesWishpond Landing Page AssignmentTerrence CroweNo ratings yet
- 13 17 AnswerDocument31 pages13 17 Answers2187022No ratings yet
- Network Security Part 1Document85 pagesNetwork Security Part 1amolmhNo ratings yet
- Principle of SecurityDocument73 pagesPrinciple of SecurityBab KebedeNo ratings yet
- INT 242 Network Attacks-1Document32 pagesINT 242 Network Attacks-1tech_415983648No ratings yet
- Preguntas Tres Primeros Capitulos Netacad Prueba 1 CCNP3 en InglesDocument27 pagesPreguntas Tres Primeros Capitulos Netacad Prueba 1 CCNP3 en InglesPatricioNo ratings yet
- Advanced Networks and Security Part 2 - Partial Exam 11 January 2017Document3 pagesAdvanced Networks and Security Part 2 - Partial Exam 11 January 2017diegoantivirusNo ratings yet
- TCP IP VulnerabilitiesDocument17 pagesTCP IP VulnerabilitiesHemant Sudhir WavhalNo ratings yet
- SNIFFING Gif3Document5 pagesSNIFFING Gif3khanssaoudjaffar0219No ratings yet
- Network Security Lec 1Document43 pagesNetwork Security Lec 1Snehal PoptaniNo ratings yet
- 2 Cybersecurity Fundamentals Network SecurityDocument57 pages2 Cybersecurity Fundamentals Network Securityrafaelricardo2705No ratings yet
- Cyber Sec and Digital Forensics-Lec4Document34 pagesCyber Sec and Digital Forensics-Lec4persie parkerNo ratings yet
- Đề Cương TACNN LtDocument8 pagesĐề Cương TACNN LtAnh Nguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Palo DNS SecurityDocument6 pagesPalo DNS SecurityDeepak VargheseNo ratings yet
- IP SPOOFING DocumentationDocument18 pagesIP SPOOFING DocumentationAncy AnasNo ratings yet
- Reconnaissance Scanning Gaining Access Maintaining Access Clearing TrackDocument11 pagesReconnaissance Scanning Gaining Access Maintaining Access Clearing TrackAlejo LomNo ratings yet
- Answers To Ethical Hacker Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnswers To Ethical Hacker Interview Questionstsultim bhutiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Network Security.: A. Vimal BabuDocument79 pagesIntroduction To Network Security.: A. Vimal Babukktamang09No ratings yet
- Network SniffingDocument9 pagesNetwork SniffingDr. Suman RaniNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security - Sample Short Questions1 - For StudentsDocument11 pagesCyber Security - Sample Short Questions1 - For Studentsसौभाग्य त्रिवेदीNo ratings yet
- #Session Task 15-SniffingDocument7 pages#Session Task 15-Sniffingsemperor81No ratings yet
- Cyber Security Sem6Document38 pagesCyber Security Sem6thirstyeulerNo ratings yet
- 21BCE5693Document5 pages21BCE5693VIKASH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: IS Network and Telecommunications RisksDocument34 pagesChapter Six: IS Network and Telecommunications RisksJay ManNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document34 pagesCH 4አርቲስቶቹ Artistochu animation sitcom by habeshan memeNo ratings yet
- Co6i-Eti-Unit 6 NotesDocument13 pagesCo6i-Eti-Unit 6 NotesMSBTE ObserverNo ratings yet
- 13-1 CH02.Cisco Network Security-FW, IPS, IPsec VPNsDocument92 pages13-1 CH02.Cisco Network Security-FW, IPS, IPsec VPNsSai PNo ratings yet
- Network Security: MSC Course byDocument9 pagesNetwork Security: MSC Course bymheba11No ratings yet
- Different Types of Network Attacks and Security Threats and Counter MeasuresDocument6 pagesDifferent Types of Network Attacks and Security Threats and Counter MeasuresSimar Chauhan100% (1)
- Netsec WS 20131109 BDDocument353 pagesNetsec WS 20131109 BDmmi1982100% (1)
- DFS40083 - Chapter 5Document60 pagesDFS40083 - Chapter 5F2066 MUHAMMAD JOSHWAN BIN MUHD IRWAN JOHNSONNo ratings yet
- TCP UDP AttacksDocument1 pageTCP UDP Attackstouk toukNo ratings yet
- The National Law Institute University, Bhopal: "Operational Working of Ettercap Tool"Document11 pagesThe National Law Institute University, Bhopal: "Operational Working of Ettercap Tool"Atul AroraNo ratings yet
- OSI ModelDocument8 pagesOSI ModelMr. RakeshNo ratings yet
- Domain-5 Notes PDFDocument20 pagesDomain-5 Notes PDFRayhanNo ratings yet
- 2095 ALI SHAFQAT SHAFQAT SAGHIR - Final 9890 982598084Document12 pages2095 ALI SHAFQAT SHAFQAT SAGHIR - Final 9890 982598084Ali ShafqatNo ratings yet
- Ethical Hacking TrainingDocument31 pagesEthical Hacking TrainingKhoi DangNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Chapter 16-Network SecurityDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Chapter 16-Network SecurityErickson Alex Vargas RoqueNo ratings yet
- CehexamDocument8 pagesCehexamEkaNo ratings yet
- 19cse304-Cybersecurity Answer KeyDocument19 pages19cse304-Cybersecurity Answer KeyabhiNo ratings yet
- 4 SecurityDocument34 pages4 SecurityHiwot TadesseNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 1 Ccna Security PDFDocument6 pagesCapitulo 1 Ccna Security PDFRafael RojasNo ratings yet
- General Presentation Topic: Man in The Middle AttackDocument7 pagesGeneral Presentation Topic: Man in The Middle AttackVivek JamwalNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 1 Exam AnswersDocument5 pagesCCNA Security v2.0 Chapter 1 Exam AnswersRussell FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ccna S 2.0Document116 pagesCcna S 2.0loffy hackerNo ratings yet
- 18 DataCenter Security OverviewDocument22 pages18 DataCenter Security Overviewrnaveed01No ratings yet
- CCNA Security Module 1 100%Document4 pagesCCNA Security Module 1 100%Akbal Larios100% (1)
- Network Layer SecurityDocument30 pagesNetwork Layer Securityderara jemalNo ratings yet
- Cns 1 - 5 UnitsDocument111 pagesCns 1 - 5 UnitsbhanutejakagithaNo ratings yet
- Network Infrastructure and Risk ElementsDocument13 pagesNetwork Infrastructure and Risk Elementsabdulsamad4691No ratings yet
- Wireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesFrom EverandWireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Network Security Traceback Attack and React in the United States Department of Defense NetworkFrom EverandNetwork Security Traceback Attack and React in the United States Department of Defense NetworkNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeFrom EverandCryptography and Data Security Book 1: Proper Guide to Data Security in Communication Networks. Cryptography and Data Security in PracticeNo ratings yet
- Designing and Implementing Linux Firewalls and QoS using netfilter, iproute2, NAT and l7-filterFrom EverandDesigning and Implementing Linux Firewalls and QoS using netfilter, iproute2, NAT and l7-filterNo ratings yet
- Configuring IPCop Firewalls: Closing Borders with Open SourceFrom EverandConfiguring IPCop Firewalls: Closing Borders with Open SourceNo ratings yet
- Subject Offering 1T2223 August20V.6 1Document15 pagesSubject Offering 1T2223 August20V.6 1Armel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- 6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs (1) My AnswersDocument6 pages6.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs (1) My AnswersArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Quiz-Truth Table 1Document3 pagesQuiz-Truth Table 1Armel Bacdayan Lacanaria50% (2)
- R Q R Q R Q R (Q Q (Q QV (Q R Q: Mabeninsig@uc-Bcf - Edu.phDocument1 pageR Q R Q R Q R (Q Q (Q QV (Q R Q: Mabeninsig@uc-Bcf - Edu.phArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- University of Cordilleras: College of Information Technology / Computer ScienceDocument7 pagesUniversity of Cordilleras: College of Information Technology / Computer ScienceArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- University of The Cordilleras College of Information Technology and Computer ScienceDocument1 pageUniversity of The Cordilleras College of Information Technology and Computer ScienceArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Documentation: Armel B. LacanariaDocument2 pagesDocumentation: Armel B. LacanariaArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- CC8 Determining MLBB Causes Video Game Addiction To The CITCS-1DDocument7 pagesCC8 Determining MLBB Causes Video Game Addiction To The CITCS-1DArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise in Data Structures 1Document2 pagesLaboratory Exercise in Data Structures 1Armel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- Javelin BoardDocument2 pagesJavelin BoardArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Globalization On Communication and EducationDocument2 pagesThe Impact of Globalization On Communication and EducationArmel Bacdayan LacanariaNo ratings yet
- 12mcei12 - Network Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment With Report GenerationDocument91 pages12mcei12 - Network Scanning and Vulnerability Assessment With Report GenerationproftechitspecialistNo ratings yet
- CP R77.20.20 1470 1490 ApplianceLocal AdminGuideDocument172 pagesCP R77.20.20 1470 1490 ApplianceLocal AdminGuidepaulohrodriguesNo ratings yet
- Theory Test 1 MemoDocument3 pagesTheory Test 1 MemoHenry TshafaNo ratings yet
- An Ode To Social Media - Sample PagesDocument7 pagesAn Ode To Social Media - Sample PagesAileenNo ratings yet
- Z LibraryDocument5 pagesZ LibraryKaranNo ratings yet
- Gmail - Your Plastiq Payment ID #Pny9emp Has Been Approved (Ref - 00D61alVC. - 5004N1LhgXK - Ref)Document3 pagesGmail - Your Plastiq Payment ID #Pny9emp Has Been Approved (Ref - 00D61alVC. - 5004N1LhgXK - Ref)Zearl ClarkNo ratings yet
- WEB Programming Laboratory Manual BSC 6 Sem: Web Design Lab HTMLDocument54 pagesWEB Programming Laboratory Manual BSC 6 Sem: Web Design Lab HTMLgayathrinaik12No ratings yet
- Review Test Questions: View: ID CorrectDocument2 pagesReview Test Questions: View: ID CorrectgustavoNo ratings yet
- Att Bridged Mode Vs Ip Passthrough Nov2012 v3Document5 pagesAtt Bridged Mode Vs Ip Passthrough Nov2012 v3mpkp28No ratings yet
- Project Proposal DraftDocument1 pageProject Proposal DraftCarl Axel M. FajardoNo ratings yet
- MIS607 - CybersecurityDocument9 pagesMIS607 - CybersecurityAshraful RibatNo ratings yet
- System Design and Analysis - Information Security and Cyber CrimeDocument29 pagesSystem Design and Analysis - Information Security and Cyber CrimeMilon MahatoNo ratings yet
- Harvard NotesDocument4 pagesHarvard Notesmiskinmusic123No ratings yet
- Fortigate Cli 50Document1,129 pagesFortigate Cli 50nexrothNo ratings yet
- I. Ra 10931 Beneficiary Profile Summary: (Last Name, First Name, Middle Name)Document2 pagesI. Ra 10931 Beneficiary Profile Summary: (Last Name, First Name, Middle Name)Cherelyn De LunaNo ratings yet
- Information Security Privacy SyllabusDocument1 pageInformation Security Privacy SyllabusANUPMA PRITYNo ratings yet
- Long Term Project Based EngagementsDocument4 pagesLong Term Project Based EngagementsIko JaroNo ratings yet
- Juniper CommandsDocument6 pagesJuniper CommandsYibrail Veliz PluaNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide To NMAPDocument2 pagesQuick Reference Guide To NMAPMarcelo Alexandre de FreitasNo ratings yet
- Cybersecurity 2024Document3 pagesCybersecurity 2024korodemichael81No ratings yet
- SAP MV45AFZZ Cancel Document Saving ProcessDocument4 pagesSAP MV45AFZZ Cancel Document Saving ProcessFSignettiNo ratings yet
- Cyber SecurityDocument41 pagesCyber SecuritySuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper About "Hacking The Online Scammers Who Tricked Us!"Document1 pageReaction Paper About "Hacking The Online Scammers Who Tricked Us!"Larrah Josefa BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesInterview QuestionssalimkottayilNo ratings yet
- Paket 5000 Up 531 08.25.22 25 08 2022Document7 pagesPaket 5000 Up 531 08.25.22 25 08 2022pathul azizNo ratings yet
- Web Technology Solved Mcqs Set 1Document6 pagesWeb Technology Solved Mcqs Set 1DESI DOSENo ratings yet
- How To Configure Linux Dns Server Step by Step Guide Example and ImplementationDocument85 pagesHow To Configure Linux Dns Server Step by Step Guide Example and ImplementationSujeet SinghNo ratings yet
- WebCruiser Web Vulnerability Scanner Test ReportDocument14 pagesWebCruiser Web Vulnerability Scanner Test ReportjhonassaNo ratings yet