Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Teaching: Lesson 1
Introduction To Teaching: Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Eisha Louise Broqueza VelasquezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Film Art An Introduction 11th Edition Bordwell Test BankDocument7 pagesFilm Art An Introduction 11th Edition Bordwell Test Banka367758805No ratings yet
- Approaches in Teaching Social StudiesDocument86 pagesApproaches in Teaching Social StudiesWasakna Buhay100% (6)
- Pedagogies for Student-Centered Learning: Online and On-GoundFrom EverandPedagogies for Student-Centered Learning: Online and On-GoundRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Senior Estimator Preconstruction Manager in Atlanta GA Resume Steven LosieDocument2 pagesSenior Estimator Preconstruction Manager in Atlanta GA Resume Steven LosieStevenLosieNo ratings yet
- Principles & Strategies of Teaching in Medical Laboratory Science (PSTM221)Document16 pagesPrinciples & Strategies of Teaching in Medical Laboratory Science (PSTM221)29 REYES, BERNADETTE R.No ratings yet
- Intro To Teaching - pstm211Document58 pagesIntro To Teaching - pstm211Charlen Kylha GavinoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Intro To TeachingDocument6 pagesWeek 2 - Intro To TeachingKezia MadeloNo ratings yet
- PSTM221Document10 pagesPSTM221Joyce Anne Cruz0% (1)
- Psthe MidtermsDocument15 pagesPsthe MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- PSTM Week2Document59 pagesPSTM Week2Romeo DiestaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 PSTMDocument15 pagesLesson 1 PSTMNicole Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Approach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleDocument22 pagesApproach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleJON VENNIE IBALENo ratings yet
- INSET Applied Knowledge.... DIOSA FINALDocument72 pagesINSET Applied Knowledge.... DIOSA FINALDIOSA N.CAPISTRANONo ratings yet
- PC 122Document3 pagesPC 122Carla LedinioNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Methods, Techniques StrategiesDocument21 pagesApproaches, Methods, Techniques Strategiessereen qasemNo ratings yet
- Sarmiento-Teaching Styles, Approaches, & ApproachesDocument1 pageSarmiento-Teaching Styles, Approaches, & ApproachesJoemel SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Team A - Discovery-Inquiry Based ApproachDocument32 pagesTeam A - Discovery-Inquiry Based ApproachJemuel LuminariasNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approaches Strategies Methods and Techniques AS9Document24 pagesTeaching Approaches Strategies Methods and Techniques AS9Mariane SibayNo ratings yet
- LABISTO, MARY CRIS (Collateral Reading 4)Document5 pagesLABISTO, MARY CRIS (Collateral Reading 4)Mary Cris Maragañas AnghagNo ratings yet
- Effective Pedagogies in PersonDocument24 pagesEffective Pedagogies in PersonKiwinKoreaNo ratings yet
- ApproachDocument6 pagesApproachMa Yong Rui100% (1)
- Principles of Teaching 323Document81 pagesPrinciples of Teaching 323Mark Anthony B. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityDocument10 pagesApproaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityManolo Servise HiloNo ratings yet
- 2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoDocument4 pages2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoLovely PadernaNo ratings yet
- Educ 212 Meaning and TEchniques of Teaching by Ma Salome LucasDocument4 pagesEduc 212 Meaning and TEchniques of Teaching by Ma Salome LucasSalome LucasNo ratings yet
- MS SSC 102 - Act 3Document3 pagesMS SSC 102 - Act 3Jervyn GuiananNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Methods and Techniques Promoting Learner-Centered ActivitiesDocument15 pagesApproaches, Methods and Techniques Promoting Learner-Centered ActivitiesHariette Mae OnofreNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Kepada Teori Dan Amalan Pedagogi Dalam Pengajaran PembelajaranDocument34 pagesPengenalan Kepada Teori Dan Amalan Pedagogi Dalam Pengajaran PembelajaranBrendajc Jc0% (1)
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Haha Haha100% (1)
- (Formerly Ramon Magsaysay Technological University) Iba,: College of Teacher EducationDocument16 pages(Formerly Ramon Magsaysay Technological University) Iba,: College of Teacher EducationArabela AgrabioNo ratings yet
- Approaches Techniques and Method in TeachingDocument19 pagesApproaches Techniques and Method in Teachingmarjorie gervacio100% (1)
- Approaches Techniques and Method in TeachingDocument19 pagesApproaches Techniques and Method in Teachingmarjorie gervacio100% (1)
- Module. Teaching Approaches, Methods and StrategiesDocument38 pagesModule. Teaching Approaches, Methods and StrategiesJohn Dave Mabánta0% (1)
- Lecture On Principles of TeachingDocument9 pagesLecture On Principles of Teachingmaricel cuisonNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Basic TerminologyDocument12 pagesDefinitions of Basic TerminologySeham FouadNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approaches and MethodsDocument3 pagesTeaching Approaches and MethodsKenneth Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lect1 (The Concept and Nature of Teaching)Document7 pagesLect1 (The Concept and Nature of Teaching)LUEL JAY VALMORESNo ratings yet
- Teaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionDocument2 pagesTeaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionMaricel ViloriaNo ratings yet
- TeachingDocument21 pagesTeachingRosdiyana Bahtika100% (1)
- The Teaching-Learning Process: Yenna Monica D. PDocument24 pagesThe Teaching-Learning Process: Yenna Monica D. Psanta lizardoNo ratings yet
- Simple Diagram Found Below Is An Attempt To Distinguish ThemDocument13 pagesSimple Diagram Found Below Is An Attempt To Distinguish ThemEDENINo ratings yet
- Compilation of The Different Instructional StrategiesDocument12 pagesCompilation of The Different Instructional StrategiesCatherine PanoyNo ratings yet
- Maam Saylanon NotesDocument7 pagesMaam Saylanon Noteskristelannantong3No ratings yet
- Learning Theories P Week 1Document29 pagesLearning Theories P Week 1NURUL NORSHAFIQAH AQILA BINTI SHAARINo ratings yet
- L 200 Unit 7Document19 pagesL 200 Unit 7abrokwah sethNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Rizal-1Document14 pagesPortfolio in Rizal-1Rico James Gomez EfacNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledEdel Guyuran VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in Science TeachingDocument25 pagesBest Practices in Science Teachingjo_aligora100% (2)
- Learning - TheoriesDocument31 pagesLearning - TheoriesMckoy SandersonNo ratings yet
- NE Unit II - Teaching LearningDocument72 pagesNE Unit II - Teaching LearningProf.R.Indhumathi ProfessorNo ratings yet
- An Output in MAPEH - 120Document10 pagesAn Output in MAPEH - 120Marjo AldeNo ratings yet
- Education VocabularyDocument1 pageEducation VocabularyCarlosValdesNo ratings yet
- EDU 213 Study Guide by A-Media..Document25 pagesEDU 213 Study Guide by A-Media..Aliu Ridwan BamideleNo ratings yet
- Panel DiscussionDocument13 pagesPanel Discussionjinsi georgeNo ratings yet
- 9 Colegio Dela Purisima Concepcion: Name of Topics: The Teaching Profession: An OverviewDocument7 pages9 Colegio Dela Purisima Concepcion: Name of Topics: The Teaching Profession: An OverviewAlyza Mae D. DariaNo ratings yet
- M116 - Module 1Document15 pagesM116 - Module 1Annie Rose A. MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Choosing Appropriate Method For Teaching ScienceDocument19 pagesChoosing Appropriate Method For Teaching ScienceJefrelyn Eugenio MontibonNo ratings yet
- 63-Article Text-174-1-10-20170908 PDFDocument8 pages63-Article Text-174-1-10-20170908 PDFDaniela CPNo ratings yet
- Ofelia M. Guarin Assignment 101: Learning Knowledge Skills Values Beliefs HabitsDocument10 pagesOfelia M. Guarin Assignment 101: Learning Knowledge Skills Values Beliefs HabitsOfelia MecateNo ratings yet
- PSTMLS MidtermsDocument16 pagesPSTMLS MidtermsJohn Oliver AsiaNo ratings yet
- Teaching MethodsDocument2 pagesTeaching Methodsjoel pabadoraNo ratings yet
- Competencies To Enhance Digital Teaching and LearningDocument27 pagesCompetencies To Enhance Digital Teaching and LearningMohammad Hamad HammadiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge University Reporter - 1st May 2013Document24 pagesCambridge University Reporter - 1st May 2013Fuzzy_Wood_PersonNo ratings yet
- Leadership Colloquium Sample Draft of ProgrammeDocument2 pagesLeadership Colloquium Sample Draft of Programmealdrin abdurahimNo ratings yet
- Annex A CHEDRO Eval - HD Template CHEDRO Eval. Annex ADocument5 pagesAnnex A CHEDRO Eval - HD Template CHEDRO Eval. Annex AMark Lemuel Layones ArceoNo ratings yet
- Major Personality Theorists ChartDocument3 pagesMajor Personality Theorists Chartapi-309711196100% (1)
- Piaget TheoryDocument6 pagesPiaget TheoryBenjamin KhanNo ratings yet
- Board of DirectorsDocument2 pagesBoard of DirectorsdbansalklgNo ratings yet
- Form Page2Document1 pageForm Page2Edward MirandaNo ratings yet
- CV Kevin StauntonDocument2 pagesCV Kevin Stauntonapi-270607420No ratings yet
- Value Education & Ehics Unit IDocument26 pagesValue Education & Ehics Unit IchanduNo ratings yet
- Architecture Personal StatementDocument5 pagesArchitecture Personal StatementDayanat AliyevNo ratings yet
- Parent Letter - 2Document1 pageParent Letter - 2WXMINo ratings yet
- Module 6-Instructional PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 6-Instructional PlanningTimothyLimNo ratings yet
- 201232640Document48 pages201232640The Myanmar TimesNo ratings yet
- Proposed Message of Drda Monday Flag Raising Ceremony - EditedDocument2 pagesProposed Message of Drda Monday Flag Raising Ceremony - EditedPulis Rehiyon Onse IINo ratings yet
- Ap EapcetDocument2 pagesAp EapcetAvinash PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Resume: ShivanisharmaDocument2 pagesResume: ShivanisharmaShweta SharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Paper For Second GradeDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Research Paper For Second Gradekhkmwrbnd100% (1)
- K. GUTSCHOW, Adolf Behne and Modern Architecture in Germany, 1910-1914 (2005)Document598 pagesK. GUTSCHOW, Adolf Behne and Modern Architecture in Germany, 1910-1914 (2005)Santiago de ArmaNo ratings yet
- Madyson Acers: ProfileDocument2 pagesMadyson Acers: ProfileMady AcersNo ratings yet
- CSS Monitoring Tool DRRMS Edited 18 Jan 2017Document10 pagesCSS Monitoring Tool DRRMS Edited 18 Jan 2017Lo ViNo ratings yet
- Critical Journal Review Contextual Oral Language SkillsDocument16 pagesCritical Journal Review Contextual Oral Language SkillsNurul FazirahNo ratings yet
- Ohio 22+adult Diploma Ohios Options FlyerDocument1 pageOhio 22+adult Diploma Ohios Options FlyerRuss HaxNo ratings yet
- A Self-Learning Module in English 10 1 Quarter, Module 7Document10 pagesA Self-Learning Module in English 10 1 Quarter, Module 7Yeon JunNo ratings yet
- Instituting A Policy of Inclusion and Services For Learners With Disabilities in Support of Inclusive Education ActDocument40 pagesInstituting A Policy of Inclusion and Services For Learners With Disabilities in Support of Inclusive Education ActAepple Cano RautrautNo ratings yet
- Assignment Harold - Mam MaluDocument2 pagesAssignment Harold - Mam MaluRojanie EstuitaNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its Research Design Rationale of The StudyDocument25 pagesThe Problem and Its Research Design Rationale of The StudyRhodz Rhodulf CapangpanganNo ratings yet
- Annual Plan MatusalemDocument6 pagesAnnual Plan Matusalemvirgilio roxasNo ratings yet
- UG Courses of Study 2007Document147 pagesUG Courses of Study 2007dinu1903100% (2)
Introduction To Teaching: Lesson 1
Introduction To Teaching: Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Eisha Louise Broqueza VelasquezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Teaching: Lesson 1
Introduction To Teaching: Lesson 1
Uploaded by
Eisha Louise Broqueza VelasquezCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 1 was originally evoked by another stimulus
INTRODUCTION TO TEACHING
TEACHING & LEARNING PROCESS
TEACHING defined…
▪ Refers to the process of imparting knowledge and
skills from a teacher to a learner. It encompasses the
activities of educating or instructing. It is an act or
experience that has a formative effect on the mind,
character or physical ability of an individual.
▪ A working definition of teaching is undertaking certain
ethical tasks or activities the intention of which is to
induce learning.
▪Operant Conditioning (Instrumental conditioning)
▪ it is a deliberate intervention that involves planning ▪ Described as a process that attempts to modify
and implementation of instructional activities and behavior through the use of positive and negative
experiences to meet learner outcomes according to a reinforcement. Through operant conditioning, an
teaching plan individual makes an association between a particular
Some thoughts on teaching and learning... behavior and a consequence.
▪ Clearly, not all learning is dependent on ▪Social Conditioning (Observational conditioning)
teaching...However, all teaching regardless of quality is ▪In this theory, people can learn new information and
predicated on learning..- Brown,1993 behaviors by watching other people.
▪ Teaching makes learning possible..-Ramsden,1992
LEARNING defined…
THE “HOWs” OF TEACHING
▪ Process of gaining knowledge or skill by studying, A. Strategies
practicing, being taught, or experiencing something. B. Approach
(Merriam-Webster Dictionary) C. Technique
D. Method
▪ “a persisting change in human performance or
performance potential . . . (brought) about as a result of A. Strategies
the learner’s interaction with the environment” ▪Is the art and science of directing and controlling the
(Driscoll, 1994) movements and activities of the army. If strategy is
good, we can get victory over our enemies. In teaching
▪ “the relatively permanent change in a person’s
this term is meant those procedures by which objectives
knowledge or behavior due to experience
of teaching are realized in the class. ▪Teaching strategy
▪ an enduring change in behavior, or in the capacity to is a generalized plan for a lesson which includes
behave in a given fashion, which results from practice or structure, instructional objectives and an outline of
other forms of experience” (Shuell, 1986) planned tactics, necessary to implement the strategies
LEARNING THEORIES Strategy can be summarized as
▪Teaching is the generalized plan of the whole lesson
▪Classical Conditioning (Pavlovian conditioning or
plan.
respondent conditioning)
▪ is a reflexive or automatic type of learning in which a ▪In strategy of teaching, realization of objectives is
stimulus acquires the capacity to evoke a response that given more importance than presentation of lesson.
▪A strategy does not follow a single track all the time,
but it changes according to the demands of the
situations such as age, level, needs, interests and They represent a reality within which students interact.
abilities of the students. Thus strategy is more The teacher controls the parameters of this "world" and
comprehensive than method. uses it to achieve the desired instructional results.
Students experience the reality of the scenario and
▪It is directional in nature. It refers to goal directed
gather meaning from it.
activities of the teachers. Thus, it is more close to
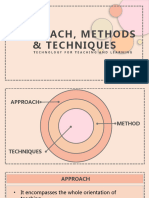
science than arts. APPROACH, METHOD & TECHNIQUE
Approach is the broadest of the three, making
TEACHING STRATEGIES technique the most specific, and the method found in
➢Brainstorming- is a large or small group activity that between approach and technique.
encourages students to focus on a topic and contribute Technique encompasses the personal style of the
to the free flow of ideas. teacher in carrying out specific steps of the teaching
➢ Case studies- are effective ways to get students to process
practically apply their skills, and their understanding of A Method, on the other hand, is an organized, orderly,
learned facts, to a real-world situation. They are systematic, and wellplanned procedure aimed at
particularly useful where situations are complex and facilitating and enhancing students’ learning.
solutions are uncertain.
B. Approach
➢ Debates- structured way of exploring the range of ▪Ways in which you try to engage students with the
views on an issue. It consists of a structured contest of subject matter (provide students with basic facts, relate
argumentation, in which two opposing individuals or new knowledge to what students already know, build in
teams defend and attack a given proposition. interaction, be passionate, be enthusiastic)
➢ Discussion- Discussion lets class members work ▪The ways in which you support your students
actively with the ideas and the concepts being pursued, (encourage questions, set formative assessments,
and discussion sessions can be an extremely effective in provide constructive feedback).
changing behaviour or attitudes. Consequently,
teachers use them frequently in instructional situations A description of your approach to teaching
includes:
➢The flipped classroom-students complete learning ▪The mode or manner of teaching (lecture, tutorial,
normally covered in the classroom in their own time (by bedside teaching, laboratory work);
watching videos and/or accessing resources), and
classroom time is dedicated to hands-on activities and ▪Some understanding of how people learn (learning
interactive, personalized learning, leading to deeper theory);
understanding. Students use class time to apply the
▪Some understanding of how to facilitate learning
theory and concepts discussed in the videos, and to
(qualities of the teacher such as passion, principles for
utilize techniques including group problem-solving and
good teaching practice such as providing timely and
team building games, simulations, case study reviews,
constructive feedback, putting educational theory into
and group discussions.
practice).
➢ Groupwork- is a method of instruction that gets
TYPES OF TEACHING APPROACH
students to work together in groups.
ACCDRD TO THE ROLE OF TEACHER
➢ Questioning- The art of asking questions is at the
➢The executive approach- views the teacher as
heart of effective communication and information
manager of complex classroom processes, a person
exchange, which underpins good teaching. If you use
charged with bringing about certain outcomes with
questioning well, you can improve the student learning
students through using the best skills and techniques
experience in a whole range of Teaching Settings.
available.
➢ Simulations- are instructional scenarios where the
learner is placed in a "world" defined by the teacher.
➢ The facilitator approach- it places a high value on solving skills, creativity, etc.),
what students bring to the classroom setting, it places (3) Promote student engagement.
considerable emphasis on making use of students’ prior
▪ An approach, which capitalizes on the child’s natural
experience.
curiosity and urge to explore the environment.
➢ The liberationist approach- is rooted in notions of ▪ The child learns by personal experience and
liberal education, wherein the goal is to liberate the experiment and this is thought to make memory more
mind to wonder, to know and understand, to imagine vivid and help in the transfer of knowledge to new
and create, using the full intellectual inheritance of situations.
civilized life
CONCEPTUAL
APPROACH ACCDRD TO NATURE OF LEARNING
▪ Choosing and defining the content of a certain
❑ Discovery Learning discipline to be taught through the use of or pervasive
➢ takes place in problem solving situations where the ideas as against the traditional practice of determining
learner draws on his own experience and prior content by isolated topics.
knowledge and is a method of instruction through ▪ not a particular teaching method with specific steps to
which students interact with their environment by follow; it is more of a viewpoint of how facts and topics
exploring and manipulating objects, wrestling with under a discipline should be dealt with.
questions and controversies, or performing ▪ involves more data collection usually through research
experiments. while the discovery approach actively involves students
to undertake experimental and investigative work.
❑ Conceptual teaching
B. CONCEPTUAL - choosing and defining the content
➢ Involves the learning of specific concepts, the nature
of a certain discipline to be taught through the use of or
of concepts, and the development of logical reasoning &
pervasive ideas as against the traditional practice of
critical thinking.
determining content by isolated topics
❑ Process writing PROCESS
➢ treats all writing as a creative act which requires time ▪An approach which provides students with an
and positive feedback to be done well. In process abundance of projects, activities, and instructional
writing, the teacher moves away from being someone designs that allow them to make decisions and solve
who sets students a writing topic and receives the problems.
finished product for correction without any intervention
in the writing process itself. ▪Through this approach students get a sense that
learning is much more than the commission of facts to
❑ Unified Teaching memory. Rather, it is what children do with that
➢ This approach lends itself smoothly to a unified knowledge that determines its impact on their attitudes
teaching-learning concept of education. The and aptitudes.
information handler, being a teacher, a student, or
another educational environment, is at the center of UNIFIED
this educational model. The main inherent ▪It is based on a breakdown of knowledge to integrated
characteristics of this model are extreme flexibility, modules of information. The basic level of breakdown is
integration, ease of interaction, and being evolutional to be used in education to buildup concepts, while the
higher ones are to be used to buildup complex concepts
A. DISCOVERY of knowledge, including those of experts. Key to the
▪ refers to various instructional design models that success of this breakdown is the relational integration
engages students in learning through discovery. of the information leading to the concept under
Usually the pedagogical aims are threefold: consideration.
(1) Promote "deep" learning, ▪This approach lends itself smoothly to a unified
(2) Promote meta-cognitive skills (develop problem- teaching-learning concept of education. The
information handler, being a teacher, a student, or
another educational environment, is at the center of - emphasizes group work and a strong sense of
this educational model. ▪The main inherent community.
characteristics of this model are extreme flexibility, - “Think-Pair-Share
integration, ease of interaction, and being evolutional.
APPROACH ACCORDING TO TEACHER-LEARNER
INTERACTION
C. Technique
▪It is a procedure by which new knowledge fixed in the
minds of students permanently. For this purpose, a
teacher does extra activities in the class. ▪These
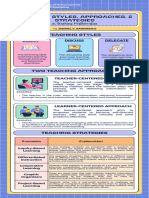
TEACHER-CENTERED APPROACH activities help the teacher to take shift from one
- It is the primary role of teachers to pass knowledge
strategy to another. Thus, teaching tactics are that
and information onto their students.
behavior of the teacher which he manifests in the class
1. Direct Instruction i.e., the developments of the teaching strategies , giving
- relies on explicit teaching through lectures and proper stimulus for timely responses, drilling the learn
teacher-led demonstrations. responses , increasing the responses by extra activities
and so on.
D. Method
▪Method of teaching is directly related to the
presentation of the lesson. Which a teacher should use,
depends on the nature of the subject, and the tact of
the teacher .
FOUR METHODS OF PRESENTING THE SUBJECT
MATTER.
1. TELLING METHOD; Lecture method, Discussion
method, Story telling method and so on.
STUDENT-CENTERED APPROACH 2 .DOING METHOD; Project method, Problem solving
- Student learning is continuously measured during method, Textbook method and so on.
teacher instruction.
3 .VISUAL METHOD; Demonstration method,
1. Inquiry Based Learning Supervised study method and so on.
- focuses on student investigation and hands-on
4 .MENTAL MEHOD; Inductive, Deductive, Analysis,
learning.
Synthesis method etc
- teacher’s primary role is that of a facilitator, providing
guidance and support for students through the learning INSTRUCTIONAL MEDIA
process
2. Cooperative Learning
You might also like
- Film Art An Introduction 11th Edition Bordwell Test BankDocument7 pagesFilm Art An Introduction 11th Edition Bordwell Test Banka367758805No ratings yet
- Approaches in Teaching Social StudiesDocument86 pagesApproaches in Teaching Social StudiesWasakna Buhay100% (6)
- Pedagogies for Student-Centered Learning: Online and On-GoundFrom EverandPedagogies for Student-Centered Learning: Online and On-GoundRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Senior Estimator Preconstruction Manager in Atlanta GA Resume Steven LosieDocument2 pagesSenior Estimator Preconstruction Manager in Atlanta GA Resume Steven LosieStevenLosieNo ratings yet
- Principles & Strategies of Teaching in Medical Laboratory Science (PSTM221)Document16 pagesPrinciples & Strategies of Teaching in Medical Laboratory Science (PSTM221)29 REYES, BERNADETTE R.No ratings yet
- Intro To Teaching - pstm211Document58 pagesIntro To Teaching - pstm211Charlen Kylha GavinoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Intro To TeachingDocument6 pagesWeek 2 - Intro To TeachingKezia MadeloNo ratings yet
- PSTM221Document10 pagesPSTM221Joyce Anne Cruz0% (1)
- Psthe MidtermsDocument15 pagesPsthe MidtermsCASTAÑEDA, Jameela AnneNo ratings yet
- PSTM Week2Document59 pagesPSTM Week2Romeo DiestaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 PSTMDocument15 pagesLesson 1 PSTMNicole Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Approach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleDocument22 pagesApproach, Methods & Techniques: Jon Vennie IbaleJON VENNIE IBALENo ratings yet
- INSET Applied Knowledge.... DIOSA FINALDocument72 pagesINSET Applied Knowledge.... DIOSA FINALDIOSA N.CAPISTRANONo ratings yet
- PC 122Document3 pagesPC 122Carla LedinioNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Methods, Techniques StrategiesDocument21 pagesApproaches, Methods, Techniques Strategiessereen qasemNo ratings yet
- Sarmiento-Teaching Styles, Approaches, & ApproachesDocument1 pageSarmiento-Teaching Styles, Approaches, & ApproachesJoemel SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Team A - Discovery-Inquiry Based ApproachDocument32 pagesTeam A - Discovery-Inquiry Based ApproachJemuel LuminariasNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approaches Strategies Methods and Techniques AS9Document24 pagesTeaching Approaches Strategies Methods and Techniques AS9Mariane SibayNo ratings yet
- LABISTO, MARY CRIS (Collateral Reading 4)Document5 pagesLABISTO, MARY CRIS (Collateral Reading 4)Mary Cris Maragañas AnghagNo ratings yet
- Effective Pedagogies in PersonDocument24 pagesEffective Pedagogies in PersonKiwinKoreaNo ratings yet
- ApproachDocument6 pagesApproachMa Yong Rui100% (1)
- Principles of Teaching 323Document81 pagesPrinciples of Teaching 323Mark Anthony B. AquinoNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityDocument10 pagesApproaches, Techniques, Methods, & Strategies, ActivityManolo Servise HiloNo ratings yet
- 2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoDocument4 pages2 TERM (S.Y. 2021-2022) BPHE-II: Philippine Normal University MindanaoLovely PadernaNo ratings yet
- Educ 212 Meaning and TEchniques of Teaching by Ma Salome LucasDocument4 pagesEduc 212 Meaning and TEchniques of Teaching by Ma Salome LucasSalome LucasNo ratings yet
- MS SSC 102 - Act 3Document3 pagesMS SSC 102 - Act 3Jervyn GuiananNo ratings yet
- Approaches, Methods and Techniques Promoting Learner-Centered ActivitiesDocument15 pagesApproaches, Methods and Techniques Promoting Learner-Centered ActivitiesHariette Mae OnofreNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan Kepada Teori Dan Amalan Pedagogi Dalam Pengajaran PembelajaranDocument34 pagesPengenalan Kepada Teori Dan Amalan Pedagogi Dalam Pengajaran PembelajaranBrendajc Jc0% (1)
- Chapter 4Document16 pagesChapter 4Haha Haha100% (1)
- (Formerly Ramon Magsaysay Technological University) Iba,: College of Teacher EducationDocument16 pages(Formerly Ramon Magsaysay Technological University) Iba,: College of Teacher EducationArabela AgrabioNo ratings yet
- Approaches Techniques and Method in TeachingDocument19 pagesApproaches Techniques and Method in Teachingmarjorie gervacio100% (1)
- Approaches Techniques and Method in TeachingDocument19 pagesApproaches Techniques and Method in Teachingmarjorie gervacio100% (1)
- Module. Teaching Approaches, Methods and StrategiesDocument38 pagesModule. Teaching Approaches, Methods and StrategiesJohn Dave Mabánta0% (1)
- Lecture On Principles of TeachingDocument9 pagesLecture On Principles of Teachingmaricel cuisonNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Basic TerminologyDocument12 pagesDefinitions of Basic TerminologySeham FouadNo ratings yet
- Teaching Approaches and MethodsDocument3 pagesTeaching Approaches and MethodsKenneth Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Lect1 (The Concept and Nature of Teaching)Document7 pagesLect1 (The Concept and Nature of Teaching)LUEL JAY VALMORESNo ratings yet
- Teaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionDocument2 pagesTeaching Multi-Grade Classes: Topic 16. Direct and Indirect Strategy Direct InstructionMaricel ViloriaNo ratings yet
- TeachingDocument21 pagesTeachingRosdiyana Bahtika100% (1)
- The Teaching-Learning Process: Yenna Monica D. PDocument24 pagesThe Teaching-Learning Process: Yenna Monica D. Psanta lizardoNo ratings yet
- Simple Diagram Found Below Is An Attempt To Distinguish ThemDocument13 pagesSimple Diagram Found Below Is An Attempt To Distinguish ThemEDENINo ratings yet
- Compilation of The Different Instructional StrategiesDocument12 pagesCompilation of The Different Instructional StrategiesCatherine PanoyNo ratings yet
- Maam Saylanon NotesDocument7 pagesMaam Saylanon Noteskristelannantong3No ratings yet
- Learning Theories P Week 1Document29 pagesLearning Theories P Week 1NURUL NORSHAFIQAH AQILA BINTI SHAARINo ratings yet
- L 200 Unit 7Document19 pagesL 200 Unit 7abrokwah sethNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Rizal-1Document14 pagesPortfolio in Rizal-1Rico James Gomez EfacNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledEdel Guyuran VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in Science TeachingDocument25 pagesBest Practices in Science Teachingjo_aligora100% (2)
- Learning - TheoriesDocument31 pagesLearning - TheoriesMckoy SandersonNo ratings yet
- NE Unit II - Teaching LearningDocument72 pagesNE Unit II - Teaching LearningProf.R.Indhumathi ProfessorNo ratings yet
- An Output in MAPEH - 120Document10 pagesAn Output in MAPEH - 120Marjo AldeNo ratings yet
- Education VocabularyDocument1 pageEducation VocabularyCarlosValdesNo ratings yet
- EDU 213 Study Guide by A-Media..Document25 pagesEDU 213 Study Guide by A-Media..Aliu Ridwan BamideleNo ratings yet
- Panel DiscussionDocument13 pagesPanel Discussionjinsi georgeNo ratings yet
- 9 Colegio Dela Purisima Concepcion: Name of Topics: The Teaching Profession: An OverviewDocument7 pages9 Colegio Dela Purisima Concepcion: Name of Topics: The Teaching Profession: An OverviewAlyza Mae D. DariaNo ratings yet
- M116 - Module 1Document15 pagesM116 - Module 1Annie Rose A. MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Choosing Appropriate Method For Teaching ScienceDocument19 pagesChoosing Appropriate Method For Teaching ScienceJefrelyn Eugenio MontibonNo ratings yet
- 63-Article Text-174-1-10-20170908 PDFDocument8 pages63-Article Text-174-1-10-20170908 PDFDaniela CPNo ratings yet
- Ofelia M. Guarin Assignment 101: Learning Knowledge Skills Values Beliefs HabitsDocument10 pagesOfelia M. Guarin Assignment 101: Learning Knowledge Skills Values Beliefs HabitsOfelia MecateNo ratings yet
- PSTMLS MidtermsDocument16 pagesPSTMLS MidtermsJohn Oliver AsiaNo ratings yet
- Teaching MethodsDocument2 pagesTeaching Methodsjoel pabadoraNo ratings yet
- Competencies To Enhance Digital Teaching and LearningDocument27 pagesCompetencies To Enhance Digital Teaching and LearningMohammad Hamad HammadiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge University Reporter - 1st May 2013Document24 pagesCambridge University Reporter - 1st May 2013Fuzzy_Wood_PersonNo ratings yet
- Leadership Colloquium Sample Draft of ProgrammeDocument2 pagesLeadership Colloquium Sample Draft of Programmealdrin abdurahimNo ratings yet
- Annex A CHEDRO Eval - HD Template CHEDRO Eval. Annex ADocument5 pagesAnnex A CHEDRO Eval - HD Template CHEDRO Eval. Annex AMark Lemuel Layones ArceoNo ratings yet
- Major Personality Theorists ChartDocument3 pagesMajor Personality Theorists Chartapi-309711196100% (1)
- Piaget TheoryDocument6 pagesPiaget TheoryBenjamin KhanNo ratings yet
- Board of DirectorsDocument2 pagesBoard of DirectorsdbansalklgNo ratings yet
- Form Page2Document1 pageForm Page2Edward MirandaNo ratings yet
- CV Kevin StauntonDocument2 pagesCV Kevin Stauntonapi-270607420No ratings yet
- Value Education & Ehics Unit IDocument26 pagesValue Education & Ehics Unit IchanduNo ratings yet
- Architecture Personal StatementDocument5 pagesArchitecture Personal StatementDayanat AliyevNo ratings yet
- Parent Letter - 2Document1 pageParent Letter - 2WXMINo ratings yet
- Module 6-Instructional PlanningDocument12 pagesModule 6-Instructional PlanningTimothyLimNo ratings yet
- 201232640Document48 pages201232640The Myanmar TimesNo ratings yet
- Proposed Message of Drda Monday Flag Raising Ceremony - EditedDocument2 pagesProposed Message of Drda Monday Flag Raising Ceremony - EditedPulis Rehiyon Onse IINo ratings yet
- Ap EapcetDocument2 pagesAp EapcetAvinash PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Resume: ShivanisharmaDocument2 pagesResume: ShivanisharmaShweta SharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Paper For Second GradeDocument5 pagesHow To Write A Research Paper For Second Gradekhkmwrbnd100% (1)
- K. GUTSCHOW, Adolf Behne and Modern Architecture in Germany, 1910-1914 (2005)Document598 pagesK. GUTSCHOW, Adolf Behne and Modern Architecture in Germany, 1910-1914 (2005)Santiago de ArmaNo ratings yet
- Madyson Acers: ProfileDocument2 pagesMadyson Acers: ProfileMady AcersNo ratings yet
- CSS Monitoring Tool DRRMS Edited 18 Jan 2017Document10 pagesCSS Monitoring Tool DRRMS Edited 18 Jan 2017Lo ViNo ratings yet
- Critical Journal Review Contextual Oral Language SkillsDocument16 pagesCritical Journal Review Contextual Oral Language SkillsNurul FazirahNo ratings yet
- Ohio 22+adult Diploma Ohios Options FlyerDocument1 pageOhio 22+adult Diploma Ohios Options FlyerRuss HaxNo ratings yet
- A Self-Learning Module in English 10 1 Quarter, Module 7Document10 pagesA Self-Learning Module in English 10 1 Quarter, Module 7Yeon JunNo ratings yet
- Instituting A Policy of Inclusion and Services For Learners With Disabilities in Support of Inclusive Education ActDocument40 pagesInstituting A Policy of Inclusion and Services For Learners With Disabilities in Support of Inclusive Education ActAepple Cano RautrautNo ratings yet
- Assignment Harold - Mam MaluDocument2 pagesAssignment Harold - Mam MaluRojanie EstuitaNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its Research Design Rationale of The StudyDocument25 pagesThe Problem and Its Research Design Rationale of The StudyRhodz Rhodulf CapangpanganNo ratings yet
- Annual Plan MatusalemDocument6 pagesAnnual Plan Matusalemvirgilio roxasNo ratings yet
- UG Courses of Study 2007Document147 pagesUG Courses of Study 2007dinu1903100% (2)