Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 viewsAssessment of A Pregnant Family
Assessment of A Pregnant Family
Uploaded by
Luna Sang-anThis document outlines a prenatal health assessment for a pregnant patient. It includes sections on reviewing the patient's systems, assessing health status during pregnancy, common nursing diagnoses, implementing care during pregnancy, and common gynecologic disorders seen in pregnancy. The assessment covers the patient's medical history, physical exam including vital signs and pelvic exam, and lab tests. Nursing goals are to educate the patient, identify risks, and minimize complications through anticipating and preventing problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Rabbit Farming Business Plan PDFDocument78 pagesRabbit Farming Business Plan PDFson87% (15)
- Normal NewbornDocument19 pagesNormal Newbornkozume kenmaNo ratings yet
- Catheterization: NCM 107 LabDocument4 pagesCatheterization: NCM 107 LabCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Leopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionDocument3 pagesLeopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionJyra Mae TaganasNo ratings yet
- Presentation Dengue FeverDocument21 pagesPresentation Dengue Feverpolarbear12121250% (2)
- Ch09Document32 pagesCh09Bridget Shienne DaculaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Module-5 - Conception-NOTESDocument2 pagesNCM 107 Module-5 - Conception-NOTESKisha BethelNo ratings yet
- Placenta Abruptio - Topic OverviewDocument8 pagesPlacenta Abruptio - Topic OverviewLei AbellarNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing RLEDocument1 pageCommunity Health Nursing RLERaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Burns Rule of Nines 2013Document1 pageBurns Rule of Nines 2013ellenningrumNo ratings yet
- NonStress TestDocument2 pagesNonStress TestRama_ichiNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument5 pagesEssential Newborn CareJig PirameNo ratings yet
- Oc Ob Set ADocument10 pagesOc Ob Set AmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument8 pagesChapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- Health Teaching and Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching and Discharge Plankamalab04No ratings yet
- Vital SignDocument40 pagesVital SignYoelBagusGiarto0% (1)
- 3.3 Family PlanningDocument9 pages3.3 Family PlanningGayle Regine DaquialNo ratings yet
- FNCP Form Health Deficit AsthmaDocument3 pagesFNCP Form Health Deficit Asthmakappa100% (1)
- Sem2 Anti TB DrugsDocument35 pagesSem2 Anti TB DrugsZijieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Maternal ConceptsDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Maternal ConceptsEunice TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Assessment of NewbornDocument26 pagesAssessment of Newbornaybee_14No ratings yet
- Kozier Nanda PDFDocument1 pageKozier Nanda PDFanindcNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesNCM 112 Lecture NotesSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child HealthDocument7 pagesMaternal and Child HealthNessa Layos MorilloNo ratings yet
- Systemic Changes During PregnancyDocument2 pagesSystemic Changes During PregnancyARAugusto67% (3)
- Newborn Physical Assessment by Ms. Mevelle L. AsuncionDocument91 pagesNewborn Physical Assessment by Ms. Mevelle L. AsuncionRizzamwah CatagueNo ratings yet
- Describe Your Family MembersDocument2 pagesDescribe Your Family MembersVictor MorenoNo ratings yet
- Procedure-Assessing Fetal Heart ToneDocument1 pageProcedure-Assessing Fetal Heart ToneCyril Joy N. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems InfancyDocument147 pagesCommon Health Problems Infancymark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor BrochureDocument2 pagesStages of Labor Brochureapi-273000494100% (1)
- EPIGLOTTITISDocument11 pagesEPIGLOTTITISMinutes in MEDITATIONNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluids PDFDocument10 pagesIntravenous Fluids PDFGReadRNo ratings yet
- CHN Health Care Process PDFDocument9 pagesCHN Health Care Process PDFKathleen AngNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The NewbornDocument86 pagesNursing Care of The Newbornjapzee1988100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Child With LIFE THREATENING CONDITIONSDocument70 pagesNursing Care of Child With LIFE THREATENING CONDITIONSinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The BreastDocument11 pagesAssessment of The BreastSIR ONENo ratings yet
- Finals Scope - Genetic.childbirthDocument4 pagesFinals Scope - Genetic.childbirthSharmaine MadlaNo ratings yet
- Fundal Height DefinedDocument2 pagesFundal Height Definedervin0122No ratings yet
- Managing Discomforts During PregnancyDocument3 pagesManaging Discomforts During PregnancyMariana Mikaela AlagarNo ratings yet
- Bubbles HeDocument39 pagesBubbles HePerrilyn PereyNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanningDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanningAthena Irish LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Heart and Neck VesselsDocument3 pagesHeart and Neck VesselsMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesGestational Diabetes MellitusCzarina PorciunculaNo ratings yet
- Theories of LabourDocument22 pagesTheories of LaboursubashikNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument6 pagesIntestinal ObstructionCling Cruza0% (1)
- of ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALISDocument12 pagesof ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALISMaricel Agcaoili GallatoNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Pre Natal - FinalDocument6 pagesCase Scenario Pre Natal - Finalgwyne laguardiaNo ratings yet
- Child Health Nursing: MumpsDocument25 pagesChild Health Nursing: MumpsmanibharathiNo ratings yet
- Complication of PregnancyDocument44 pagesComplication of PregnancyJharaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Immune SystemDocument75 pagesDrugs For Immune SystemDhonat FlashNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemJerica Jaz F. Vergara100% (1)
- Notes - MCHN - Chapter 1Document12 pagesNotes - MCHN - Chapter 1Jamaica mitalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Nutrition in AdulthoodDocument25 pagesUnit 3: Nutrition in AdulthoodCar OrdzNo ratings yet
- 6-Health Problems Common in PreschoolerDocument36 pages6-Health Problems Common in PreschoolerPam Lala100% (2)
- Complication During PregnancyDocument43 pagesComplication During PregnancyRizza Domalaon BalangitanNo ratings yet
- Individual PediaDocument37 pagesIndividual PediaLianna M. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- The Child With Hematologic DisordersDocument149 pagesThe Child With Hematologic DisordersNics FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManueverDocument5 pagesLeopold's Manuevermanhua fanaticNo ratings yet
- EINC ReviewDocument14 pagesEINC ReviewRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- NCM107 - Chapter 04-Lesson 3 Postpartal CareDocument22 pagesNCM107 - Chapter 04-Lesson 3 Postpartal CareJosephine LoriaNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Sang-An, Dalugdug, Lao-As (Bsn-2a) - Activity 5 - Public Health Lawas PortfolioDocument64 pagesSang-An, Dalugdug, Lao-As (Bsn-2a) - Activity 5 - Public Health Lawas PortfolioLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Airway: Newborn Priorities in The First Days of LifeDocument9 pagesAirway: Newborn Priorities in The First Days of LifeLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Activity NCM 66 DARWINDocument8 pagesActivity NCM 66 DARWINLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Smoking) : Diabetes Mellitus Endovascular Procedure Hypertension TraumaDocument3 pagesSmoking) : Diabetes Mellitus Endovascular Procedure Hypertension TraumaLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Loan Application - Sosyo Sa Purok 2Document1 pageLoan Application - Sosyo Sa Purok 2Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Learning Feedbacking Diary - Darwin Jay L. Sang-An (Bsn-2a)Document4 pagesActivity 1 - Learning Feedbacking Diary - Darwin Jay L. Sang-An (Bsn-2a)Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Cabalgada BSN 2C Pen33Document3 pagesQuiz 3 Cabalgada BSN 2C Pen33Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Case Study - Pre-Eclampsia Drugs:: Calcium Iron 2 Doses of Tetanus ToxoidDocument9 pagesWeek 3: Case Study - Pre-Eclampsia Drugs:: Calcium Iron 2 Doses of Tetanus ToxoidLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument3 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Theories of DevelopmentDocument2 pagesActivity 2 Theories of DevelopmentLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusDocument15 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusLuna Sang-an100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Theories of Development: Topic OutlineDocument3 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Theories of Development: Topic OutlineLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care R/T Psychological & Physiologic Changes of PregnancyDocument3 pagesNursing Care R/T Psychological & Physiologic Changes of PregnancyLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusDocument5 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Make A Philosophical BeliefDocument1 pageMake A Philosophical BeliefLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care To Promote Fetal Maternal HealthDocument3 pagesNursing Care To Promote Fetal Maternal HealthLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Jerry O. Deligero JR Bsabe1: "Bukidnon My Home"Document1 pageJerry O. Deligero JR Bsabe1: "Bukidnon My Home"Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- BornDocument4 pagesBornLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- What Are Anotia and Microtia?Document7 pagesWhat Are Anotia and Microtia?Anonymous MWd5UOUuiyNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues Pertaining To AbortionDocument38 pagesEthical Issues Pertaining To AbortionRoman MamunNo ratings yet
- How To Slay The Dragon BAR EXAMDocument22 pagesHow To Slay The Dragon BAR EXAMProfessor DimaampaoNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care & ManagementDocument22 pagesAntenatal Care & ManagementPabhat Kumar80% (5)
- Nurse's Pocket GuideDocument11 pagesNurse's Pocket GuideRaf_Harold_427No ratings yet
- PHS2010 March13.CompressedDocument231 pagesPHS2010 March13.CompressedK EV INNo ratings yet
- Lay Z Spa Premium Platinum User ManualDocument44 pagesLay Z Spa Premium Platinum User Manualbetterknow100% (1)
- An Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezDocument11 pagesAn Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezMica BongalaNo ratings yet
- High Risk WomenDocument17 pagesHigh Risk WomenamitNo ratings yet
- Need of New Born and Parenting ProcessDocument13 pagesNeed of New Born and Parenting ProcessKrini Tandel100% (3)
- New PPT PresentationPRE TESTDocument22 pagesNew PPT PresentationPRE TESTLAZABELLE BAGALLONNo ratings yet
- Piramal Swasthya ChallengeDocument9 pagesPiramal Swasthya ChallengeShivran RoyNo ratings yet
- Entitlement: The SSS Maternity Notification Form (MN Form)Document2 pagesEntitlement: The SSS Maternity Notification Form (MN Form)Joy DuremdesNo ratings yet
- 2 PolyhydramniosDocument8 pages2 PolyhydramniosNovhy GanggutNo ratings yet
- Basic Maternity ConceptsDocument14 pagesBasic Maternity ConceptsDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- Diet For Pregnancy and Lactating WomenDocument49 pagesDiet For Pregnancy and Lactating WomenrjNo ratings yet
- RH Isoimmunization (PritDocument23 pagesRH Isoimmunization (PritmaezuNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing QuestionsDocument2 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing QuestionsCayla Mae CarlosNo ratings yet
- PNLE NCLEX Practice Exam For Maternal and Child Health Nursing 2Document5 pagesPNLE NCLEX Practice Exam For Maternal and Child Health Nursing 2bobtaguba100% (1)
- Vacuum Extraction in Preterm DeliveriesDocument27 pagesVacuum Extraction in Preterm DeliveriesJennifer TiosannaNo ratings yet
- Beachcomber Hot Tub Owners GuideDocument40 pagesBeachcomber Hot Tub Owners GuideStan VigNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8 JoanneDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8 JoanneLANI JOY TABAMONo ratings yet
- Case Study 25: Obstetrics: Reduced Fetal MovementDocument10 pagesCase Study 25: Obstetrics: Reduced Fetal MovementNorzahidah Mohd KhairNo ratings yet
- 54 Fetal Death of A Twin PDFDocument3 pages54 Fetal Death of A Twin PDFrajma2006No ratings yet
- Referensi No 7Document5 pagesReferensi No 7Bagus Wanda HabibullahNo ratings yet
- CDHDocument47 pagesCDHSameeta PrabhuNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Midwifery & Gynaecology Nursing Papers QPDocument14 pages3.1 Midwifery & Gynaecology Nursing Papers QPTapobrata Sarkar100% (1)
- Asthma in PregnancyDocument22 pagesAsthma in PregnancyPramita PurbandariNo ratings yet
- Term Paper About Abortion TagalogDocument7 pagesTerm Paper About Abortion TagalogWriteMyPaperKansasCity100% (1)
Assessment of A Pregnant Family
Assessment of A Pregnant Family
Uploaded by
Luna Sang-an0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views4 pagesThis document outlines a prenatal health assessment for a pregnant patient. It includes sections on reviewing the patient's systems, assessing health status during pregnancy, common nursing diagnoses, implementing care during pregnancy, and common gynecologic disorders seen in pregnancy. The assessment covers the patient's medical history, physical exam including vital signs and pelvic exam, and lab tests. Nursing goals are to educate the patient, identify risks, and minimize complications through anticipating and preventing problems.
Original Description:
Original Title
ASSESSMENT-OF-A-PREGNANT-FAMILY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines a prenatal health assessment for a pregnant patient. It includes sections on reviewing the patient's systems, assessing health status during pregnancy, common nursing diagnoses, implementing care during pregnancy, and common gynecologic disorders seen in pregnancy. The assessment covers the patient's medical history, physical exam including vital signs and pelvic exam, and lab tests. Nursing goals are to educate the patient, identify risks, and minimize complications through anticipating and preventing problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views4 pagesAssessment of A Pregnant Family
Assessment of A Pregnant Family
Uploaded by
Luna Sang-anThis document outlines a prenatal health assessment for a pregnant patient. It includes sections on reviewing the patient's systems, assessing health status during pregnancy, common nursing diagnoses, implementing care during pregnancy, and common gynecologic disorders seen in pregnancy. The assessment covers the patient's medical history, physical exam including vital signs and pelvic exam, and lab tests. Nursing goals are to educate the patient, identify risks, and minimize complications through anticipating and preventing problems.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
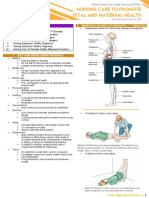
Maternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 65):
NURSING CARE r/t ASSESSMENT OF
A PREGNANT FAMILY
Ms. Grace Bautista | Sept. 15, 2021
OUTLINE
I. Prenatal Health Assessment
A. Review of Systems
II. Assessing Health Status During Pregnancy
III. Nursing Diagnoses: Prenatal Health Assessment
IV. Implementing Care During Pregnancy
V. Common Gynecologic Disorders Seen in Pregnancy
I. PRENATAL HEALTH ASSESSMENT
• Reasons for assessment
1. Establish baseline for present health
2. Determine gestational age of fetus
3. Monitor fetal development and maternal well-being
4. Identify women at risk for complications
5. Minimize risk of possible complications by anticipating
and preventing problems before they occur
6. Provide education about pregnancy, lactation, and
newborn care
• Preconceptual visit
o Accurate reproductive life planning information
o Assurance about fertility based on health history and
PE
o Identification of any problems needing correction
o Hemoglobin level and blood type determined
o Pap smear taken
• Choosing a healthcare provider who will:
1. Provide care throughout pregnancy and birth
2. Initiate prenatal care early
o Nurse’s role:
1. Educate
2. Listen
3. Counsel
o Include support people
• Typical day and social history for a pregnant:
o Nutrition
o Exercise
o Hobbies
o Tobacco, alcohol, drug consumption
o Medication and herbal therapy
o Intimate partner violence
Forro, Gwyn Oona Florence L. | 1
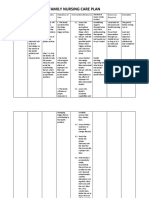
A. REVIEW OF SYSTEMS II. ASSESSING HEALTH STATUS DURING PREGNANCY
• Baseline height/weight • Types of pelvises:
• Vital sign measurement
• Body systems
o General appearance and mental status
o Head and scalp
o Eyes
o Nose and sinuses
o Ears
o Mouth, teeth, throat
o Neck
o Lymph nodes
o Breasts
o Heart
o Lungs
o Back
o Rectum
o Extremities and skin
• Physical examination
o Appearance of cervix:
• Estimating pelvic size by
o Diagonal conjugate
o Ischial tuberosity diameter
• Laboratory assessments
o Blood serum studies
CBC; genetic screen
Serologic test for syphilis
Blood typing and Rh factor
Maternal serum for AFP and PAPP-A
Cultures for chlamydia and gonorrhea
Indirect Coombs test
Serum antibody titers
HIV screening
Glucose challenge test
o Pelvis (establishing adequacy for childbirth): o Urinalysis
o Tuberculosis screening
o Ultrasonography
III. NURSING DIAGNOSES: PRENATAL HEALTH ASSESSMENT
• Health-seeking behaviors r/t guidelines for nutrition and
activity during pregnancy
• Deficient knowledge regarding exposure to teratogens during
pregnancy
• Health-seeking behaviors r/t strong cultural desire to have a
healthy child
• Risk for injury to fetus r/t lifestyle choices
IV. IMPLEMENTING CARE DURING PREGNANCY
• Danger signs to report during pregnancy
1. Vaginal bleeding
2. Persistent vomiting
3. Chills and fever
4. Escape of fluid from vagina
5. Abdominal or chest pain
6. Swelling of face and fingers
7. Vision changes or continuous headache
8. Rhythmic cramping
9. Burning with urination
10. Pronounced decrease in fetal movement
11. Uterine contraction before 37 wks of pregnancy
Forro, Gwyn Oona Florence L. | 2
V. COMMON GYNECOLOGIC DISORDERS SEEN IN
PREGNANCY
Forro, Gwyn Oona Florence L. | 3
Q&A
A woman’s diagonal conjugate measurement is 10.5 cm. You would
interpret that her pelvis is which of the following?
A. Adequate for childbearing
B. Narrow anterior-posterior
C. Narrow transversely
D. Larger than normal
Which of the following suggestion would be the best technique to help
a patient relax during a pelvic examination?
A. “Bear down as if you have to move your bowels.”
B. “Take a deep breath and hold it.”
C. “Count backward from 20 at a steady pace.”
D. “Tense your abdominal muscles so the uterus contracts less.”
Forro, Gwyn Oona Florence L. | 2
You might also like
- Rabbit Farming Business Plan PDFDocument78 pagesRabbit Farming Business Plan PDFson87% (15)
- Normal NewbornDocument19 pagesNormal Newbornkozume kenmaNo ratings yet
- Catheterization: NCM 107 LabDocument4 pagesCatheterization: NCM 107 LabCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Leopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionDocument3 pagesLeopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionJyra Mae TaganasNo ratings yet
- Presentation Dengue FeverDocument21 pagesPresentation Dengue Feverpolarbear12121250% (2)
- Ch09Document32 pagesCh09Bridget Shienne DaculaNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Module-5 - Conception-NOTESDocument2 pagesNCM 107 Module-5 - Conception-NOTESKisha BethelNo ratings yet
- Placenta Abruptio - Topic OverviewDocument8 pagesPlacenta Abruptio - Topic OverviewLei AbellarNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing RLEDocument1 pageCommunity Health Nursing RLERaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Burns Rule of Nines 2013Document1 pageBurns Rule of Nines 2013ellenningrumNo ratings yet
- NonStress TestDocument2 pagesNonStress TestRama_ichiNo ratings yet
- Essential Newborn CareDocument5 pagesEssential Newborn CareJig PirameNo ratings yet
- Oc Ob Set ADocument10 pagesOc Ob Set AmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusDocument8 pagesChapter 9: Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy and Care of The Developing FetusAlyssaGrandeMontimor100% (1)
- Health Teaching and Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesHealth Teaching and Discharge Plankamalab04No ratings yet
- Vital SignDocument40 pagesVital SignYoelBagusGiarto0% (1)
- 3.3 Family PlanningDocument9 pages3.3 Family PlanningGayle Regine DaquialNo ratings yet
- FNCP Form Health Deficit AsthmaDocument3 pagesFNCP Form Health Deficit Asthmakappa100% (1)
- Sem2 Anti TB DrugsDocument35 pagesSem2 Anti TB DrugsZijieNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Maternal ConceptsDocument8 pagesUnit 4 Maternal ConceptsEunice TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Assessment of NewbornDocument26 pagesAssessment of Newbornaybee_14No ratings yet
- Kozier Nanda PDFDocument1 pageKozier Nanda PDFanindcNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesNCM 112 Lecture NotesSureen RegularNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child HealthDocument7 pagesMaternal and Child HealthNessa Layos MorilloNo ratings yet
- Systemic Changes During PregnancyDocument2 pagesSystemic Changes During PregnancyARAugusto67% (3)
- Newborn Physical Assessment by Ms. Mevelle L. AsuncionDocument91 pagesNewborn Physical Assessment by Ms. Mevelle L. AsuncionRizzamwah CatagueNo ratings yet
- Describe Your Family MembersDocument2 pagesDescribe Your Family MembersVictor MorenoNo ratings yet
- Procedure-Assessing Fetal Heart ToneDocument1 pageProcedure-Assessing Fetal Heart ToneCyril Joy N. FernandoNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems InfancyDocument147 pagesCommon Health Problems Infancymark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Labor BrochureDocument2 pagesStages of Labor Brochureapi-273000494100% (1)
- EPIGLOTTITISDocument11 pagesEPIGLOTTITISMinutes in MEDITATIONNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Fluids PDFDocument10 pagesIntravenous Fluids PDFGReadRNo ratings yet
- CHN Health Care Process PDFDocument9 pagesCHN Health Care Process PDFKathleen AngNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The NewbornDocument86 pagesNursing Care of The Newbornjapzee1988100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Child With LIFE THREATENING CONDITIONSDocument70 pagesNursing Care of Child With LIFE THREATENING CONDITIONSinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The BreastDocument11 pagesAssessment of The BreastSIR ONENo ratings yet
- Finals Scope - Genetic.childbirthDocument4 pagesFinals Scope - Genetic.childbirthSharmaine MadlaNo ratings yet
- Fundal Height DefinedDocument2 pagesFundal Height Definedervin0122No ratings yet
- Managing Discomforts During PregnancyDocument3 pagesManaging Discomforts During PregnancyMariana Mikaela AlagarNo ratings yet
- Bubbles HeDocument39 pagesBubbles HePerrilyn PereyNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanningDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanningAthena Irish LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Heart and Neck VesselsDocument3 pagesHeart and Neck VesselsMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesGestational Diabetes MellitusCzarina PorciunculaNo ratings yet
- Theories of LabourDocument22 pagesTheories of LaboursubashikNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument6 pagesIntestinal ObstructionCling Cruza0% (1)
- of ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALISDocument12 pagesof ERYTHROBLASTOSIS FETALISMaricel Agcaoili GallatoNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario Pre Natal - FinalDocument6 pagesCase Scenario Pre Natal - Finalgwyne laguardiaNo ratings yet
- Child Health Nursing: MumpsDocument25 pagesChild Health Nursing: MumpsmanibharathiNo ratings yet
- Complication of PregnancyDocument44 pagesComplication of PregnancyJharaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Immune SystemDocument75 pagesDrugs For Immune SystemDhonat FlashNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesDrugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemJerica Jaz F. Vergara100% (1)
- Notes - MCHN - Chapter 1Document12 pagesNotes - MCHN - Chapter 1Jamaica mitalNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Nutrition in AdulthoodDocument25 pagesUnit 3: Nutrition in AdulthoodCar OrdzNo ratings yet
- 6-Health Problems Common in PreschoolerDocument36 pages6-Health Problems Common in PreschoolerPam Lala100% (2)
- Complication During PregnancyDocument43 pagesComplication During PregnancyRizza Domalaon BalangitanNo ratings yet
- Individual PediaDocument37 pagesIndividual PediaLianna M. MilitanteNo ratings yet
- The Child With Hematologic DisordersDocument149 pagesThe Child With Hematologic DisordersNics FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManueverDocument5 pagesLeopold's Manuevermanhua fanaticNo ratings yet
- EINC ReviewDocument14 pagesEINC ReviewRifa'atul MahmudahNo ratings yet
- NCM107 - Chapter 04-Lesson 3 Postpartal CareDocument22 pagesNCM107 - Chapter 04-Lesson 3 Postpartal CareJosephine LoriaNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Sang-An, Dalugdug, Lao-As (Bsn-2a) - Activity 5 - Public Health Lawas PortfolioDocument64 pagesSang-An, Dalugdug, Lao-As (Bsn-2a) - Activity 5 - Public Health Lawas PortfolioLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Airway: Newborn Priorities in The First Days of LifeDocument9 pagesAirway: Newborn Priorities in The First Days of LifeLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Activity NCM 66 DARWINDocument8 pagesActivity NCM 66 DARWINLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Smoking) : Diabetes Mellitus Endovascular Procedure Hypertension TraumaDocument3 pagesSmoking) : Diabetes Mellitus Endovascular Procedure Hypertension TraumaLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Loan Application - Sosyo Sa Purok 2Document1 pageLoan Application - Sosyo Sa Purok 2Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Learning Feedbacking Diary - Darwin Jay L. Sang-An (Bsn-2a)Document4 pagesActivity 1 - Learning Feedbacking Diary - Darwin Jay L. Sang-An (Bsn-2a)Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Cabalgada BSN 2C Pen33Document3 pagesQuiz 3 Cabalgada BSN 2C Pen33Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Week 3: Case Study - Pre-Eclampsia Drugs:: Calcium Iron 2 Doses of Tetanus ToxoidDocument9 pagesWeek 3: Case Study - Pre-Eclampsia Drugs:: Calcium Iron 2 Doses of Tetanus ToxoidLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument3 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Theories of DevelopmentDocument2 pagesActivity 2 Theories of DevelopmentLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusDocument15 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusLuna Sang-an100% (1)
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Theories of Development: Topic OutlineDocument3 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing Theories of Development: Topic OutlineLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care R/T Psychological & Physiologic Changes of PregnancyDocument3 pagesNursing Care R/T Psychological & Physiologic Changes of PregnancyLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusDocument5 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Make A Philosophical BeliefDocument1 pageMake A Philosophical BeliefLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care To Promote Fetal Maternal HealthDocument3 pagesNursing Care To Promote Fetal Maternal HealthLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Jerry O. Deligero JR Bsabe1: "Bukidnon My Home"Document1 pageJerry O. Deligero JR Bsabe1: "Bukidnon My Home"Luna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- BornDocument4 pagesBornLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- What Are Anotia and Microtia?Document7 pagesWhat Are Anotia and Microtia?Anonymous MWd5UOUuiyNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues Pertaining To AbortionDocument38 pagesEthical Issues Pertaining To AbortionRoman MamunNo ratings yet
- How To Slay The Dragon BAR EXAMDocument22 pagesHow To Slay The Dragon BAR EXAMProfessor DimaampaoNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care & ManagementDocument22 pagesAntenatal Care & ManagementPabhat Kumar80% (5)
- Nurse's Pocket GuideDocument11 pagesNurse's Pocket GuideRaf_Harold_427No ratings yet
- PHS2010 March13.CompressedDocument231 pagesPHS2010 March13.CompressedK EV INNo ratings yet
- Lay Z Spa Premium Platinum User ManualDocument44 pagesLay Z Spa Premium Platinum User Manualbetterknow100% (1)
- An Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezDocument11 pagesAn Ethical Comparison - Vitro Fertilization: Rev. Juan R. VélezMica BongalaNo ratings yet
- High Risk WomenDocument17 pagesHigh Risk WomenamitNo ratings yet
- Need of New Born and Parenting ProcessDocument13 pagesNeed of New Born and Parenting ProcessKrini Tandel100% (3)
- New PPT PresentationPRE TESTDocument22 pagesNew PPT PresentationPRE TESTLAZABELLE BAGALLONNo ratings yet
- Piramal Swasthya ChallengeDocument9 pagesPiramal Swasthya ChallengeShivran RoyNo ratings yet
- Entitlement: The SSS Maternity Notification Form (MN Form)Document2 pagesEntitlement: The SSS Maternity Notification Form (MN Form)Joy DuremdesNo ratings yet
- 2 PolyhydramniosDocument8 pages2 PolyhydramniosNovhy GanggutNo ratings yet
- Basic Maternity ConceptsDocument14 pagesBasic Maternity ConceptsDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- Diet For Pregnancy and Lactating WomenDocument49 pagesDiet For Pregnancy and Lactating WomenrjNo ratings yet
- RH Isoimmunization (PritDocument23 pagesRH Isoimmunization (PritmaezuNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing QuestionsDocument2 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing QuestionsCayla Mae CarlosNo ratings yet
- PNLE NCLEX Practice Exam For Maternal and Child Health Nursing 2Document5 pagesPNLE NCLEX Practice Exam For Maternal and Child Health Nursing 2bobtaguba100% (1)
- Vacuum Extraction in Preterm DeliveriesDocument27 pagesVacuum Extraction in Preterm DeliveriesJennifer TiosannaNo ratings yet
- Beachcomber Hot Tub Owners GuideDocument40 pagesBeachcomber Hot Tub Owners GuideStan VigNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8 JoanneDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Mapeh 8 JoanneLANI JOY TABAMONo ratings yet
- Case Study 25: Obstetrics: Reduced Fetal MovementDocument10 pagesCase Study 25: Obstetrics: Reduced Fetal MovementNorzahidah Mohd KhairNo ratings yet
- 54 Fetal Death of A Twin PDFDocument3 pages54 Fetal Death of A Twin PDFrajma2006No ratings yet
- Referensi No 7Document5 pagesReferensi No 7Bagus Wanda HabibullahNo ratings yet
- CDHDocument47 pagesCDHSameeta PrabhuNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Midwifery & Gynaecology Nursing Papers QPDocument14 pages3.1 Midwifery & Gynaecology Nursing Papers QPTapobrata Sarkar100% (1)
- Asthma in PregnancyDocument22 pagesAsthma in PregnancyPramita PurbandariNo ratings yet
- Term Paper About Abortion TagalogDocument7 pagesTerm Paper About Abortion TagalogWriteMyPaperKansasCity100% (1)